The growing amount of data exchanged over the internet has made it imperative for organizations to prioritize the monitoring and prevention of security breaches. Intrusion detection systems (IDS) play a vital role in protecting networks and hosts from unauthorized access and malicious activities.
Host-based intrusion detection systems (HIDS) focus on analyzing and monitoring activities within a single host or system. These systems rely on signature-based analysis, which involves comparing the behavior of the host against a database of known attack signatures. This enables the detection of specific malware or intrusion attempts targeting the host.
On the other hand, network-based intrusion detection systems (NIDS) monitor and analyze network traffic to identify and respond to potential security incidents. NIDS use a combination of signature-based and behavior-based analysis to detect anomalies in network traffic. By analyzing patterns and monitoring for unusual activity, NIDS can detect both known and unknown attacks.
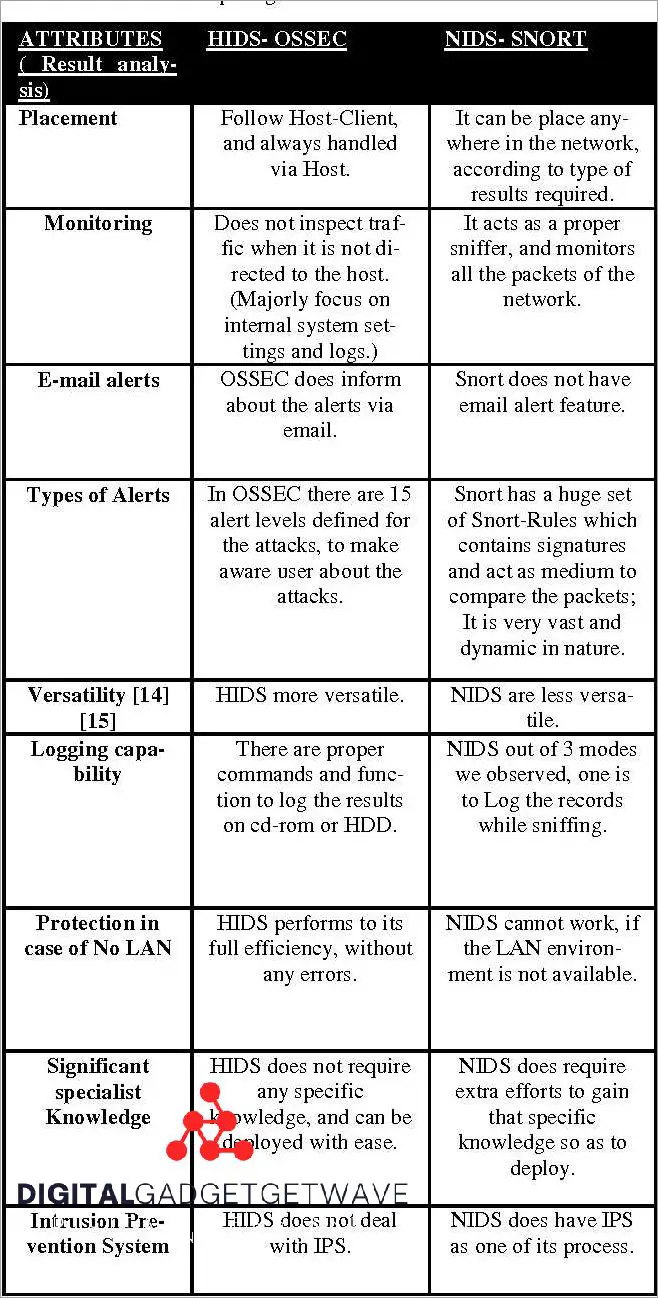
While HIDS and NIDS serve the same purpose of detecting and responding to intrusions, they differ in their focus and approach. HIDS are more adept at detecting host-specific attacks, such as malware infections or unauthorized access attempts. NIDS, on the other hand, excel at detecting network-wide attacks and anomalies that may go unnoticed by individual hosts.
Ultimately, the choice between HIDS and NIDS depends on the specific needs and requirements of an organization. A combination of both systems can provide a comprehensive and layered approach to intrusion detection and prevention. By leveraging the strengths of both HIDS and NIDS, organizations can enhance their overall network security posture and effectively mitigate the risks posed by cyber attacks.
Contents
- 1 Definition of Intrusion Detection Systems
- 2 Purpose of Intrusion Detection Systems
- 3 Difference Between HIDS and NIDS
- 4 Host-based Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS)
- 5 Network-based Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS)
- 6 Comparison of HIDS and NIDS
- 7 FAQ about topic “HIDS vs NIDS: A Comparison of Host-based and Network-based Intrusion Detection Systems”
- 8 What is the difference between HIDS and NIDS?
- 9 Which type of IDS is more effective?
- 10 Can HIDS and NIDS be used together?
- 11 Are HIDS and NIDS suitable for all types of organizations?
- 12 What are some common challenges in implementing HIDS and NIDS?
Definition of Intrusion Detection Systems
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) are security mechanisms that monitor and analyze the behavior of a host or network to identify and detect any unauthorized intrusion or malicious activity. They play a crucial role in the prevention and response to security incidents, helping to protect sensitive data and defend against various types of attacks, such as malware or network-based intrusions.
There are two main types of IDS: Network-based Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS) and Host-based Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS). NIDS monitor network traffic and analyze it for any signs of intrusion or unusual behavior, while HIDS focus on the individual host or system, analyzing local logs and files to detect any anomalies or signs of compromise.
IDS can utilize different methods for intrusion detection, including signature-based detection and anomaly-based detection. Signature-based detection involves comparing network or host activity against a predefined set of known attack patterns or signatures. If a match is found, it indicates a possible intrusion. Anomaly-based detection, on the other hand, looks for deviations from normal behavior, identifying unusual or suspicious activities that may indicate an intrusion.
Once an intrusion is detected, IDS can trigger automated responses or alerts to notify administrators of the incident. These responses can include blocking the source of the intrusion, collecting additional data for analysis, or initiating incident response procedures to mitigate the impact and minimize the damage caused by the intrusion.
Overall, IDS serve as a critical component of a comprehensive security strategy, providing real-time monitoring, rapid incident identification, and effective detection of unauthorized activities. By continuously analyzing and evaluating network and host behaviors, IDS help to enhance the security posture of an organization and protect against potential threats and attacks.
Purpose of Intrusion Detection Systems
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) are important tools in network and host security. The main purpose of IDS is to detect unauthorized access or malicious activities in a system or network. IDS can be either network-based or host-based, each with their own advantages and purposes.
Network-based IDS (NIDS) are designed to monitor and analyze network traffic. They inspect packets passing through the network and compare them against known patterns or signatures of known attacks. NIDS are effective in identifying and alerting security teams about potential threats or attacks targeting the network. They provide real-time analysis and can detect a wide range of attacks, including malware infections, port scanning, and denial of service attacks.
Host-based IDS (HIDS) are focused on monitoring the activities and behaviors of individual hosts or systems. They analyze system logs, files, and activities to detect any anomalous or suspicious behavior. HIDS can identify attacks that may have bypassed network-based detection systems, as they focus on the specific host and its activities. HIDS can also help in incident response by providing detailed information about the attack, allowing for quicker identification and response.
The purpose of IDS is not only detection but also prevention. IDS can provide early warning alerts, allowing security teams to take necessary actions to mitigate the risk and prevent further damage. They provide vital information for incident response and aid in forensic analysis after an intrusion has occurred.
IDS serve as a proactive security measure, protecting systems and networks from unauthorized access and malicious activities. They constantly monitor and analyze data and network traffic, raising alarms when suspicious activities or patterns are detected. IDS play a crucial role in safeguarding data and ensuring the integrity and availability of systems.
In conclusion, the purpose of intrusion detection systems is to detect, identify, and respond to any unauthorized or malicious intrusion into a system or network. Both network-based and host-based IDS are essential components of a comprehensive security strategy.
Difference Between HIDS and NIDS
A Host-based Intrusion Detection System (HIDS) is a type of intrusion detection system that is designed to monitor and detect suspicious activities on a specific host or computer system. It focuses on analyzing the behavior and activities of the host, such as log files, system calls, and network traffic, to identify any potential security incidents or attacks.
On the other hand, a Network-based Intrusion Detection System (NIDS) is designed to monitor and detect suspicious activities on a network level. It analyzes network traffic and looks for anomalies or patterns that may indicate a potential intrusion or attack. NIDS can detect attacks at a larger scale, covering multiple hosts and systems within a network.
One of the key differences between HIDS and NIDS is the level at which they operate. HIDS operates at the host or individual system level, while NIDS operates at the network level. HIDS focuses on monitoring and protecting the specific host, while NIDS monitors network traffic and detects potential threats across the entire network.
Another difference is the type of data they analyze and the methods they use for detection. HIDS analyzes the behavior and activities of the host, such as log files, system calls, and network traffic, to identify anomalies or suspicious behavior. NIDS, on the other hand, analyzes network traffic and looks for patterns, signatures, or known attack patterns to identify potential threats.
HIDS and NIDS also differ in their response and prevention capabilities. HIDS can take specific actions on the host, such as generating alerts, blocking connections, or implementing access controls, in response to a detected intrusion or attack. NIDS, on the other hand, is primarily focused on detection and monitoring. It can generate alerts and notifications but may rely on other security systems or personnel for response and prevention.
In summary, HIDS and NIDS are two different types of intrusion detection systems that operate at different levels and focus on different aspects of security. HIDS is host-based, focused on monitoring individual systems, and analyzes host behavior, while NIDS is network-based, focused on monitoring network traffic, and analyzes network behavior. Both play important roles in the overall security and protection of a system or network against intrusions and attacks.
Host-based Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS)

Host-based Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS) are security systems that focus on monitoring and detecting suspicious activity on individual computers or hosts within a network. HIDS employ various techniques such as signature-based detection, anomaly detection, and behavior analysis to identify potential intrusions or security breaches.
HIDS work by monitoring the activities and behavior of the host system, including the data being processed and the actions taken by various processes. This approach allows HIDS to detect and prevent both known and unknown threats, including malware infections, unauthorized access attempts, and unusual behavior patterns that may indicate a potential intrusion.
One of the key advantages of HIDS is its ability to provide real-time monitoring and detection capabilities. By continuously analyzing system logs, file integrity, and network traffic, HIDS can quickly identify and respond to security incidents, minimizing the potential impact on the host system and the overall network.
In addition to detection, HIDS also play a crucial role in incident response and prevention. Once an intrusion is detected, HIDS can generate alerts or initiate automated responses to mitigate the impact of the attack. This may involve blocking network connections, isolating compromised hosts, or notifying system administrators for further investigation and remediation.
Overview of HIDS
A Host-based Intrusion Detection System (HIDS) is a security system that is installed on individual hosts or servers within a network to monitor and analyze data traffic. It operates by collecting data from various sources on the host, such as log files, system files, and network traffic, and then analyzing this data for any anomalous behavior or signs of intrusion. HIDS focuses on identifying and alerting the system administrators about any potential security incidents or attacks targeting the host.
HIDS performs real-time monitoring of the host’s activities and compares the observed behavior against known signatures of malicious activity or patterns of abnormal behavior. This allows it to detect and identify various types of intrusions, including malware infections, unauthorized access attempts, and other security threats. HIDS also has the capability to respond to detected incidents by triggering an appropriate response or alerting the system administrators for further investigation and response.
One of the main advantages of HIDS is its ability to analyze the internal activities of a host, including processes, file system changes, and user activities, which can often go undetected by network-based intrusion detection systems (NIDS). HIDS can detect anomalous behavior that may indicate an ongoing intrusion or compromise of a host’s security. It provides an additional layer of defense and complements the network-based intrusion detection and prevention systems.
HIDS leverages various techniques for intrusion detection, including signature-based detection, anomaly detection, and behavior analysis. Signature-based detection relies on a database of known attack signatures and is effective at detecting known threats. Anomaly detection, on the other hand, looks for deviations from normal behavior and can detect previously unknown or zero-day attacks. Behavior analysis involves monitoring patterns of behavior within the host to detect any malicious or suspicious activity.
In conclusion, HIDS plays a critical role in securing a host by monitoring its activities, detecting and identifying intrusions, and triggering appropriate incident response actions. It provides a valuable layer of security against various types of attacks and helps mitigate potential risks to the overall network security.
Advantages of HIDS
A Host-based Intrusion Detection System (HIDS) offers several advantages in the context of incident detection and response.
In-depth system analysis: HIDS provides a detailed analysis of a host system, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of its behavior and identifying any anomalies or suspicious activities.
Identification of known attacks: HIDS uses signature-based detection to identify and respond to known attacks or malware, based on a database of predefined patterns or signatures.
Real-time monitoring: HIDS continuously monitors the host system, providing real-time alerts and notifications when it detects any intrusion attempts or unusual behavior.
Network-independent detection: Unlike Network-based Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS), HIDS operates directly on the host system, making it effective in detecting intrusions even in isolated or disconnected network environments.
Behavior-based detection: HIDS can also employ behavior-based detection techniques to identify abnormal patterns of activities or deviations from normal system behavior, helping to detect zero-day attacks or unknown malware.
Quick response and prevention: With its capability to detect and respond to intrusions in real-time, HIDS allows for swift action to mitigate any potential damages and prevent further compromise of the host system or network.
Protection of sensitive data: By monitoring the activities and data on a host system, HIDS can help identify and protect sensitive information from unauthorized access or exfiltration.
Complementing network security measures: HIDS can be used in conjunction with network-based intrusion detection and prevention systems to provide a layered approach to security, enhancing overall protection against a wide range of threats.
Overall, HIDS offers a proactive approach to intrusion detection, leveraging its ability to analyze system behavior, identify known attacks, and respond in real-time, thereby bolstering the security posture of a host system and the network it is connected to.
Limitations of HIDS
Limited scope: HIDS can only monitor and protect the host on which it is installed. It cannot detect attacks or anomalous behavior on other hosts or network segments. As a result, HIDS cannot provide a comprehensive view of the entire network.
Dependency on host: HIDS is dependent on the host’s resources and capabilities for monitoring and analysis. If the host is compromised or becomes unavailable, the effectiveness of the HIDS is significantly reduced.
No prevention capabilities: HIDS is primarily focused on detection and monitoring, but it lacks the ability to prevent or stop attacks in real time. It can only alert the system administrator or security team about potential incidents.
Signature-based detection limitations: HIDS relies on signature-based detection to identify known malware and attacks. However, it may not be effective against zero-day or previously unknown threats that do not have existing signatures. New and advanced malware can evade detection by HIDS.
Behavior-based detection challenges: HIDS relies on analyzing the behavior of processes and activities on the host to detect anomalies or suspicious behavior. However, it can be challenging to distinguish between normal and abnormal behavior, and false positives and false negatives can occur.
Network-based attacks: HIDS is not optimized for detecting network-based attacks that do not directly target the host. It may not be capable of detecting attacks that bypass the host and directly target other network devices or segments.
Heavy reliance on host resources: HIDS can consume significant system resources, such as CPU and memory, which may impact the performance of the host. The host’s primary functions and tasks may be affected, especially in high-traffic environments.
Lack of network-wide incident response: HIDS cannot provide network-wide incident response capabilities. It can only provide information about incidents occurring on the host it is installed on, limiting its ability to coordinate response actions across the network.
Network-based Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS)

A Network-based Intrusion Detection System (NIDS) is a security system that monitors and analyzes network traffic to identify and respond to potential security breaches and intrusions. Unlike host-based intrusion detection systems (HIDS) that focus on the activity within a specific host or device, NIDS works at the network level, monitoring all incoming and outgoing traffic.
NIDS operates by analyzing network traffic and comparing it against a database of known attack signatures to detect and identify potential threats. This signature-based approach allows NIDS to detect and prevent known types of attacks, such as malware infections and data breaches.
In addition to signature-based detection, NIDS can also analyze network traffic for anomalies or abnormal patterns that may indicate a potential intrusion. This behavior-based detection helps identify new or unknown types of attacks, as well as insider threats and sophisticated attacks that do not have a known signature.
NIDS plays a crucial role in network security by providing real-time monitoring and detection of suspicious activity, allowing for the immediate response and prevention of security incidents. By analyzing network traffic, NIDS can detect and respond to intrusion attempts, unauthorized access attempts, and other potential security breaches.
Furthermore, NIDS enables the collection of network data for forensic analysis, helping security professionals identify the source and nature of an incident. This data can be used to conduct further investigation, enhance incident response, and strengthen overall network security.
In summary, Network-based Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS) are essential components of a comprehensive network security strategy. By monitoring network traffic, analyzing for signature-based and behavior-based anomalies, and providing real-time identification and prevention of intrusions, NIDS helps protect the integrity and confidentiality of network data.
Overview of NIDS
NIDS, or Network-based Intrusion Detection System, is a security solution designed to monitor and detect unauthorized activity on a network. It is specifically focused on the detection of network-based intrusions, such as malware attacks or unauthorized access attempts. NIDS works by analyzing network traffic in real-time and comparing it against known signatures and behavioral patterns of malicious activity.
NIDS operates by passively monitoring network traffic, analyzing packets and looking for patterns or anomalies that may indicate an intrusion. It utilizes signature-based detection, which involves comparing the characteristics of network traffic against a database of known attack signatures. Any matches or suspicious activity are flagged for further investigation or response.
One of the key advantages of NIDS is its ability to detect malicious activity at the network level. This means that it can identify threats and intrusions that may not be apparent on individual host systems. By monitoring the network as a whole, NIDS can provide a broader view of potential security incidents and help to identify and prevent attacks before they can compromise the network.
In addition to monitoring network traffic, NIDS can also collect and analyze data from various sources, such as log files, network devices, and even host systems. This allows for a more comprehensive analysis and detection of intrusions, as it can correlate information from multiple sources and detect patterns that may not be visible from one perspective alone.
Once an intrusion or suspicious activity is detected, NIDS can trigger a response, such as generating an alert or taking automated actions to mitigate the threat. It can also provide valuable information and insights for incident response, helping security professionals to identify the source of the intrusion, assess its impact, and take appropriate actions to contain and remediate the incident.
Advantages of NIDS
NIDS, which stands for Network-based Intrusion Detection System, offers several advantages in terms of monitoring and detecting potential security threats in a network environment.
1. Comprehensive Network Monitoring: NIDS provides a holistic view of the network traffic, allowing for the monitoring and analysis of all incoming and outgoing data packets. This enables the system to detect various types of network-based attacks, including unauthorized access attempts, malware infections, and suspicious behavior.
2. Centralized Incident Identification: With NIDS, incidents are identified and logged in a centralized location, making it easier for security teams to identify and analyze potential threats. This allows for a faster response and minimizes the risk of overlooking critical security incidents.
3. Signature-based Detection: NIDS uses signature-based detection techniques to compare network traffic against known patterns of known attacks. This approach allows for the identification of specific types of attacks, such as known malware or common exploit attempts, based on their unique signatures.
4. Anomaly Behavior Analysis: NIDS can also analyze network traffic for anomalous behavior that may indicate the presence of previously unknown or zero-day attacks. By flagging deviations from normal network behavior, NIDS can help detect and prevent emerging threats that may not have a known signature.
5. Real-time Monitoring: NIDS continuously monitors network traffic in real-time, providing immediate detection and response capabilities. This allows for the timely mitigation of security incidents, minimizing potential damage and preventing further network breaches.
6. Prevention and Response: NIDS not only detects security incidents but also provides options for prevention and response. It can automatically block or filter network traffic associated with detected threats, preventing further intrusion attempts. Additionally, NIDS can generate alerts and notifications to inform security teams about potential incidents, enabling them to take appropriate action.
In conclusion, NIDS plays a crucial role in enhancing network security by providing comprehensive monitoring, detection, and prevention capabilities. Its ability to detect both known and unknown threats, along with real-time monitoring and response, makes it an essential component of a robust network security infrastructure.
Limitations of NIDS
1. Incomplete Network Analysis: Network-based Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS) have limitations in fully capturing and analyzing all network traffic. They may only monitor certain network segments or protocols, leaving other areas vulnerable to potential attacks.
2. Signature-based Detection: NIDS primarily rely on signature-based detection, which means they can only identify known patterns of attacks. New or modified attacks may go undetected if they do not match the existing signature database.
3. Limited Behavior Analysis: NIDS lack the capability to analyze the behavior of individual hosts on the network. They focus on detecting network-level anomalies and may miss host-level incidents and anomalies that could indicate a security breach.
4. Data Encryption: NIDS face challenges in monitoring encrypted network traffic, as they cannot inspect the content of encrypted data packets. This limitation significantly reduces their effectiveness in detecting intrusion attempts within encrypted connections.
5. Response and Prevention: NIDS primarily function as detection systems and have limited capabilities in responding to or preventing attacks. They may alert administrators or initiate predefined actions, but they do not offer proactive incident response capabilities like Host-based Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS) do.
6. False Positives and Negatives: NIDS may generate false positives, triggering alerts for legitimate network activities, or false negatives, failing to detect actual intrusions. This can result in an inefficient allocation of resources and increase the risk of undetected security incidents.
7. Network Load and Scalability: NIDS require continuous monitoring of network traffic, which generates additional network load. This can impact the performance and scalability of the system, especially in high-traffic environments.
8. Intrusion Identification: NIDS can detect intrusion attempts, but they often lack the ability to accurately identify the source and intent of the attacker. This limitation makes it challenging to take appropriate actions to mitigate the security risk effectively.
9. Limited Monitoring Capabilities: NIDS may not be able to monitor all types of network environments, such as wireless networks or virtualized environments. This restricts their effectiveness in providing comprehensive network security coverage.
Overall, while NIDS provide valuable network-level intrusion detection capabilities, these limitations highlight the need for a multi-layered and holistic security approach that combines NIDS with other security measures, such as HIDS and proactive incident response strategies.
Comparison of HIDS and NIDS
Host-based Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS) and Network-based Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS) are two security technologies used for the detection, analysis, and prevention of intrusions or attacks on computer systems and networks. While both systems serve a similar purpose, there are some key differences between them.
HIDS focuses on protecting individual host systems by monitoring and analyzing the activity and behavior of the operating system, applications, and user accounts. It uses various techniques such as log analysis, file integrity checking, and system call monitoring to detect any anomalies or suspicious activities that may indicate an intrusion. HIDS provides a detailed and granular level of security, allowing for the identification of specific incidents and the collection of valuable data for forensic analysis.
NIDS, on the other hand, is a network-centric technology that monitors and analyzes network traffic to detect and identify potential security threats or attacks. It analyzes network packets in real-time, looking for signatures or patterns associated with known attacks or abnormal behavior. NIDS is effective for detecting network-based attacks such as unauthorized access, network scanning, and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks.
One notable difference between HIDS and NIDS is the level of coverage they provide. While HIDS is primarily focused on securing individual host systems, NIDS offers a broader scope by monitoring all network traffic. This allows NIDS to detect attacks that may bypass HIDS, as well as provide early warning of potential threats before they reach the host systems.
Additonally, HIDS operates at the host level, allowing for more detailed monitoring and analysis of system activities, while NIDS operates at the network level, providing a holistic view of the network traffic and enabling detection of attacks that target multiple hosts.
In terms of response and prevention, HIDS is typically better suited for incident response and forensic analysis, where it can provide detailed information about the attack and assist in the recovery process. NIDS, on the other hand, excels in real-time prevention and detection of network-based attacks, allowing for immediate action to be taken to mitigate potential threats.
In conclusion, both HIDS and NIDS play important roles in ensuring the security of computer systems and networks. While HIDS offers detailed host-level monitoring and analysis, NIDS provides a broader network-centric approach to intrusion detection and prevention. A combination of both systems can provide a comprehensive security solution, covering both host and network-based attacks.
Effectiveness in Detecting Attacks
Intrusion detection systems (IDS) play a crucial role in ensuring the security of networks and hosts. They are designed to monitor network or host activity and identify any suspicious or malicious behavior that may indicate an intrusion or attack. The effectiveness of IDS in detecting attacks depends on the type of system used, whether it’s network-based (NIDS) or host-based (HIDS), as well as the methodology employed.
Network-based IDS rely on monitoring network traffic and analyzing it for known attack signatures. These systems are effective in detecting attacks that match predefined signatures, such as known malware or intrusion patterns. However, they may struggle to identify new or unknown attacks that do not have a signature in their database. Network-based IDS are best suited for monitoring large-scale networks where it may be challenging to deploy HIDS on every host.
On the other hand, host-based IDS focus on monitoring the activities and behaviors of individual hosts. They can provide a more detailed and granular level of monitoring compared to network-based IDS. Host-based IDS can detect both known attack signatures and anomalous behavior that deviates from the expected patterns. This makes them more effective at identifying new or unknown attacks, as they do not solely rely on matching signatures. However, deploying and managing HIDS on each host can be more time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Both network-based and host-based IDS have their strengths and weaknesses in terms of effectiveness in detecting attacks. It is often recommended to use a combination of both to maximize the chances of detecting and preventing a wide range of attacks. Additionally, IDS should be complemented with intrusion prevention systems (IPS), which can automatically respond to detected incidents and mitigate the impact of attacks. Regular updates and maintenance of IDS databases and signatures are also crucial to ensure their effectiveness in detecting the latest types of attacks.
Deployment Considerations
When considering the deployment of an intrusion detection system (IDS), various factors need to be taken into account. This includes the choice between a host-based IDS (HIDS) and a network-based IDS (NIDS), as well as the monitoring capabilities, anomaly detection, and response analysis of the system.
In a network-based IDS, the focus is on monitoring network traffic and detecting attacks in real-time. This type of IDS is installed at strategic points within the network infrastructure, allowing it to analyze traffic and identify potential intrusions. It can detect the behavior of various hosts and identify any unusual network activities that may indicate the presence of an intruder or malicious activity.
On the other hand, a host-based IDS is installed directly on individual systems, allowing for a more detailed analysis of system behavior. It examines the activities and processes occurring on a specific host and can detect any abnormal behavior or activity that may indicate the presence of malware or an attack. This type of IDS can also provide incident response capabilities, allowing for the prevention, detection, and response to security incidents.
Both network-based and host-based IDS systems use different methods for intrusion detection. Network-based IDS systems rely on the analysis of network traffic and the use of signatures to identify known attack patterns. Host-based IDS systems, on the other hand, focus on the analysis of system logs, file integrity checking, and the identification of anomalous system behavior.
When deploying an IDS, it is crucial to consider the specific needs and requirements of the organization. Factors such as network architecture, the number of hosts, the sensitivity of data, and the types of threats expected should be taken into account. Additionally, the system should be regularly updated with the latest threat intelligence and signature databases to ensure the detection of new and emerging threats.
In conclusion, the deployment of an intrusion detection system requires careful consideration of the type of IDS to be used, the monitoring capabilities, anomaly detection, and response analysis. Whether choosing a network-based or host-based IDS, organizations need to evaluate their specific needs and ensure that the system is regularly updated to effectively identify and respond to intrusions and security incidents.
Cost and Scalability
When evaluating intrusion detection systems (IDS), cost and scalability are important factors to consider. Both host-based and network-based IDS have different cost structures and scalability capabilities.
A host-based IDS (HIDS) requires individual software installations on each host within a system. The cost of purchasing and installing the HIDS software on multiple hosts can be high, especially for large networks. Additionally, maintaining and updating the software on each host can add to the cost. However, HIDS can be more scalable compared to network-based IDS (NIDS) as it allows for detailed analysis of behavior and activity on each host.
On the other hand, a network-based IDS (NIDS) is placed at specific points within a network to monitor and analyze network traffic. The cost of implementing and maintaining NIDS hardware and software across a network can be significant. However, NIDS is generally more scalable compared to HIDS as it can cover a larger network area with a single installation.
In terms of analysis capabilities, HIDS has the advantage of conducting in-depth analysis of host behavior and detecting anomalies specific to each host. It can detect and analyze potentially malicious activities such as malware infections or unauthorized access attempts. NIDS, on the other hand, focuses on analyzing network traffic to identify known signatures of attacks. It is effective in detecting network-based attacks but may struggle with identifying new or unknown threats.
From a cost perspective, HIDS may be more cost-effective for smaller networks where the number of hosts is limited. However, as the network grows, the cost of maintaining and updating HIDS software on each host can increase significantly. NIDS, on the other hand, can provide cost savings for larger networks by covering multiple hosts with a single installation.
In terms of scalability, NIDS has an advantage as it can monitor network traffic across multiple hosts and can be easily expanded to cover larger networks. HIDS, while providing detailed host data, may require additional installations and configurations as the network expands, making it less scalable in comparison.
In conclusion, when considering the cost and scalability of intrusion detection systems, the specific needs and size of the network should be taken into account. While HIDS provides detailed host analysis, it may be more costly and less scalable for larger networks. NIDS, on the other hand, can cover a larger network area with a single installation but may have limitations in detecting new or unknown threats.
FAQ about topic “HIDS vs NIDS: A Comparison of Host-based and Network-based Intrusion Detection Systems”
What is the difference between HIDS and NIDS?
HIDS (Host-based Intrusion Detection System) and NIDS (Network-based Intrusion Detection System) are two different types of intrusion detection systems. HIDS monitors and analyzes activities on a single host or endpoint, while NIDS monitors network traffic and analyzes data packets to detect possible intrusions. HIDS focuses on the activities happening directly on the host, while NIDS provides a broader view of the network as a whole.
Which type of IDS is more effective?
The effectiveness of an IDS depends on the specific use case and the organization’s needs. HIDS can detect attacks targeting a specific host, such as malware infections or unauthorized access attempts. NIDS, on the other hand, is better suited for detecting network-wide attacks, such as DDoS or port scanning. Both types of IDS have their advantages and limitations, so it’s important to choose the one that best meets the requirements of the organization.
Can HIDS and NIDS be used together?
Yes, it is possible to use HIDS and NIDS together to provide a more comprehensive intrusion detection solution. By combining the two, organizations can have a layered approach to security, where HIDS can monitor the activities happening on individual hosts, while NIDS can analyze network traffic for signs of intrusion. This combination allows for a more holistic view of the security landscape and can enhance the overall effectiveness of the intrusion detection system.
Are HIDS and NIDS suitable for all types of organizations?
HIDS and NIDS can be implemented in various types of organizations, but their suitability may vary depending on the specific requirements and resources of the organization. For smaller organizations with limited resources, HIDS may be a more cost-effective solution as it focuses on monitoring activities within a single host. On the other hand, larger organizations with complex network infrastructures may benefit more from NIDS, which provides a broader scope of monitoring. Ultimately, the decision to implement HIDS, NIDS, or both depends on the specific needs and capabilities of the organization.
What are some common challenges in implementing HIDS and NIDS?
Implementing HIDS and NIDS can come with its challenges. One challenge is the initial setup and configuration of the systems. Both HIDS and NIDS require careful setup and tuning to ensure they have proper access to the necessary resources and can accurately detect intrusions without generating excessive false positives. Another challenge is the ongoing maintenance and monitoring of the systems. Regular updates and patches are necessary to keep the IDS up to date and effective. Additionally, monitoring and analyzing the vast amount of data generated by the IDS can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. Organizations need to have dedicated personnel and the necessary infrastructure to manage and make use of the data collected by the IDS.


