
In the world of networking, twisted pair cables are a vital component for the transmission of data. These cables consist of pairs of insulated copper wires that are twisted together, hence the name. They are commonly used in both residential and commercial settings for various applications, such as local area networks (LANs) and Ethernet connections.
There are two main types of twisted pair cables: unshielded twisted pair (UTP) and shielded twisted pair (STP). UTP cables are the most commonly used in the industry due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of installation. They are capable of transmitting data at high speeds, making them ideal for everyday use.
On the other hand, STP cables are designed with an additional shield to protect the signal from electromagnetic interference. This shielding helps to maintain the integrity of the transmitted data, making STP cables a preferred choice in environments with high levels of interference, such as industrial settings.
Twisted pair cables are typically categorized based on their performance and features. The most commonly used categories are Cat 5, Cat 6, and Cat 7. The higher the category, the greater the bandwidth and transmission speed that the cable is capable of supporting. This makes it important to choose the appropriate category of cable based on the specific networking requirements.
Twisted pair cables have been the go-to option for networking for many years, and they continue to be widely used despite the emergence of alternative transmission technologies such as fiber optics. With their versatility, cost-effectiveness, and compatibility with a wide range of connectors, twisted pair cables remain a reliable choice for transmitting data in various applications within the networking industry.
Contents
- 1 What are Twisted Pair Cables?
- 2 How do Twisted Pair Cables Work?
- 3 Twisted Pair Cable Construction
- 4 Applications of Twisted Pair Cables
- 5 Networking and Data Transmission
- 6 Choosing the Right Twisted Pair Cable
- 7 Factors to Consider
- 8 FAQ about topic “Twisted Pair Cables: A Comprehensive Guide”
- 9 What are twisted pair cables?
- 10 What are the advantages of using twisted pair cables?
- 11 How do twisted pair cables reduce interference?
- 12 What are the different categories of twisted pair cables?
- 13 Can twisted pair cables be used for long-distance transmissions?
What are Twisted Pair Cables?
Twisted Pair Cables, also known as UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) cables, are a type of communication cable widely used in the industry for transmitting data signals. They consist of pairs of insulated copper wires that are twisted together. Each pair carries a different signal, and the twisting helps to reduce the interference or crosstalk between the pairs.
There are different categories of twisted pair cables, such as Category 5 (Cat5) and Category 6 (Cat6), which are commonly used in Ethernet networking. These cables have different specifications and capabilities, with Cat6 cables being capable of higher data transmission speeds.
Twisted pair cables offer several advantages for communication. They are cost-effective compared to other types of cables such as fiber optic cables. They are easy to install and maintain, as they can be terminated with standard connectors. Additionally, they are widely compatible and can be used for various networking applications.
The twisted pair cables are widely used in Local Area Networks (LANs) and other networking environments. They provide reliable transmission of data signals over relatively short distances. They can be used for connecting devices such as computers, routers, switches, and other networking equipment.
In conclusion, twisted pair cables are a popular choice for communication and networking due to their reliability, cost-effectiveness, and compatibility. They play a crucial role in the transmission of data signals in various industries and are widely used in Ethernet networks for connecting devices and ensuring efficient communication.
Definition of Twisted Pair Cables
Twisted pair cables are a type of copper cable commonly used in networking and data transmission applications. They consist of a pair of insulated conductors that are twisted together to minimize electromagnetic interference.
There are two main types of twisted pair cables: unshielded twisted pair (UTP) and shielded twisted pair (STP). UTP cables are widely used in Local Area Networks (LANs) and are the most common type of Ethernet cable. They are cost-effective and provide reliable data transmission in most industry standard applications.
STP cables, on the other hand, have an additional metallic shield that provides extra protection against electromagnetic interference. This makes them suitable for environments with high levels of interference, such as industrial settings or areas with heavy machinery. STP cables are commonly used in fiber optic and long-distance networking applications.
Twisted pair cables are classified into different categories based on their performance capabilities. The most commonly used categories are Cat 5e, Cat 6, and Cat 6a. These categories differ in terms of their bandwidth, data transmission speed, and frequency range.
Twisted pair cables are typically terminated with RJ-45 connectors that are compatible with Ethernet ports. These connectors make it easy to plug and unplug the cables, allowing for easy installation and maintenance.
In summary, twisted pair cables are a popular choice for ethernet and networking applications due to their reliable data transmission, cost-effectiveness, and versatility in different environments. Whether it’s for a small office LAN or a large-scale industrial network, twisted pair cables are an essential component in the modern data-driven world.
Types of Twisted Pair Cables
In the world of networking and Ethernet transmission, twisted pair cables play a vital role in connecting devices and facilitating data communication. These cables are widely used in the industry due to their reliable signal transmission and cost-effectiveness.
There are two main types of twisted pair cables: shielded twisted pair (STP) and unshielded twisted pair (UTP). Both types consist of multiple pairs of copper wires that are twisted together to reduce electromagnetic interference.
Shielded twisted pair (STP) cables, as the name suggests, have an additional metallic shield around the twisted pairs. This shield helps to minimize the crosstalk and external interference, making them ideal for environments with high levels of electromagnetic interference, such as industrial settings. STP cables are commonly used in Ethernet networks and data communication systems.
On the other hand, unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cables do not have the added metallic shield. Despite this, UTP cables are widely used in LAN (local area network) setups and data transmission applications. They are cost-effective and suitable for most residential and small office environments where electromagnetic interference is minimal.
Twisted pair cables also come in different categories, denoted by the generic term “CAT” followed by a number. The higher the category number, the better the cable’s performance in terms of bandwidth and data transmission speed. For example, CAT5, CAT5e, and CAT6 cables are commonly used for Ethernet and high-speed data transmission. These cables can support speeds up to 1000 Mbps and beyond.
In recent years, fiber optic cables have become increasingly popular due to their ability to transmit data at much higher speeds and over longer distances compared to twisted pair cables. However, twisted pair cables, particularly UTP, still dominate the industry and are widely used for various networking and communication applications.
Advantages of Twisted Pair Cables
Twisted pair cables offer numerous advantages in the field of data communication and networking. Here are some of the key benefits:
1. Cost-effectiveness: Twisted pair cables, especially unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cables, are more affordable compared to other types of cables such as fiber optic cables. This makes them a preferred choice for small to medium-sized businesses and home networks.
2. Flexibility: Twisted pair cables are highly flexible, making them easier to install and manage in various networking environments. They can be easily bent and routed around corners without affecting their performance, making them ideal for both indoor and outdoor installations.
3. Compatibility: Twisted pair cables are widely used in the industry and are compatible with a wide range of networking devices and connectors. They can be easily terminated with RJ-45 connectors, which are commonly used in Ethernet networks.
4. Reliable transmission: Twisted pair cables provide reliable data transmission over long distances. The twisted pairs help to reduce crosstalk and electromagnetic interference, resulting in higher data transfer rates and better signal quality.
5. Versatility: Twisted pair cables come in different categories, such as Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat7, each offering specific performance characteristics. This allows users to choose the right cable category based on their networking requirements, whether it’s for a local area network (LAN) or for high-speed data transmission.
6. Copper-based technology: Twisted pair cables are made of copper, which is a highly conductive material. Copper-based cables offer excellent conductivity and are capable of transmitting signals over longer distances without significant loss in quality.
7. Shielded options: In addition to unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cables, there are also shielded twisted pair (STP) cables available. STP cables have an extra layer of shielding, which provides superior protection against external noise and interference.
Overall, twisted pair cables offer a cost-effective, reliable, and flexible solution for data transmission and communication in various networking environments. Their compatibility, versatility, and copper-based technology make them a popular choice in the industry.
How do Twisted Pair Cables Work?
Twisted pair cables are a common type of communication cable used in networking and data transmission. They consist of multiple pairs of insulated copper wires that are twisted together. The twisting of the wires helps to reduce interference and crosstalk, allowing for more reliable and robust data transmission.
There are different categories of twisted pair cables, such as Category 5e, Category 6, and Category 7. These categories determine the maximum data transfer rates and frequencies supported by the cable. Higher category cables generally offer better performance and higher speeds.
Twisted pair cables can be either shielded or unshielded. Shielded twisted pair (STP) cables have an additional layer of shielding around the twisted pairs, which helps to further reduce interference from external sources. Unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cables do not have this shielding but are still effective in most non-industrial environments.
The twisted pair cables are typically terminated with connectors, such as RJ45 connectors, which are commonly used in Ethernet and LAN connections. These connectors provide a secure and reliable connection between the cable and the device.
Twisted pair cables are widely used in the industry due to their cost-effectiveness and compatibility with various networking technologies. They can transmit both voice and data signals, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
In comparison to other types of cables, such as fiber optic cables, twisted pair cables have limitations in terms of their maximum transmission distance and bandwidth. However, they are still widely used in many networking and communication applications due to their affordability and versatility.
Twisted Pair Cable Construction
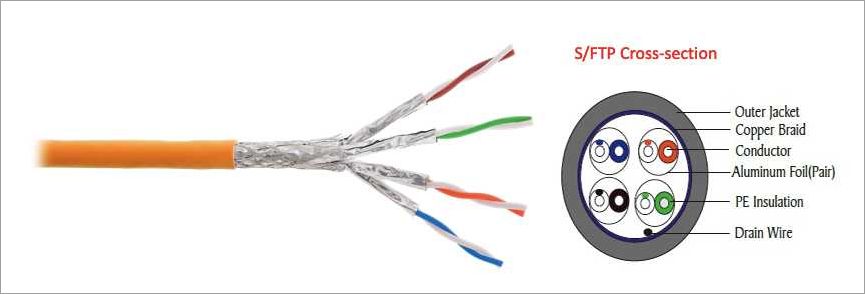
A twisted pair cable is a type of cable used for data transmission in networking and communication industry. It consists of multiple pairs of copper wires that are twisted together to reduce interference and crosstalk.
The most common types of twisted pair cables are unshielded twisted pair (UTP) and shielded twisted pair (STP). UTP cables are widely used in Ethernet networking and are the most cost-effective option. They have four pairs of twisted wires, with each pair being color-coded for easy identification.
STP cables, on the other hand, have an additional layer of shielding that helps protect the signal from interference and external electromagnetic radiation. This makes them more suitable for environments with higher levels of interference, such as industrial settings.
The construction of a twisted pair cable involves tightly twisting two insulated copper wires together to form a pair. This twisting helps to cancel out electromagnetic interference and crosstalk, as any interference induced in one wire is canceled out by the opposite polarity of the other wire in the pair.
The number of twists per inch can vary depending on the category of the cable. For example, Category 5e cables typically have 2 twists per inch, while Category 6 cables have 2.5 twists per inch. The tighter the twists, the better the cable can resist interference.
At each end of the cable, there are connectors that allow the cable to be connected to devices such as computers, routers, and switches. The most common connector used in twisted pair cables is the RJ-45 connector, which is widely used in Ethernet LAN connections.
In conclusion, twisted pair cables are an essential component in the data transmission and networking industry. They provide a reliable and cost-effective solution for transmitting data over long distances while minimizing interference and crosstalk.
Twisted Pair Cable Anatomy
A twisted pair cable is a type of cable commonly used in networking and communication industry, particularly for LAN (Local Area Network) connections. It consists of two insulated copper wires that are twisted together, hence the name “twisted pair”.
The main purpose behind the twisted pair design is to minimize electrical interference and crosstalk between the wires. This interference can occur when multiple cables are installed closely together, leading to a degraded signal quality. The twisting of the wires helps to cancel out the interference, improving the overall transmission quality of the data or signal.
There are two main types of twisted pair cables: unshielded twisted pair (UTP) and shielded twisted pair (STP). UTP cables do not have any additional shielding, while STP cables are wrapped in a protective shield to further reduce electromagnetic interference.
The connectors commonly used for twisted pair cables are RJ-45 connectors, which are specifically designed for Ethernet connections. These connectors have eight pins that match the eight wires within the cable, allowing for the transmission of data at high speeds.
Twisted pair cables are widely used in various applications, including Ethernet networking, telephone networks, and even some fiber optic communication systems. They are categorized into different categories based on their performance, with Category 5e and Category 6 being commonly used for Ethernet networks.
In summary, twisted pair cables are an essential component of modern networking and communication systems. Their twisted design helps to minimize interference and crosstalk, ensuring reliable data transmission. Whether it’s for residential or commercial use, twisted pair cables play a crucial role in the connectivity and data transfer within the digital world.
Twisted Pair Cable Functionality
A twisted pair cable is a type of LAN cable that is widely used in the networking industry for communication purposes. It consists of two insulated copper wires that are twisted together in a helical pattern. The primary function of a twisted pair cable is to transmit data signals from one device to another, making it essential for networking and communication.
The twisted pair cable utilizes the concept of twisted pairs to enhance its performance. By twisting the wires together, the cable minimizes electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk, which can degrade the quality of the signal. This ensures reliable and efficient transmission of data over long distances.
There are two main types of twisted pair cables: unshielded twisted pair (UTP) and shielded twisted pair (STP). UTP cables are commonly used in Ethernet networks and are more cost-effective. They are suitable for most applications where electromagnetic interference is not a major concern. On the other hand, STP cables have an additional layer of shielding, which provides better protection against EMI. They are commonly used in industrial and high-noise environments.
The twisted pair cables are categorized based on their performance characteristics, which are defined by the industry standards. The most widely used categories are CAT5, CAT5e, CAT6, and CAT6a. These categories determine the maximum data transmission speeds and frequencies that the cable can support. CAT6 and CAT6a cables are becoming increasingly popular due to their higher performance capabilities, especially for gigabit Ethernet and high-speed data transmission.
In addition to copper-based twisted pair cables, there are also fiber optic twisted pair cables available. These cables use optical fibers instead of copper wires for data transmission. Fiber optic twisted pair cables offer higher bandwidth and longer transmission distances compared to copper-based cables. They are commonly used in high-speed networking and long-distance communication applications.
In conclusion, twisted pair cables play a crucial role in the functionality of LAN networks and other communication systems. With the ability to minimize interference and provide reliable data transmission, they are the preferred choice for many networking applications. Whether it’s UTP or STP, copper-based or fiber optic, twisted pair cables are an essential component of modern communication infrastructure.
Twisted Pair Cable Transmission
The transmission of data through a twisted pair cable is an essential component of modern networking systems. Twisted pair cables, often referred to as Ethernet cables, are widely used for LAN communication and play a crucial role in connecting devices within a network.
The cable consists of pairs of twisted copper wires, which help to minimize signal interference and enhance transmission quality. Twisting the wires helps to cancel out electromagnetic interference from external sources, improving the overall reliability of the cable.
There are two main types of twisted pair cables: unshielded twisted pair (UTP) and shielded twisted pair (STP). UTP cables are commonly found in home and office settings, offering cost-effective solutions for data transmission. In contrast, STP cables provide additional protection against electromagnetic interference and are often used in industrial environments.
Within the industry, twisted pair cables are categorized according to different specifications, known as categories. The most common categories include Category 5e (Cat5e) and Category 6 (Cat6), which provide higher data transmission speeds and improved performance compared to earlier versions.
Twisted pair cables offer several advantages over other types of transmission media, such as fiber optics. They are cost-effective, easy to install, and can support various networking technologies, including Ethernet. Additionally, they can transmit both power and data, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
In conclusion, twisted pair cable transmission plays a critical role in modern networking systems. Whether it is for LAN communication or connecting devices within a network, twisted pair cables provide reliable and efficient data transmission. The use of twisted pairs helps to minimize signal interference, ensuring high-quality communication even in challenging environments.
Applications of Twisted Pair Cables
The use of twisted pair cables is widespread in various fields and industries, thanks to their versatility and efficient signal transmission capabilities. Here are some of the key applications of twisted pair cables:
- Communication Networks: Twisted pair cables are commonly used in communication networks to transmit data and voice signals. These cables are widely used in office buildings, homes, and other environments to establish local area networks (LANs) and provide internet connectivity. They are also used in telephone networks for reliable and efficient communication.
- Ethernet Networking: Twisted pair cables, particularly the unshielded twisted pair (UTP) variety, are the standard choice for Ethernet networking. They are used to connect devices such as computers, switches, routers, and servers, enabling high-speed data transmission over local and wide area networks. Twisted pair cables are available in different categories, such as Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat6a, each with varying speeds and bandwidth capabilities.
- Data Centers: In data center environments, twisted pair cables are used extensively for connectivity within racks, between racks, and across different sections of the facility. They enable efficient data transmission and ensure reliable connections between servers, storage systems, and networking equipment.
- Industrial Applications: Twisted pair cables are also utilized in various industrial applications, including factory automation, process control systems, and robotics. They provide reliable and secure transmission of signals in these settings, enabling efficient control and monitoring of industrial processes.
- Audio and Video Systems: Twisted pair cables, both shielded (STP) and unshielded (UTP), are commonly used for audio and video applications. They are used to transmit video signals in CCTV systems, as well as audio signals in sound systems, speakers, and multimedia setups.
- Fiber Optic Integration: Twisted pair cables are often used alongside fiber optic cables in networking setups. They serve as connectors between fiber optic cables and copper-based devices, enabling seamless integration and transmission of signals between the two mediums.
In summary, twisted pair cables find wide-ranging applications in the industry, including communication networks, Ethernet networking, data centers, industrial automation, audio and video systems, and fiber optic integration. Their versatility, reliability, and cost-effectiveness make them a popular choice for various signal transmission needs.
Networking and Data Transmission
Data transmission is a crucial aspect of networking and communication in the modern era. Twisted pair cables play a significant role in transmitting data efficiently and securely over local area networks (LANs) and other communication systems. These cables are made of two copper conductors twisted together, which helps reduce electromagnetic interference from external sources, resulting in reliable data transmission.
One of the most common types of twisted pair cables used in networking is unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cable. UTP cables are widely used in Ethernet networks due to their affordable cost and ease of installation. They are categorized into different categories like Cat5, Cat6, and Cat7, each offering varying levels of performance and bandwidth.
In addition to UTP cables, there are shielded twisted pair (STP) cables that offer extra protection against electromagnetic interference. STP cables have a foil or braided shielding around the twisted pair, which helps in reducing signal degradation and crosstalk. These cables are commonly used in industrial environments where there is a higher chance of interference.
While twisted pair cables have been the go-to choice for networking, there is also a growing use of fiber optic cables in the industry. Fiber optic cables use light signals for data transmission instead of electrical signals, allowing for faster and longer distance transmission. They have become popular in high-speed networks and data centers where speed and scalability are crucial.
Networking and data transmission rely on the proper selection of cables, connectors, and equipment to ensure efficient signal transmission. Whether it is the traditional copper-based twisted pair cables or the advanced fiber optic cables, choosing the right cable for the network infrastructure is essential for achieving reliable and high-speed data transmission.
Twisted Pair Cables in Ethernet
Ethernet, the most widely used communication standard in the networking industry, relies heavily on twisted pair cables for data transmission. These cables are built using multiple pairs of insulated copper wires twisted together, which helps to reduce electromagnetic interference and crosstalk.
Twisted pair cables used in Ethernet can be either shielded or unshielded. Shielded twisted pair (STP) cables have an additional layer of shielding to protect the signal from external interference, making them more suitable for high-speed and long-distance transmission. Unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cables, on the other hand, do not have this additional shielding.
In Ethernet, twisted pair cables are classified into different categories based on their specifications and performance. Category 5e (Cat5e) and Category 6 (Cat6) cables are commonly used in LAN networks, offering improved data rates and reduced crosstalk compared to earlier versions. Cat6 cables are often preferred in industries where high-speed data transmission is required, such as in data centers and server rooms.
Fiber optic cables are also used for Ethernet networking, offering even higher data transmission rates and longer distance capabilities. However, twisted pair cables remain popular due to their cost-effectiveness and compatibility with existing infrastructure.
Twisted pair cables in Ethernet use RJ-45 connectors, which have eight pins that correspond to the eight wires within the cable. These connectors ensure a secure and reliable connection between network devices and the cable, allowing for efficient data transfer.
In summary, twisted pair cables play a crucial role in Ethernet communication, providing a reliable and cost-effective solution for data transmission. The use of twisted pair cables in Ethernet networks has revolutionized the way we connect and communicate in the digital age.
Twisted Pair Cables in Telephone Systems
Twisted pair cables are an essential component in telephone systems, enabling the transmission of signals over long distances. These cables consist of multiple pairs of insulated copper wires that are twisted together. The twisting of the wires helps to minimize electromagnetic interference and crosstalk, ensuring clear and reliable communication.
In telephone systems, twisted pair cables are commonly used for both voice and data transmission. They are widely used in local area networks (LANs) for connecting telephones and equipment to the network. The cables are capable of transmitting data at high speeds, making them ideal for communication in the digital age.
There are different types of twisted pair cables used in the telephone industry, including unshielded twisted pair (UTP) and shielded twisted pair (STP). UTP cables are the most common and cost-effective choice for telephone systems. They are used for a variety of applications, ranging from home telephone wiring to large-scale networking projects in businesses and organizations.
STP cables, on the other hand, have an additional layer of shielding to protect against electromagnetic interference. They are commonly used in environments where there is a high risk of interference, such as in industrial settings or areas with heavy electrical equipment.
The use of twisted pair cables has become even more prevalent with the rise of fiber optic technology. While fiber optic cables offer faster data transmission speeds over longer distances, twisted pair cables are still commonly used for the final connection from the network to the end user. This is because they are more cost-effective and easier to install than fiber optic cables.
In summary, twisted pair cables play a crucial role in telephone systems, providing a reliable and efficient means of communication. Whether it is for voice or data transmission, these cables are widely used in the industry and have proven to be a reliable choice for many networking applications.
Twisted Pair Cables in Audio and Video Systems
Twisted pair cables are widely used in the audio and video industry for their reliable and efficient transmission capabilities. These cables consist of multiple pairs of copper wires that are twisted together to minimize interference and enhance signal quality.
Within the audio and video industry, different categories of twisted pair cables are used depending on the specific requirements of the application. Category 5e (Cat5e) cables are commonly used for high-quality audio transmission, while Category 6 (Cat6) cables are suitable for both audio and video data.
Unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cables are commonly used in audio applications as they provide cost-effective and reliable transmission. These cables are ideal for short-distance audio connections within a studio or between audio devices.
For video systems that require higher data rates and longer transmission distances, shielded twisted pair (STP) cables are often employed. These cables have an additional layer of shielding that helps to protect the audio and video signal from electromagnetic interference.
Twisted pair cables are also widely used in local area networks (LAN) and networking applications. They are the standard choice for Ethernet connections due to their ability to transmit data at high speeds and provide reliable communication. The twisted pair design helps to minimize crosstalk and interference, ensuring a clear and uninterrupted signal transmission.
When it comes to connectors for twisted pair cables in audio and video systems, RJ45 connectors are commonly used. These connectors provide a secure and reliable connection, making them suitable for professional audio and video installations.
In summary, twisted pair cables play a crucial role in audio and video systems, providing efficient and reliable transmission of signals. They are versatile and can be used in various applications within the industry, ranging from audio connections within a studio to video transmission over long distances. Whether using unshielded or shielded twisted pair cables, their twisted design helps to enhance signal quality and minimize interference, making them an essential component in modern audio and video systems.
Choosing the Right Twisted Pair Cable
When it comes to selecting the right twisted pair cable for your communication or data transmission needs, there are several factors to consider. One of the main considerations is the type of cable, which can vary depending on the specific requirements of your application.
There are two main types of twisted pair cables: unshielded twisted pair (UTP) and shielded twisted pair (STP). UTP cables are the most commonly used in the industry, thanks to their affordability and versatility. These cables consist of several pairs of insulated copper wires twisted together, and they are suitable for a wide range of applications, including Ethernet and LAN connectivity.
On the other hand, STP cables are similar to UTP cables, but with an added layer of shielding to protect the transmission signal from external interference. This makes STP cables more resistant to electromagnetic interference, making them ideal for environments where there may be a lot of electrical noise.
Another important consideration when choosing a twisted pair cable is the category. Twisted pair cables are categorized based on their performance characteristics, with higher categories offering greater bandwidth and faster data transmission speeds. The most commonly used categories are Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat6a. Cat5e cables are suitable for basic Ethernet and LAN connectivity, while Cat6 and Cat6a cables can support faster data speeds and are often used in more demanding applications.
In addition to considering the cable type and category, it is also important to choose the right connectors for your twisted pair cable. RJ-45 connectors are commonly used in Ethernet and LAN applications, but there are also other connector options available.
Overall, choosing the right twisted pair cable is essential for ensuring reliable and efficient communication and data transmission. By considering factors such as cable type, category, and connectors, you can select the cable that best suits your specific needs.
Factors to Consider
When it comes to choosing the right twisted pair cable for communication and data transmission, several factors need to be considered:
- Cable Category: Different categories of twisted pair cables, such as Cat5, Cat6, and Cat7, offer varying levels of performance and bandwidth. Choose the appropriate category that meets your networking requirements.
- Shielded or Unshielded: Twisted pair cables can be either shielded (STP) or unshielded (UTP). Shielded cables provide better protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk, but they are generally more expensive than unshielded ones.
- Pair Configuration: Twisted pair cables consist of pairs of copper wires twisted together. The number of pairs in a cable can vary, and it affects the maximum data transmission rate and capabilities of the cable.
- Connector Compatibility: Consider the types of connectors used in your networking devices and ensure they are compatible with the twisted pair cable you choose. Common connectors include RJ-45 for Ethernet connections.
- Fiber Optic vs Copper: While twisted pair cables are commonly used for networking, fiber optic cables are gaining popularity due to their higher bandwidth, longer transmission distances, and immunity to interference.
Considering these factors is crucial in selecting the right twisted pair cable for your communication and data transmission needs. Whether you opt for shielded or unshielded, choose the appropriate category and pair configuration, and ensure compatibility with your networking devices. Additionally, evaluate the advantages of fiber optic cables for high-speed and interference-free data transmission in your industry.
Cable Category and Speed
The speed and performance of twisted pair cables depend on their category and the level of shielding they provide. The most common categories of twisted pair cables are STP (Shielded Twisted Pair) and UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair).
UTP cables are widely used in the industry for LAN (Local Area Network) and data communication. These cables consist of four pairs of twisted copper wires and are designed for transmission of Ethernet signals. UTP cables are easy to install, flexible, and cost-effective. However, they are more susceptible to electromagnetic interference and signal loss compared to shielded cables.
STP cables, on the other hand, provide additional shielding for better signal quality and less interference. They have a metal foil or braid that wraps around each individual pair of twisted wires, protecting them from external electromagnetic interference. This makes STP cables more suitable for environments with higher levels of interference, such as industrial settings or areas with a lot of electronic equipment.
The performance of twisted pair cables is also determined by their category. Each category represents a different level of performance and transmission speed. For example, Category 5e cables can support speeds up to 1000 Mbps (megabits per second) and are commonly used for Ethernet networks. Category 6 cables offer even higher speeds, up to 10 Gbps (gigabits per second), making them ideal for high-speed internet connections and demanding applications.
It’s important to note that while twisted pair cables are widely used, they are not the only option for data transmission. Fiber optic cables, for instance, offer even higher speeds and larger bandwidth. However, twisted pair cables remain popular due to their affordability and compatibility with existing infrastructure. They continue to be the go-to choice for many Ethernet and communication applications.
Shielding and Noise Immunity
Shielding is an important aspect of networking cables, especially in environments where electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI) are present. Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) cables are the most commonly used type of Ethernet cable in the industry. While they are effective for general data transmission, they may be susceptible to noise and interference.
Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) cables, on the other hand, have an additional layer of shielding, typically made of metal foil or braided copper. This shielding helps to reduce the impact of external electromagnetic interference, improving the overall noise immunity of the cable. STP cables are ideal for environments with high levels of EMI and RFI, such as industrial settings or areas with a lot of electrical equipment.
Pair twisting is another technique used to minimize noise in networking cables. Twisted pair cables feature two insulated copper wires twisted around each other. This twisting helps to cancel out the electromagnetic interference that may be picked up during transmission. The higher the number of twists per inch, the better the noise cancellation.
The shielding and noise immunity capabilities of a cable are often specified by the category of the cable. For example, Category 5e (Cat 5e) cables are unshielded and provide good noise immunity for typical LAN communication. Category 6 (Cat 6) cables, on the other hand, are shielded and offer even better noise immunity, making them suitable for both Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet transmission.
In addition to shielding, proper termination with shielded connectors is crucial for maintaining the cable’s noise immunity. Shielded connectors ensure that the shielding is properly grounded, preventing the interference from entering the network. It is important to use the correct connectors and follow proper installation practices to maximize the cable’s noise immunity and minimize data loss or transmission errors.
Cable Length and Installation Requirements
When it comes to ethernet and fiber communication, cable length and installation requirements play a crucial role in ensuring optimal network performance. Ethernet cables, particularly twisted pair cables, are widely used in the networking industry for data transmission.
Ethernet cables are available in different categories, such as CAT 5, CAT 6, and CAT 7, each with its own maximum length specifications. For example, CAT 5 cables can typically transmit data up to 100 meters, while CAT 6 and CAT 7 cables can achieve lengths of up to 55 meters and 100 meters, respectively.
To achieve longer cable lengths, fiber optic cables are often preferred over copper cables. Fiber optic cables utilize light signals for data transmission, allowing for greater distances without signal degradation. They are commonly used in long-distance communication and high-speed networking applications.
When installing twisted pair cables, it is important to consider the type of cable being used. Shielded twisted pair (STP) cables provide better protection against electromagnetic interference, making them suitable for environments with high electrical noise. Unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cables, on the other hand, are more commonly used in residential and small office LAN installations.
The installation of twisted pair cables also requires attention to proper grounding and termination. Suitable connectors and termination techniques, such as RJ-45 connectors and punch-down blocks, are used to ensure a secure and reliable connection. The cable should be properly routed and secured to avoid damage or signal loss.
In summary, cable length and installation requirements are important considerations in the networking industry. Choosing the appropriate cable category, such as CAT 5, CAT 6, or CAT 7, and understanding the advantages of fiber optic cables versus copper cables, can greatly impact the performance of a communication network. Attention to details like shielding, grounding, and termination techniques is crucial for maintaining signal integrity and ensuring a reliable network connection.
FAQ about topic “Twisted Pair Cables: A Comprehensive Guide”
What are twisted pair cables?
Twisted pair cables are a type of wiring commonly used in telecommunications and computer networks. They consist of pairs of insulated copper wires that are twisted together in a specific pattern to reduce interference and crosstalk.
What are the advantages of using twisted pair cables?
There are several advantages of using twisted pair cables. Firstly, they are relatively inexpensive compared to other types of cables. Secondly, they are easy to install and terminate. Thirdly, they provide good resistance to external interference. Finally, twisted pair cables are capable of carrying both voice and data signals, making them versatile for various applications.
How do twisted pair cables reduce interference?
Twisted pair cables reduce interference by using a technique called “twisting”. The twisting pattern of the wires causes the electromagnetic fields generated by the signals in each wire to cancel each other out. This helps to prevent the signals from one wire from interfering with the signals in another wire, which improves the overall performance and reliability of the cable.
What are the different categories of twisted pair cables?
Twisted pair cables are classified into different categories based on their performance characteristics. The commonly used categories are Cat 3, Cat 5, Cat 5e, Cat 6, and Cat 6a. Each category has specific specifications regarding data transmission rates, maximum cable lengths, and interference resistance. It is important to choose the right category of cable based on the intended application.
Can twisted pair cables be used for long-distance transmissions?
Yes, twisted pair cables can be used for long-distance transmissions, but the maximum distance depends on the category of cable being used. Cat 5 and Cat 5e cables can support distances of up to 100 meters for Ethernet data transmission. Cat 6 and Cat 6a cables can support even longer distances, with Cat 6 capable of supporting up to 55 meters for 10GBASE-T Ethernet and Cat 6a capable of supporting up to 100 meters for 10GBASE-T Ethernet.

