In the context of computer networks and the internet, routing plays a crucial role in ensuring that data packets are efficiently and accurately delivered from source to destination. But what does redundancy in routing mean?
Routing redundancy refers to the practice of creating multiple paths for data packets to reach their destinations. This redundancy serves as a backup mechanism in case any of the primary paths fail or become congested.
In essence, redundancy in routing is a means of providing fault tolerance and high availability in network communication. By having multiple redundant paths, the network can continue to function even if there is a failure or disruption in one of the paths. This ensures that data packets can still be delivered reliably and efficiently, even in the face of unexpected events or issues.
Contents
Why Redundancy is Important
In the context of internet routing, redundancy refers to the duplication of network links or routers in order to provide backup and alternative paths for data transmission. But what does redundancy really mean and why is it important?
Redundancy in internet routing is a crucial factor that ensures the reliability and availability of data transmission. It means having multiple paths or options to send and receive data, so that if one path fails or becomes congested, another path can be used instead. This redundancy helps prevent downtime, improves network resilience, and enhances overall performance.
With redundancy in place, internet traffic can be automatically rerouted in case of failures or congestion, ensuring that critical data continues to flow without interruption. This is particularly important for businesses and organizations that rely heavily on the internet for their operations, as any downtime or disruption can result in significant financial losses and damage to their reputation.
Redundancy also plays a key role in preventing single points of failure in internet routing. By having multiple alternative paths, the risk of a single link or router failure bringing down the entire network is greatly reduced. This ensures that even in the face of failure or attacks, the network remains operational and continues to function.
Furthermore, redundancy can help distribute network traffic more efficiently, balancing the load across multiple paths and reducing congestion. This can lead to faster data transmission and improved user experience, especially during peak traffic periods.
In summary, redundancy in internet routing is important because it ensures reliability, availability, and resilience of data transmission. It helps prevent downtime, improves network performance, and mitigates the risks of single points of failure. By providing backup and alternative paths, redundancy enhances the overall stability and robustness of the internet infrastructure.
The Need for Reliable Internet Connections
In today’s digital age, the internet has become an integral part of our lives, enabling us to connect with others, access information, and conduct business. However, relying on the internet means that we depend on a stable and consistent connection. Any disruption can have significant consequences, especially in the context of routing.
Routing is the process of directing network traffic from one device to another, ensuring that data packets reach their intended destination. In this context, reliability refers to the ability of the internet to consistently deliver data without interruptions or delays. The need for reliable internet connections arises from the fact that many important tasks and activities rely on the continuous flow of data.
So, what does redundancy have to do with it? Redundancy, in the context of internet routing, involves the existence of multiple paths for data to travel from one network to another. This redundancy is crucial because it provides backup options in case of failures or congestions in the network. With redundant routing, if one path becomes unavailable or congested, the data can be automatically rerouted through an alternative path.
Without redundancy, a single point of failure in the routing process can lead to a complete loss of connectivity, resulting in disruptions and downtime for users. Redundant routing ensures that even if one path fails, there are alternative routes available to maintain connectivity and prevent data loss. It increases the reliability of internet connections by providing backup options and minimizing the impact of failures.
In conclusion, reliable internet connections are essential in today’s interconnected world, and redundancy plays a crucial role in ensuring this reliability. By providing backup paths and minimizing the impact of failures, redundant routing enhances the stability and consistency of internet connections. It is an important aspect to consider in network design and implementation to ensure uninterrupted access to the digital resources we have come to rely on.
The Role of Redundancy in Ensuring Network Stability
In the context of routing, redundancy refers to the use of multiple paths or alternative routes to ensure continuous network connectivity. It is a crucial element in maintaining network stability and resilience. But what does redundancy exactly mean and how does it contribute to the stability of internet routing?
Redundancy, in the context of internet routing, means that there are multiple routes available for data to traverse from one network to another. This is achieved through the use of multiple routers, links, and protocols. When a packet is sent from one network, it can be transmitted through different routes, and if one of the routes fails or becomes congested, the packet can take an alternative path to reach its destination.
By having redundant routes, network operators can ensure that there is no single point of failure that can disrupt connectivity. This is particularly important in scenarios where critical services or applications are dependent on continuous network availability. Redundancy helps to mitigate the impact of network outages or failures, providing a resilient and reliable network infrastructure.
Redundancy also plays a role in load balancing and optimizing network performance. When there are multiple paths available, traffic can be distributed across these paths, preventing congestion and ensuring efficient utilization of network resources. It allows for better management of network traffic and helps to improve overall network performance.
In conclusion, redundancy in internet routing is essential for ensuring network stability and reliability. It provides alternative paths for data transmission, mitigates the impact of failures, and helps to optimize network performance. By implementing redundancy measures, network operators can enhance the resilience of their networks and ensure continuous connectivity for their users.
Types of Redundancy in Internet Routing
Redundancy in internet routing refers to the presence of multiple paths that data can take to reach its destination. This is essential for maintaining a reliable and efficient internet infrastructure. There are several types of redundancy that are commonly used in internet routing:
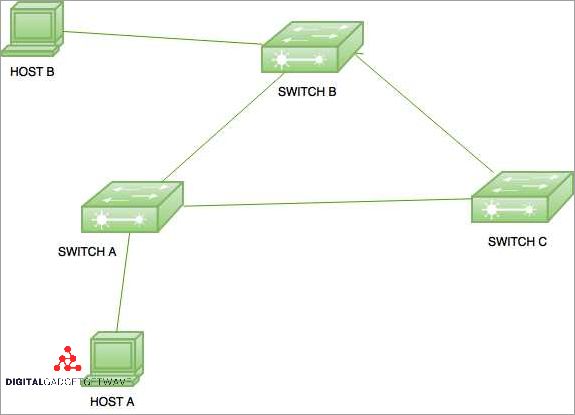
- Link Redundancy: Link redundancy involves having multiple physical connections between routers or network devices. This ensures that if one link fails or becomes congested, data can be rerouted through a different link, reducing downtime and improving overall network performance.
- Router Redundancy: Router redundancy involves having multiple routers in a network that can take over each other’s duties in case of a failure. This is typically achieved through technologies like Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) or Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP), which allow for automatic failover when a primary router becomes unavailable.
- Path Redundancy: Path redundancy involves having multiple paths or routes that data can take to reach its destination. This is often achieved through the use of routing protocols such as Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) which allows multiple routes to be advertised for a specific destination. Path redundancy helps to ensure that if one path fails or becomes congested, data can be rerouted through an alternative path.
- Provider Redundancy: Provider redundancy involves using multiple internet service providers (ISPs) to connect to the internet. This ensures that if one ISP experiences an outage or connectivity issues, traffic can be automatically routed through another ISP. Provider redundancy is commonly used by large organizations or internet service providers themselves to ensure high availability and minimize disruptions.
Each type of redundancy plays a crucial role in ensuring the stability and reliability of internet routing. By implementing these redundancies, the internet can continue to function even in the face of failures or disruptions, providing users with uninterrupted access to online services and information.
Physical Redundancy: Diverse Network Infrastructure
In the context of internet routing, physical redundancy refers to the use of multiple network infrastructure components to ensure the reliability and availability of internet connectivity. It involves the deployment of diverse routes and equipment to mitigate various potential failures and improve the overall performance and resilience of the network.
Physical redundancy plays a critical role in ensuring uninterrupted communication for organizations and individuals. By having multiple physical pathways and infrastructure components, network operators can minimize the impact of a single point of failure, such as a fiber cut or equipment malfunction.
What does physical redundancy mean in the context of internet routing? It means that network operators invest in redundant routers, switches, and transmission lines to create alternative paths for data traffic. This diversification allows packets to be rerouted around failures, ensuring that communication continues despite disruptions in the network.
The use of physical redundancy in internet routing helps to maintain high uptime and minimize downtime. By creating diverse routes and using multiple physical connections, network operators can ensure that data can still flow even if one or more components fail. This level of redundancy also facilitates load balancing and enables efficient utilization of network resources.
Physical redundancy can be achieved through various means, such as deploying redundant fiber-optic cables, using multiple carriers, establishing redundant power and cooling systems, and implementing redundancy protocols and mechanisms at various network layers. These measures help to create a robust and resilient network infrastructure that can withstand unexpected failures and maintain reliable internet connectivity.
Logical Redundancy: Multiple Paths and Protocols
When it comes to internet routing, redundancy is a crucial concept. In the context of routing, redundancy refers to the existence of multiple paths that can be used to transmit data packets from one point to another. But what does redundancy really mean in this context?
Simply put, redundancy in internet routing means having multiple routes available to reach a destination. This ensures that even if one route fails or experiences congestion, there are alternative paths that can be used to deliver the data packets.
One way to achieve redundancy is by using multiple protocols. Different protocols can offer different paths for packet transmission, increasing the chances of successful delivery. By employing multiple protocols such as Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), internet routers can have a range of options when it comes to selecting the best path for data transmission.
Another approach to redundancy is using multiple paths within a single protocol. This can be achieved through techniques such as Equal-Cost Multi-Path (ECMP) routing, where data packets are divided across different paths to ensure load balancing and fault tolerance. Each path may have its own unique characteristics, such as varying latency or bandwidth, and multiple paths can provide flexibility and resiliency in case of failures.
Overall, logical redundancy in internet routing is essential for maintaining a robust and reliable network infrastructure. Whether through the use of multiple protocols or multiple paths within a single protocol, redundancy ensures that data packets have alternative routes to reach their destination, minimizing the impact of failures and congestion.
Implementing Redundancy in Internet Routing
In the context of internet routing, redundancy refers to the implementation of backup paths and systems to ensure uninterrupted connectivity. Routing in the internet is the process of directing data packets from one network to another. It involves choosing the most optimal path for the data to travel. However, what does redundancy mean in this context?
Redundancy in internet routing means having alternative paths and systems in place to ensure that if one path or system fails, there are backups available to maintain connectivity. This is important because a single point of failure can disrupt the flow of data and result in service interruptions. Having redundant paths and systems increases the reliability and resilience of the internet infrastructure.
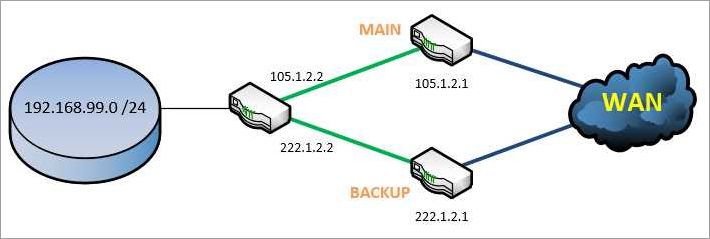
Implementing redundancy in internet routing involves various techniques. One approach is to establish multiple physical connections between different network nodes. These connections can be diverse in terms of their paths, ensuring that if one connection fails, the others can still carry the traffic. Additionally, protocols like Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) can be used to dynamically reroute traffic in case of failures.
Another aspect of implementing redundancy is the use of redundant network equipment. This can include having duplicate routers, switches, and other networking devices configured in a redundant manner. In case one device fails, the backup device takes over to maintain the network’s operation. This redundancy at the hardware level helps in minimizing downtime and ensures continuous availability of internet services.
In conclusion, implementing redundancy in internet routing means having backup paths and systems to ensure uninterrupted connectivity. It involves establishing multiple physical connections, using protocols for dynamic rerouting, and deploying redundant network equipment. By implementing redundancy, the internet infrastructure becomes more reliable, resilient, and less susceptible to disruptions caused by failures.
Load Balancing Techniques for Optimal Resource Utilization
In the context of understanding redundancy in internet routing, the concept of load balancing techniques comes into play. But what does load balancing mean in this context? Load balancing refers to the distribution of network traffic across multiple routes or servers, with the goal of optimizing resource utilization and ensuring efficient and reliable delivery of data.
When it comes to redundancy in routing, load balancing techniques are crucial. Redundancy is the presence of multiple paths or alternative routes that data can take to reach its destination. By implementing load balancing techniques, network administrators can make use of this redundancy to distribute the traffic evenly across these paths, ensuring that no single path is overloaded and achieving optimal resource utilization.
Load balancing techniques can be implemented in various ways. One common method is round-robin load balancing, where requests are distributed sequentially among the available paths or servers. Another approach is weighted load balancing, where different paths or servers are assigned different weights based on their capacity or performance, with more traffic being directed towards the higher-capacity paths.
A more advanced technique is dynamic load balancing, which involves continuously monitoring the network conditions and adjusting the traffic distribution in real-time based on factors such as server load, network congestion, and latency. This allows for optimal resource utilization, as traffic is dynamically redirected to less loaded paths or servers to ensure efficient delivery.
In summary, load balancing techniques play a crucial role in achieving optimal resource utilization in the context of redundancy in internet routing. By evenly distributing network traffic across multiple paths or servers, these techniques ensure efficient and reliable data delivery while maximizing resource utilization. Whether through round-robin, weighted, or dynamic load balancing, network administrators can leverage redundancy to achieve optimal performance and maintain a robust and reliable network infrastructure.
Automatic Failover Mechanisms for Seamless Network Connection
When it comes to routing, redundancy plays a crucial role in ensuring seamless network connectivity. But what does redundancy mean in the context of routing? In simple terms, redundancy refers to the presence of multiple interconnected paths for data transmission within a network. The use of redundant paths allows the network to continue functioning even if one or more paths fail.
Automatic failover mechanisms are essential in ensuring uninterrupted network connection in the event of path failures. These mechanisms are designed to detect failures in the primary path and automatically switch traffic to an alternate path. This ensures that the network remains operational and data can continue to flow without any noticeable interruption.
One of the commonly used automatic failover mechanisms is the use of dynamic routing protocols. These protocols, such as OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) or BGP (Border Gateway Protocol), constantly exchange information about network topology and calculate the best available paths for data transmission. In the event of a path failure, these protocols can quickly adapt and reroute traffic through an alternate path, minimizing the impact on network performance.
Another mechanism for automatic failover is the use of link-state monitoring. This involves continuously monitoring the state of network links and detecting any link failures. When a failure is detected, the network can automatically switch to an alternate link, ensuring uninterrupted connectivity. This can be achieved through techniques such as link-state advertisements or periodic probing of link availability.
To ensure seamless failover, it is also important to have redundant hardware and devices in the network infrastructure. For example, having multiple routers or switches configured in a redundant setup can help distribute traffic and provide backup in case of a device failure. Additionally, redundant power supplies, network cables, and other critical components can further enhance network reliability.
In conclusion, automatic failover mechanisms are crucial for maintaining seamless network connectivity in the face of path failures. By utilizing redundant paths, dynamic routing protocols, link-state monitoring, and redundant hardware, networks can ensure uninterrupted data transmission and provide a reliable experience for end-users.
Challenges and Considerations in Redundancy
Understanding redundancy in the context of internet routing is crucial for ensuring reliable and stable network connections. But what does redundancy mean in this context?
In simple terms, redundancy refers to the duplication of network pathways or components to provide backup options in case of failures. It is a proactive approach to mitigate the impact of single points of failure and prevent network downtime. However, implementing redundancy comes with its own set of challenges and considerations.
Firstly, redundancy adds complexity to the network infrastructure. Multiple paths and components need to be configured and maintained, which increases the chances of misconfigurations and introduces the need for robust management and monitoring systems.
Secondly, redundancy requires additional resources. Duplicate network links or devices mean extra costs for procurement, installation, and maintenance. Organizations need to carefully assess the trade-off between the potential benefits of redundancy and the associated expenses.
Another challenge lies in ensuring seamless failover. Redundancy is only effective if it can automatically and quickly switch to backup paths or components when primary ones fail. Achieving this responsiveness requires careful planning and configuration to minimize downtime and maintain uninterrupted service.
Furthermore, organizations must also consider the potential impact of redundancy on network performance. By introducing redundant pathways or components, there can be an increase in network traffic, which may affect overall speed and latency. Balancing redundancy and performance is a critical consideration.
Overall, the implementation of redundancy in internet routing involves assessing the trade-offs between complexity, cost, failover capabilities, and performance impact. Careful planning, configuration, and ongoing management are essential to maximize the benefits of redundancy and ensure a reliable network infrastructure.
Cost-Effectiveness and Scalability
In the context of internet routing, cost-effectiveness and scalability are crucial factors to consider.
When we talk about cost-effectiveness, we refer to the efficiency and economic feasibility of implementing routing solutions. Cost-effective routing solutions aim to minimize the expenses associated with maintaining and managing the network infrastructure. This involves optimizing the utilization of resources, such as bandwidth and hardware, to provide a reliable and high-performing routing system.
Scalability, on the other hand, relates to the ability of the routing system to handle increasing traffic demands and accommodate the growing number of connected devices. Scalability is vital as the internet continues to expand with more users and devices coming online every day. A scalable routing architecture ensures that the network can handle the increased data traffic while maintaining performance and reliability.
Routing in the internet context refers to the process of directing data packets from their source to their destination across multiple networks. It involves making decisions on the most efficient path for data transmission, taking into account factors such as latency, network congestion, and reliability.
So, what does cost-effectiveness and scalability mean for internet routing? It means that routing solutions need to be designed and implemented in a way that maximizes efficiency and minimizes costs, while also being able to handle the growing demands of the internet. This requires careful planning, optimization, and the use of advanced technologies to ensure a cost-effective and scalable routing infrastructure.
Network Complexity and Increased Latency
In the context of internet routing, network complexity refers to the intricate web of connections and routes that data must traverse in order to reach its intended destination. With the ever-growing number of devices connected to the internet, the complexity of these networks has also increased.
As more routes and connections are added to the network, the mean number of hops that data packets must take to reach their destination also increases. This can result in increased latency, or delay, in the delivery of data. Latency refers to the time it takes for a data packet to travel from its source to its destination, and increased latency can have a negative impact on the performance and responsiveness of internet applications.
Routing plays a crucial role in managing network complexity and reducing latency. Routing algorithms determine the most efficient path for data to travel through the network, taking into account factors such as network congestion and link quality. However, as the complexity of networks increases, the task of finding optimal routes becomes more challenging.
The internet itself is a prime example of network complexity. It is a global network of interconnected networks, each with its own routing protocols and infrastructure. What this means is that data traveling across the internet may have to pass through multiple networks and routers before reaching its final destination.
To overcome the challenges presented by network complexity and reduce latency, various techniques and technologies have been developed. These include load balancing, where traffic is distributed across multiple paths to avoid congestion, and the use of content delivery networks (CDNs) to bring data closer to the end users.
FAQ about topic “Demystifying Internet Routing Redundancy: An In-Depth Explanation”
What is redundancy in internet routing?
Redundancy in internet routing refers to the practice of having multiple paths for data to travel between networks. This ensures that if one path fails, the data can still reach its destination via an alternate path.


