In the world of encoding and streaming, bitrate plays a crucial role in determining the overall quality of audio and video content. Bitrate, simply put, refers to the amount of data that is transmitted or processed over a given period of time. It is commonly measured in bits per second (bps) and is influenced by factors such as resolution, quality, and format.
When it comes to video content, the bitrate is heavily dependent on the resolution and quality of the footage. Higher resolution and better quality require more data to be transmitted, resulting in a higher bitrate. On the other hand, lower resolution and lower quality can result in a lower bitrate, as less data needs to be transmitted.
Bandwidth also plays a significant role in determining the bitrate of streaming content. Bandwidth refers to the amount of data that can be transmitted over a network connection in a given period of time. If the available bandwidth is limited, it can restrict the bitrate of the content being streamed. This can lead to buffering issues and lower quality playback.
In order to reduce the amount of data being transmitted without compromising the quality too much, compression techniques are used. Compression can be either lossless or lossy. Lossless compression reduces the file size without losing any data, while lossy compression discards certain data to achieve a higher level of compression. Codecs, such as H.264 or AAC, are commonly used to compress audio and video data.
Understanding bitrate is essential for anyone involved in encoding, streaming, or transmission of audio and video data. It allows the optimization of file sizes and streaming quality, ensuring the best possible experience for the end users. By carefully managing the bitrate, system administrators and content creators can strike the right balance between file size, streaming speed, and visual or audio quality.
Contents
- 1 What is Bitrate?
- 2 Types of Bitrate
- 3 Factors Affecting Bitrate
- 4 Choosing the Right Bitrate
- 5 FAQ about topic “Understanding Bitrate in Systems: Everything You Need to Know”
- 6 What is bitrate and why is it important in systems?
- 7 How does bitrate affect the quality of audio and video files?
- 8 Does bitrate affect the file size of audio and video files?
- 9 What factors should be considered when choosing the appropriate bitrate for data transmission?
- 10 Is higher bitrate always better for all types of data transmission?
What is Bitrate?
Bitrate refers to the amount of data that is transmitted or processed over a network or system within a specific timeframe. It is typically measured in bits per second (bps) and indicates the speed at which data is transferred.
In the context of streaming, bitrate is crucial as it determines the quality of the video or audio being transmitted. The higher the bitrate, the better the quality, but also the more bandwidth is required for transmission.
When it comes to encoding and compression, bitrate plays a major role. In a compressed file, a higher bitrate generally results in better quality, but also a larger file size. Conversely, a lower bitrate leads to a smaller file size, but also lower quality.
The bitrate of a video or audio stream is influenced by several factors, including resolution, format, codec, and network conditions. Higher resolutions and more complex formats generally require higher bitrates for optimal quality.
Streaming platforms and networks often use adaptive bitrate streaming, which automatically adjusts the bitrate based on the user’s network conditions. This ensures a smooth and uninterrupted streaming experience by dynamically adapting to the available bandwidth.
Overall, bitrate is a crucial aspect in understanding the quality and transmission of data in systems. It directly affects the speed, quality, and file size of a transmission, whether it be for audio, video, or any other form of data.
Definition of Bitrate
Bitrate refers to the speed at which data is transmitted or streamed over a network. It is a measure of the amount of data that is processed per unit of time, usually expressed in kilobits per second (Kbps) or megabits per second (Mbps).
When it comes to streaming video or audio, bitrate plays a crucial role in determining the quality of the content. Higher bitrates result in better quality, while lower bitrates may cause degradation in the audio or video stream.
The bitrate is directly related to the resolution and complexity of the content being streamed. Videos with higher resolutions and more intricate scenes require higher bitrates to maintain optimal quality. On the other hand, simpler content with lower resolutions can be streamed at lower bitrates without compromising the viewing experience.
To achieve efficient transmission and storage of data, compression techniques are employed. Codecs, such as H.264 or AAC, are used to compress the audio and video data, reducing the overall size without sacrificing quality. The bitrate of a compressed stream is typically lower than that of the original, uncompressed data.
It’s important to note that bitrate affects both the quality of audio and video streams. Higher bitrates result in better audio fidelity and more detail in the video, while lower bitrates can lead to audio artifacts and decreased image clarity.
Bandwidth is another key factor that influences bitrate. A network with limited bandwidth may struggle to handle high bitrates, resulting in buffering, lag, or dropped frames. Therefore, it is essential to consider the available bandwidth when selecting the appropriate bitrate for streaming.
In summary, bitrate is a fundamental aspect of any streaming system. It determines the amount of data that can be transmitted per unit of time and affects the quality of audio and video streams. By using compression techniques and considering the available bandwidth, the bitrate can be optimized to deliver an optimal viewing or listening experience.
How Bitrate is Measured
Bitrate refers to the amount of data transmitted or processed per unit of time. In the context of video and audio systems, it is commonly used to measure the speed at which data is encoded, transmitted, and decoded. It plays a crucial role in determining the quality, size, and compatibility of video and audio files.
The measurement of bitrate depends on various factors, including the chosen codec, file format, resolution, and compression algorithm. Codecs, such as H.264 or MPEG-4, determine how the video or audio is encoded and decoded, affecting the size and quality of the file. Lossless codecs retain all the original data, resulting in higher file sizes but maintaining the highest quality. On the other hand, lossy codecs reduce file sizes by selectively discarding data, compromising some quality.
Bandwidth is another important factor that affects bitrate. It refers to the maximum data transfer rate of a network or transmission system. Limited bandwidth can lead to lower bitrates, affecting the quality and smoothness of video or audio streams. Higher bandwidth allows for higher bitrate transmissions, resulting in better quality and faster data transfer.
The resolution of the video or audio plays a significant role in determining the bitrate. Higher resolutions, such as 4K or 1080p, require more data to accurately represent the image or sound, resulting in higher bitrates. Lower resolutions, like 720p or lower, require less data, resulting in lower bitrates.
Furthermore, the bitrate can vary throughout a video or audio file. Constant bitrate (CBR) means that the bitrate remains the same throughout the entire file, while variable bitrate (VBR) allows for changes in the bitrate depending on the complexity of the content. VBR is often used to optimize file sizes and maintain quality, as it allocates more bits to complex scenes and fewer bits to simpler ones.
In conclusion, bitrate is a key measure in video and audio systems that determines the amount of data transferred per unit of time. It is influenced by various factors, including codec, file format, resolution, and compression. Understanding bitrate is crucial for optimizing file size, quality, and ensuring compatibility in different network and system environments.
Importance of Bitrate in Video and Audio Streaming
Bitrate plays a crucial role in video and audio streaming. It determines the amount of data that is transmitted per unit of time, thereby influencing the quality of the stream. Bitrate is affected by various factors, including the format, codec, resolution, and encoding used in the streaming system.
Video and audio files come in different formats, and each format requires specific codecs for decoding. The codec used in the streaming system determines the efficiency of compression and the resulting file size. Higher bitrates often indicate better quality, but they also require more bandwidth for transmission.
Streaming systems need to strike a balance between bitrate and quality to ensure smooth playback without interruptions. A low bitrate may result in loss of details and a decrease in audio or video quality, while a high bitrate can strain the network and cause buffering issues.
Bitrate is particularly important in streaming audio, as it affects the audio fidelity and clarity. Higher bitrates result in better sound quality, allowing for richer tones and details. Lossless audio encoding, which preserves the original audio data without any compression, requires a significantly higher bitrate compared to lossy compression methods.
In video streaming, bitrate impacts the level of detail and sharpness of the video. Higher bitrates result in smoother motion, better color reproduction, and reduced compression artifacts. However, higher bitrates also require faster transmission speed and more network bandwidth.
Overall, bitrate is a critical factor in video and audio streaming, as it determines the level of quality in the transmitted data stream. Streaming systems must carefully consider the bitrate to optimize both the quality and smoothness of the playback while utilizing the available network resources efficiently.
Types of Bitrate
In systems that involve data compression, bitrate is an important concept that affects the speed, quality, and efficiency of data transmission. There are different types of bitrate that are commonly used in various audio and video systems.
1. Constant Bitrate (CBR): With constant bitrate encoding, data is encoded at a fixed rate. This means that each second of audio or video content will have the same number of bits. CBR is useful in situations where a consistent transmission speed is required, such as in streaming or broadcasting.
2. Variable Bitrate (VBR): Variable bitrate encoding adjusts the bitrate based on the complexity of the content being encoded. This allows for a higher bitrate during complex scenes, and a lower bitrate during simpler scenes. VBR can result in higher quality audio or video with more efficient use of bandwidth.
3. Average Bitrate (ABR): Average bitrate encoding aims to maintain a consistent average bitrate throughout the encoding process. It dynamically adjusts the bitrate based on the complexity of the content, but caps the maximum and minimum bitrates to ensure a consistent average. ABR strikes a balance between CBR and VBR, offering a compromise between consistent transmission speed and efficient use of bandwidth.
4. Lossless Bitrate: Lossless compression is a method of encoding data without any loss of quality. Lossless audio codecs, for example, compress the audio data but are able to fully reconstruct the original audio during decoding. Lossless bitrate refers to the bitrate required to maintain the full quality of the uncompressed audio or video.
5. Lossy Bitrate: Lossy compression is a method of encoding data where some amount of quality is sacrificed to achieve higher compression ratios. Lossy audio and video codecs discard or approximate certain data during compression, resulting in smaller file sizes but a loss of some quality. The bitrate for lossy compression refers to the amount of data transmitted per unit of time.
In summary, bitrate types such as constant, variable, average, lossless, and lossy, play an important role in determining the quality, efficiency, and speed of data transmission in audio and video systems. Each type has its own advantages and trade-offs, and the choice of bitrate type depends on the specific requirements of the system and the desired balance between file size, bandwidth usage, and audio/video quality.
Constant Bitrate (CBR)
Constant Bitrate (CBR) is a transmission format commonly used for video and audio streaming. It ensures a consistent speed and quality for the encoded data stream.
CBR uses a fixed bitrate throughout the entire transmission, regardless of the content being streamed. This means that the same amount of data is transmitted at a constant rate every second, resulting in a predictable file size.
When using CBR, a codec or encoding system is employed to compress the video or audio stream. This codec compresses the data in a specific format, reducing its size while maintaining acceptable quality.
One advantage of CBR is that it allows for easy planning and allocation of bandwidth. Since the bitrate remains constant, network administrators can calculate the required bandwidth for streaming and allocate resources accordingly.
However, CBR may not be the most efficient option for all situations. For example, if the video or audio being streamed contains significant variations in complexity, a constant bitrate may result in inefficient encoding. In such cases, a Variable Bitrate (VBR) format may be more suitable.
In summary, Constant Bitrate (CBR) is a transmission format that ensures a consistent speed and quality for the encoded data stream. It uses a fixed bitrate throughout the transmission, allowing for easy planning and allocation of bandwidth. However, it may not be the most efficient option for content with significant variations in complexity.
Advantages of CBR
CBR, or Constant Bitrate, is a format used in the transmission and streaming of audio and video data. It offers several advantages over other formats.
One of the main advantages of CBR is the consistent quality it provides. By using a constant bitrate, the compressed data is encoded at a fixed rate, ensuring that the quality remains consistent throughout the entire stream. This is particularly important for streaming services that require a high level of quality and reliability.
Another advantage of CBR is its compatibility with various systems and codecs. Since CBR uses a fixed bitrate, it can be easily decoded by any system or codec that supports the format. This makes it an ideal choice for streaming platforms and devices that may have different capabilities and requirements.
CBR also allows for easier management of network bandwidth. By using a constant bitrate, it is easier to estimate the required bandwidth for streaming audio or video content. This is particularly useful for live streaming or when dealing with limited network resources, as it helps to ensure a smooth and uninterrupted stream.
Furthermore, CBR is beneficial for content creators who want to control the size of their files. Since CBR uses a fixed bitrate, it allows for more accurate prediction of file sizes, making it easier to manage storage and distribution. This can be especially important in scenarios where limited storage space or bandwidth is a concern.
In summary, CBR offers advantages such as consistent quality, compatibility with different systems, easier management of network bandwidth, and control over file sizes. These benefits make it a preferred choice for encoding and streaming audio and video content.
Disadvantages of CBR
While Constant Bit Rate (CBR) has its advantages, it also has several disadvantages in the context of streaming systems:
- Wasted bandwidth: CBR allocates a fixed amount of bandwidth for streaming, regardless of the complexity or content of the video. This can lead to wasted bandwidth if the video doesn’t require the allocated bit rate, resulting in inefficient use of network resources.
- Inconsistent quality: Due to the fixed bit rate, CBR doesn’t account for variations in the content complexity. As a result, some scenes with high motion or complexity may suffer from compression artifacts or reduced video quality, while other scenes may have excessive bit rates that aren’t necessary.
- Limited adaptability: CBR is not adaptable to changing network conditions. If there is a fluctuation in available bandwidth, CBR will struggle to maintain a steady video stream. This can lead to buffering or interruptions in the streaming experience.
- Inefficient storage utilization: CBR doesn’t take advantage of variable bit rate encoding, resulting in inefficient storage utilization. In cases where the content doesn’t require a constant high bit rate, CBR can result in larger file sizes compared to variable bit rate encoding methods.
- Loss of quality: CBR does not prioritize maintaining consistent video quality over a consistent bit rate. This can result in reduced quality for complex scenes or high-motion content, as the encoding prioritizes bit rate stability over maintaining visual fidelity.
These disadvantages make CBR less suitable for streaming systems where adaptive bit rate streaming, efficient use of network resources, and consistent video quality are important considerations. Variable bit rate encoding methods, such as adaptive bit rate streaming or constant quality encoding, are often preferred in such scenarios.
Variable Bitrate (VBR)
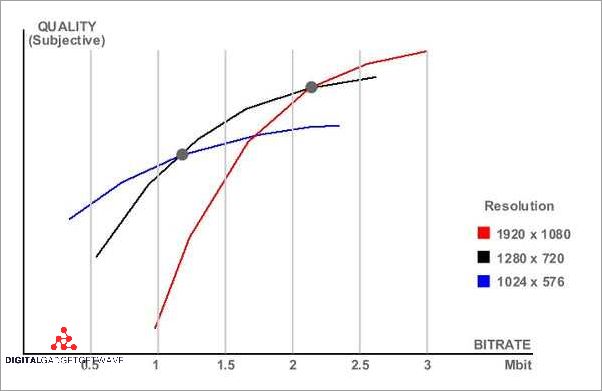
Variable Bitrate (VBR) is a type of audio or video encoding where the bitrate is allowed to vary throughout the duration of the file or stream. Unlike Constant Bitrate (CBR) encoding, which maintains a fixed bitrate throughout, VBR adjusts the bitrate based on the complexity or difficulty of the audio or video being encoded.
One of the advantages of VBR is that it can provide higher audio or video quality for complex or demanding sections of the content, while using lower bitrates for simpler or less demanding parts. This allows for more efficient use of bandwidth and transmission resources, especially in situations where the network or internet connection may have limited capacity.
VBR is particularly useful in scenarios where both audio and video are being transmitted or streamed over a network, as it can dynamically adjust the bitrate based on the available bandwidth. This helps to ensure a smooth playback experience for the user, without interruptions or buffering.
The use of VBR requires a codec or encoding system that supports variable bitrate encoding. This means that it must be able to adapt the level of compression and encoding complexity based on the desired quality level and available bitrate. Common codecs that support VBR include MP3 and AAC for audio, and H.264 and VP9 for video.
Overall, VBR is a flexible and efficient method of encoding audio and video, allowing for variable bitrates that can adapt to the complexity of the content being encoded. It helps to optimize the use of network bandwidth and provides high-quality playback experiences for users.
Advantages of VBR
VBR, or Variable Bitrate, is a method of encoding files that allows for more efficient utilization of bandwidth and storage space. This encoding technique adjusts the bitrate of the file dynamically based on the complexity of the content being encoded. Here are some advantages of VBR:
- Improved file size: VBR can reduce the file size without compromising the quality of the content. It allocates higher bitrates to more complex scenes or audio passages and lower bitrates to less complex ones, resulting in smaller file sizes.
- Better video and audio quality: VBR ensures that the bitrate allocation matches the needs of the content, resulting in higher quality video and audio. It allows for more detailed scenes or demanding audio passages to be encoded with higher bitrates, ensuring a better overall experience for the viewer or listener.
- Efficient network transmission: VBR uses bandwidth more efficiently by dynamically adjusting the bitrate based on the content complexity. This can help reduce the network load and improve streaming performance, especially in situations with limited bandwidth.
- Reduced buffering and streaming interruptions: With VBR, files can be encoded with lower bitrates during less complex scenes, resulting in smoother streaming and reduced buffering issues. This can improve the overall streaming experience, especially for users with slower internet connections.
- Compatibility with various devices and platforms: VBR can be used with different codecs and streaming platforms, making it a versatile option. It works well with both lossless and lossy compression formats, providing flexibility for encoding and decoding across a wide range of devices and systems.
Disadvantages of VBR
The Variable Bitrate (VBR) encoding method, while offering benefits in terms of file size and overall quality, does have some disadvantages that users should be aware of.
One of the main disadvantages of VBR is that it can introduce compatibility issues with certain playback devices or software. This is because VBR-encoded files can have varying bitrates throughout the duration of the video or audio, which may not be supported by all devices or players.
Another disadvantage is that VBR encoding can be slower than Constant Bitrate (CBR) encoding. This is because the VBR algorithm needs to analyze the entire audio or video file in order to adjust the bitrate dynamically. This can result in longer encoding times, especially for larger files.
VBR encoding can also result in slight quality variations between different sections of the file. This is because VBR optimizes the bitrate allocation based on the complexity of the content, allocating a higher bitrate to more complex or detailed scenes and a lower bitrate to simpler scenes. While this can result in overall better quality, it may also introduce slight variations in quality that are noticeable to some viewers or listeners.
Additionally, VBR-encoded files can be more difficult to transmit and stream over networks with limited bandwidth. The varying bitrate can put strain on the network and result in buffering or playback issues, especially when streaming high-definition or high-bitrate content.
Lastly, VBR encoding may not be the ideal choice for archival or lossless audio formats. This is because the variable bitrate may introduce small amounts of compression artifacts in the audio, which may not be desirable when aiming for perfect audio quality.
In conclusion, while VBR encoding offers advantages in terms of file size and overall quality, users should consider the potential disadvantages, such as compatibility issues, slower encoding times, quality variations, difficulties in transmission and streaming, and limitations for lossless formats, when deciding which encoding method to use.
Factors Affecting Bitrate
The bitrate of a video is influenced by several factors, including the codec used for compression, the resolution and format of the video, and the transmission speed and bandwidth of the network.
One of the key factors affecting bitrate is the codec used for encoding the video. Different codecs employ different algorithms to compress the video data, resulting in varying levels of compression and quality. For example, a lossless codec preserves the original quality of the video but requires a higher bitrate compared to a lossy codec, which sacrifices some quality to achieve a lower bitrate.
The resolution and format of the video also play a significant role in determining the bitrate. Higher resolutions, such as 4K or 8K, require more data to represent the increased level of detail, resulting in higher bitrates. Additionally, different video formats may have varying levels of efficiency in terms of compression, which can affect the required bitrate.
The transmission speed and bandwidth of the network are critical factors in determining the bitrate of a video. If the network has limited bandwidth or slow transmission speeds, the video may need to be compressed at a lower bitrate to ensure smooth playback. On the other hand, a high-speed network with ample bandwidth allows for higher bitrates and higher quality video streaming.
It’s important to note that bitrate is not only applicable to video but also applies to audio files. When audio is included in a video file, it contributes to the overall bitrate of the file. Higher quality audio, such as uncompressed or lossless formats, will increase the overall bitrate.
In conclusion, the bitrate of a video is influenced by various factors, including the codec used for compression, the resolution and format of the video, and the transmission speed and bandwidth of the network. By understanding these factors, we can optimize the bitrate to balance quality and file size, ensuring optimal streaming and playback experiences.
Resolution
The resolution refers to the quality of an image or video displayed on a system. It is determined by the number of pixels in a frame, which directly affects the level of detail and clarity. In digital systems, resolution is expressed in terms of horizontal and vertical dimensions, such as 1920×1080 pixels.
The bitrate, represented in bits per second (bps), is a crucial factor in encoding and transmitting high-resolution content. Higher resolutions require more data to accurately represent the image, which results in a higher bitrate. For example, a 4K video has a higher resolution compared to a 1080p video, thus requiring a higher bitrate for smooth streaming.
Various compression techniques and formats, such as encoding and codecs, are used to reduce the size of high-resolution video and audio files. Lossless compression is preferred in applications where quality is of utmost importance, while lossy compression sacrifices some quality to achieve smaller file sizes and increased transmission speeds.
When streaming high-resolution content, the network bandwidth plays a significant role. Insufficient bandwidth can result in buffering or poor quality streams. It is essential to ensure that both the streaming service and the user’s internet connection can handle the required bitrate for the chosen resolution.
In summary, resolution is a key aspect of digital content, determining the level of detail and clarity. Higher resolutions require higher bitrates for smooth streaming, while compression techniques and codecs help reduce file sizes without compromising quality. Network bandwidth is crucial for delivering high-resolution video and audio streams, ensuring a seamless viewing experience.
Compression Algorithms
Compression algorithms play a crucial role in optimizing the bitrate of data transmission over a network. Whether it is audio, video, or any other type of file, compression algorithms help reduce the file size without compromising the quality of the content.
When it comes to audio and video files, compression is achieved by encoding the data using a specific format. This encoding process utilizes different codecs, which are software or hardware tools designed to compress and decompress audio and video files.
The choice of codec can greatly impact the quality, compression speed, and file size of the encoded data. Some popular codecs include MPEG-4, H.264, and AAC, which are widely used for audio and video streaming.
Compression algorithms consider various factors to achieve optimal results. These factors include the resolution, bitrate, and bandwidth available for transmission. By reducing the bitrate, compression algorithms can decrease the amount of data that needs to be transmitted, resulting in faster streaming and reduced bandwidth requirements.
Additionally, compression algorithms also take into account the perceived quality of the content. They aim to achieve a balance between file size reduction and maintaining an acceptable level of audio or video quality. Different compression algorithms may prioritize different aspects, such as preserving details in visuals or minimizing audio artifacts.
In summary, compression algorithms are essential for reducing the bitrate of data transmission and optimizing the quality and file size of audio and video files. They utilize codecs to encode the content and consider factors like resolution, bandwidth, and perceived quality to achieve the best possible compression results.
Frame Rate
The frame rate refers to the speed at which individual frames of data are encoded and transmitted in a video or audio stream. It is measured in frames per second (fps) and determines the smoothness of motion in a video or the fidelity of sound in an audio file.
When encoding a video or audio file, the frame rate is a critical parameter that affects the bitrate, file size, and quality of the output. Higher frame rates require more data to be encoded and transmitted, resulting in larger file sizes and higher bandwidth requirements.
The frame rate also plays a crucial role in streaming and network transmission of video and audio content. Different streaming platforms and networks have specific requirements for the frame rate of the encoded streams to ensure optimal playback and compatibility.
Choosing the right frame rate depends on the specific requirements of the system and the content being encoded. Higher frame rates, such as 60fps, are commonly used in gaming and sports videos to capture fast-paced action accurately. On the other hand, lower frame rates, such as 24fps or 30fps, are commonly used in movies and television shows to create a cinematic or natural viewing experience.
The frame rate is closely related to the resolution and format of the video or audio stream. Higher resolutions and formats require more data to be encoded and transmitted, which can affect the overall bitrate and quality of the stream. Additionally, the chosen audio or video codec and compression method can also impact the frame rate and overall bitrate of the encoded content.
While it is essential to consider the frame rate in video and audio encoding, it is equally important to ensure the system and network can handle the chosen frame rate. If the frame rate is too high for the system’s capabilities or the network’s bandwidth, it may result in buffering, lag, or decreased playback quality.
Content Complexity
The complexity of content refers to the level of detail and intricacy present within the data being compressed, encoded, and transmitted in a system. In the context of video and audio streaming, content complexity plays a significant role in determining the required bitrate and the overall quality of the stream.
When it comes to video, content complexity includes factors such as resolution, frame rate, color depth, and the amount of movement or action within the scene. Higher resolution videos with more rapid movements and a wide range of colors require a higher bitrate for optimal quality. Similarly, in audio, complexity is determined by the number of channels, sample rate, and audio format.
In order to efficiently transmit content with varying complexity, codecs are utilized. Codecs are software or hardware algorithms that compress and decompress data, reducing the size of the file or stream for efficient transmission and storage. Lossless codecs aim to preserve all the original data while lossy codecs sacrifice some data to achieve higher compression ratios. Choosing the appropriate codec based on content complexity is crucial for maintaining the desired quality.
Furthermore, content complexity also affects the encoding and decoding speed within a system. The more complex the content, the longer it takes to encode and decode the data. This can have an impact on real-time streaming applications, where delays in encoding and decoding can cause latency issues and affect the overall user experience.
Understanding the content complexity is essential for determining the required bitrate in a streaming system. The bitrate refers to the amount of data transmitted per unit of time and is generally measured in bits per second (bps). Higher complexity content requires a higher bitrate to maintain the quality, while lower complexity content can be efficiently transmitted at a lower bitrate.
In summary, content complexity plays a vital role in bitrate determination, codec selection, and overall streaming quality. Assessing the resolution, frame rate, color depth, movement, audio format, and other content-specific factors enables effective encoding, transmission, and decoding of data in streaming systems.
Choosing the Right Bitrate
When it comes to choosing the right bitrate for your network, there are several factors to consider. One of the most important factors is the speed of your network connection. If you have a high-speed network connection, you can afford to use a higher bitrate for your streaming or file transmission. On the other hand, if your network connection is slow, you may need to reduce the bitrate to ensure smooth playback or transmission.
The format and resolution of your audio or video file also play a role in determining the appropriate bitrate. Lossless formats, such as FLAC for audio or RAW for video, require higher bitrates to preserve the quality of the original data. On the other hand, compressed formats like MP3 or MP4 can achieve similar quality at lower bitrates due to the use of compression algorithms.
The choice of codec can also impact the bitrate requirements. Some codecs, like H.264 or AAC, are more efficient in terms of compression and can achieve better quality at lower bitrates compared to older codecs. Therefore, it is important to choose a codec that can deliver the desired quality within the available bandwidth.
When encoding a video or audio stream, it is important to strike a balance between the desired quality and the available bandwidth. Higher bitrates generally result in better quality, but they require more bandwidth for transmission. Lower bitrates may result in lower quality, especially for high-resolution content, but they require less bandwidth. It is important to find the right balance that suits the specific requirements of your system.
In conclusion, choosing the right bitrate involves considering factors like network speed, lossless or compressed format, codec efficiency, bandwidth limitations, and desired quality. By understanding these factors and finding the right balance, you can ensure optimal streaming or file transmission in your system.
Considerations for Video Streaming
When it comes to video streaming, there are several key considerations to keep in mind to ensure a smooth and high-quality viewing experience for the audience. One of the most important factors is compression. Video files are typically large in size, so compression techniques are applied to reduce the file size while maintaining acceptable quality.
Another crucial consideration is the bandwidth available for streaming. Bandwidth refers to the amount of data that can be transmitted over a network connection. Insufficient bandwidth can result in buffering or lagging issues, causing interruptions in the video stream. It is essential to have a reliable and fast network connection to support seamless video streaming.
The quality of the video stream is also determined by the bitrate. Bitrate refers to the amount of data that is transmitted or processed per unit of time. Higher bitrates result in better quality videos but require more bandwidth. It is crucial to find the right balance between quality and speed to ensure smooth streaming without excessive buffering.
The video format and encoding codec also play a significant role in video streaming. Different formats and codecs have varying levels of efficiency in compressing and decompressing video data. The choice of format and codec can impact the overall quality and compatibility of the video stream across different devices and platforms.
Furthermore, audio transmission is another consideration in video streaming. The audio component of a video stream requires additional bandwidth and must be properly synchronized with the video. It is essential to use efficient audio codecs and ensure seamless integration with the video stream to deliver a synchronized and immersive viewing experience.
To optimize video streaming, it is advisable to consider the capabilities of the system and adjust the encoding settings accordingly. Lossless encoding can provide the highest quality, but it requires significantly more bandwidth and processing power. By understanding the trade-offs between quality and efficiency, you can fine-tune the streaming settings to achieve the desired balance.
In conclusion, video streaming involves various considerations, including compression, file format, bitrate, network bandwidth, encoding codecs, and audio transmission. By carefully addressing these factors, you can ensure a smooth and high-quality streaming experience for your audience.
Internet Connection Speed
An internet connection speed refers to the rate at which data can be transmitted and received over a network. It plays a crucial role in determining the quality and performance of various online activities, such as streaming video and audio, downloading files, and browsing the web. The faster the internet connection speed, the more data can be transmitted in a given time frame.
Bandwidth is a key factor that influences internet connection speed. Bandwidth refers to the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted in a given period of time. It is typically measured in bits per second (bps). Higher bandwidth allows for faster transmission of data, which means smoother streaming and quicker downloads.
When it comes to streaming video and audio, internet connection speed plays a vital role in ensuring a buffer-free experience. Higher connection speeds enable the streaming of high-resolution video and lossless audio formats without interruptions or delays. Additionally, faster internet speeds also enable quicker file downloads, reducing waiting times for large files.
Internet connection speed is affected by various factors, including network congestion, distance from the server, and the capabilities of the user’s device. It can be measured using online speed test tools that determine the download and upload speeds. Different activities may require different connection speeds, with video streaming typically requiring higher speeds compared to web browsing or email.
Various technologies and encoding techniques are used to optimize data transmission and improve internet connection speeds. Codecs and compression algorithms are employed to reduce the size of data, making it easier to transmit over networks. Additionally, encoding techniques and protocols such as TCP/IP help in efficient data transmission and error detection and correction.
It is important for users to have a sufficient internet connection speed to ensure a smooth and seamless online experience. Slow connection speeds can result in buffering or lagging during video streaming, poor audio quality, and slow file downloads. Assessing and upgrading internet connection speeds can be beneficial for individuals who heavily rely on streaming, online gaming, or large file transfers.
User Viewing Devices
When it comes to user viewing devices, there are several factors to consider in relation to bitrate and data transmission. The device’s capability to support different file formats, codecs, and bit rates plays a crucial role in determining the overall quality and speed of the streaming system.
One important consideration is the device’s resolution and screen size. Devices with higher resolutions and larger screens typically require higher bitrates to maintain a certain level of video quality. For example, a 4K video streamed on a device with a smaller screen may not require the same bitrate as when viewed on a larger screen to achieve the same level of visual clarity.
The type of content being streamed also impact the required bitrate. Lossless audio or high-definition video files require higher bitrates compared to compressed formats to retain the same level of audio or video quality. Therefore, the device’s compatibility with different codecs and file formats is crucial to ensure smooth streaming and optimal audio and video quality.
Furthermore, the network capabilities of the user’s device play a significant role in determining the suitable bitrate for streaming. The strength and stability of the network connection can affect the ability to stream high-quality audio and video content without buffering or lag. Devices with faster internet connections can support higher bitrates, resulting in a smoother and uninterrupted streaming experience.
In conclusion, understanding the capabilities of user viewing devices is essential for optimizing the bitrate and data transmission in a streaming system. Factors such as device resolution, codec compatibility, network speed, and file format determine the overall streaming quality and user experience.
Considerations for Audio Streaming
When it comes to audio streaming, there are several important considerations that need to be taken into account. One of the main considerations is the choice of codec and bitrate. Codec refers to the software used to compress and decompress audio files, while bitrate determines the amount of data transmitted per unit of time.
The choice of codec and bitrate affects the overall quality of the streamed audio. Lossless codecs, such as FLAC or ALAC, provide high-quality audio that is almost identical to the original uncompressed file. However, lossless compression requires a higher bitrate, resulting in larger file sizes and increased bandwidth requirements.
On the other hand, lossy codecs, like MP3 or AAC, provide a smaller file size by discarding some of the audio data that is considered less essential. This compression technique allows for lower bitrates and reduced bandwidth requirements, but it also results in some loss of audio quality. The choice between lossless and lossy codecs depends on the specific needs of the audio streaming system.
The bitrate chosen for audio streaming is also crucial for determining the quality of the stream. Higher bitrates result in better audio quality, as more data is transmitted per unit of time. However, higher bitrates also require more bandwidth. In contrast, lower bitrates reduce the bandwidth requirements but may result in a reduction in audio quality.
Another consideration for audio streaming is the network speed and stability. Since audio files need to be transmitted in real-time for streaming, a stable and fast network is essential to avoid interruptions or buffering. The available network bandwidth should be able to handle the bitrate chosen for the audio stream to ensure a smooth and uninterrupted streaming experience.
In conclusion, when setting up an audio streaming system, the choice of codec and bitrate, as well as the network speed and stability, are important factors to consider. Understanding the impact of these factors on audio quality, file size, and bandwidth requirements is crucial for providing a high-quality audio streaming experience.
Audio Quality Requirements
When it comes to audio streaming, ensuring the right audio quality is crucial. The audio quality requirements often depend on various factors including the transmission or streaming system, network capabilities, and user preferences.
One of the key factors that determine audio quality is the bitrate. Bitrate refers to the number of bits per second that are used to encode the audio data. Higher bitrate usually implies better audio quality, as it allows for more data to be transmitted in a given amount of time, resulting in more accurate and detailed audio reproduction.
The audio format and encoding also play a significant role in determining audio quality. Various audio formats and codecs are available, each with their own compression and encoding techniques. Lossless audio formats, such as FLAC, preserve the original audio quality without any loss of data, while lossy formats, like MP3, compress the audio data to reduce file size but may result in a slight reduction in audio quality.
Moreover, the speed and stability of the network connection can impact audio quality during streaming. A slow or unstable network can lead to buffering issues and audio interruptions, which can degrade the listening experience. To ensure optimal audio quality, it is important to have a stable and high-speed network connection.
Another factor to consider is the audio resolution or quality level. Higher-resolution audio files tend to have better audio quality due to their ability to capture and reproduce more nuances and details in the sound. However, higher-resolution files also require more bandwidth and storage space, which may not be feasible in certain situations.
Internet Bandwidth Limitations
The internet bandwidth limitations refer to the constraints and limitations imposed by the available network speed and capacity when transmitting data, audio, and video over the internet. These limitations can affect the quality and performance of streaming services, particularly when it comes to resolution, compression, and bitrate.
Resolution refers to the quality and clarity of an image or video. Higher resolution requires more data to be transmitted, which can put a strain on the available bandwidth. Compression techniques are used to reduce the file size of digital media, but excessive compression can result in loss of quality. It is essential to strike a balance between file size and the visual or audio experience.
Bitrate is the amount of data that is transmitted per unit of time. It is commonly used to measure the quality of audio and video streams. Higher bitrates result in better quality, but they also require more bandwidth. Choosing the appropriate bitrate is crucial to ensure smooth streaming without interruptions caused by insufficient bandwidth.
The available network speed and capacity determine the maximum bitrate that can be achieved. If the network has limited bandwidth, it may not be able to handle high-quality video streams with high bitrates. In such cases, the streaming system may need to adjust the bitrate dynamically to maintain a smooth playback experience for the users.
Depending on the encoding format and codec used, different levels of compression and bitrate can be achieved. Lossless codecs preserve the original quality of the audio or video file but require higher bitrates and bandwidth. Lossy codecs, on the other hand, achieve higher compression by sacrificing some quality.
To optimize streaming performance and minimize the impact of internet bandwidth limitations, streaming systems may use adaptive streaming techniques. These techniques dynamically adjust the quality and bitrate of the video or audio stream based on the available bandwidth. This ensures a smooth playback experience while utilizing the available network resources efficiently.
FAQ about topic “Understanding Bitrate in Systems: Everything You Need to Know”
What is bitrate and why is it important in systems?
Bitrate refers to the rate at which data is processed or transmitted in a system. It represents the amount of information that can be processed or transmitted per unit of time. Bitrate is important in systems because it determines the quality and efficiency of data transmission. Higher bitrate allows for faster and smoother data transfer, while lower bitrate may result in slower and less reliable data transmission.
How does bitrate affect the quality of audio and video files?
The bitrate of audio and video files directly affects their quality. Higher bitrate typically means better quality, as more data is being transmitted per unit of time. In audio files, higher bitrate results in clearer and more detailed sound, while lower bitrate may lead to compression artifacts and loss of audio quality. Similarly, in video files, higher bitrate ensures sharper and more detailed visuals, while lower bitrate can cause pixelation and blurring of the video.
Does bitrate affect the file size of audio and video files?
Yes, bitrate plays a significant role in determining the file size of audio and video files. Higher bitrate means more data is being processed or transmitted per unit of time, resulting in larger file size. For example, an audio file with a higher bitrate will have a larger file size compared to the same audio file with a lower bitrate. Similarly, a video file with a higher bitrate will have a larger file size compared to the same video file with a lower bitrate. It is important to strike a balance between bitrate and file size to ensure optimal storage and data transfer.
What factors should be considered when choosing the appropriate bitrate for data transmission?
Several factors should be considered when choosing the appropriate bitrate for data transmission. Firstly, the available bandwidth or data transfer speed should be taken into account. If the bandwidth is limited, a lower bitrate may be necessary to ensure smooth data transmission. Secondly, the nature of the data being transmitted should be considered. For example, high-quality audio or video files may require a higher bitrate to preserve their quality. Finally, the requirements of the receiving device or system should be considered. Some devices or systems may have limitations on the maximum bitrate they can handle, so it is important to ensure compatibility.
Is higher bitrate always better for all types of data transmission?
No, higher bitrate is not always better for all types of data transmission. While higher bitrate generally results in better quality and faster data transfer, it also requires more bandwidth and storage space. In certain situations where bandwidth or storage space is limited, a lower bitrate may be preferred to ensure smooth data transmission. Additionally, for certain types of data where high quality is not crucial (e.g. text-based information), lower bitrate can be sufficient without any noticeable loss in quality. It is important to consider the specific requirements and constraints of the data transmission system when deciding on the appropriate bitrate.

