
Business Service Management (BSM) is a comprehensive approach to managing and optimizing IT services to meet the needs of the business. It involves aligning IT services with the goals and objectives of the organization, and ensuring that IT services are delivered in a reliable and efficient manner.
At its core, BSM is about managing the entire service lifecycle, from initial development to monitoring and continuous improvement. This includes incident management, problem management, service-level management, configuration management, and change management.
One of the key components of BSM is the monitoring of IT services and infrastructure. This involves the use of specialized software solutions to track and analyze the performance of IT systems, processes, and services. By monitoring key metrics and indicators, organizations can identify and resolve issues before they become major problems.
In addition to monitoring, BSM also focuses on managing and optimizing IT processes. This includes defining and documenting processes, establishing service-level agreements (SLAs), and implementing best practices to ensure that IT services are delivered consistently and efficiently.
Overall, BSM provides organizations with a framework for managing IT services in a way that is aligned with the needs and goals of the business. By implementing BSM practices and solutions, organizations can improve the performance and reliability of their IT services, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Contents
- 1 Definition and Importance of BSM
- 2 Key Concepts and Components of BSM
- 3 Benefits and Advantages of Implementing BSM
- 4 Implementation of Business Service Management
- 5 Tools and Technologies for Business Service Management
- 6 Future Trends and Developments in Business Service Management
- 7 FAQ about topic “What is BSM: A Guide to Understanding Business Service Management”
- 8 What is BSM?
- 9 How does BSM work?
- 10 What are the benefits of implementing BSM?
- 11 What are the key components of BSM?
- 12 How can an organization implement BSM?
Definition and Importance of BSM
Business Service Management (BSM) is a comprehensive approach to aligning and monitoring IT services with the goals and processes of the business. It provides a framework for managing and optimizing the performance and availability of IT services in order to meet the needs of the business.
BSM is based on the principles of ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library), a globally recognized set of best practices for IT service management. It encompasses various areas such as incident management, change management, service-level agreements, and configuration management.
The importance of BSM lies in its ability to bridge the gap between IT and the business. By aligning IT services with the goals and processes of the business, BSM enables organizations to prioritize and manage IT resources effectively. It helps in identifying and resolving IT-related issues proactively, thereby minimizing downtime and improving the overall performance of the business.
BSM also plays a crucial role in problem management. It provides a systematic approach for identifying and analyzing the root causes of recurring incidents, and for implementing long-term solutions to prevent similar issues from occurring in the future.
Furthermore, BSM enables organizations to establish clear service-level agreements with their customers or stakeholders. These agreements outline the expected performance levels of IT services and help in managing customer expectations. BSM also facilitates the monitoring and reporting of key performance indicators, allowing organizations to measure and demonstrate the value and impact of their IT services on the business.
With the help of specialized software tools, BSM provides organizations with real-time visibility into the performance and availability of their IT services. It enables proactive monitoring, alerting, and reporting of any deviations from the defined service levels, allowing IT teams to take timely actions and minimize the impact on the business.
In conclusion, BSM is a critical component of effective IT service management. By aligning IT services with the business, it helps organizations optimize performance, minimize downtime, and deliver value to their customers and stakeholders.
Key Concepts and Components of BSM
BSM, or Business Service Management, is a framework that helps organizations align their IT services with the goals of the business. It involves managing and monitoring the performance of various business services to ensure they meet the service-level agreements (SLAs) and support the overall business objectives.
One of the key concepts in BSM is incident management. This involves identifying, documenting, and resolving any issues that may occur in the IT infrastructure or systems. Incident management ensures that any disruptions to the business services are addressed quickly and efficiently, minimizing their impact on the business operations.
Another important component of BSM is configuration management. This involves maintaining a detailed and accurate record of the configuration items (CIs) that make up the IT infrastructure. It helps in understanding the relationships between different CIs and enables effective change management processes.
Change management is another crucial aspect of BSM. It involves managing and controlling any changes to the IT infrastructure or systems to minimize the impact on the business services. Change management ensures that changes are planned, tested, and implemented in a controlled manner, following the best practices and guidelines, such as ITIL (IT Infrastructure Library).
Problem management is also a part of BSM. It focuses on identifying and resolving the underlying causes of recurring incidents or problems in the IT systems. Problem management aims to minimize the impact of these problems on the business services and prevent them from occurring in the future.
BSM also includes the concept of solution management, which involves identifying, developing, and implementing solutions to address the challenges and issues faced by the business services. Solution management aims to improve the performance and efficiency of the business services in line with the business goals.
Monitoring and performance management are integral components of BSM. They involve continuously monitoring the performance of the business services and IT infrastructure to identify any deviations from the desired service levels. Monitoring tools and software are used to collect data and generate reports to evaluate the performance and identify areas for improvement.
In summary, BSM encompasses various key concepts and components, such as incident management, configuration management, change management, problem management, solution management, and monitoring and performance management. These components work together to ensure that the IT services are aligned with the business goals and meet the service-level agreements, thus supporting the overall success of the organization.
Benefits and Advantages of Implementing BSM
Implementing Business Service Management (BSM) can provide a number of significant benefits and advantages for organizations. One of the main advantages is that BSM helps in identifying and solving complex business problems more efficiently. By aligning IT processes with business objectives, BSM enables organizations to quickly identify the root cause of a problem and take appropriate actions to resolve it.
Another advantage of BSM is improved performance. By implementing BSM practices, organizations are able to closely monitor their IT services and ensure that they are performing optimally. This helps in maintaining high service-level agreements (SLAs) and meeting customer expectations. BSM also enables organizations to proactively identify potential performance issues and take preventive measures to avoid any disruption to the business.
BSM also offers advantages in change management. By implementing a BSM framework, organizations can effectively manage and control changes to their IT environment. This includes managing software updates, configuration changes, and other modifications to IT infrastructure. BSM provides a structured approach to change management, ensuring that changes are implemented smoothly and minimizing any negative impact on the business.
Furthermore, BSM helps in improving incident management. With BSM, organizations can streamline the process of identifying, tracking, and resolving incidents. By implementing incident management software and processes, organizations can ensure that incidents are promptly addressed, minimizing the impact on business operations. BSM also provides a framework for analyzing incidents and identifying trends, helping organizations to take preventive actions to avoid similar incidents in the future.
Lastly, BSM aligns IT with business goals. By implementing BSM practices, organizations can ensure that their IT services are aligned with the overall business objectives. BSM helps in establishing clear goals and objectives for IT services, and provides a framework for measuring and monitoring the performance of these services. This alignment between IT and business goals leads to improved efficiency, productivity, and customer satisfaction.
Implementation of Business Service Management
Implementing Business Service Management (BSM) involves the adoption of a comprehensive solution that aligns IT processes and performance with the goals of the business. One common framework used during the implementation process is ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library), which provides a set of best practices for IT service management. By following ITIL guidelines, organizations can ensure that their BSM initiatives are in line with industry standards and are focused on improving overall business outcomes.
During the implementation of BSM, it is crucial to align IT services with the specific needs and priorities of the business. This involves defining the services provided by IT and establishing service-level agreements (SLAs) that outline the expectations and responsibilities of both the IT department and the business. By clearly defining these agreements, organizations can ensure that IT services are in line with the overall objectives of the business.
Change management is another important aspect of BSM implementation. Organizations must develop robust processes for managing changes to IT infrastructure, software, and configuration. This includes assessing the potential impact of changes, planning for their implementation, and effectively communicating any necessary updates or modifications to the relevant stakeholders. By having a well-defined change management process in place, organizations can minimize disruptions to business services and maintain a stable IT environment.
Incident and problem management are also key components of BSM implementation. Organizations should have efficient processes for identifying, resolving, and learning from incidents and problems that may affect the performance and availability of IT services. This includes implementing software and tools for incident tracking and resolution, as well as establishing protocols for root cause analysis and continuous improvement. By effectively managing incidents and problems, organizations can minimize downtime and improve the overall quality and reliability of IT services.
Monitoring and performance management are essential for successful BSM implementation. Organizations should implement tools and systems for monitoring the performance of IT services, as well as establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure and track the effectiveness of these services. By monitoring performance and analyzing the data collected, organizations can identify areas for improvement and make informed decisions to optimize IT service delivery. Additionally, proactive monitoring allows organizations to quickly identify and address any potential issues before they affect the business.
In conclusion, the implementation of Business Service Management requires a comprehensive approach that aligns IT management processes and performance with the goals of the business. By following frameworks such as ITIL, organizations can establish best practices and guidelines for effective IT service management. By ensuring clear alignment with business objectives, implementing robust change management processes, effectively addressing incidents and problems, and monitoring performance, organizations can optimize their IT services to meet the needs of the business and drive overall success.
Steps and Strategies for Implementing BSM
Implementing Business Service Management (BSM) requires a systematic approach and careful planning. Here are some steps and strategies to help you successfully adopt the BSM framework:
- Assess your current state: Start by evaluating your existing business and IT processes, tools, and systems. Identify areas that need improvement and determine how BSM can address these issues. This assessment will enable you to understand the extent of change required and set realistic goals for implementing BSM.
- Define your processes: Establish a set of processes and procedures that align with BSM principles. This may involve mapping out incident management, problem management, change management, and service level management processes. Consider adopting the ITIL framework, which provides guidelines for best practices in IT service management.
- Select the right software solution: Choose a BSM software solution that meets your organization’s specific needs. Look for features such as performance monitoring, configuration management, and service level agreement tracking. The software should provide visibility into the entire service lifecycle and enable proactive problem resolution.
- Align IT with business goals: Ensure that your IT department is aligned with the overall business objectives. BSM should enable IT to deliver services that directly support and contribute to the achievement of these goals. Regular communication and collaboration between IT and business stakeholders are vital for successful BSM implementation.
- Train and educate staff: Provide comprehensive training to your IT staff on BSM concepts and methodologies. This will ensure that everyone understands their roles and responsibilities within the new framework. Additionally, educate the rest of the organization about the benefits and implications of BSM to foster support and cooperation.
- Monitor and measure performance: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to track the effectiveness of your BSM implementation. Regularly monitor these KPIs to identify any gaps or areas for improvement. Use the data collected to make data-driven decisions and continuously optimize your BSM processes.
By following these steps and strategies, organizations can successfully implement BSM and realize its benefits, including improved service quality, enhanced customer satisfaction, and increased efficiency in managing IT services.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing BSM
Processes: Implementing BSM involves defining and aligning different processes within an organization. This can be challenging as it requires coordination and collaboration across teams and departments. It is important to carefully analyze existing processes and identify areas for improvement to ensure a smooth implementation of BSM.
ITIL: BSM is based on the ITIL framework, which provides best practices for IT service management. Implementing BSM requires a good understanding of ITIL processes and the ability to customize them according to the organization’s specific needs. This may involve training employees and investing in ITIL-compliant software solutions.
Incident and Problem Management: BSM aims to improve incident and problem management by providing a holistic view of the business services. However, this can be challenging as it requires integration of different systems for monitoring, logging, and tracking incidents and problems. It is important to choose the right software solutions and establish effective workflows to ensure timely resolution of issues.
Configuration and Change Management: BSM involves managing the configuration items and changes that impact business services. This requires implementing a centralized configuration management database (CMDB) and establishing change management processes. It is important to carefully plan and communicate changes to minimize disruptions to business services.
Service-Level Agreement and Performance Monitoring: Implementing BSM requires defining service-level agreements (SLAs) and monitoring the performance of business services. This involves setting measurable goals, establishing monitoring mechanisms, and analyzing performance data. It is important to continuously monitor and improve service performance to meet customer expectations and business objectives.
Case Studies and Success Stories of BSM Implementation
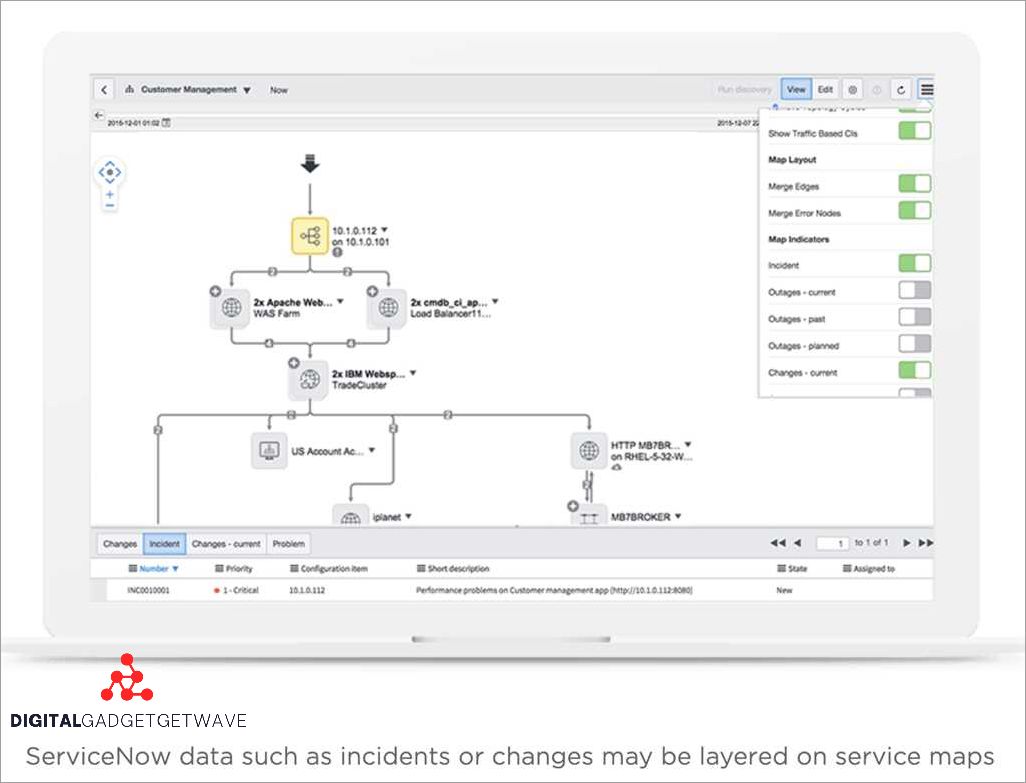
Implementing Business Service Management (BSM) has proved to be a game-changer for many organizations, helping them achieve their goals and navigate the complexities of modern business environments. Numerous case studies and success stories demonstrate the impact and benefits of BSM implementation.
One such case study involves a large multinational corporation that wanted to improve its IT service management processes and enhance the alignment of IT with the overall business objectives. By implementing BSM, the company was able to streamline its service monitoring and problem resolution capabilities, resulting in reduced downtime and increased operational efficiency.
In another success story, a financial services firm implemented BSM to improve its ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) compliance. By leveraging BSM software, the company was able to automate incident management and align service-level agreements with business objectives. This resulted in improved service performance and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Yet another case study highlights a telecommunications company that sought to optimize its network configuration management. By implementing a BSM solution, the company was able to automate and centralize the management of its network configuration, resulting in improved operational efficiency and reduced downtime.
These case studies demonstrate how BSM implementation can bring about positive changes in various aspects of business operations. By leveraging the BSM framework, organizations can align their IT services with business processes, improve service-level agreements, and enhance performance management. BSM offers a holistic approach to managing IT services, enabling businesses to achieve their goals in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Tools and Technologies for Business Service Management
Business Service Management (BSM) is a framework that allows organizations to align their IT services with the goals of the business. Several tools and technologies are available to support the implementation of BSM.
One important tool for BSM is ITIL (IT Infrastructure Library), which provides a set of best practices for IT service management. ITIL helps organizations define and implement processes for managing their IT services, including incident management, change management, and configuration management.
Another important tool for BSM is service-level agreement (SLA) management software. SLAs define the performance goals and expectations for IT services, and SLA management software helps organizations monitor and enforce these agreements. It allows businesses to maintain visibility into service performance and ensure that service level targets are met.
Monitoring tools are also key to BSM, as they enable organizations to track the performance of their IT services in real time. These tools provide insights into the availability, performance, and usage of IT resources, helping organizations identify and resolve issues before they become major problems.
Change management tools are necessary for BSM, as they help organizations manage and track changes to their IT infrastructure. These tools ensure that changes are implemented in a controlled and coordinated manner, minimizing the impact on IT services and the business as a whole.
Overall, implementing BSM requires a combination of tools and technologies that support the management of IT services in alignment with the goals of the business. By utilizing these tools, organizations can effectively address incidents, manage changes, monitor performance, and achieve their business objectives.
Monitoring and Analytical Tools for BSM
In order to effectively manage business services and ensure that they align with the goals of the organization, monitoring and analytical tools play a crucial role. These tools provide valuable insights into various aspects of the service delivery process and help identify any issues or incidents that may arise.
Incident management software, for example, helps track and resolve any disruptions or problems that occur during service delivery. It allows IT teams to quickly identify and address any issues that may impact the business. This software is essential for maintaining service-level agreements and ensuring that customers receive the level of service they expect.
Monitoring tools are also important for BSM as they allow organizations to track and measure the performance of their services. These tools monitor key metrics such as response time, availability, and throughput, providing valuable data for analysis. By analyzing this data, organizations can identify any bottlenecks or areas of improvement in their service delivery processes.
Analytical tools, on the other hand, help organizations gain a deeper understanding of their services by providing detailed reports and analysis. These tools can help identify trends, patterns, and anomalies in service delivery, allowing organizations to make informed decisions and take proactive measures to improve performance.
Configuration management tools are another important component of BSM as they help organizations manage and control the configuration of their IT infrastructure. These tools ensure that all components of the service are properly configured and aligned with the needs of the business. They help in maintaining consistency, reducing errors, and avoiding any potential disruptions.
Overall, monitoring and analytical tools are essential for achieving effective BSM. They provide organizations with the necessary insights and data to manage their services, identify and resolve any issues that may arise, and continuously improve performance to meet the goals of the business.
Incident and Problem Management Tools for BSM
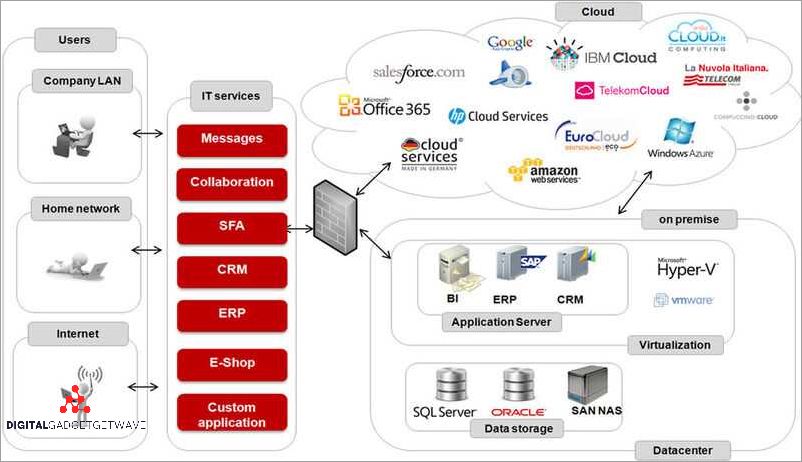
In the context of Business Service Management (BSM), incident and problem management tools play a crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation of business processes. These tools are designed to identify and resolve any issues that may arise, impacting the performance of the business services.
Incident management tools help in monitoring the IT infrastructure and detecting any incidents or disruptions in the service delivery. They provide real-time alerts and notifications, enabling quick response and resolution of incidents to minimize the impact on business operations. These tools also facilitate incident tracking and management by providing a centralized platform for recording and documenting incidents.
Problem management tools, on the other hand, focus on the root cause analysis of recurring incidents. They help in identifying the underlying problems that are causing incidents to occur repeatedly and suggest preventive measures to address them. By analyzing the patterns and trends of incidents, these tools enable IT organizations to proactively resolve problems and prevent future incidents from occurring.
ITIL (IT Infrastructure Library) principles and practices are often incorporated into incident and problem management tools for BSM. These tools are aligned with ITIL guidelines and provide a structured approach to incident and problem management. They follow ITIL processes such as incident classification, prioritization, and escalation, as well as problem identification, analysis, and resolution.
Configuration management databases (CMDBs) are commonly integrated with incident and problem management tools to provide a comprehensive view of the IT infrastructure and its configuration items. This integration enables efficient impact analysis of incidents and problems, as well as effective change management. By linking incidents and problems to the corresponding configuration items, BSM solutions ensure that changes to the IT infrastructure are properly assessed and their impact on business services is managed.
Service-level agreement (SLA) monitoring is another important feature of incident and problem management tools for BSM. These tools enable organizations to track and measure the performance of IT services against agreed-upon goals and objectives. By providing real-time reports and dashboards, the tools help in identifying any deviations from the SLA and taking appropriate actions to meet the agreed service levels.
Integration and Automation Tools for BSM

Alignment between business and IT is crucial for the successful implementation of Business Service Management (BSM). To achieve this alignment, integration and automation tools play a vital role in ensuring that IT processes are in line with the goals and objectives of the business.
One of the key frameworks used in BSM is the IT Infrastructure Library (ITIL), which provides a set of best practices for IT service management. Integration and automation tools help organizations implement ITIL processes by providing solutions for service-level agreement (SLA) management, configuration management, problem management, and change management.
Monitoring and performance management are also important aspects of BSM. Integration and automation tools help businesses monitor the performance of their IT services and identify any issues or bottlenecks that may be affecting service delivery. These tools provide real-time insights into the performance of the IT infrastructure and allow businesses to proactively address any problems before they impact the overall service.
Integration and automation tools also help streamline the processes involved in managing IT services. They provide a centralized platform for managing service requests, incident tickets, and change requests, allowing for faster and more efficient resolution of issues. These tools enable businesses to automate routine tasks and workflows, reducing the manual effort required for managing IT services.
Overall, integration and automation tools are essential components of a BSM solution. They help businesses align their IT processes with their overall business goals, improve service delivery and performance, and enhance the overall efficiency of IT service management.
Future Trends and Developments in Business Service Management
In the evolving landscape of IT and business, the field of Business Service Management (BSM) continues to develop and adapt to new trends and technologies. BSM involves the monitoring and managing of IT services to ensure they are aligned with the business goals and objectives. It focuses on the service-level agreements (SLAs) and aims to provide a holistic view of the entire business service lifecycle.
One of the future trends in BSM is the increasing integration of BSM solutions with ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library), a widely adopted framework for IT service management. This integration helps organizations to improve their incident, problem, and change management processes, leading to better service performance and customer satisfaction. BSM solutions integrated with ITIL provide a centralized platform for managing and tracking incidents, problems, and changes, thereby streamlining business operations.
Another trend in BSM is the emphasis on configuration management. As business services become more complex and interconnected, it becomes crucial to have accurate and up-to-date information about the configuration items (CIs) that support these services. BSM solutions are evolving to include advanced configuration management capabilities, enabling organizations to effectively track and manage the various components and dependencies of their business services.
Furthermore, the future of BSM will likely see advancements in analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. These technologies will enable BSM solutions to analyze large volumes of data and identify patterns, correlations, and anomalies that can help organizations proactively address potential issues and optimize their business services. With AI-powered BSM solutions, organizations can gain deeper insights into their service performance and make data-driven decisions to improve overall efficiency and effectiveness.
In conclusion, the future of Business Service Management holds promising developments and trends that will help organizations enhance their service management processes. Integration with ITIL, increased focus on configuration management, and advancements in analytics and AI technologies are shaping the future landscape of BSM. As businesses continue to rely on IT for their operations, BSM will play a critical role in ensuring that IT services are aligned with business goals and deliver optimal performance.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in BSM

Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) play a significant role in the field of Business Service Management (BSM). With the increasing complexity of IT environments and growing volumes of data, AI and ML technologies bring efficiency, accuracy, and intelligence to BSM processes.
One area where AI and ML are widely used in BSM is service-level monitoring. AI algorithms can analyze large amounts of data from different sources, identify patterns, and detect anomalies that could indicate potential service-level incidents. ML models can then learn from these patterns and predict future incidents, allowing businesses to proactively address them before they impact services.
Another area where AI and ML are utilized is incident and problem management. By continuously analyzing historical incident and problem data, AI systems can identify common root causes, recurring issues, and patterns that lead to service disruptions. These insights can help organizations identify and address underlying problems, improving overall service performance.
Furthermore, AI and ML technologies can also support configuration and change management processes in BSM. By analyzing historical and real-time data, AI models can provide recommendations for change requests, assess the impact of proposed changes, and help businesses ensure that changes are aligned with their goals and agreed-upon service level agreements.
Integration of AI and ML into BSM software frameworks empowers businesses to automate routine tasks, reduce manual intervention, and leverage data-driven insights for improved decision-making. By combining the best practices of BSM with AI and ML capabilities, organizations can enhance their service management processes, optimize IT performance, and align IT services with overall business objectives.
Cloud-based BSM Solutions
Cloud-based BSM solutions offer a flexible and scalable approach to managing business services. These solutions leverage the power of cloud computing to deliver a comprehensive framework for aligning IT services with business goals. By deploying BSM software in the cloud, organizations can streamline their processes and improve overall performance.
One key advantage of cloud-based BSM solutions is their ability to provide real-time monitoring of business services. Using service-level agreement (SLA) monitoring and incident management tools, organizations can track the performance of their services and quickly address any issues that arise. This helps ensure that business processes are running smoothly and that any disruptions are promptly resolved.
Cloud-based BSM solutions also offer robust configuration and change management capabilities. Organizations can use these tools to effectively manage and track changes to their IT infrastructure, ensuring that any modifications are implemented in a controlled and coordinated manner. This helps minimize the risk of service disruptions and ensures that business operations can continue uninterrupted.
Furthermore, cloud-based BSM solutions are often built on the principles of IT Infrastructure Library (ITIL), a widely adopted framework for IT service management. This means that organizations can benefit from best practices and standardized processes for incident management, problem management, and change management. By aligning with ITIL guidelines, organizations can optimize their IT services and improve overall efficiency.
In summary, cloud-based BSM solutions offer organizations a comprehensive and scalable approach to managing their business services. By leveraging the power of cloud computing, organizations can align their IT services with business goals, monitor service performance in real-time, and effectively manage configuration and change. Additionally, these solutions often adhere to ITIL principles, providing organizations with best practices and standardized processes. Overall, cloud-based BSM solutions help organizations enhance their service delivery and achieve their business objectives.
The Role of BSM in Digital Transformation
Business Service Management (BSM) plays a crucial role in the process of digital transformation for organizations. BSM is a comprehensive approach to managing IT services and aligning them with the business goals. It provides a solution for organizations to optimize their IT service delivery and ensure that it is aligned with the needs of the business.
BSM utilizes ITIL (IT Infrastructure Library) framework, a set of best practices for IT service management, to guide the implementation of IT processes. By following ITIL guidelines, organizations can ensure that their IT services are managed efficiently and effectively.
One of the key areas of BSM is incident management. This involves the identification, logging, and resolution of incidents that occur in the IT environment. BSM software can help organizations automate the incident management process, ensuring that incidents are quickly identified and resolved, minimizing any impact on the business.
Another important aspect of BSM is change management. This involves managing any changes to the IT infrastructure or services in a controlled and systematic manner. BSM software can help organizations track and control the configuration of their IT assets, ensuring that any changes are properly documented and approved.
BSM also focuses on service-level management, which involves the negotiation and management of service-level agreements (SLAs) between the IT department and the business. BSM software can provide organizations with a centralized platform for monitoring and reporting on the performance of IT services, ensuring that they are meeting the agreed-upon SLAs.
In summary, BSM is an essential component of digital transformation for organizations. It helps align IT services with business goals, optimize IT service delivery, and ensure efficient incident and change management. By implementing BSM software and following ITIL guidelines, organizations can improve their IT processes and ultimately enhance their overall business performance.
FAQ about topic “What is BSM: A Guide to Understanding Business Service Management”
What is BSM?
BSM stands for Business Service Management. It is a holistic approach to managing and optimizing IT services to meet the needs of the business. BSM focuses on aligning IT services with business goals and objectives, improving service quality and reducing costs.
How does BSM work?
BSM works by providing a framework for monitoring, managing and optimizing IT services. It involves the use of tools and processes to track performance, identify issues, and implement improvements. BSM also includes communication and collaboration between IT and business teams to ensure that IT services are meeting the needs of the business.
What are the benefits of implementing BSM?
Implementing BSM can lead to several benefits for an organization. It can improve the quality and reliability of IT services, reduce downtime and outages, increase customer satisfaction, optimize resource utilization, and align IT services with business objectives. BSM can also help in identifying and resolving issues quickly, reducing costs, and improving overall efficiency.
What are the key components of BSM?
The key components of BSM include service monitoring and management, performance management, incident and problem management, change and configuration management, service level management, and financial management. These components work together to ensure that IT services are delivered effectively and efficiently.
How can an organization implement BSM?
An organization can implement BSM by following a step-by-step process. It involves defining business goals and objectives, identifying IT services that support those goals, establishing performance metrics and benchmarks, implementing monitoring and management tools, analyzing performance data, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing changes as necessary. It is important to involve both IT and business teams in the implementation process to ensure alignment and collaboration.

