VMware Snapshot is a powerful feature in virtualization technology that allows you to take a snapshot of a virtual machine’s system state at a specific point in time.
Virtualization, which is the process of creating a virtual version of a physical machine, has become an essential technology in today’s computing world. One of the key components of virtualization is the hypervisor, which is software that enables multiple operating systems to run on a single physical machine.
The snapshotting feature provided by VMware software allows you to capture a virtual machine’s entire state at a particular moment. This includes the operating system, applications, and any data that is stored within the virtual machine. With a snapshot, you can create a backup of your virtual machine, revert to a previous state, or even clone a virtual machine for testing or deployment purposes.
With the increasing popularity of cloud computing, snapshot technology has become indispensable. The ability to capture an image of a virtual machine’s system state at a specific point in time provides a convenient method for creating backups and restoring systems. This technology has made it easier for businesses to virtualize their infrastructure and ensure the availability and reliability of their systems.
In conclusion, VMware Snapshot is a powerful technology that allows you to create a virtualized image of a virtual machine’s system state at a particular moment. This feature provides a variety of benefits, including backup and restore capabilities, the ability to revert to a previous state, as well as the ability to clone virtual machines for testing or deployment purposes. Whether you are a small business or a large enterprise, VMware Snapshot can be an invaluable tool in your virtualization arsenal.
Contents
- 1 What is VMware Snapshot
- 2 Benefits of Using VMware Snapshot
- 3 Common Use Cases for VMware Snapshot
- 4 How to Create a VMware Snapshot
- 5 Step 1: Open the VMware vSphere Client
- 6 Step 2: Select the Virtual Machine
- 7 Step 3: Create a Snapshot
- 8 Managing VMware Snapshots
- 9 Viewing Snapshots
- 10 Reverting to a Snapshot
- 11 Deleting Snapshots
- 12 Best Practices for Using VMware Snapshots
- 13 Regularly Consolidate Snapshots
- 14 Monitor Snapshot Size
- 15 Avoid Long-Term Snapshot Retention
- 16 FAQ about topic “What is VMware Snapshot: A Complete Guide”
- 17 What is a VMware Snapshot?
- 18 Why would I want to use VMware Snapshots?
- 19 How do I create a VMware Snapshot?
- 20 Can I take multiple snapshots of a virtual machine?
- 21 What are the limitations of VMware Snapshots?
What is VMware Snapshot
VMware Snapshot is a technology that allows you to take a “snapshot” of a virtual machine, capturing its current state and data. It is a key feature of VMware’s virtualization software, which helps to virtualize resources and enables the creation of multiple virtual machines within a single physical server.
With snapshotting, you can create a point-in-time image of a virtual machine, which includes its operating system, applications, and data. This image can be used as a backup or to revert the virtual machine to a previous state, if needed. Snapshots are especially useful for testing and development purposes, as they allow you to quickly restore a virtual machine to a known good state.
In a cloud or virtualized environment, VMware Snapshot provides an efficient way to manage data and resources. Instead of creating multiple copies of entire virtual machines, you can simply take snapshots of individual virtual machines, saving storage space and reducing resource consumption. This makes it easier to deploy, clone, and restore virtual machines as needed.
The snapshotting process is performed by the underlying hypervisor software, such as VMware ESXi. When a snapshot is created, the hypervisor takes a “delta” image of the virtual machine’s disk files, capturing only the changes made since the snapshot was taken. This allows for efficient storage and reduced impact on system performance.
To use a VMware Snapshot, you can simply select the virtual machine and choose the “Snapshot” option in the VMware software. You can then manage the snapshots, such as taking additional snapshots, reverting to a snapshot, or deleting snapshots. This gives you full control over your virtual machines and allows for easy backup and restoration of data.
Benefits of Using VMware Snapshot
The use of VMware Snapshot offers several benefits to users in a virtualized environment. The snapshot feature allows users to create a point-in-time image of a virtual machine (VM). This image can be used for a variety of purposes, including testing, troubleshooting, and disaster recovery.
One of the major advantages of using VMware Snapshot is that it allows users to clone virtual machines quickly and easily. By creating a snapshot of a VM, users can create a new virtual machine that is an exact copy of the original. This is especially helpful when provisioning multiple VMs or setting up a development or testing environment.
Another benefit of using VMware Snapshot is the ability to revert a VM to a previous state. If any changes or updates cause issues with the VM, users can easily roll back to a snapshot taken before the changes were made. This helps to minimize downtime and ensure system stability.
Snapshotting also provides a convenient backup solution for virtual machines. By taking regular snapshots, users can capture the state of the VM at various points in time. In the event of data loss or system failure, these snapshots can be used to restore the VM to a previous state and recover important data.
Utilizing VMware Snapshot within a virtualization technology brings added flexibility to the management of virtual environments. It allows users to virtualize their infrastructure and take advantage of the benefits offered by cloud computing and software-defined networking.
In summary, the use of VMware Snapshot provides users with the ability to create virtual machine clones, revert to previous system states, and easily backup and restore data. These features enhance the efficiency and reliability of virtualized environments and help users take full advantage of the benefits of virtualization technology.
Common Use Cases for VMware Snapshot
1. Testing and Development: VMware snapshots are often used in software testing and development environments. Developers can create a snapshot of the virtual machine (VM) before making changes to the software. If the changes do not produce the desired results, the developer can easily revert back to the snapshot and start again. This allows for quick and easy experimentation without the risk of damaging the original system.
2. Backup and Restore: Snapshots are an essential component of the backup and restore process in VMware environments. Administrators can create snapshots of virtual machines as a form of backup, capturing the entire state of the system at a specific point in time. This snapshot can then be used to restore the system in the event of a failure or data loss. This ensures that critical data and applications are protected from any potential issues.
3. Patch and Update Management: When applying patches or updates to a virtual machine, administrators can use VMware snapshots as a safety net. By creating a snapshot before the updates are applied, any issues or conflicts that arise can be easily resolved by reverting back to the snapshot. This eliminates the risk of system instability or data corruption that can occur during the patching and updating process.
4. Disaster Recovery: In case of a disaster or system failure, having a recent snapshot of a virtual machine can greatly expedite the recovery process. Snapshots allow administrators to quickly restore the virtual machine to a known working state, minimizing the downtime and impact on business operations. This makes disaster recovery more efficient and reliable in VMware environments.
5. Software Testing and Rollback: Snapshots are widely used in software testing scenarios to roll back the system to a clean state after each test run. This ensures that each test begins with a fresh environment, free from any remnants of previous tests. By creating and using snapshots, developers can accelerate the testing process and identify and fix bugs more effectively.
6. Virtual Machine Consolidation: VMware snapshots can also be used as a part of virtual machine consolidation efforts. By creating snapshots of VMs and migrating them to a consolidated infrastructure, organizations can reduce hardware costs and increase operational efficiency. The snapshots serve as a temporary checkpoint while the virtual machines are being migrated, ensuring data integrity and minimizing disruptions.
Overall, VMware snapshots are a versatile and powerful technology that allows users to create point-in-time backups, test new software configurations, and recover from system failures quickly and efficiently. Their flexibility and ease of use make them an essential tool for virtualization and cloud environments.
How to Create a VMware Snapshot
Creating a VMware snapshot is a straightforward process that allows you to capture the current state of a virtual system. With VMware’s virtualization technology, snapshotting provides a convenient way to preserve the data and settings of a virtual machine at a specific moment in time.
To create a VMware snapshot, follow these steps:
- Open the VMware vSphere or VMware Workstation application.
- Select the virtual machine you want to snapshot from the list of available virtual machines.
- Click on the “Snapshot” option in the menu bar or right-click on the virtual machine and choose “Snapshot”.
- Provide a descriptive name for the snapshot to easily identify it later.
- Optionally, include a description to provide additional context about the snapshot.
- Click on the “Take Snapshot” or “Create Snapshot” button to initiate the snapshot creation process.
- Wait for the process to complete, which may take a few seconds or minutes depending on the size and complexity of the virtual machine.
- After the snapshot is created, you can find it listed in the snapshot manager, where you can manage and restore it as needed.
Creating a VMware snapshot allows you to restore your virtual machine to a specific point in time quickly. It saves a full image of the virtual machine’s disks and a set of files that capture the virtual machine’s memory state and settings. In case of any issues or changes made to the virtual machine, you can easily revert to the snapshot and restore it to its previous state.
Snapshots can also be used for other purposes, such as cloning a virtual machine or creating a backup for disaster recovery. They offer flexibility and efficiency in managing virtualized environments, enabling users to experiment with system changes and configurations without any risks to the underlying system.
In summary, VMware snapshots provide a powerful feature in virtualization technology, allowing users to capture and restore the state of a virtual machine quickly. By following the steps outlined above, you can create a snapshot of your virtual machine and have the ability to revert back to it whenever needed. This functionality is valuable for system administrators, developers, and anyone working with virtualized environments in the cloud or on-premises.
Step 1: Open the VMware vSphere Client
To begin using VMware Snapshot, you need to open the VMware vSphere Client. This client is a user interface that allows you to manage and operate your virtual infrastructure. It provides a centralized platform where you can access, monitor, and control your virtual machines.
The VMware vSphere Client is part of the VMware vSphere suite, which is a powerful system for virtualization and cloud computing. It is a hypervisor-based technology that enables you to create and manage virtual machines. With VMware vSphere Client, you can perform various tasks such as creating a clone of a virtual machine, restoring an image, or snapshotting your virtual machine.
By opening the VMware vSphere Client, you gain access to a wide range of features and tools that allow you to effectively manage your virtual environment. It provides a user-friendly interface where you can easily navigate through the different settings and options.
Once you have opened the VMware vSphere Client, you can start working with VMware Snapshot. This feature allows you to take a point-in-time snapshot of your virtual machine. It captures the entire state of the virtual machine, including its memory, disks, and configuration settings. This snapshot acts as a backup of your virtual machine’s data, and you can use it to revert back to a previous state if needed.
Step 2: Select the Virtual Machine
Once you have familiarized yourself with VMware Snapshot technology and understand its benefits, it’s time to select the virtual machine for which you want to create a snapshot. In VMware, a virtual machine (VM) is an emulation of a computer system and operates within a host server using virtualization software, known as a hypervisor.
To select the virtual machine, you can navigate through your VMware software’s interface and locate the VM you wish to snapshot. This can be done by browsing through the list of available VMs or by using the search function to find a specific VM. It’s important to select the correct VM to ensure that the snapshot captures the desired data and system state.
Virtual machines are commonly used in cloud computing and virtualized environments, as they offer a flexible and efficient way to run multiple operating systems and applications on a single physical server. They allow organizations to save costs, optimize resources, and improve scalability. VMware is a leading software provider in the virtualization industry and offers a range of solutions for virtual machine management.
When selecting a virtual machine, it’s important to consider the purpose of the snapshot. Snapshots are typically used for purposes such as creating a backup of the VM’s current state, testing new configurations or software updates, or reverting to a previous state if needed. Depending on the specific use case, different VMs may need to be selected. It’s also worth noting that a VM can have multiple snapshots, allowing for different points in time to be saved and restored.
In summary, selecting the virtual machine is a crucial step in the VMware snapshotting process. As virtualization continues to be an essential technology for modern IT environments, understanding how to effectively create and manage snapshots is vital for ensuring the integrity and recoverability of virtualized data and systems.
To create, virtualize, and backup a virtual machine, we need software that provides the necessary tools for snapshotting. One such technology is VMware, a leading company in the field of virtualization and hypervisor software. With VMware, you can easily take snapshots of your virtual machines to restore them to a previous state if needed.
Once you have launched the VMware software and selected the virtual machine you want to work with, navigate to the Snapshot tab. This tab will provide you with all the options related to snapshot creation, management, and restoration. It is a crucial step in the process as it allows you to take a “picture” or image of your virtual machine’s current state, preserving its data and settings.
Within the Snapshot tab, you will find various options to create, manage, and revert snapshots. Using the create snapshot option, you can take an instant backup of your virtual machine and save it as a separate entity. This snapshot serves as a point-in-time representation of your virtual machine, allowing you to restore it to that specific state at any time.
Furthermore, the Snapshot tab also provides options to manage existing snapshots. You can view a list of all available snapshots, along with their details such as date and time of creation, size, and description. This allows you to keep track of multiple snapshots and restore the virtual machine to any desired snapshot as needed.
In summary, navigating to the Snapshot tab is an essential substep when working with VMware. It allows you to create, manage, and restore snapshots of your virtual machines, providing you with a reliable and efficient backup solution for your data. By utilizing this snapshot functionality, you can easily revert to a previous state of your virtual machine, ensuring the safety and integrity of your virtualized system.
Step 3: Create a Snapshot
In the world of cloud computing, virtualization technology plays a crucial role in managing and optimizing data and resources. VMware, a leading hypervisor provider, offers a wide range of virtualization solutions to help businesses simplify their IT infrastructure. Creating a snapshot is one of the key functionalities that VMware provides, allowing users to swiftly capture and preserve the current state of a virtual machine.
To create a snapshot in VMware, users can follow a few simple steps. First, select the virtual machine that you want to snapshot. This virtual machine can be running, powered off, or suspended. A snapshot is essentially an image of the virtual machine’s data at a specific point in time, ensuring that you have a backup to revert to if necessary.
Once you have selected the virtual machine, you can proceed to create a snapshot by right-clicking on the VM and selecting the “Snapshot” option. A dialog box will appear, allowing you to provide a name and description for the snapshot. It is recommended to give it a descriptive name that effectively conveys the state of the virtual machine at that particular moment.
After providing the necessary details, click on the “Take Snapshot” button to initiate the snapshot creation process. This will capture the current state of the virtual machine, including its memory, disk, and other system settings. VMware’s snapshotting technology enables you to easily create multiple snapshots for a single virtual machine, allowing for greater flexibility and control.
Once the snapshot is created, it will be listed in the snapshot manager. From here, you can manage the snapshot, including reverting back to it, deleting it, or creating clones of the virtual machine based on the snapshot. Snapshots provide a reliable way to restore a virtual machine to a previous state, ensuring that any changes or modifications can be easily reversed if needed.
In summary, creating a snapshot in VMware is a straightforward process that allows users to preserve the current state of a virtual machine. By taking advantage of VMware’s powerful virtualization technology, businesses can ensure the safety and integrity of their data and systems, making it easier to manage and scale their IT infrastructure.
Substep: Name the Snapshot
After you have successfully created a snapshot of your virtual machine using VMware snapshotting software, it is important to take the time to name your snapshot. Giving your snapshot a descriptive and meaningful name will help you easily identify it later on if you need to restore or revert back to a certain point in time.
When naming your snapshot, consider including information such as the date and time it was created, as well as any specific changes or updates that were made to the virtual machine. This will make it easier to track multiple snapshots and select the correct one when needed.
A well-named snapshot can also serve as a backup of your virtual machine system. It acts as an image of the virtualized environment at a specific point in time, allowing you to capture the current state of the system, including the data and configuration settings.
Furthermore, if you are using a cloud-based virtualization platform, naming your snapshots becomes even more crucial. In the cloud, where multiple virtual machines may be running simultaneously, having an organized naming convention for snapshots can help you keep track of your data and ensure you are restoring the correct one.
In conclusion, naming your VMware snapshots is an essential step in the virtualization process. It helps you easily identify and manage your snapshots, making it easier to restore or revert back to a specific point in time. Additionally, a well-named snapshot can serve as a backup of your virtual machine and its data, providing an extra layer of protection for your system.
Substep: Take a Snapshot

In the world of virtualization technology, a snapshot is a powerful feature that allows users to capture the current state of a virtual machine’s disk and memory. VMware snapshotting software enables users to take a snapshot of their virtual machine, creating a point-in-time image. This image can be used to restore the virtual machine to its previous state, revert back to a saved configuration, or even clone the virtual machine.
When taking a snapshot, it is important to understand that it captures the entire state of the virtual machine at a particular moment. This includes all data, system settings, and installed software. This makes it an effective tool for creating backups of critical systems, as the captured image can be used to restore the entire system in case of a failure or data loss.
The process of taking a snapshot in VMware is quite straightforward. Users can simply right-click on the virtual machine in the VMware hypervisor interface and select “Take Snapshot”. A dialog box will then prompt the user to provide a name and description for the snapshot. Once the snapshot is taken, it can be accessed and managed through the VMware management console.
It is worth noting that snapshots are not a substitute for regular backups. While snapshots provide a quick way to capture the state of a virtual machine, they are not designed for long-term storage or offsite storage. Regular backups should still be performed to ensure that critical data is protected and can be restored in case of a catastrophic failure.
In summary, taking a snapshot in VMware allows users to create a point-in-time image of a virtual machine, which can be used to restore the system, revert back to a saved configuration, or clone the virtual machine. While snapshots are a useful tool for managing and protecting data in the virtual environment, they should not replace regular backups as a long-term storage solution. By combining the power of snapshotting software with regular backups, users can ensure the safety and availability of their virtualized systems and data.
Managing VMware Snapshots
When using VMware snapshots, it is important to understand how to effectively manage them to maintain the stability and performance of your virtualized systems. Reverting to a previous snapshot can be useful when testing software or making changes to a virtual machine. However, it is essential to carefully plan and execute these operations to avoid data loss and other potential issues.
One way to manage VMware snapshots is to clone them. Cloning a snapshot creates an exact copy of the virtual machine at a specific point in time. This can be useful for creating backup images or for testing different configurations without affecting the original system. By cloning a snapshot, you can preserve the state of the virtual machine and use it as a template for future deployments.
Another important aspect of managing VMware snapshots is understanding the impact they can have on storage and performance. Snapshots consume disk space, so it is important to regularly monitor and manage them to prevent excessive storage usage. Additionally, having too many snapshots can negatively impact the performance of the virtual machine and the underlying hypervisor. It is recommended to regularly consolidate and delete unnecessary snapshots to optimize the overall system performance and storage utilization.
Creating a snapshot is a simple process that involves capturing the current state of a virtual machine. This snapshot serves as a point-in-time image of the entire system, including its configuration, data, and other settings. It enables you to easily revert back to a known working state in case of any issues or to create a backup for disaster recovery purposes. VMware’s snapshotting technology provides a powerful tool for virtualizing and managing complex systems in the cloud or on-premises.
Aside from managing snapshots, it is also important to understand the backup and restore capabilities offered by VMware. While snapshots serve as a temporary solution for managing changes and testing, regular backups are essential for long-term data protection and recovery. VMware provides various backup and restore solutions that can integrate seamlessly with its virtualization technology, ensuring data integrity and business continuity.
In conclusion, managing VMware snapshots is crucial for maintaining the stability and performance of virtualized systems. By understanding how to effectively revert, clone, and manage snapshots, you can ensure the integrity of your virtual machines and optimize storage usage and system performance. Additionally, leveraging backup and restore technologies provided by VMware can further enhance data protection and disaster recovery capabilities.
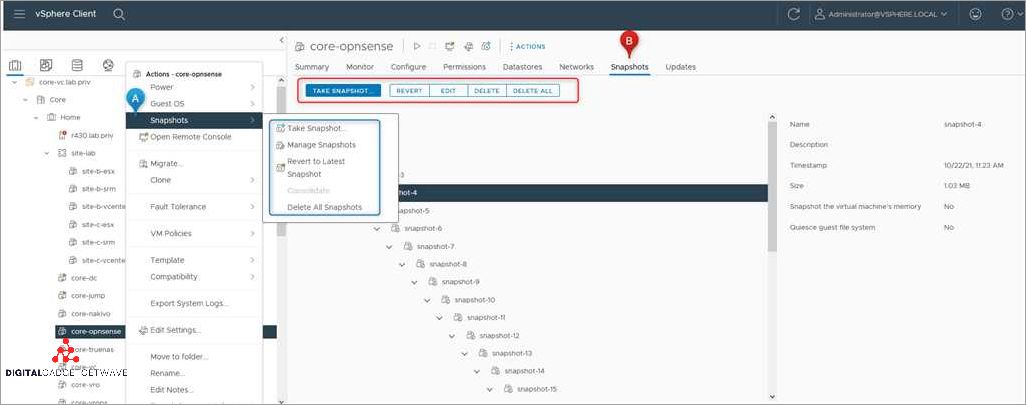
Viewing Snapshots
When working with VMware Snapshot, it is important to be able to easily view the snapshots that have been created. This allows you to have a visual representation of the various states your virtual machine has been in at different points in time. Viewing snapshots provides you with a way to revert back to a previous state of your virtual machine, which can be incredibly useful in a variety of scenarios.
Using VMware Snapshot technology, you can take a snapshot of your virtual machine’s current state, creating an image of the entire system. This snapshot captures the data and settings of the virtual machine at the time it was taken and allows you to revert your virtual machine back to that specific point in time. This technology is crucial in virtualization and cloud environments, as it enables you to easily manage and restore your virtual machines.
To view snapshots in VMware, you can use the Snapshot Manager tool provided by the software. This tool allows you to see all the snapshots that have been taken for a particular virtual machine. The Snapshot Manager displays the name of each snapshot, along with the date and time it was created. It also provides options to create new snapshots, clone a virtual machine from a snapshot, and revert the virtual machine back to a previous snapshot.
When viewing snapshots, it is important to keep in mind that each snapshot is essentially a point-in-time copy of your virtual machine. This means that the data and settings captured by the snapshot are frozen and preserved, while any changes made to the virtual machine after the snapshot was taken are not included. This allows you to easily restore your virtual machine to a previous state, without affecting any new changes or data that were added since that snapshot was created.
In summary, viewing snapshots in VMware Snapshot is an essential part of managing and restoring your virtual machines. With the ability to create, backup, and restore snapshots, you can easily roll back your virtual machine to a previous state, ensuring the stability and integrity of your virtualized environment.
Reverting to a Snapshot
When working with virtualized systems, it is important to have a reliable backup and restore mechanism in place. VMware Snapshot technology is one such solution that allows users to capture the state of a virtual machine at a specific point in time, creating a backup image of the entire system.
Reverting to a snapshot is a process that allows users to restore their virtual machine to a previously captured state. This can be useful in a variety of situations, such as when testing software or making changes to the system configuration. By reverting to a snapshot, users can quickly and easily revert any changes made to the system, effectively rolling back to a previous version.
To revert to a snapshot, users simply need to select the desired snapshot from a list of available snapshots. The hypervisor will then restore the virtual machine to the selected snapshot, effectively discarding any changes made since that point in time. This process is quick and efficient, allowing users to quickly restore their virtual machines to a known good state.
It is important to note that reverting to a snapshot is not the same as creating a clone or a backup of the virtual machine. While reverting to a snapshot will restore the virtual machine to a previous state, it does not create a separate copy of the virtual machine or its data. This means that any changes made to the system after the snapshot was taken will be lost. To create a separate copy of the virtual machine, users should consider creating a clone or performing a backup.
In conclusion, reverting to a VMware Snapshot is a powerful feature that allows users to quickly restore their virtual machines to a previously captured state. This can be useful for testing purposes, system configuration changes, or simply to roll back to a known good state. By understanding how to revert to a snapshot, users can take full advantage of VMware’s snapshot technology and ensure the stability and integrity of their virtualized systems.
Deleting Snapshots
When working with VMware, creating snapshots can be a valuable tool for managing and protecting your virtual machines. However, at times you may need to delete snapshots to free up storage space or manage the performance of your virtual environment. Deleting snapshots can be done easily through the VMware software interface.
To delete a snapshot, you first need to ensure that the virtual machine is powered off. Once the virtual machine is powered off, navigate to the snapshot manager in the VMware software. From here, you will see a list of all the snapshots associated with the virtual machine. Select the snapshot you want to delete and click on the “Delete” button.
Deleting a snapshot will remove that particular point-in-time image of the virtual machine. It’s important to note that deleting a snapshot does not impact the virtual machine itself. The virtual machine will still be available and can be powered on and used as usual. However, any changes made to the system since the snapshot was taken will be lost.
It’s also worth mentioning that deleting snapshots can take some time, especially if the snapshot is large or if there are multiple snapshots to delete. During the deletion process, the virtual machine may experience a temporary performance impact. It’s important to plan the deletion of snapshots accordingly, taking into consideration the impact on your virtual environment.
In summary, deleting snapshots in VMware is a simple process that can free up storage space and optimize the performance of your virtual environment. By removing snapshots, you can restore your virtual machines to a more stable and efficient state. With the power of virtualization and snapshotting technology, you can confidently manage and protect your data in the cloud or on-premises.
Best Practices for Using VMware Snapshots
In the world of virtualization, VMware stands out as a leading provider of state-of-the-art technology. One of its key features is the snapshotting functionality, which allows users to capture the current state of a virtual machine or cloud environment. Here are some best practices to consider when utilizing VMware snapshots:
- Create regular snapshots: It is recommended to create snapshots at regular intervals, especially before making any critical changes to a virtual machine or system. This helps ensure that you have a recent backup to revert back to if needed.
- Document snapshot purpose: When creating a snapshot, it’s a good practice to provide a descriptive name and note the purpose of the snapshot. This makes it easier to identify and manage snapshots later on.
- Monitor snapshot growth: Snapshots can consume a significant amount of storage space, especially if they are kept for an extended period. It’s essential to monitor snapshot growth and regularly consolidate or delete unnecessary snapshots to free up disk space.
- Use multiple snapshots cautiously: While VMware allows the creation of multiple snapshots, it’s important to use them judiciously. Excessive use of snapshots can negatively impact virtual machine performance and increase the risk of snapshot corruption.
- Plan for backup: Snapshots should not be used as a substitute for regular backups. While snapshots provide a convenient way to revert to a previous state, they are not designed for long-term data protection. It’s crucial to implement a comprehensive backup strategy in parallel with snapshotting.
- Understand snapshot dependencies: It’s important to be aware of snapshot dependencies when reverting or deleting snapshots. Snapshots have a hierarchical relationship, and deleting a parent snapshot can affect the integrity of its child snapshots. Always follow a top-down approach when working with multiple snapshots.
- Test snapshot restoration: Regularly test the process of restoring a virtual machine from a snapshot to ensure it functions as expected. This helps validate the effectiveness of the snapshotting and restoration process and ensures that critical data and systems can be recovered efficiently.
By following these best practices, users can make the most of VMware snapshots and leverage this powerful feature for efficient virtual machine management, data protection, and disaster recovery.
Regularly Consolidate Snapshots
Snapshots are a valuable tool in virtualization technology, allowing system administrators to create a point-in-time image of a virtual machine. However, if snapshots are not managed properly, they can quickly consume storage space and impact system performance. That’s why it is important to regularly consolidate snapshots.
Consolidating snapshots involves merging multiple snapshots into a single image. This process eliminates redundant data and improves the efficiency of the virtual machine. By consolidating snapshots, system administrators can reduce storage requirements, optimize performance, and ensure data integrity.
Consolidation should be performed regularly to prevent snapshot sprawl and maintain optimal system performance. It is recommended to consolidate snapshots during periods of low activity or scheduled maintenance windows to minimize disruption to users.
VMware provides tools and utilities that make it easy to consolidate snapshots. The VMware hypervisor offers features like snapshot manager and snapshot consolidation, which allow administrators to easily manage and consolidate snapshots for virtual machines. These tools provide a simple and efficient way to manage snapshots and ensure that the virtual environment remains stable and performant.
In addition to regular consolidation, it is also important to regularly backup and restore snapshots. Backing up snapshots provides an additional layer of data protection and allows for quick recovery in the event of data loss or system failure. Restoring snapshots is a straightforward process that allows system administrators to revert to a previously saved state of the virtual machine.
Overall, regularly consolidating snapshots is a crucial task for system administrators to maintain the health and performance of their virtualized environments. By properly managing snapshots and regularly consolidating them, organizations can optimize storage utilization, improve system performance, and ensure the integrity of their data.
Monitor Snapshot Size
To effectively manage your virtualized environment and optimize storage usage, it is important to monitor the size of your VMware snapshots. Snapshotting is a powerful feature of virtualization software, such as VMware, that allows you to create a point-in-time image of a virtual machine’s system and data. These snapshots serve as a backup or clone of the virtual machine, capturing its entire state at a specific moment.
By monitoring the size of your snapshots, you can ensure that they are not consuming excessive storage space in your infrastructure. Snapshots can quickly grow in size if changes are made to the virtual machine after the snapshot is taken. This growth is due to the nature of snapshotting: any changes made to the virtual machine are stored in separate files, which can accumulate over time.
It is recommended to regularly check the size of your snapshots, especially if you have a large number of virtual machines or a limited storage capacity. This can be done using VMware tools or third-party monitoring solutions. By monitoring the size, you can identify any snapshots that have become unusually large and take necessary actions.
If you find that a snapshot has grown to a size that is too large, you may want to consider deleting or consolidating it. Deleting a snapshot will remove it completely from your system, freeing up storage space. Consolidating a snapshot involves merging its changes back into the original virtual machine, effectively eliminating the need for the snapshot file and reducing the overall size.
Avoid Long-Term Snapshot Retention
When using VMware snapshot technology, it is important to avoid long-term snapshot retention. While snapshots can be a useful tool for backing up virtual machines, they should not be relied upon as a long-term backup solution.
Although snapshots provide a convenient way to capture the state of a virtual machine at a specific point in time, they are not designed for long-term retention. Snapshots are intended to be temporary and should be used as a short-term backup method before transferring the data to a more permanent storage solution.
Storing snapshots for an extended period of time can lead to a number of issues. Firstly, snapshots consume valuable disk space on the hypervisor, potentially causing performance degradation and slower system operation. Additionally, maintaining a large number of snapshots can make it more challenging to manage and navigate the virtual environment.
Another potential issue with long-term snapshot retention is the risk of data corruption. Over time, the snapshot file may become fragmented or encounter errors, leading to potential data loss or inconsistencies. It is important to regularly monitor and maintain the snapshot files to ensure their integrity.
Instead of relying solely on snapshots for backup purposes, it is recommended to utilize a comprehensive backup and recovery solution. This may involve creating regular backups of the virtual machines and storing them in a secure offsite location, such as a cloud-based backup service. By utilizing a dedicated backup software, it is possible to create cloned images of the virtual machines that can be easily restored or reverted to a specific point in time.
FAQ about topic “What is VMware Snapshot: A Complete Guide”
What is a VMware Snapshot?
A VMware Snapshot is a saved state of a virtual machine at a specific point in time. It captures the entire virtual machine’s disk and memory state, allowing you to revert back to that specific point in time if needed.
Why would I want to use VMware Snapshots?
There are several reasons why you would want to use VMware Snapshots. Firstly, it allows you to take a snapshot of a virtual machine before making any major changes or updates, providing a safety net in case something goes wrong. Secondly, it enables you to quickly revert back to a previous state if you encounter any issues or errors. Lastly, it can be used for testing and development purposes, allowing you to easily create different scenarios without affecting the original virtual machine.
How do I create a VMware Snapshot?
To create a VMware Snapshot, you can use the vSphere Web Client or the vSphere Client. Simply right-click on the virtual machine you want to create a snapshot for, go to “Snapshot” and select “Take Snapshot”. Give the snapshot a name and description if desired, and click “OK”. The snapshot will then be created.
Can I take multiple snapshots of a virtual machine?
Yes, you can take multiple snapshots of a virtual machine. Each snapshot you take captures the current state of the virtual machine at that point in time. You can also create a snapshot while a previous snapshot is still in use, creating a “snapshot tree” with multiple snapshots.
What are the limitations of VMware Snapshots?
While VMware Snapshots can be a valuable tool, there are some limitations to be aware of. Firstly, snapshots can take up a significant amount of storage space, as they capture the entire state of the virtual machine. This can potentially lead to storage issues if not managed properly. Secondly, snapshots can impact the performance of the virtual machine, especially if there are multiple snapshots or if the snapshots are kept for a long period of time. Lastly, snapshots are not a substitute for regular backups, as they are not designed for long-term retention and can be lost if there is a storage failure.

