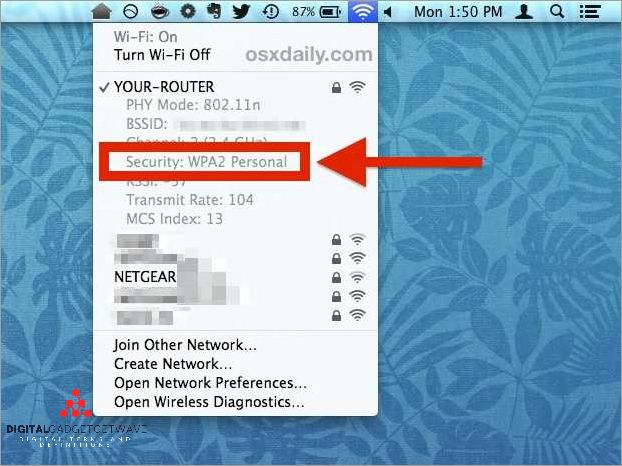
When setting up a WiFi network, ensuring its security should be a top priority. Understanding the security type of your WiFi network is essential to protect your personal information, data, and privacy from potential hacking and unauthorized access. WiFi security refers to the measures put in place to safeguard the wireless network from vulnerabilities and cyber threats. It involves setting up a password, encryption, and authentication protocols to secure the network.
The first step in determining the security type of your WiFi network is to identify the SSID, which stands for Service Set Identifier. SSID is the name of your WiFi network and is used to distinguish it from others in the surrounding area. Router manufacturers typically assign a default SSID, but it is recommended to change it to something unique and not easily guessed to enhance security.
Next, you need to check the type of encryption and authentication protocols used by your WiFi network. The most common encryption protocols include Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP), Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA), and WPA2. WEP is the least secure as it can easily be cracked, whereas WPA2 provides a higher level of encryption and protection against hacking attempts.
In addition to encryption, authentication protocols play a vital role in WiFi security. The authentication process verifies the identity of the users trying to access the network. Open authentication allows anyone to connect without entering a password, while shared key authentication requires a password to gain access. It is recommended to use WPA2 with a strong password as it offers the highest level of protection.
Furthermore, implementing a firewall on your router can add an extra layer of security. A firewall acts as a barrier between your WiFi network and the internet, monitoring and filtering incoming and outgoing traffic to prevent unauthorized access. Configuring a firewall correctly and keeping it up to date can significantly enhance the security of your WiFi network.
In conclusion, understanding the security type of your WiFi network is crucial for protecting your privacy and data. By identifying the SSID, encryption protocols, authentication methods, and implementing additional security measures such as firewalls, you can ensure that your wireless network is secure from potential vulnerabilities and hacking attempts. Investing in cybersecurity measures is essential in today’s connected world to maintain the integrity and confidentiality of your online activities.
Contents
- 1 Section 1: Understanding WiFi Security
- 2 Section 2: Identifying Your WiFi Security Type
- 3 Section 3: How to Secure Your WiFi Network
- 4 Section 4: Additional Tips for WiFi Security
- 5 FAQ about topic “How to Determine the Security Type of Your WiFi Network”
- 6 How can I check the security type of my WiFi network?
- 7 What is the recommended security type for a WiFi network?
- 8 Can I change the security type of my WiFi network?
- 9 What are the disadvantages of using WEP security?
- 10 What should I do if my router only supports WEP security?
Section 1: Understanding WiFi Security
WiFi security is an essential aspect of protecting your network from unauthorized access and potential hacking. It involves implementing measures to secure the wireless router and the data transmitted over the network. Understanding WiFi security types and their vulnerabilities is crucial for maintaining a secure network.
One common WiFi security type is WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy), which uses a password to authenticate access to the network. However, WEP has several vulnerabilities that make it relatively easy for attackers to crack the password and gain unauthorized access to the network.
Another popular WiFi security type is WPA (WiFi Protected Access), which provides better protection through improved encryption. WPA replaces the weak encryption of WEP with stronger encryption algorithms to secure the data transmitted over the network. This enhances the security of the WiFi network and reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
Authentication is another crucial aspect of WiFi security. It involves verifying the identity of devices attempting to connect to the wireless network. By implementing strong authentication protocols, such as using a unique password and enabling two-factor authentication, you can ensure that only authorized devices can access your network.
Firewalls are also instrumental in WiFi security, as they act as a barrier between the internal network and the external world. They monitor and control the traffic flow and protect against potential security threats. Configuring a firewall on your wireless router adds an extra layer of protection to your network.
It is essential to regularly update your router firmware and configure security settings to ensure the highest level of protection. Additionally, it is recommended to change the default SSID (Service Set Identifier), which is the name of your wireless network, as it can provide valuable information to potential attackers.
In summary, WiFi security is vital for safeguarding your network from cybersecurity threats. Understanding the different security types, such as WEP and WPA, and implementing strong authentication protocols, firewalls, and regular updates can significantly enhance the security and privacy of your wireless network.
The Importance of WiFi Security
WiFi security is of utmost importance in today’s digital age. With the increasing use of wireless networks, it is crucial to ensure that your WiFi network is properly secured to protect against cyber threats and unauthorized access.
Your WiFi network security type determines the level of protection it offers. The security measures implemented on your router help to safeguard your network from potential attacks and vulnerabilities.
Authentication and encryption are two key aspects of WiFi security. Proper authentication ensures that only authorized users can access the network, while encryption protects the data transmitted over the wireless network from being intercepted or tampered with.
Without proper security measures in place, your WiFi network becomes vulnerable to hacking attempts. Attackers can exploit weaknesses in your network’s security protocols, gaining unauthorized access to your personal information, passwords, and sensitive data.
By setting up a strong and unique password for your WiFi network, you add an extra layer of protection. A complex password makes it difficult for hackers to guess or crack it, reducing the chances of unauthorized access.
Along with password protection, enabling additional security features such as a firewall can further enhance the security of your WiFi network. A firewall acts as a barrier between your network and potential threats, filtering out malicious traffic and protecting your devices from unauthorized access.
Choosing the right security type for your WiFi network is essential. The widely recommended security type is WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) as it provides a higher level of security compared to older protocols like WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy).
Regularly updating your router firmware and keeping your devices up-to-date with the latest security patches is also crucial for maintaining the security of your WiFi network. This helps to prevent vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit.
Protecting the privacy of your WiFi network is vital for ensuring the security of your personal and confidential information. Securing your network by enabling the appropriate security measures, changing default settings, hiding your SSID (Service Set Identifier), and monitoring connected devices can help maintain the privacy and integrity of your WiFi network.
In conclusion, WiFi security plays a crucial role in safeguarding your network and protecting your data from potential threats. It is essential to understand the different security measures available and implement them effectively to ensure the highest level of protection for your wireless network.
Common WiFi Security Types
WiFi networks use different security protocols to protect the data transmitted over the network and ensure the privacy and security of users.
1. WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy): WEP is the oldest and most basic type of security protocol. It uses a shared key authentication and RC4 encryption. However, it is highly vulnerable to hacking and should not be used for secure networks.
2. WPA (WiFi Protected Access): WPA is an improvement over WEP and offers better security. It uses Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) or Counter Mode Cipher Block Chaining Message Authentication Code Protocol (CCMP) for encryption. WPA also supports a variety of authentication methods.
3. WPA2 (WiFi Protected Access 2): WPA2 is the most commonly used WiFi security protocol today. It provides stronger encryption and better security compared to WEP and WPA. WPA2 uses Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) and supports enterprise-level authentication methods.
4. WPA3 (WiFi Protected Access 3): WPA3 is the newest and most secure WiFi security protocol. It enhances the security features of WPA2 and introduces new encryption capabilities. WPA3 also improves the authentication process and provides enhanced security for open networks.
5. Open Network: An open network does not have any security type enabled. This means anyone can connect to the network without a password. It is highly recommended to enable encryption and password protection to secure your network and prevent unauthorized access.
It is important to choose the appropriate security type for your WiFi network to protect your data and maintain cybersecurity. Remember to regularly update your router firmware and use strong, unique passwords to further enhance the security of your wireless network.
Why Knowing Your WiFi Security Type Matters
Understanding your WiFi security type is crucial for ensuring the protection and privacy of your wireless network. By knowing the security type, you can take appropriate measures to safeguard your network from potential vulnerabilities and hacking attempts.
The security type of your WiFi network determines the level of authentication and encryption used to secure the data transmitted over the network. It is essential to choose a strong security type to prevent unauthorized access to your network and protect your personal information from being intercepted.
WiFi security types include WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy), WPA (WiFi Protected Access), and WPA2 (WiFi Protected Access 2). WEP is the oldest and least secure type, using a static password for authentication. It is susceptible to hacking and should be avoided.
WPA and WPA2 are more advanced security types that use stronger encryption algorithms and regularly change the encryption keys to enhance the security of your network. They offer a higher level of protection against potential security threats and should be preferred over WEP.
Knowing your WiFi security type also allows you to configure your router’s firewall settings appropriately. A firewall acts as a barrier between your network and the internet, monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic. Proper configuration of the firewall can help prevent unauthorized access and protect your network from malicious activities.
Additionally, if you are connecting to a public WiFi network, such as in a coffee shop or airport, knowing the security type can help you make an informed decision about whether to connect or not. Public WiFi networks may have weaker security measures in place, making them more vulnerable to hacking and unauthorized access. Understanding the security type can help you assess the level of risk and take precautions to protect your personal information.
In conclusion, knowing your WiFi security type is essential for ensuring the privacy and protection of your network. By choosing a strong security type, configuring your router’s firewall, and being aware of the security vulnerabilities associated with public WiFi networks, you can stay one step ahead of potential cybersecurity threats and keep your network safe.
Section 2: Identifying Your WiFi Security Type
When it comes to protecting your wireless network, it is crucial to understand the different types of security protocols available. By identifying the security type of your WiFi network, you can assess its vulnerability to potential cyber threats and take appropriate measures to enhance its protection.
The security type of a WiFi network is determined by the authentication protocol it uses. The most commonly used protocols are WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy), WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access), and WPA2. Each protocol provides a different level of security and encryption to safeguard your network.
The first step to identifying your WiFi security type is to access your router’s settings. You can do this by typing the router’s IP address in your web browser and entering the login credentials. Once you are logged in, navigate to the wireless settings page, which will display the security type and its associated settings.
The security type is often indicated by the SSID (Service Set Identifier) name and the password used to access the network. If your network uses a WEP security type, it is highly recommended to upgrade to a more secure protocol like WPA or WPA2. WEP is known to have significant vulnerabilities that can be exploited by attackers.
WPA provides a higher level of security than WEP by using a stronger encryption algorithm. It is a widely adopted security standard that offers a good balance between security and compatibility. If your network uses WPA, it is important to regularly update your password and enable additional security features such as a firewall to enhance the overall protection.
WPA2 is currently the most secure wireless security protocol available. It provides advanced encryption and authentication methods, making it highly resistant to hacking attempts. If your network is secured with WPA2, you can be confident in its security level, but it is still advisable to update your password and regularly review your network’s settings to minimize any potential vulnerabilities.
In summary, identifying the security type of your WiFi network is essential for ensuring its protection against potential cyber threats. By understanding the different protocols and their associated vulnerabilities, you can implement the necessary security measures to safeguard your network and maintain your privacy in the digital world.
Checking your Router’s Security Settings
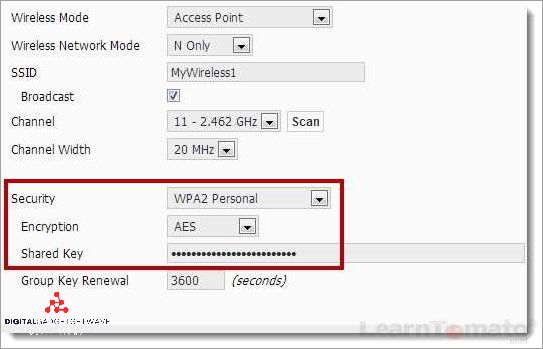
Ensuring the security of your wireless network is essential to prevent unauthorized access and hacking attempts. One of the first steps in securing your network is to check your router’s security settings. Here are some important aspects to consider:
- Password: The password for your router’s admin interface should be strong and unique. Avoid using common passwords and change it regularly to minimize the risk of unauthorized access.
- SSID: The Service Set Identifier (SSID) is the name of your network. It is recommended to change the default SSID to something unique and not easily guessable.
- Network Encryption: Use a strong encryption protocol, such as WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2), to ensure that the data transmitted over your wireless network is protected from eavesdropping and unauthorized access.
- Firewall: Enable the built-in firewall on your router to prevent unauthorized access to your network. A firewall acts as a barrier between your network and the internet, filtering incoming and outgoing traffic.
- Privacy Settings: Disable features like remote management and guest networks if you don’t need them. These features can potentially introduce vulnerabilities to your network.
- Access Control and Authentication: Consider implementing MAC (Media Access Control) address filtering and enable authentication for devices connecting to your network. This adds an extra layer of protection by allowing only authorized devices to connect.
Regularly checking and updating your router’s security settings is crucial to ensure the safety of your wireless network. By following these recommendations, you can enhance the security and protect your network from potential cybersecurity threats.
Using Network Analyzer Tools
Network analyzer tools are essential for determining the security type of your WiFi network. These tools examine the network traffic and provide valuable insights into the security protocols and vulnerabilities present in your wireless network.
One important aspect of network analyzer tools is their ability to detect the encryption protocols used in your network. They can analyze the packets exchanged between devices and identify whether the network is using WEP or WPA/WPA2 encryption. This information is crucial as it determines the level of protection and privacy your network offers.
In addition to encryption protocols, network analyzer tools can also assess the strength of your WiFi password. They can check if the password is using a combination of characters, numbers, and symbols, ensuring that it is not easily guessable. By evaluating the strength of your password, you can enhance the security of your network and reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
Cybersecurity is another aspect that network analyzer tools can address. They can detect any potential vulnerabilities in your network, such as open ports, weak firewall settings, or outdated firmware. By identifying these vulnerabilities, you can take the necessary steps to strengthen the security of your network and protect it from hacking attempts.
Authentication protocols are also examined by network analyzer tools. They can determine whether your network is using WPA-PSK (Pre-Shared Key) or WPA-Enterprise authentication. WPA-Enterprise offers a higher level of security as it utilizes individual usernames and passwords for authentication, making it more resistant to unauthorized access.
Furthermore, network analyzer tools can help identify the SSID (Service Set Identifier) broadcasted by your WiFi network. By revealing the SSID, potential attackers can gain valuable information about your network and potentially launch targeted attacks. Disabling the SSID broadcast can increase the privacy and security of your wireless network.
In summary, network analyzer tools are invaluable in determining the security type of your WiFi network. By examining encryption protocols, password strength, cybersecurity vulnerabilities, authentication protocols, and SSID broadcasting, these tools provide essential insights into the security settings of your network. Utilizing network analyzer tools can help you enhance the protection and privacy of your wireless network and mitigate the risk of unauthorized access or hacking attempts.
Section 3: How to Secure Your WiFi Network
Securing your WiFi network is crucial for protecting your personal data and preventing unauthorized access to your wireless network. By implementing the right security measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of cybersecurity threats and ensure the privacy of your WiFi network.
1. Choose the Right Security Type: The first step in securing your WiFi network is to select the appropriate security type. The most secure option is WPA (WiFi Protected Access) or WPA2 encryption. It provides stronger encryption and improved authentication protocols compared to the outdated WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) protocol.
2. Change the Default Router Password: To enhance security, it is crucial to change the default password of your WiFi router. Hackers often target default passwords, as they are easy to guess. Create a unique and strong password that is not easily guessable, including a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters.
3. Enable Network Encryption: Enable network encryption to protect the data transmitted over your WiFi network. Use WPA or WPA2 encryption, as they offer stronger encryption algorithms. This ensures that even if someone intercepts your wireless network traffic, they won’t be able to decipher it without the encryption key.
4. Disable SSID Broadcasting: By disabling SSID broadcasting, you make your WiFi network less visible to potential attackers. This feature prevents your network name (SSID) from appearing in the list of available networks, making it harder for hackers to identify and target your network.
5. Implement a Firewall: Install and configure a firewall to add an extra layer of protection to your WiFi network. A firewall monitors and filters incoming and outgoing network traffic, blocking any malicious activities or unauthorized access attempts. This helps protect your network against various vulnerabilities and potential hacking attempts.
6. Regularly Update Router Firmware: Keep your router’s firmware up to date by regularly checking for updates from the manufacturer. Router firmware updates often include security patches and bug fixes, which help address vulnerabilities and strengthen the security of your WiFi network.
7. Enable MAC Address Filtering: Consider enabling MAC (Media Access Control) address filtering on your WiFi router. This feature allows you to specify which devices are allowed to connect to your network based on their unique MAC addresses. By configuring MAC address filtering, you can effectively restrict access to your network and prevent unauthorized devices from connecting.
Conclusion: By following these steps, you can significantly improve the security of your WiFi network, safeguard your personal information, and reduce the risk of cyber attacks. Implementing a combination of encryption protocols, strong passwords, and additional security measures will help ensure the privacy and security of your wireless network.
Updating Your Router’s Firmware
Updating your router’s firmware is crucial for maintaining the security and performance of your wireless network. Firmware is a type of software that is embedded into your router’s hardware. It controls the router’s functionality, including its wireless capabilities, firewall, and security features.
Regular firmware updates are essential because they often include important patches and bug fixes that address vulnerabilities and improve the overall security of your network. By keeping your router’s firmware up to date, you can ensure that your network is protected against potential hacking attempts and other cybersecurity threats.
One significant benefit of updating your router’s firmware is the ability to take advantage of the latest security protocols and encryption methods. Older routers may only support outdated security types like WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy), which is known for its vulnerability to hacking. However, by updating your firmware, you can enable more robust security options, such as WPA (WiFi Protected Access) or WPA2, which provide better authentication and encryption.
When updating your router’s firmware, it is crucial to follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully. Usually, this involves accessing the router’s administrative console through a web browser and locating the firmware update option. You may need to download the firmware file from the manufacturer’s website and then upload it to your router.
Before initiating the firmware update, it’s important to back up your router’s settings in case anything goes wrong during the process. Additionally, you should ensure that your router is connected to a stable power source to prevent any interruptions during the update.
In conclusion, keeping your router’s firmware up to date is an essential step in maintaining the security and functionality of your wireless network. By updating your firmware, you can take advantage of the latest security protocols, address vulnerabilities, and protect your network from potential cybersecurity threats.
Changing the Default Router Password
The default password for your router is set by the manufacturer and is often easily guessable or well-known. This poses a security risk as anyone with access to your network can potentially gain access to sensitive information or even control your router. Changing the default password is an essential step in securing your network.
By changing the default router password, you are adding an extra layer of protection to your network. It acts as a firewall against unauthorized access and improves the overall security of your system. Without a strong and unique password, your network is vulnerable to hacking attempts and unauthorized access.
The router password is used for authentication, allowing only authorized devices to connect to your network. It is crucial to choose a strong password that combines uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Avoid using easily guessable information, such as your name or address, to prevent hackers from cracking the password.
Changing the default router password is relatively simple. Start by accessing your router’s settings through a web interface or a dedicated app provided by the manufacturer. Locate the section for changing passwords, which may be under the “Wireless” or “Security” tab. Follow the on-screen instructions to create a new, strong password for your router.
Once you have changed the default password for your router, it is recommended to update the password for your Wi-Fi network as well. This will ensure that only authorized devices with the correct Wi-Fi password can access your network. Choose a Wi-Fi password that is different from your router password and uses a strong encryption protocol, such as WPA or WPA2, to enhance the privacy and security of your wireless network.
In conclusion, changing the default router password is a critical step in ensuring the security and privacy of your Wi-Fi network. It helps protect against unauthorized access and potential vulnerabilities in the router’s security. By following the recommended practices for selecting a strong password, you can greatly reduce the risk of cyber threats and maintain a secure network environment.
Enabling Encryption on Your WiFi Network
Enabling encryption on your WiFi network is an essential step in ensuring the security and privacy of your wireless connection. Encryption technology protects the data transmitted between your devices and the router, making it unreadable to anyone attempting to intercept it. This prevents unauthorized access and helps to safeguard against potential hacking attempts.
There are several encryption protocols available, including WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) and WPA2. These protocols provide advanced security features such as encryption algorithms and authentication methods to protect your network. It is important to choose the strongest encryption protocol that is supported by your router to maximize its effectiveness.
When enabling encryption, you will need to configure a security key or password, known as the Wi-Fi Protected Access Pre-Shared Key (WPA-PSK). This key is used to authenticate devices attempting to access your network. It should be a complex and unique combination of letters, numbers, and special characters to enhance the security of your network.
Your router’s administration interface will typically have settings to enable encryption and choose the encryption type. The most common encryption types are WPA, WPA2, and WPA3. WPA2 is currently the most secure encryption type, offering robust protection against vulnerabilities and attacks.
Enabling encryption on your WiFi network helps ensure that your personal and sensitive data remains protected. It adds an extra layer of security against unauthorized access and intercepting of your network traffic. By implementing strong encryption and regularly updating your router’s firmware, you can enhance the security of your network and minimize potential cybersecurity threats.
Section 4: Additional Tips for WiFi Security
To enhance the protection of your wireless network and ensure the privacy of your data, it is important to take additional steps to enhance the security of your WiFi network. Here are some additional tips:
- Use stronger security protocols: Instead of using the older and less secure Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) protocol, it is recommended to use the Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) or WPA2 protocols. These protocols provide better encryption and authentication mechanisms, making it more difficult for hackers to access your network.
- Change the default SSID and password: The SSID (Service Set Identifier) is the name of your WiFi network, and the password is the key that allows you to access it. Changing the default SSID and password provided by the router manufacturer adds an extra layer of security, as it makes it more difficult for attackers to guess your network details.
- Enable MAC address filtering: Most wireless routers have the option to enable MAC address filtering, which allows you to specify the devices that are allowed to connect to your network. By enabling this feature and adding the MAC addresses of your devices, you can prevent unauthorized access to your network.
- Keep your router firmware up to date: Router manufacturers often release firmware updates that include security patches and fixes for vulnerabilities. It is important to regularly check for and install these updates to ensure that your router is protected against the latest threats.
- Enable a firewall: A firewall acts as a barrier between your network and the internet, monitoring and controlling the incoming and outgoing network traffic. By enabling a firewall on your router, you can add an extra layer of security and prevent unauthorized access to your network.
- Disable remote access: Some routers allow remote access, which means that you can manage your router’s settings from outside your home network. However, this feature can also be exploited by attackers. It is recommended to disable remote access unless you specifically need it.
- Regularly monitor your network: Keep an eye on the devices connected to your WiFi network and check for any suspicious activity. If you notice any unauthorized devices or unusual network behavior, it could be a sign of a security breach. Take immediate action to investigate and resolve the issue.
By following these additional tips, you can strengthen the security of your WiFi network and reduce the vulnerability to cyber attacks. Remember that maintaining a strong and secure wireless network is crucial for protecting your sensitive data and ensuring the privacy of your online activities.
Regularly Updating Your WiFi Password
Keeping your WiFi network secure is crucial for protecting your personal data and privacy. One of the most effective ways to enhance the security of your network is by regularly updating your WiFi password. By doing so, you can prevent unauthorized access and reduce the vulnerability of your network to hacking attempts.
When setting up your WiFi network, it is important to choose a strong password that is difficult to guess. A strong password should be at least eight characters long and include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Avoid using common words or easily guessable information such as your name or address.
As technology evolves, so do the methods used by hackers to gain access to private networks. Regularly updating your WiFi password ensures that you stay one step ahead of potential threats. It is recommended to change your password every few months or whenever you suspect a security breach.
In addition to changing your WiFi password, it is also advisable to consider other security measures. These may include enabling encryption protocols such as WPA (WiFi Protected Access) or WPA2, which provide stronger authentication and encryption for your wireless network. Furthermore, activating a firewall on your router can help to safeguard your network against unauthorized access and potential cyber attacks.
By regularly updating your WiFi password and implementing additional security measures, you can significantly enhance the protection of your network and mitigate the risks of hacking or unauthorized access. It is important to prioritize cybersecurity and take proactive steps to ensure the privacy and security of your wireless network.
Disabling Remote Management
One important step in securing your wireless network is to disable remote management on your router. Remote management allows you to access your router’s settings and make changes from anywhere, but it also presents a potential vulnerability that can be exploited by hackers.
When remote management is enabled, it opens up a port on your router that allows external access. If a hacker gains access to your network, they can potentially take control of your router and compromise the security of your network.
Disabling remote management is a simple but effective way to improve your network’s cybersecurity. By disabling this feature, you are closing off the access point that hackers could exploit to gain unauthorized access to your router.
To disable remote management, you will need to log in to your router’s settings. This is usually done by entering the router’s IP address into a web browser and entering the appropriate username and password. Once logged in, navigate to the remote management settings and disable the feature.
It is also a good idea to change the default username and password for your router’s administration settings. This will provide an additional layer of security and protection against unauthorized access.
By disabling remote management and changing the default login credentials, you are taking important steps to ensure the privacy and security of your wireless network. These simple measures can greatly reduce the risk of hacking and protect your network from potential vulnerabilities.
Keeping Your WiFi Network Hidden (SSID Broadcasting)
In addition to securing your wireless network with a strong password and encryption, you can also hide the name of your WiFi network, known as the Service Set Identifier (SSID). This feature, called SSID broadcasting, prevents your network from being easily discovered by unauthorized users.
By default, most routers have SSID broadcasting enabled, which means that your WiFi network’s name is visible to anyone within range. However, when you disable SSID broadcasting, your network becomes “hidden” and only users who specifically know the name of the network can connect to it.
Disabling SSID broadcasting can add an extra layer of security to your network by making it less visible to potential hackers. While it doesn’t provide complete protection, it can deter casual attempts at unauthorized access.
Keep in mind that hiding your SSID alone is not enough to fully protect your network. It should be used in conjunction with other security measures, such as using WPA or WPA2 as the authentication protocol, instead of the less secure WEP. Additionally, regularly updating your router’s firmware and using a strong, unique password for your WiFi network are essential for maintaining network security.
Although hiding your SSID can enhance the security of your WiFi network, it is not foolproof. There are tools and techniques that can still be used to identify and connect to hidden networks. Therefore, it is important to regularly review and update your security settings to stay ahead of potential vulnerabilities and to follow best practices in cybersecurity.
FAQ about topic “How to Determine the Security Type of Your WiFi Network”
How can I check the security type of my WiFi network?
To check the security type of your WiFi network, you can access the router settings by typing the router’s IP address in your web browser. Once you have accessed the settings, look for the wireless security tab or a similar option. Here, you will be able to see the security type of your WiFi network, such as WEP, WPA, or WPA2.
What is the recommended security type for a WiFi network?
The recommended security type for a WiFi network is WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2). WPA2 provides a higher level of security compared to older security types like WEP or WPA. It uses a stronger encryption algorithm, making it more difficult for unauthorized users to gain access to your network.
Can I change the security type of my WiFi network?
Yes, you can change the security type of your WiFi network. To do this, you need to access the router settings by typing the router’s IP address in your web browser. Once you have accessed the settings, look for the wireless security tab or a similar option. Here, you can select a different security type, such as WEP, WPA, or WPA2, depending on the capabilities of your router.
What are the disadvantages of using WEP security?
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is an older security type for WiFi networks. It has several disadvantages, including weak encryption, making it easier for hackers to crack the security key and gain access to your network. WEP is also susceptible to various attacks, such as replay attacks and brute force attacks. Due to these vulnerabilities, it is highly recommended to use a more secure security type, such as WPA or WPA2.
What should I do if my router only supports WEP security?
If your router only supports WEP security and does not have the option to upgrade to a more secure security type like WPA or WPA2, there are a few things you can do to improve the security of your WiFi network. First, you can consider upgrading your router to a newer model that supports more secure security types. Alternatively, you can use additional security measures, such as enabling MAC address filtering or using a virtual private network (VPN) to encrypt your internet traffic.


