Ethernet port aggregation, also known as link aggregation, is a networking technique that combines multiple physical network ports into a single logical port. It is commonly used to increase bandwidth, improve network performance, and provide redundancy in case of link failure. By aggregating multiple ports, the overall speed and capacity of the network are increased, allowing for faster data transfer and better connectivity.
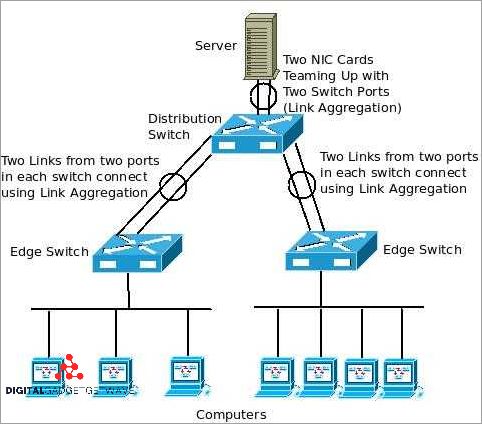
Port aggregation is particularly beneficial in high-demand environments where a single port may not be sufficient to handle the load. By linking several switches together, a network administrator can create an aggregate link that offers higher bandwidth and increased resilience. This aggregation can be achieved through various technologies, such as LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol) or EtherChannel, which provide protocols for load balancing and fault tolerance.
One of the key benefits of port aggregation is the ability to balance the load across multiple links. This means that traffic can be evenly distributed across the aggregated links, preventing any single link from becoming overloaded. By spreading the data traffic, the network can effectively utilize the available bandwidth and prevent bottlenecks. Additionally, in case of a link failure, the traffic can be automatically redirected to the remaining links, ensuring uninterrupted connectivity.
Configuration of port aggregation involves grouping the physical ports into a logical bundle and assigning them a single IP address. This configuration can be done on a switch or a network router that supports link aggregation. It is important to understand the specific requirements of the network equipment and choose the appropriate aggregation method. Additionally, best practices should be followed to ensure proper configuration and optimal performance of the network.
In conclusion, Ethernet port aggregation offers numerous benefits for networks, including increased bandwidth, load balancing, and improved fault tolerance. By combining multiple physical ports into a single logical port, organizations can optimize their network connectivity and ensure reliable data transfer. Understanding the configuration options and following best practices are key to successfully implementing and maintaining an aggregated Ethernet network.
Contents
- 1 Understanding Ethernet Port Aggregation
- 2 Benefits of Ethernet Port Aggregation
- 3 Configuration of Ethernet Port Aggregation
- 4 Best Practices for Ethernet Port Aggregation
- 5 FAQ about topic “Understanding Ethernet Port Aggregation: Benefits, Configuration, and Best Practices”
- 6 What is Ethernet port aggregation?
- 7 What are the benefits of Ethernet port aggregation?
- 8 How can I configure Ethernet port aggregation?
- 9 What are the best practices for Ethernet port aggregation?
- 10 Can I aggregate ports with different speeds?
Understanding Ethernet Port Aggregation
Ethernet port aggregation, also known as link aggregation or network trunking, is a method of combining multiple Ethernet ports into a single link to increase data throughput, redundancy, and availability in a network. This technology allows for the creation of a virtual link, known as an aggregate or a bundle, which increases the overall bandwidth and speed of the network.
In Ethernet port aggregation, multiple physical ports on a switch are grouped together to form a single logical port. This logical port acts as a single high-bandwidth link, providing increased speed and connectivity to network devices. By combining multiple ports into one, it is possible to achieve higher data rates and better load balancing across the network.
The primary benefits of Ethernet port aggregation are increased bandwidth, improved redundancy, and enhanced network performance. By aggregating multiple links, the available bandwidth is effectively increased, allowing for higher data transfer rates and improved network speed. Additionally, port aggregation provides redundancy, as if one physical link fails, traffic can be automatically rerouted to the remaining active links. This increases network availability and minimizes downtime.
Ethernet port aggregation is commonly used in data centers, large enterprise networks, and high-performance computing environments. It is especially useful in scenarios where high bandwidth and reliable connectivity are required, such as server clustering, storage area networks, and network backbone infrastructure.
Switches and network devices that support Ethernet port aggregation typically use the Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) or the static mode configuration to establish and manage the aggregated links. LACP allows for dynamic link negotiation and automatic link failover, while static mode requires manual configuration and does not provide the same level of flexibility.
In conclusion, Ethernet port aggregation is a powerful technique that combines multiple physical ports into a single logical link, providing increased bandwidth, redundancy, and performance in a network. It is an essential tool for managing and optimizing network connectivity, routing, and switching, enabling efficient use of available bandwidth and ensuring the smooth operation of critical network applications and services.
Benefits of Ethernet Port Aggregation
Ethernet port aggregation provides several benefits in terms of bandwidth, connectivity, and network efficiency.
- Increased bandwidth: By aggregating multiple Ethernet ports, the total bandwidth available for data transfer is increased. This allows for faster and more efficient transmission of large files and high-resolution multimedia content.
- Improved switching and routing: Ethernet port aggregation allows for the creation of virtual ports, known as trunks, which can handle increased traffic loads. This improves the overall switching and routing capacity of the network.
- Enhanced connectivity: Aggregating Ethernet ports enables better connectivity by providing redundant links between switches. In the event of a link failure, the network can automatically switch to an alternative link, ensuring uninterrupted connectivity.
- Load balancing: Port aggregation also enables load balancing across multiple links, distributing network traffic evenly among the aggregated ports. This improves the overall performance and efficiency of the network.
- High speed data transfer: By aggregating Ethernet ports, the network can achieve higher speeds, allowing for faster data transfer between devices. This is particularly beneficial in environments where large amounts of data need to be transferred quickly, such as in data centers or video streaming applications.
- Better network resilience: Ethernet port aggregation increases network resilience by providing redundant links. If one link fails, the network can automatically reroute traffic through an alternate link, minimizing downtime and ensuring continuous operation.
In summary, Ethernet port aggregation offers numerous benefits such as increased bandwidth, improved switching and routing, enhanced connectivity, load balancing, high-speed data transfer, and better network resilience. Implementing port aggregation can greatly improve the efficiency and performance of a network, ensuring smooth and uninterrupted data transmission.
Increased Bandwidth
Ethernet port aggregation, also known as link aggregation or bonding, is a technique that allows multiple Ethernet ports to be combined into a single logical link. This method provides increased bandwidth by load balancing the traffic across all the aggregated ports.
When traffic is distributed evenly across multiple links, it helps to utilize the available bandwidth more effectively. By aggregating ports, a network can effectively bond the speed of each individual link, resulting in a higher overall data transfer rate.
Switches that support ethernet port aggregation allow multiple links to be combined into a single aggregated link. This aggregated link acts as a single logical link, but with increased bandwidth. The aggregated link can span multiple physical switches, allowing for greater scalability in network design.
In an Ethernet port aggregation setup, the switch acts as a load balancer, evenly distributing the traffic across the aggregated ports. This load balancing ensures that no single link is overloaded, maximizing the utilization of the available bandwidth.
With increased bandwidth through port aggregation, applications that require high-speed connectivity, such as video streaming, large file transfers, or data-intensive tasks, can benefit from improved performance and reduced latency. The use of ethernet port aggregation is a best practice for organizations looking to maximize their network bandwidth and ensure efficient data transmission.
Improved Redundancy
In a network setup, having a high level of redundancy is essential for ensuring smooth and uninterrupted operations. Ethernet port aggregation, also known as link bonding or link aggregation, plays a crucial role in improving redundancy in a LAN environment.
By combining multiple Ethernet ports into a single logical link, port aggregation enhances connectivity by providing multiple paths for routing data. In case one of the links fails, the other links in the aggregated group automatically take over, ensuring uninterrupted data transfer.
Port aggregation is commonly implemented using switches that support this feature. By linking multiple Ethernet ports together, the aggregated link can handle higher bandwidth requirements and distribute the load across the available connections. This improves the overall speed and efficiency of the network.
By aggregating multiple ports, the network gains the ability to balance the load among the links, thereby preventing congestion and ensuring optimal performance. In case one link becomes overloaded, the data can be automatically redirected to the other links in the aggregation, ensuring a smooth flow of data.
In summary, Ethernet port aggregation provides improved redundancy in a network setup by combining multiple physical links into a single logical link. This enables the network to handle higher bandwidth requirements, balance the load among links, and automatically redirect data in case of failures. By implementing port aggregation, organizations can enhance the reliability and efficiency of their network infrastructure.
Flexible Network Design
In the world of Ethernet networks, flexibility is key. With the increasing demand for faster and more reliable data transfer, network administrators are constantly looking for ways to optimize their systems. One way to achieve this is through Ethernet port aggregation or bonding.
Ethernet port aggregation, also known as link aggregation or trunking, is the process of combining multiple physical Ethernet ports into a single logical port. This allows for increased bandwidth and improved network performance. By aggregating multiple ports, network administrators can effectively create a higher-speed link between devices.
Port aggregation is particularly useful in Local Area Network (LAN) environments where there is a need for high-speed connectivity between switches or between switches and servers. It can help balance the traffic load across the aggregated ports, ensuring that no single link becomes a bottleneck for data transfer. This is especially important in busy networks where a high volume of data needs to be transferred simultaneously.
By linking multiple Ethernet ports together, network administrators can achieve redundancy and resiliency in case of port or link failure. If one port were to fail, the traffic can automatically be rerouted to the remaining active ports, minimizing downtime and maintaining network connectivity. This provides a level of reliability that is crucial in mission-critical environments.
Overall, Ethernet port aggregation offers a flexible network design solution that can improve network performance, provide higher bandwidth, and enhance traffic load balancing. Network administrators can configure port aggregation on compatible switches or network devices, allowing for a more efficient and robust network infrastructure. By utilizing this technology, organizations can meet their growing data transfer needs and ensure a stable and reliable network environment.
Configuration of Ethernet Port Aggregation
Ethernet Port Aggregation, also known as link aggregation or port trunking, is a technique that combines multiple network ports into a single logical interface to increase the overall bandwidth and improve connectivity. The configuration of Ethernet Port Aggregation involves several steps to ensure optimal performance of the aggregated ports and the network as a whole.
First, the switch or router needs to support Ethernet Port Aggregation. This feature allows the device to aggregate multiple ports into a single logical interface. It is important to check the device’s documentation or consult with the vendor to determine if it supports this feature.
Once the device supports Ethernet Port Aggregation, the ports that will be aggregated need to be identified. These ports should be on the same LAN and connected to the same switches. It is recommended to use ports with the same speed and capabilities to avoid potential issues.
Next, the ports need to be bonded together using a specific bonding protocol, such as LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol) or static mode. LACP is a dynamic protocol that automatically negotiates the aggregation between devices, while static mode requires manual configuration. LACP is generally recommended for its flexibility and ability to handle changes in the network.
After the bonding protocol is chosen, the ports are linked together to form an aggregated link. This link now acts as a single high-speed connection, combining the bandwidth of the individual ports. This allows for load balancing and increased fault tolerance, as traffic can be distributed across the ports in the aggregation.
Finally, the network should be tested to ensure that the Ethernet Port Aggregation is working correctly. This can be done by transferring data between devices connected to the aggregated ports and monitoring the link utilization. If any issues arise, such as uneven distribution of traffic or slow speeds, adjustments may need to be made to the configuration.
In conclusion, the configuration of Ethernet Port Aggregation involves identifying the ports, bonding them together using a bonding protocol, creating an aggregated link, and testing the network for optimal performance. This technique provides increased bandwidth, improved connectivity, and load balancing capabilities for the network, making it a valuable tool for optimizing network infrastructure.
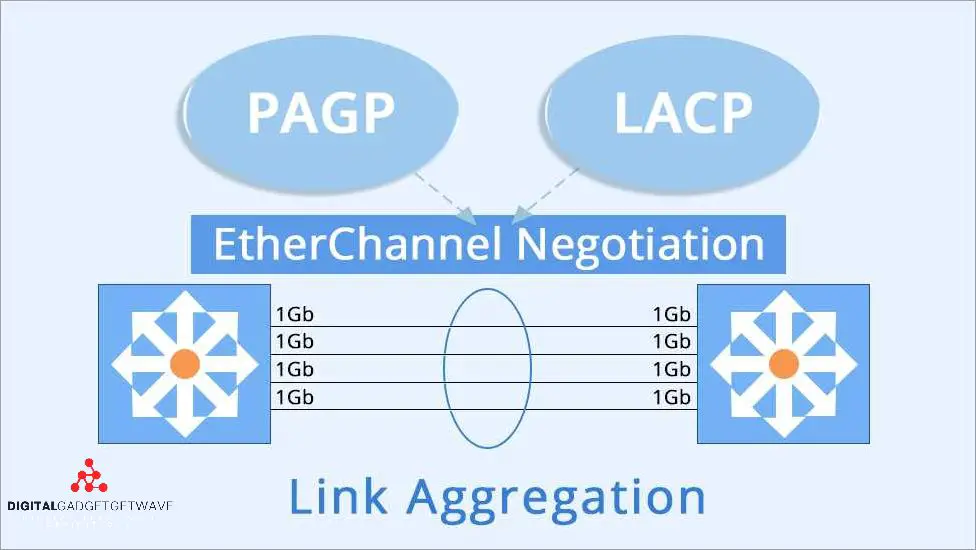
Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
The Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) is a standard method for aggregating or bonding multiple Ethernet ports into a single logical link, also known as a link aggregation group (LAG) or a port channel. LACP provides a mechanism for automated negotiation and management of the link aggregation, ensuring optimal connectivity and load balancing within a network.
When LACP is enabled on the switches, it allows multiple physical Ethernet links to behave as a single logical link, thereby increasing the overall bandwidth and providing redundancy. By linking multiple ports together, LACP enables higher throughput and improved reliability for data transmission, as well as improved fault tolerance in case of a link failure.
With LACP, switches on both ends of the link negotiate and agree on the parameters for the link aggregation, such as the link speed, bandwidth, and load balancing mechanisms. This negotiation process ensures that the link aggregation is properly configured and maintained, optimizing the overall performance of the network.
LACP supports dynamic distribution of traffic across the aggregated links, allowing for efficient utilization of available bandwidth. It provides a load balancing function, which distributes data packets across the member links based on a variety of algorithms, such as source IP address, destination IP address, or Layer 4 port number.
By using LACP, organizations can achieve improved scalability, redundancy, and performance in their network infrastructure. The link aggregation provided by LACP allows for increased bandwidth and fault tolerance, while also simplifying the network configuration and reducing the administrative overhead associated with managing multiple individual links.
Static Port Aggregation
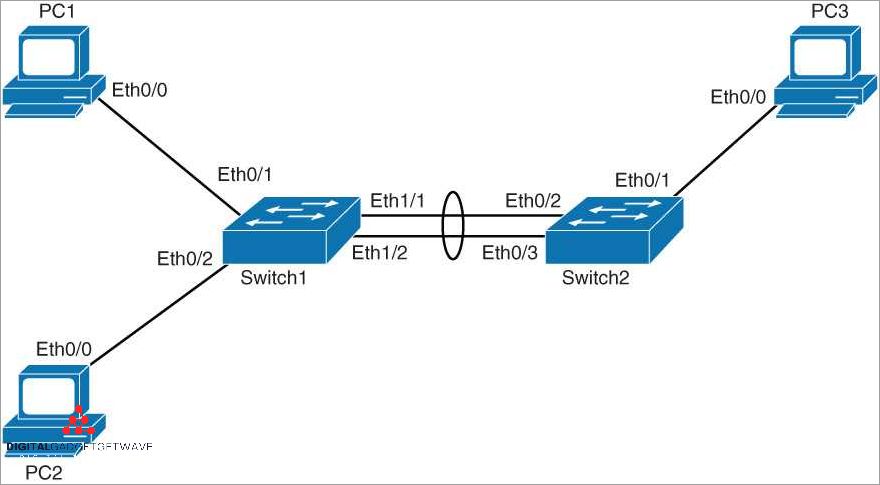
Static port aggregation, also known as Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP), is a technique used in Ethernet switch networks to combine multiple physical links into a single logical link. It allows for the load balancing of traffic across the aggregated links, increasing overall network bandwidth and providing link redundancy.
With static port aggregation, multiple Ethernet ports are grouped together to form a single logical link. This aggregation improves the speed and efficiency of data transmission by distributing the traffic load across the available links. In addition, it provides link redundancy, ensuring continuous connectivity even if one or more links fail.
Static port aggregation operates at the link layer of the OSI model, allowing for seamless integration with existing LAN, routing, and switching technologies. It is commonly used in scenarios where high bandwidth and reliable network connections are essential, such as server farms, data centers, and network backbones.
Switches that support static port aggregation enable administrators to configure and manage the aggregated links. The switches distribute traffic between the links, optimizing the use of available bandwidth and preventing bottlenecks. The aggregation is typically achieved through a process known as link bonding or trunking, which combines the individual links into an aggregate link with increased speed and capacity.
Overall, static port aggregation provides numerous benefits for network administrators, including increased bandwidth, improved network performance, and enhanced link redundancy. By leveraging the power of multiple physical links, organizations can optimize their network infrastructure and handle growing data demands more efficiently.
Load Balancing Algorithms
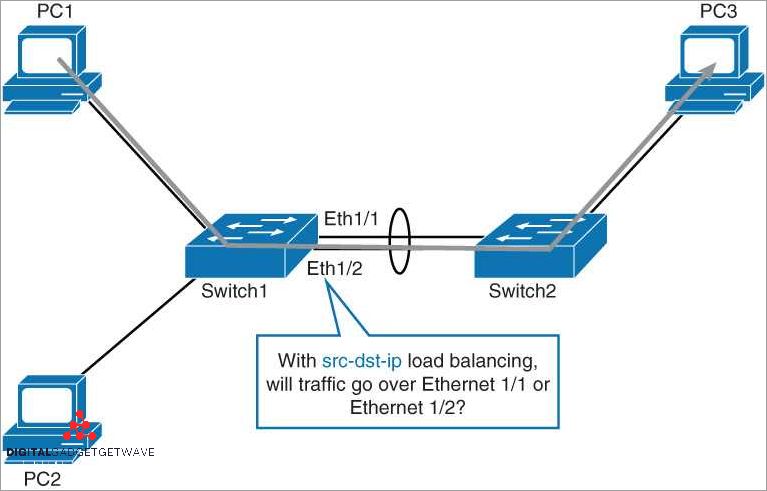
Load balancing algorithms are used to distribute network traffic across multiple Ethernet ports in order to optimize performance, increase bandwidth, and improve network connectivity. By aggregating or bundling multiple ports together, switches and network devices can balance the load and evenly distribute data across the available links.
Load balancers, also known as network bonding or trunking devices, use various algorithms to determine how to distribute the data. These algorithms take into account factors such as link speed, port availability, and current network conditions to ensure efficient data routing.
One common load balancing algorithm is round-robin, which evenly distributes data packets across the ports in a sequential manner. This ensures that each port receives an equal amount of traffic, which helps to optimize bandwidth usage.
Another popular algorithm is least connections, where the load balancer routes traffic to the port with the fewest active connections. This is useful in situations where some ports may be more heavily utilized than others.
Weighted round-robin is another algorithm that assigns each port a weight based on its capabilities, such as link speed or available bandwidth. This allows the load balancer to distribute more traffic to the higher-capacity ports, ensuring optimal load balancing.
Load balancing algorithms are an important aspect of Ethernet port aggregation, as they ensure that network traffic is evenly distributed and that each port is utilized efficiently. By using these algorithms, networks can achieve higher performance, better reliability, and improved connectivity for data switching and routing.
Best Practices for Ethernet Port Aggregation
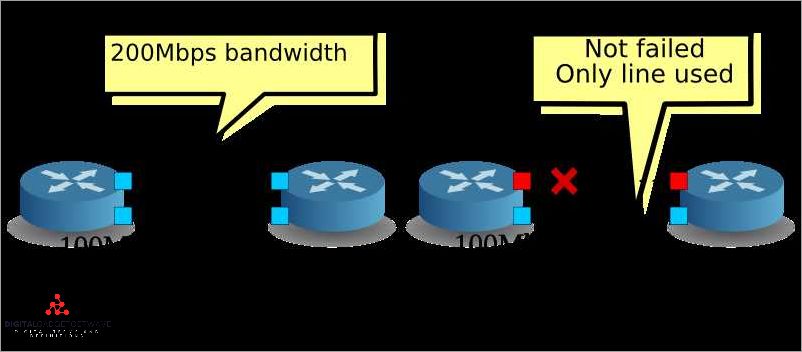
Ethernet Port Aggregation (also known as link aggregation or bonding) is a technique used in network switches to combine multiple physical Ethernet ports into a single logical port. This provides increased bandwidth, improved fault tolerance, and better load balancing.
To ensure the smooth functioning of Ethernet Port Aggregation, it is important to follow these best practices:
- Choose compatible switches: It is crucial to use switches that support Ethernet Port Aggregation and provide the necessary features for configuring and managing the aggregate links.
- Use the same speed and duplex settings: All the ports participating in the aggregation should have the same speed and duplex settings to avoid any compatibility issues and ensure proper data transmission.
- Configure the aggregation mode: Decide on the appropriate aggregation mode based on your network requirements. Common modes include static mode (where the links are manually configured) and dynamic mode (where a protocol like LACP automatically negotiates and manages the aggregation).
- Ensure balanced traffic distribution: Distribute the traffic evenly across the aggregated links to maximize bandwidth utilization and prevent bottleneck situations. This can be achieved through load balancing algorithms like source/destination IP address, MAC address, or round-robin.
- Enable Spanning Tree Protocol (STP): STP helps in preventing network loops and ensures redundant links do not create a broadcast storm. Enabling STP on the switch ports involved in the aggregation is crucial for maintaining network stability.
- Regular monitoring and maintenance: Continuously monitor the aggregation links for any errors, congestion, or anomalies. It is important to regularly update the firmware of the switches and apply any necessary patches or bug fixes to ensure optimal performance.
By following these best practices, Ethernet Port Aggregation can greatly enhance network connectivity, increase available bandwidth, and improve overall reliability and performance for data routing and switching within a LAN environment.
Consider Network Switch Capabilities
When implementing Ethernet port aggregation, it is important to consider the capabilities of the network switches being used. Not all switches are equipped to handle port aggregation, so it is necessary to ensure that the switches in use support this feature. It is also important to consider the type of switches being used, such as LAN switches or data center switches, as their capabilities may differ.
One key capability to look for in network switches is trunking support. Trunking allows multiple ports to be combined into a single logical link, increasing the available bandwidth for data transmission. This is especially important in port aggregation scenarios, as combining multiple ports into an aggregate link requires trunking support to ensure proper connectivity.
Another important capability to consider is load balancing. Network switches with load balancing capabilities can distribute incoming data across the aggregated ports, optimizing the use of available bandwidth and improving overall network performance. This is particularly beneficial in scenarios where high bandwidth applications or large amounts of data transfer are involved.
In addition to trunking and load balancing, it is important to consider the routing capabilities of the network switches. Aggregating ports can impact the routing of data within the network, so switches with advanced routing capabilities can help manage the flow of data and ensure efficient communication between devices.
Overall, the capabilities of the network switches used in Ethernet port aggregation play a crucial role in the success of the implementation. Trunking, load balancing, and routing capabilities are key factors to consider when selecting switches, as they directly impact the performance, bandwidth, and connectivity of the network.
Use Compatible Network Hardware
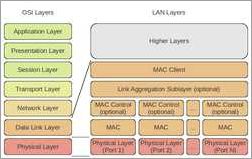
Routing: When setting up an Ethernet port aggregation, it is important to ensure compatibility between the network hardware components. This includes the routers, switches, and load balancers that will be involved in the network setup. Using compatible hardware ensures smooth data flow and seamless connectivity.
Aggregation and Bandwidth: Compatible network hardware facilitates the aggregation of multiple Ethernet ports, allowing for increased bandwidth and faster data transfer speeds. This is crucial for businesses and organizations that require high-speed and reliable network connectivity to support their operations.
Switches and Port Linking: The use of compatible switches with support for port linking or trunking is essential when implementing Ethernet port aggregation. These switches should have the ability to bond multiple ports together to create an aggregated link that can handle the increased bandwidth and data load.
Load Balancer and Network Bonding: Employing a compatible load balancer in the network setup enables efficient distribution and balancing of network traffic across aggregated Ethernet ports. Network bonding ensures that the available bandwidth is utilized optimally, preventing bottlenecks and ensuring smooth connectivity for users.
Ethernet Speed and Switching: It is important to choose network hardware that supports the desired Ethernet speed for the aggregation. The network switches should be capable of handling the increased data transfer rates resulting from the aggregation. Compatibility in terms of switching technology ensures efficient data flow and minimal packet loss.
Summary:
- Ensure compatibility between network hardware components for smooth data flow and connectivity;
- Use switches that support port linking or trunking to aggregate Ethernet ports;
- Employ a compatible load balancer for efficient traffic distribution;
- Choose network hardware that supports the desired Ethernet speed;
- Compatibility in switching technology ensures efficient data flow and minimal packet loss.
Properly Configure Load Balancing
Load balancing is a critical aspect of Ethernet port aggregation that helps distribute data traffic across multiple ports in order to maximize network performance and ensure efficient utilization of available bandwidth. By properly configuring load balancing, network administrators can optimize the use of their network infrastructure and enhance overall connectivity.
Load balancing can be achieved through various methods, such as bonding or aggregation of multiple Ethernet ports. This process allows combining the bandwidth of multiple ports into a single logical link, thereby increasing the overall capacity available for data transmission.
When configuring load balancing, it is important to consider the specific needs and requirements of the network. Different load balancing algorithms can be implemented, such as round-robin, least connections, or source-destination IP hashing, to evenly distribute traffic across the ports.
Another important consideration is the underlying routing or switching technology. Load balancing can be implemented at the switch level or at the network level. At the switch level, multiple physical links can be aggregated into a single logical link, known as a trunk or an aggregated link. This allows for load balancing and redundancy at the switch level, providing improved connectivity and fault tolerance.
Network administrators should also pay attention to the compatibility of the load balancer with the connected devices. It is important to ensure that the load balancer supports the necessary protocols and standards, such as IEEE 802.3ad Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) or Cisco’s Port Aggregation Protocol (PAgP), in order to establish successful link aggregation and load balancing.
In summary, properly configuring load balancing is essential for optimizing network performance and ensuring efficient utilization of available bandwidth. By carefully considering the load balancing algorithms, underlying routing or switching technology, and compatibility with connected devices, network administrators can create a robust and high-performing network infrastructure.
FAQ about topic “Understanding Ethernet Port Aggregation: Benefits, Configuration, and Best Practices”
What is Ethernet port aggregation?
Ethernet port aggregation, also known as link aggregation or port trunking, is the process of combining multiple Ethernet ports together to form a single logical connection. This allows for increased bandwidth, redundancy, and load balancing for network devices.
What are the benefits of Ethernet port aggregation?
Ethernet port aggregation provides several benefits including increased bandwidth, improved network reliability, and load balancing. By combining multiple ports, the overall bandwidth is increased, allowing for faster data transfer. Redundancy is achieved by having multiple ports serve as backup connections in case one fails. Load balancing evenly distributes network traffic across multiple ports, optimizing network performance.
How can I configure Ethernet port aggregation?
Configuring Ethernet port aggregation typically involves accessing the network device’s management interface and enabling the appropriate aggregation protocols such as Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) or Static Link Aggregation. LACP is a dynamic protocol that automatically negotiates the aggregation between devices, while Static Link Aggregation requires manual configuration on both ends.
What are the best practices for Ethernet port aggregation?
When implementing Ethernet port aggregation, it is important to follow several best practices. These include using matching hardware on both ends, configuring the ports with the same speed and duplex settings, and using a compatible aggregation protocol. It is also recommended to monitor the aggregated link for performance and to regularly update firmware and drivers to ensure compatibility and security.
Can I aggregate ports with different speeds?
Yes, it is possible to aggregate ports with different speeds, but it is generally not recommended. Aggregating ports with different speeds can lead to suboptimal performance and may cause compatibility issues. It is best to use ports with the same speed when configuring Ethernet port aggregation.


