
When it comes to data transfer measurements, it’s essential to understand the difference between gibibytes (GiB) and gigabytes (GB). These two terms are often used interchangeably, but they represent different units of measurement in the digital world.
A gibibyte (GiB) is a binary unit of storage that equals 1,073,741,824 bytes. It closely approximates a billion bytes, which is why it is often confused with a gigabyte (GB). On the other hand, a gigabyte (GB) is a decimal unit of storage that equals 1,000,000,000 bytes. This difference in units can lead to confusion and misunderstanding when it comes to calculating and comparing data transfer rates.
One of the reasons for this confusion is that computer systems typically use binary calculations, meaning that data is transferred in units of 2, as opposed to the decimal calculations used by hard drive manufacturers. This can lead to discrepancies between the actual amount of data transferred and the amount reported by the operating system or storage device.
To ensure accurate measurements and avoid confusion, it is important to use the appropriate units of measurement when discussing data transfer rates. Understanding the difference between gibibytes (GiB) and gigabytes (GB) can help clarify discussions and ensure that data transfer measurements are accurate and understood by all parties involved.
Contents
- 1 Data transfer measurements
- 2 Understanding Gibibytes (GiB)
- 3 Differences between Gibibytes and Gigabytes
- 4 Choosing the right measurement
- 5 FAQ about topic “Gib to GB: Understanding Data Transfer Measurements”
- 6 What is the difference between gibibyte (GiB) and gigabyte (GB)?
- 7 Why do we need different measurements for data transfer?
- 8 How can I convert gibibytes (GiB) to gigabytes (GB)?
- 9 What are some common data transfer measurements used in everyday life?
- 10 Why is it important to understand data transfer measurements?
Data transfer measurements
When it comes to measuring data transfer, it is important to understand the different units used. One commonly used unit is the gibibit, or gib, which is a unit of digital information equal to 1024 mebibits. This unit is often used in the context of computer and data storage.
The use of gib as a data transfer measurement is important because it allows for more accurate calculations and comparisons. By using this unit, it is easier to understand the amount of data that can be transferred or stored, and make informed decisions based on those measurements.
One practical application of gib is in internet speed calculations. Internet service providers often advertise their speeds in terms of gigabits per second (Gbps), which can be converted to gibibits per second (Gib/s) for more accurate measurements. This allows users to understand the actual data transfer rates they can expect when using different internet services.
In addition to internet speeds, gib is also used in measuring data transfer rates for other digital devices, such as hard drives and solid-state drives. These devices often have their storage capacities listed in gibibytes (GiB), which can be used to calculate the potential data transfer rates based on the device’s specifications.
Overall, understanding data transfer measurements, including the use of gib, is crucial in today’s digital world. Whether it’s for internet speeds or storage capacities, being able to accurately measure and compare data transfer rates allows for more informed decisions and better utilization of digital resources.
Understanding Gibibytes (GiB)
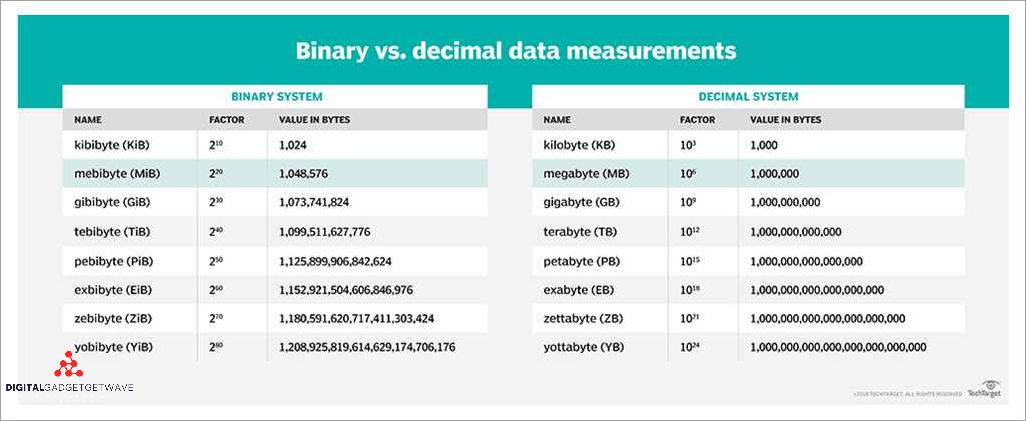
A Gibibyte (GiB) is a unit of digital information storage that is equal to 1,073,741,824 bytes. It is a binary multiple of a byte, unlike a Gigabyte (GB) which is a decimal multiple of a byte. The use of Gibibytes is common in computer science and information technology, especially when dealing with memory and storage capacities.
One Gibibyte is equivalent to 1024 Mebibytes (MiB), which are themselves equivalent to 1024 Kibibytes (KiB). This binary structure allows for easier calculations and conversions within the digital storage realm.
When it comes to data transfer rates, it is important to understand the distinction between Gibibytes and Gigibytes (GB). Gibibytes represent a binary measurement, while Gigibytes represent a decimal measurement. This means that when considering data transfer speeds, a Gibibyte will be smaller than a Gigibyte.
For example, if you are transferring a file that is 1 GiB in size, it would take less time to transfer than a file that is 1 GB in size. This is because the Gibibyte measurement accounts for the binary nature of data transfer, while the Gigibyte measurement does not.
Understanding the difference between Gibibytes and Gigibytes is essential for accurately representing and calculating data storage capacities and transfer speeds in the digital world. Whether you are managing computer memory or transferring large files, having a clear understanding of these measurements will help ensure accurate and efficient data handling.
Definition and purpose

The terms “gb” and “gib” are used to measure the amount of digital data transferred. “gb” stands for gigabyte, while “gib” stands for gibibyte. Both are units of measurement for digital storage, with a gigabyte equal to 1,000 megabytes or 1 billion bytes, and a gibibyte equal to 1,024 mebibytes or 1,073,741,824 bytes.
The purpose of using these measurements is to accurately quantify and understand the amount of data being transferred or stored. Data transfer measurements are important in various fields, including computer science, information technology, and telecommunications, where accurate measurements are essential for managing storage capacities, bandwidth allocation, network performance, and data consumption.
These measurements are particularly useful when dealing with large files or data sets, as they provide a standardized way to estimate the size and capacity requirements. For example, in cloud storage or data backup services, understanding data transfer measurements helps users determine how much storage space they need and how long it will take to transfer or download their files.
It is important to note that “gb” and “gib” are not interchangeable, as they represent different quantities of data. The use of gibibytes is often preferred in technical contexts to ensure accuracy and avoid confusion between decimal and binary multiples. However, gigabytes are still commonly used in everyday language and marketing materials.
To better understand data transfer measurements, it is also helpful to familiarize oneself with related terms and abbreviations, such as “mb” for megabytes, “tb” for terabytes, and “pb” for petabytes. Additionally, knowing the conversion factors between these units can aid in calculations and comparisons, allowing for more efficient data management and decision-making.
In summary, the definition and purpose of “gb” and “gib” as data transfer measurements lie in accurately quantifying and managing digital storage capacities, bandwidth allocation, and data consumption. These measurements play a vital role in various fields, helping individuals and organizations make informed decisions related to data transfer and storage.
Conversion to gigabytes (GB)

When it comes to measuring digital storage, there are two main units commonly used: gibibytes (GiB) and gigabytes (GB). While these units may sound similar, they have different numerical values due to differences in the base for calculations.
A gibibyte (GiB) is a binary measurement unit that represents 2^30 bytes, which is equal to 1,073,741,824 bytes. On the other hand, a gigabyte (GB) is a decimal measurement unit that represents 10^9 bytes, equivalent to 1,000,000,000 bytes.
Converting from gibibytes (GiB) to gigabytes (GB) involves applying the appropriate conversion factor. To convert from gibibytes to gigabytes, you can multiply the gibibyte value by 1.074. For example, if you have 100 gibibytes, you can calculate the equivalent in gigabytes by multiplying 100 by 1.074, which gives you approximately 107.4 gigabytes.
It’s important to note that when dealing with data transfer measurements, devices and systems may use either gibibytes or gigabytes. This can lead to some confusion, as the same value in gibibytes will be represented by a different numerical value in gigabytes. Therefore, it’s essential to be mindful of which unit is being used in order to accurately interpret and calculate data storage or transfer capacities.
In summary, converting from gibibytes to gigabytes involves multiplying the gibibyte value by 1.074. Understanding the difference between these two units is crucial when it comes to interpreting data storage and transfer capacities. Being aware of the units being used and applying the appropriate conversion factors will help avoid any misunderstandings or miscalculations.
Differences between Gibibytes and Gigabytes
Gibibytes (GiB) and Gigabytes (GB) are both units of digital information storage capacity, but they differ in their measurements and usage.
Measurement Difference:
1 Gibibyte is equal to 1,073,741,824 bytes, while 1 Gigabyte is equal to 1,000,000,000 bytes. This means that a Gibibyte is slightly larger than a Gigabyte in terms of storage capacity.
Binary vs. Decimal:
Gibibytes are based on a binary system, while Gigabytes are based on decimal system. Binary system is used in computers, where each unit is a power of 2 (2^10, 2^20, 2^30, etc.), whereas the decimal system is based on powers of 10 (10^9, 10^12, 10^15, etc.). This leads to the slight difference in measurements between Gibibytes and Gigabytes.
Usage Difference:
Gibibytes are commonly used in the field of computing and digital storage, particularly when measuring RAM or disk storage on a computer. In contrast, Gigabytes are more commonly used in everyday consumer devices and storage media, such as hard drives, USB flash drives, and SD cards.
Representation:
Gibibytes are often represented using the symbol “GiB”, while Gigabytes are represented using the symbol “GB”. This helps to differentiate between the two units and avoid confusion.
Example Conversion:
| Gibibytes (GiB) | Gigabytes (GB) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1.074 |
| 10 | 10.74 |
| 100 | 107.37 |
In summary, the main differences between Gibibytes and Gigabytes lie in their measurement systems, usage, and representation. Understanding these differences is important in order to accurately interpret and compare storage capacities.
Binary vs. decimal-based calculations
When it comes to measuring data transfer, it is important to understand the difference between binary-based and decimal-based calculations. Most computer systems use binary (base-2) calculations, while decimal-based calculations are commonly used in everyday life.
In binary-based calculations, a gigabyte (GB) is equal to 1,073,741,824 bytes. This is because computers use a binary system where each unit is represented by a power of 2. In this system, 1 GB is equal to 2^30 bytes.
However, in decimal-based calculations, a gigabyte is equal to 1,000,000,000 bytes. This is because the decimal system uses powers of 10. In this system, 1 GB is equal to 10^9 bytes.
It is important to note that this difference can lead to confusion and discrepancies when comparing data transfer measurements. For example, if you have a 1 GB file and you want to transfer it from one computer to another, the actual amount of data transferred may differ depending on whether binary or decimal-based calculations are used.
To avoid confusion, it is recommended to use binary-based measurements, especially when dealing with computer systems and storage devices. This ensures that you have an accurate understanding of the actual amount of data being transferred or stored.
Implications for data storage and transfer
The use of “gib” as a unit of data storage and transfer has important implications for various aspects of technology.
When it comes to data storage, using gibibytes (GiB) instead of gigabytes (GB) allows for a more precise measurement, as it aligns with the binary system used in computing. This means that storage devices, such as hard drives and solid-state drives, can accurately represent the amount of data they can hold. Additionally, file sizes can be accurately measured in gibibytes, ensuring that users have a clear understanding of how much space their files occupy.
In terms of data transfer, using gibibits (Gibit) instead of gigabits (Gb) provides a more accurate measurement. This is particularly important in scenarios where large amounts of data need to be transferred quickly, such as in network communications or streaming services. By using gibibits, the speed and capacity of data transfer can be more precisely communicated.
Furthermore, the use of gibibytes and gibibits allows for more consistent and reliable calculations when it comes to data storage and transfer. This is because the binary nature of the units aligns with the way computers process and store data. It eliminates the confusion that can arise from the decimal-based system used in gigabytes and gigabits, which can lead to misunderstandings and inaccuracies when it comes to estimating storage or transfer requirements.
Choosing the right measurement
When it comes to measuring data transfer, it is important to choose the right measurement unit. One commonly used unit is the gibibyte (gib), which is a unit of digital information that is often used to measure data storage capacity.
The gibibyte is based on the binary system, which means that it is equal to 2^30 bytes. This is different from the gigabyte (gb), which is based on the decimal system and equal to 10^9 bytes.
When choosing the right measurement, it is important to consider the context in which the data transfer is happening. For example, if you are measuring the capacity of a hard drive or a memory card, it would be more appropriate to use gibibytes. On the other hand, if you are measuring the speed of a data transfer, it would be more appropriate to use gigabytes, as this is a commonly used unit for measuring data transfer speed.
It is also important to note that when data is transferred between different devices or systems, there may be some conversion factors that need to be taken into account. For example, if you are transferring data from a computer to a smartphone, the data may need to be compressed or converted into a format that is compatible with the smartphone. In this case, it would be important to consider any potential conversion factors when choosing the right measurement unit.
Considerations for different scenarios

When it comes to data transfer measurements, it is important to consider the specific scenario in order to accurately determine the amount of data in GB. Different scenarios may have different factors and considerations that can affect the data transfer measurements. Below are a few scenarios to consider:
- Internet Service Providers: ISPs often advertise their internet plans in terms of data transfer measurements, such as megabits per second or GB per month. When choosing an internet plan, it is important to consider the specific needs of your household or business. Factors such as number of users, types of activities (streaming, gaming, browsing), and data limitations should be taken into account to ensure sufficient data transfer capacity.
- Cloud Storage: Many individuals and businesses use cloud storage services to store and share files. In this scenario, it is important to consider the size of the files being uploaded or downloaded and the frequency of these activities. Understanding the data transfer measurements is crucial to accurately estimate the storage space needed and to manage any potential data transfer limitations imposed by the cloud storage provider.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Backing up and recovering data is essential for data protection. When considering data transfer measurements in this scenario, the size of the data being backed up or recovered and the frequency of these activities should be taken into consideration. Additionally, factors such as the speed of the backup and recovery process and any data transfer limitations set by the backup service provider should be carefully evaluated.
- Media Streaming: With the increasing popularity of video and audio streaming services, it is important to understand the data transfer measurements in this scenario. Streaming content consumes data, and the quality of the streaming (SD, HD, Ultra HD) will affect the amount of data transferred. For individuals with limited data caps, it is important to consider the data usage of streaming services to prevent exceeding the given limit.
- Mobile Data Plans: Mobile data plans often come with specific data transfer measurements, such as GB per month. When selecting a mobile data plan, it is important to consider the specific needs of mobile usage, including browsing, social media, video streaming, and app downloads. Understanding the data transfer measurements in this scenario will help in selecting a plan that provides sufficient data for your mobile needs.
In summary, understanding and considering the data transfer measurements in different scenarios is crucial for effectively managing data usage and ensuring sufficient capacity for your specific needs. Taking into account factors such as file size, frequency of activities, and any limitations imposed by service providers will help in making informed decisions and preventing any unexpected data transfer issues.
Common misconceptions and pitfalls

When it comes to data transfer measurements, there are some common misconceptions and pitfalls that many people fall into. One of the major misconceptions is the confusion between gibibytes (gib) and gigabytes (gb). While both terms refer to a unit of digital storage, they have different values. A gibibyte is equal to 1,073,741,824 bytes, while a gigabyte is equal to 1,000,000,000 bytes. This means that when you see a measurement in gibibytes, it will appear larger than the same measurement in gigabytes.
Another common misconception is the assumption that data transfer speeds are the same as download speeds. In reality, data transfer speed refers to the rate at which data can be transmitted between devices, while download speed specifically refers to the rate at which data can be downloaded from the internet. This means that even if you have a fast data transfer speed, your download speed may be limited by other factors such as your internet connection.
One pitfall to be aware of is the use of incorrect units when measuring data transfer. While most people are familiar with kilobytes (KB), megabytes (MB), and gigabytes (GB), there are also smaller and larger units such as terabytes (TB) and petabytes (PB). It’s important to use the correct unit of measurement to accurately represent the amount of data being transferred. Using the wrong unit can lead to confusion and inaccurate calculations.
Finally, it’s important to understand that data transfer measurements can vary depending on the context. For example, when referring to data transfer rates, a higher number indicates faster speeds. However, when referring to data storage capacities, a higher number indicates more storage space. It’s important to be clear about the context in which data transfer measurements are being used to avoid confusion and miscommunication.
FAQ about topic “Gib to GB: Understanding Data Transfer Measurements”
What is the difference between gibibyte (GiB) and gigabyte (GB)?
Gibibyte (GiB) and gigabyte (GB) are both measurements of digital storage capacity, but they represent different values. A gibibyte is equal to 1,073,741,824 bytes, while a gigabyte is equal to 1,000,000,000 bytes. The difference arises from the fact that computers use a binary system, where each unit is a power of 2, while the metric system uses a decimal system, where each unit is a power of 10. Therefore, when it comes to measuring storage capacity, 1 GiB is larger than 1 GB.
Why do we need different measurements for data transfer?
Different measurements for data transfer, such as gibibytes (GiB) and gigabytes (GB), are used to accurately represent the amount of data being transferred. As technology has advanced, the size of digital files and data has increased significantly. Using smaller units, such as kilobytes or megabytes, may not provide an accurate representation of the data being transferred. Therefore, larger units, such as gibibytes or gigabytes, are used to ensure precision in measuring data transfer.
How can I convert gibibytes (GiB) to gigabytes (GB)?
To convert gibibytes to gigabytes, you can use the following formula: 1 GiB = 1.074 GB. Therefore, to convert a certain amount of data in gibibytes to gigabytes, simply multiply the number of gibibytes by 1.074. For example, if you have 100 gibibytes, the equivalent in gigabytes would be 107.4 GB.
What are some common data transfer measurements used in everyday life?
In everyday life, some common data transfer measurements include kilobits per second (Kbps), megabits per second (Mbps), and gigabits per second (Gbps). These measurements are often used when referring to internet or network connection speeds. Kilobits per second is the slowest measurement, followed by megabits per second, and gigabits per second is the fastest. These measurements help us understand the speed at which data can be transferred over a network.
Why is it important to understand data transfer measurements?
Understanding data transfer measurements is important for several reasons. Firstly, it allows us to accurately estimate the time it will take to transfer or download a certain amount of data. For example, if we know the speed of our internet connection in megabits per second and the size of the file we want to download in gigabytes, we can calculate approximately how long it will take to complete the transfer. Secondly, understanding data transfer measurements helps us make informed decisions when it comes to choosing internet or network service providers. By comparing the speeds offered by different providers, we can choose the one that best meets our needs.

