
If you’re a Mac user, you may already be familiar with the Finder app, which allows you to easily navigate through files and folders on your computer. However, sometimes you may find it more convenient to use the Terminal app, also known as the shell, to navigate your computer’s directory structure.
The Terminal app lets you open a command line interface where you can enter commands to manipulate files and directories on your Mac. It provides a powerful way to explore, view, and change the directory structure on your computer.
Changing directories in the Terminal is a fundamental skill that every Mac user should learn. By using the “cd” command, you can easily switch to different directories, move up and down the directory tree, and show a list of files and folders in the current directory.
In this step-by-step guide, we’ll show you how to change directories in the Mac Terminal. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced user, this guide will help you master the art of navigating your computer’s directory structure using the Terminal app.
Contents
- 1 Understanding the macOS Terminal
- 2 Opening Terminal on your Mac
- 3 Command to Change Directory
- 4 Additional Tips and Tricks
- 5 FAQ about topic “How to Change Directory in Mac Terminal: Step-by-Step Guide”
- 6 What is the Mac Terminal?
- 7 Why would I need to change directories in the Mac Terminal?
- 8 How do I view the current directory in the Mac Terminal?
- 9 How can I change to a specific directory in the Mac Terminal?
- 10 Can I navigate to a directory using its relative path?
Understanding the macOS Terminal
The macOS Terminal is a powerful tool that allows users to interact with their computer using command line interface. It provides a text-based interface for executing commands and performing various tasks. Unlike the graphical user interface provided by the Finder, the Terminal allows users to navigate the file system using commands and paths.
When you open the Terminal on your Mac, you will see a command prompt where you can type commands. The Terminal acts as a shell, which is the interface between the user and the operating system. It provides a way to interact with the underlying system and perform tasks that may not be possible or efficient with a graphical interface.
By using commands, you can navigate through folders, view files, open applications, and perform other tasks. The Terminal uses a hierarchical file system, where each folder is represented by a path. A path is a string of characters that specifies the location of a folder or file in the file system. You can use commands to switch between folders, explore their contents, and perform operations on files and folders.
One of the most common commands used in the Terminal is the “cd” command, which stands for “change directory”. This command allows you to navigate to a different folder in the file system. By specifying the path of the folder you want to switch to, you can easily move between directories.
The Terminal also provides various other commands that allow you to perform tasks such as listing the contents of a directory, creating or deleting folders, moving or copying files, and executing programs. These commands can be combined and used in different ways to accomplish specific tasks.
Overall, the macOS Terminal provides a powerful and flexible environment for users to interact with their Mac. It allows you to navigate the file system, execute commands, and perform various tasks efficiently. By learning how to use the Terminal, you can unlock a wide range of capabilities and enhance your overall experience with your Mac.
What is macOS Terminal?
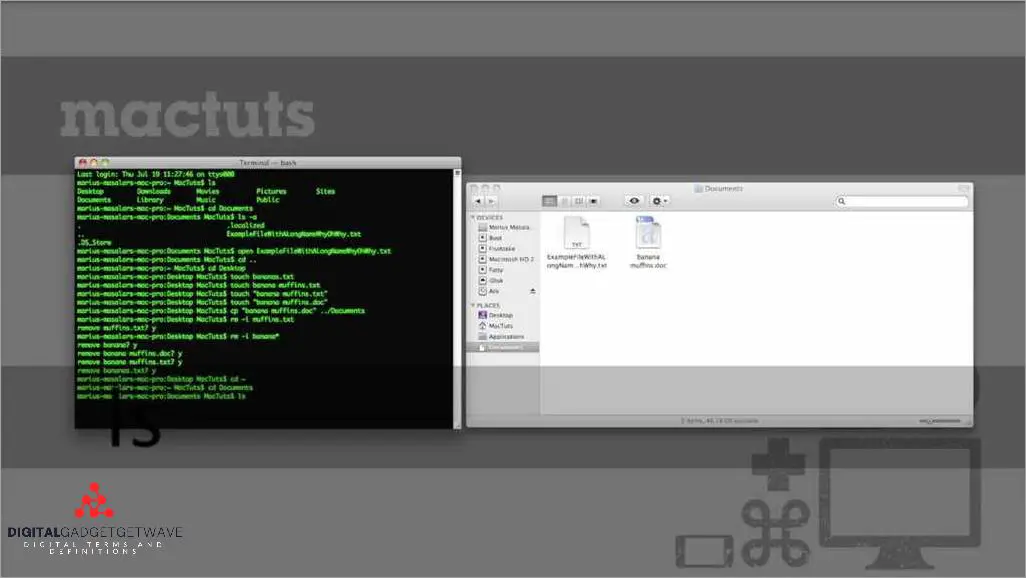
macOS Terminal is a command-line interface (CLI) application for the Mac operating system. It provides a text-based environment in which users can navigate through directories, open files, run commands, and perform various tasks using text commands.
The Terminal allows users to interact with their Mac using a shell, which is a program that interprets and executes commands entered by the user. The default shell on macOS is called Bash, but other shells like Zsh can also be used.
With macOS Terminal, users can navigate through the file system by using commands to switch directories, view and list files and folders, create, delete, and modify files, and perform other file operations. The Terminal provides a powerful and efficient way to explore and manage files and directories on a Mac.
Unlike the graphical user interface (GUI) of the Finder, which provides a visual representation of files and folders, the Terminal allows users to directly interact with the underlying file system by typing commands. This can be especially useful for users who prefer a text-based interface or need to perform complex tasks efficiently.
In summary, macOS Terminal is a versatile tool for navigating, exploring, and managing files and directories on a Mac. By providing a command-line interface, it allows users to perform various tasks using text commands, providing a powerful alternative to using the Finder.
Why Should You Use Terminal?
Mac users often rely on Finder to navigate and manage their files and folders. However, there are situations where using the Terminal can be more efficient and powerful.
1. Command-line control: The Terminal allows you to perform a wide range of tasks and operations using commands. You can view, edit, and manipulate files and directories without relying on a graphical user interface.
2. Efficient navigation: With the Terminal, you can quickly switch between directories and navigate through the file system using command-line shortcuts. This can be especially helpful when dealing with deeply nested folders or when you need to access hidden files.
3. Advanced file operations: The Terminal provides a variety of commands that allow you to perform advanced file operations. You can easily move, copy, rename, and delete files and folders using simple commands.
4. Scripting and automation: The Terminal enables you to write shell scripts and automate repetitive tasks. You can create powerful scripts that perform complex operations, saving you time and effort.
5. Real-time feedback: When using the Terminal, you get immediate feedback on your commands. This can be helpful for troubleshooting and debugging, as the Terminal shows you the output and error messages in real time.
6. Access to system settings: The Terminal allows you to access and modify various system settings and preferences that are not easily accessible through other means. This gives you more control over your Mac and allows you to customize your environment.
Overall, using the Terminal provides a more flexible and powerful way to interact with your Mac. It gives you the ability to explore and manipulate your files and folders in ways that may not be possible using the Finder alone. Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced user, learning how to use the Terminal can greatly enhance your Mac experience.
Opening Terminal on your Mac

The Terminal is a powerful tool that allows you to interact with your Mac’s operating system using text commands. To open the Terminal, you have a few options:
From the Dock: The Terminal can be found in the Utilities folder in your Mac’s Applications folder. To open it from the Dock, click the Finder icon, navigate to Applications, then to Utilities, and finally click on Terminal.
Using Spotlight: If you prefer a quicker method, you can use Spotlight to search for the Terminal. Simply press Command + Space to open Spotlight, type “Terminal” into the search bar, and press Enter to open it.
Using Finder: Another option is to open the Terminal from the Finder. Open a Finder window, navigate to Applications, then to Utilities, and double-click on Terminal.
Using a Shortcut: If you frequently use the Terminal, you can create a shortcut to open it. Right-click on the Terminal icon in the Utilities folder, click on “Make Alias,” and then drag the alias to your desktop or another convenient location.
Once you have opened the Terminal, a command line interface will appear, allowing you to start navigating your Mac’s filesystem. If you are familiar with the Finder, think of the Terminal as a way to explore your Mac using text commands instead of visual navigation.
The Terminal is like a virtual shell that allows you to interact with your Mac’s operating system. It provides a way to change directories, execute commands, view and manipulate files, and perform a wide range of tasks.
Using Finder
To navigate and explore directories and folders on a Mac, you can use Finder, the default file manager. With Finder, you can easily move, open, and close directories and folders, making it a convenient tool for managing your files.
Here are some actions you can perform using Finder:
- Switch directories: To switch to a different directory, simply click on it in the Finder window. This will change the current directory you are viewing and allow you to explore its contents.
- View and explore folders: You can open folders in Finder by double-clicking on them. This will show you the files and subfolders within the selected folder, allowing you to navigate and access their contents.
- List directory contents: To see a list of files and folders within a directory, you can select the directory in Finder and press the “Command” and “2” keys on your keyboard. This will change the view to list mode, displaying a detailed list of the directory’s contents.
- Show directory path: To display the path of the current directory you are viewing, you can select the directory in Finder and press the “Command” and “P” keys on your keyboard. This will show you the full path of the selected directory in a small drop-down window.
Using Finder, you can easily navigate and manage your directories and folders on a Mac. It provides a user-friendly interface and various tools for efficient file management. Whether you need to switch directories, explore folder contents, or list directory contents, Finder offers a convenient way to work with your files.
Command to Change Directory
The command to change directory, or simply navigate through folders, in a Mac Terminal is a very useful and essential tool for many Mac users. With this command, you can easily switch between different directories or folders without having to open the Finder or explore the directories in the graphical user interface.
To change directory in Mac Terminal, you can use the command cd, which stands for “change directory”. This command is followed by the path of the directory you want to navigate to. The path can be either an absolute path or a relative path.
An absolute path is the complete and exact location of the directory or folder on your Mac. It includes the root directory, all the parent directories, and the directory you want to navigate to. For example, the absolute path of a directory named “Documents” located in the user’s home directory is /Users/username/Documents.
A relative path, on the other hand, is the location of the directory or folder relative to your current directory. For example, if you are currently in the “Documents” directory and you want to navigate to a directory named “Downloads”, you can simply use the command cd Downloads.
It is important to note that the directory you want to navigate to must exist in order for the command to work successfully. If the directory does not exist, the command will result in an error message.
The cd command is a powerful tool that allows you to quickly and efficiently move through directories and folders in the Mac Terminal. Whether you need to view, list, or change directories, this command is a fundamental part of navigating the file system in the Terminal shell.
In conclusion, the cd command in the Mac Terminal is the command used to change directory or navigate through folders. By using this command, you can easily switch between different directories and folders without having to open the Finder or explore the directories in the graphical user interface. Whether you want to view, list, or change directories, the cd command is an essential tool for any Mac user who works with the Terminal.
Basic Command
When using a Mac terminal, there are several basic commands that you need to know in order to navigate, explore, and move around the directory system.
Show Current Directory
To view your current directory in the Mac terminal, you can use the pwd command. This command will display the full path to the current directory.
List Files and Folders
If you want to see a list of files and folders in your current directory, you can use the ls command. This command will display all the files and folders in the current directory.
Change Directory
To switch to a different directory, you can use the cd command followed by the path of the folder you want to navigate to. For example, cd Documents would take you to the “Documents” folder.
Close Finder Windows
If you want to close all Finder windows, you can use the killall Finder command. This command will close all open Finder windows.
View Hidden Files
To view hidden files in the Finder, you can use the defaults write com.apple.finder AppleShowAllFiles TRUE command. After running this command, you need to relaunch the Finder for the changes to take effect.
Navigate to Home Directory
If you want to quickly navigate to your home directory, you can use the cd command followed by the tilde symbol (~). For example, cd ~ will take you to your home directory.
Create a New Directory
To create a new directory in the current directory, you can use the mkdir command followed by the desired name of the new directory. For example, mkdir NewFolder will create a new folder named “NewFolder”.
Remove a Directory
If you want to remove a directory and all its contents, you can use the rm -r command followed by the name of the directory. For example, rm -r OldFolder will remove the “OldFolder” directory and all its contents.
Advanced Command
The Mac Terminal offers a range of advanced commands that can greatly enhance your navigation and file management capabilities. These commands allow you to perform more complex tasks and manipulate your files and folders with greater precision.
1. Finder Command: The “finder” command is a powerful tool that enables you to open a new Finder window directly from the Terminal. This command is particularly useful when you need to quickly navigate to a specific folder or file in the Finder.
2. Move Command: The “move” command allows you to move files or folders from one location to another. This command is especially useful when you need to organize your files and folders by transferring them to different directories.
3. Switch Command: The “switch” command enables you to switch between different open Finder windows. This command is handy when you have multiple Finder windows open and want to quickly move between them without having to close and reopen each window.
4. Change Directory Command: The “cd” command is an essential command for navigating through directories in the Terminal. With this command, you can easily change your current directory to another directory and work with files and folders within that directory.
5. Show Hidden Files Command: The “defaults write com.apple.finder AppleShowAllFiles true” command allows you to show hidden files in the Finder. This command is helpful when you need to access and work with hidden files that are not visible by default.
6. Explore Command: The “open” command allows you to open a file or folder in its associated application. This command is useful when you want to quickly view or edit a file without navigating through the Finder manually.
7. List Command: The “ls” command is used to list the contents of a directory. It displays the files and folders within the current directory, allowing you to easily view the files and folders present in a directory without having to open the Finder.
8. View Directory Command: The “ls -l” command is an extended version of the “ls” command that displays additional information about the files and folders in a directory. It provides a detailed view of the directory, including file size, permissions, and modification dates.
These advanced commands can greatly enhance your efficiency and productivity when working with files and folders in the Mac Terminal. By utilizing these commands, you can easily navigate, explore, and manage your directories without relying solely on the graphical interface of the Finder.
Additional Tips and Tricks
If you’re used to navigating through Finder to switch directories, you might find it helpful to know that the Terminal provides an alternative way to do this using the command line. This can be especially useful if you prefer working with the command line or if you need to perform specific actions that are not easily accomplished through the graphical user interface of Finder.
To view the current directory in the Terminal, you can use the “pwd” command followed by pressing enter. This will display the full path of the current directory you are in. You can also use the “ls” command to show the contents of the current directory in a list format.
If you want to move to a different directory in the Terminal, you can use the “cd” command followed by the path of the directory you want to change to. You can specify a full path or a relative path depending on your needs. For example, to change to a directory named “Documents” in your home directory, you can use the command “cd ~/Documents/”.
If you want to explore the contents of a directory without actually changing to it, you can use the “ls” command followed by the path of the directory. This will list the contents of the specified directory without changing your current directory.
If you find it cumbersome to type out long directory paths, you can use the “tab” key to autocomplete directory and file names. Simply type the first few letters of the directory or file name and then press the “tab” key to have the Terminal automatically complete the rest. This can save time and reduce the likelihood of making mistakes.
To quickly switch back to the previous directory you were in, you can use the “cd -” command. This will move you back to the previous directory you were in, allowing for quick navigation between different directories.
If you want to close the Terminal window without exiting the Shell, you can use the “exit” command. This will close the Terminal window but keep the Shell session running in the background.
By using these additional tips and tricks, you can enhance your navigation and efficiency when working with directories in the Mac Terminal.
Viewing Current Directory
In order to view the current directory, you can use different commands in the Mac Terminal. These commands allow you to list and show the contents of the current directory, move between directories, close and open directories, and navigate through the file system.
One way to view the current directory is by using the ls command. This command lists all the files and folders in the current directory, displaying their names and other information such as permissions, ownership, and size. It provides a quick overview of the files and folders in the current directory.
Another way to view the current directory is by using the pwd command. This command displays the path of the current directory, allowing you to see the exact location of the directory within the file system. It shows the complete path from the root directory to the current directory.
If you want to explore the current directory further, you can use the cd command to change your directory to a different location. By typing cd folder_name, you can switch to a specific folder within the current directory. This allows you to navigate through the file system and explore different folders.
In addition to the Terminal, you can also view the current directory using the Finder on your Mac. The Finder provides a graphical interface for navigating and exploring the file system. You can open the Finder and click on the current directory in the navigation pane to view its contents.
Overall, there are multiple methods for viewing the current directory in the Mac Terminal, ranging from command-line navigation to graphical exploration. Whether you prefer the shell or the Finder, you can easily access and explore the files and folders within the current directory.
Tab Completion
Tab completion is a useful feature in the Mac Terminal that allows you to quickly navigate and explore your directory structure. It makes it easy to move between folders and execute commands without having to type out the full path or command.
When you start typing a command or directory name in the Terminal, you can press the Tab key to auto-complete the rest of the name. If there are multiple options that match what you’ve typed, pressing Tab will show a list of all possible matches. This saves time and reduces the chances of making typos.
Tab completion works not only for directory and file names, but also for commands and options. For example, if you want to use the “ls” command to list the contents of a directory, you can type “ls” and then press Tab to see a list of available options. This can help you remember all the available options and their syntax.
In addition to auto-completing names, Tab completion can also be used to quickly navigate through directories. If you want to change to a different directory, you can type part of the path and then press Tab to complete it. If there are multiple directories that match what you’ve typed, pressing Tab again will show a list of all possible matches.
Overall, Tab completion is a powerful tool that makes it easier and faster to navigate and work with directories in the Mac Terminal. Whether you’re opening files, executing commands, or exploring your file system, Tab completion can greatly improve your workflow and productivity. Give it a try and see how it can simplify your Terminal experience.
Using Shortcuts
When working in the Mac Terminal, there are several shortcuts that can make the process of switching and changing directories faster and more efficient.
One of the most common shortcuts is to use the “cd” command followed by the directory path to open a specific directory. For example, to navigate to the “Documents” folder, you can type “cd Documents” and press enter. This will change the current directory to the “Documents” folder.
Another useful shortcut is the “cd ~” command, which takes you to the home directory. This can be helpful when you want to quickly go back to the main directory.
If you want to view the list of files and folders within a directory without actually changing into it, you can use the “ls” command. For example, typing “ls Documents” will show you the contents of the “Documents” folder without actually opening it.
If you want to switch to a previous directory, you can use the “cd -” command. This is useful when you want to quickly move back and forth between two directories.
When exploring a directory, you can also use the “open” command to open a file or folder in the Finder. For example, typing “open index.html” will open the file “index.html” in the default browser.
In addition to these shortcuts, you can also use the arrow keys to navigate through your command history. This can be useful when you want to quickly repeat a command without typing it out again.
Overall, using shortcuts in the Mac Terminal can greatly improve your navigation and productivity. By learning and utilizing these shortcuts, you can quickly and efficiently switch, change, and explore directories in the Terminal.
FAQ about topic “How to Change Directory in Mac Terminal: Step-by-Step Guide”
What is the Mac Terminal?
The Mac Terminal is a command-line interface program that allows users to interact with the operating system using text commands.
Why would I need to change directories in the Mac Terminal?
You may need to change directories in the Mac Terminal to navigate to different folders or directories on your computer’s file system. This can be useful for accessing files, running scripts, or executing commands in specific locations.
How do I view the current directory in the Mac Terminal?
To view the current directory in the Mac Terminal, you can use the “pwd” command. Simply type “pwd” and press enter, and the Terminal will display the full path of the current directory.
How can I change to a specific directory in the Mac Terminal?
To change to a specific directory in the Mac Terminal, you can use the “cd” command followed by the directory path. For example, if you want to change to a directory called “Documents” located in your home directory, you can type “cd Documents” and press enter.
Yes, you can navigate to a directory using its relative path in the Mac Terminal. A relative path is a path that is relative to the current directory. For example, if you are currently in the “Documents” directory and you want to navigate to a subdirectory called “Images” that is located within the “Documents” directory, you can type “cd Images” and press enter.


