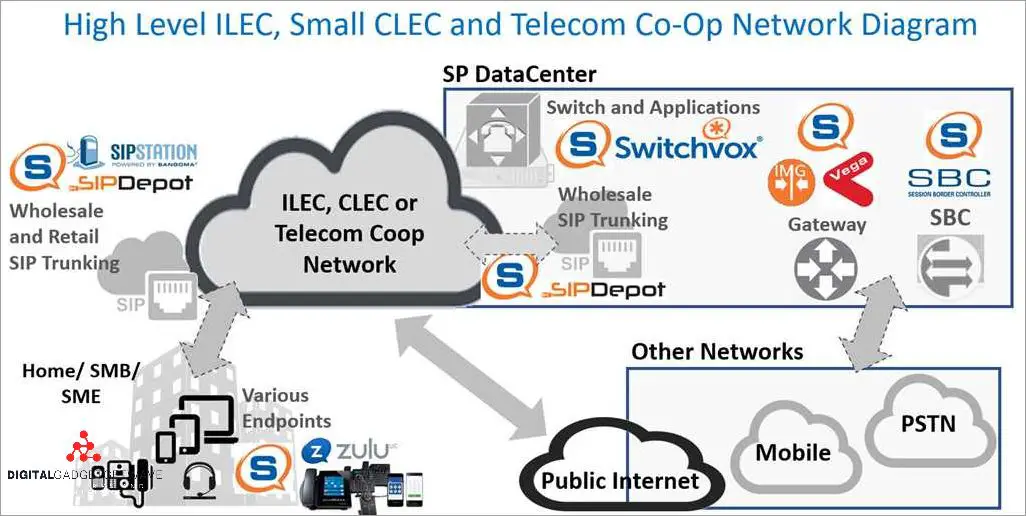
When it comes to the world of telecommunications, two acronyms commonly thrown around are ILEC and CLEC. These terms refer to different types of companies in the telecom industry and understanding the differences between them is crucial for anyone who relies on telecom services.
ILEC stands for Incumbent Local Exchange Carrier, which refers to a company that was originally established as the provider of local telephone services in a particular geographic area. These companies typically have a long history and were often the first telephone service providers in their region. They own and operate the infrastructure, known as the local network facilities, which includes telephone lines, switching centers, and other necessary equipment.
In contrast, CLEC stands for Competitive Local Exchange Carrier. These companies are newer players in the telecom industry and were established following the deregulation and unbundling of telecom services. Unlike ILECs, CLECs do not own the local network infrastructure but instead lease access to it in order to provide their services. They typically focus on offering competitive alternatives to ILECs in areas such as broadband internet, voice over IP (VoIP), and other telecom services.
The main difference between ILECs and CLECs lies in their ownership and control of the local network infrastructure. While ILECs have a monopoly over the infrastructure in their area and are subject to certain regulatory requirements, CLECs have greater flexibility and can enter into agreements with ILECs to lease access to their infrastructure. This competition between ILECs and CLECs has led to increased innovation and improved services for end-users.
Understanding the differences between ILECs and CLECs is important because it directly impacts the telecom services you receive. Depending on whether you are using an ILEC or CLEC as your service provider, you may experience differences in pricing, service quality, and available options. Additionally, the competition between ILECs and CLECs can result in better deals and options for consumers as both types of companies strive to attract and retain customers.
In conclusion, ILECs and CLECs play different roles in the telecom industry, with ILECs being the traditional local service providers and CLECs being the new competitors. Understanding the differences between these two types of companies is crucial for anyone who relies on telecom services, as it can impact the cost, quality, and options available to them. Both types of companies contribute to the overall competition and innovation in the industry, ultimately benefiting the end-users of telecom services.
Contents
- 1 What is ILEC and CLEC?
- 2 Key Differences between ILEC and CLEC
- 3 How ILEC and CLEC Impact Your Telecom Services
- 4 Choosing Between ILEC and CLEC for Your Telecom Services
- 5 FAQ about topic “ILEC vs CLEC: Understanding the Differences and How They Impact Your Telecom Services”
- 6 What is the difference between an ILEC and a CLEC?
- 7 Why are there ILECs and CLECs?
- 8 What are the advantages of using an ILEC?
- 9 What are the advantages of using a CLEC?
- 10 Can I switch from an ILEC to a CLEC or vice versa?
What is ILEC and CLEC?
ILEC and CLEC are terms used to describe different types of telecommunications providers in the United States. ILEC stands for Incumbent Local Exchange Carrier, while CLEC stands for Competitive Local Exchange Carrier.
ILECs are the traditional local telephone companies that were in operation before the deregulation of the telecommunications industry. They are often the legacy carriers that provide local telephone service within a designated geographic area. ILECs typically own and operate the infrastructure, including the copper and fiber optic cables, that provide the telephone and broadband services within their service territories.
CLECs, on the other hand, are newer entrants into the telecommunications market that emerged following the deregulation of the industry. These companies compete with the ILECs by offering their own telephone and broadband services. CLECs do not own their own infrastructure, but instead lease access to the ILEC’s facilities to provide their services. They can also leverage their own network and facilities to offer services such as VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol).
The regulation of ILECs and CLECs is overseen by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the United States. The FCC sets rules and regulations regarding interconnection and access to the incumbent’s network. These rules ensure that CLECs have fair and equal access to the ILEC’s network and facilities. One such regulation is the unbundling of the ILEC’s network, which requires the ILEC to provide CLECs with access to specific parts of their network on a wholesale basis.
In order to operate, CLECs must negotiate an interconnection agreement with the ILEC to establish the terms and conditions for connecting their network to the ILEC’s network. This interconnection allows CLECs to exchange traffic with the ILEC’s network and offer their services to customers within the ILEC’s service territory.
Overall, the distinction between ILECs and CLECs is important in understanding the competitive landscape of the telecom industry. ILECs are the traditional local telephone providers with existing infrastructure, while CLECs are the newer entrants that compete with the ILECs by leasing access to their facilities or building their own network.
ILEC Overview
An Incumbent Local Exchange Carrier (ILEC) is a telecommunications provider that was in place before the implementation of the Telecommunications Act of 1996. These providers, commonly known as ILECs, were granted certain privileges and had a dominant presence in the telecom market.
ILECs own and operate the infrastructure and facilities necessary for providing local telephone service. This includes the network access points, switching equipment, and transmission facilities required to connect customers to the telephone exchange. ILECs are responsible for maintaining and upgrading this infrastructure to ensure reliable service.
ILECs were originally granted a monopoly in their designated service areas, but the Telecommunications Act of 1996 introduced competition by allowing Competitive Local Exchange Carriers (CLECs) to enter the market. However, ILECs still hold a significant advantage due to their pre-existing infrastructure and customer base.
ILECs also have the capability to provide other telecom services, such as broadband internet access. With the emergence of fiber-optic technology, ILECs have been able to offer high-speed broadband to their customers. They are also responsible for interconnection agreements with other telecom providers to ensure connectivity between different networks.
ILECs are subject to regulation by various government agencies to ensure fair competition and quality service. They must comply with regulations that govern pricing, quality of service, interconnection, and other aspects of their operations. This regulatory oversight helps to promote competition and protect the interests of consumers.
CLEC Overview
The term CLEC stands for Competitive Local Exchange Carrier. A CLEC is a telecommunications provider that competes with the incumbent telecommunications provider, referred to as an ILEC or Incumbent Local Exchange Carrier. Unlike ILECs, which typically operate on a legacy copper network, CLECs often utilize fiber infrastructure for their telecom services.
One of the main reasons for the rise of CLECs is to promote competition in the telecom industry. CLECs offer alternative options for local voice and data services, challenging the dominance of ILECs. They provide services such as broadband internet, VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol), and other telecom services to residential and business customers.
CLECs rely on interconnection agreements with ILECs to access their local networks. Through these agreements, CLECs gain access to ILEC infrastructure and facilities, allowing them to offer services to customers in the same geographic area. This process, known as unbundling, enables CLECs to compete with ILECs without having to build their own network from scratch.
By offering local access and interconnection services, CLECs contribute to a more competitive telecom market. Customers have the option to choose between ILECs and CLECs, fostering innovation and pricing competition. This competition can lead to improved service quality, lower prices, and better customer support.
In summary, CLECs are telecom providers that offer competitive alternatives to ILECs. They rely on interconnection agreements with ILECs to gain access to local networks and provide services such as broadband internet and VoIP. By promoting competition in the telecom industry, CLECs contribute to improved choices, innovation, and pricing for customers.
Key Differences between ILEC and CLEC
ILEC (Incumbent Local Exchange Carrier) and CLEC (Competitive Local Exchange Carrier) are two types of telecommunications providers that operate in the United States. However, there are several key differences between them:
Ownership and Infrastructure: ILECs are usually large, established companies that own the telephone infrastructure within a specific geographic region. They have built and maintained the network for many years. CLECs, on the other hand, are newer entrants in the market and lease the infrastructure from ILECs or build their own facilities, such as fiber-optic lines, to provide services.
Interconnection: ILECs have the obligation to interconnect with other providers to ensure seamless communication across networks. This is because they are considered the legacy providers and have historically been the only telecom providers in their service areas. CLECs, however, are not required to interconnect with other providers unless they have a specific agreement in place.
Services: ILECs typically offer a wide range of services, including voice telephone service, broadband internet, data services, and other telecom solutions. CLECs, on the other hand, often focus on providing competitive alternatives to ILECs’ services, such as Voice over IP (VoIP) or specialized data solutions.
Competition and Regulation: ILECs were traditionally regulated by government bodies to ensure fair and reasonable pricing and service quality. CLECs, on the other hand, entered the market in response to the need for competition and are subject to different regulations that vary by state. This allows CLECs more flexibility in pricing and service offerings.
Unbundling and Access: ILECs are required to offer unbundled access to their network infrastructure, meaning that other providers can lease specific network elements to offer their own services. This promotes competition and allows CLECs to enter the market. CLECs, however, do not have the same requirement to offer unbundled access to their facilities.
In summary, ILECs and CLECs differ in terms of ownership, infrastructure, interconnection obligations, service offerings, competition, regulation, and unbundling requirements. Understanding these differences can help businesses and consumers choose the telecom provider that best suits their needs and budget.
Regulatory Environment
In the telecom industry, the regulatory environment plays a crucial role in shaping the operations and practices of both ILECs and CLECs. Regulations are in place to ensure fair competition, protect consumer interests, and promote the development of telecom infrastructure and services.
One aspect of the regulatory environment that affects both ILECs and CLECs is interconnection. Interconnection refers to the agreement between different telecom service providers to share their network facilities and allow for the exchange of traffic. This is especially important for CLECs, as they rely on the infrastructure of ILECs to reach their customers.
Another important regulation is the unbundling requirement. This regulation mandates that ILECs must offer access to their network infrastructure to other service providers, such as CLECs, at a reasonable cost. This allows CLECs to utilize the ILEC’s existing telephone lines or fiber network to provide their own services, such as VoIP or broadband.
Local loop unbundling, a specific form of unbundling, allows CLECs to lease the “last mile” infrastructure from ILECs. The last mile refers to the segment of the network that connects the ILEC’s central office to the customer’s premises. By accessing the last mile, CLECs can offer their own telephone or broadband services to customers without having to build their own network infrastructure.
The regulatory environment also covers aspects such as pricing, quality of service, and consumer protection. Regulatory bodies set guidelines on pricing structures to ensure fair competition and prevent anti-competitive practices. They also establish standards for the quality of service that telecom providers must meet to ensure that customers receive reliable and high-quality service. Additionally, regulations exist to protect consumers from unfair practices, such as unauthorized charges or misleading advertising.
Overall, the regulatory environment in the telecom industry plays a critical role in shaping the relationship between ILECs and CLECs. It ensures fair competition, promotes the development of telecom infrastructure, and protects consumer interests. Compliance with these regulations is essential for both ILECs and CLECs to operate in the industry and provide their services effectively.
Service Coverage
In the world of telecommunications, service coverage refers to the geographical area where a telecom provider can offer its services. Both ILECs and CLECs play a crucial role in providing local telephone and broadband services.
ILECs, or Incumbent Local Exchange Carriers, have historically been the dominant providers of local telecom services. They own the infrastructure, including the physical facilities and the network, necessary to deliver these services. ILECs are subject to regulation and must provide telephone service throughout their designated service areas.
CLECs, or Competitive Local Exchange Carriers, emerged as a result of the Telecommunications Act of 1996, which aimed to increase competition in the telecom industry. CLECs do not own their own infrastructure; instead, they lease or purchase network facilities from ILECs through the process known as “unbundling.” This allows CLECs to compete with ILECs by offering their own voice over IP (VoIP) services and broadband access.
Since CLECs do not have their own network infrastructure, their service coverage may be limited compared to ILECs. However, through agreements with ILECs and other CLECs, they can expand their service coverage and provide telecom services to a wider range of customers. This competition between ILECs and CLECs is essential for promoting innovation, improving service quality, and driving down prices.
In recent years, the introduction of fiber-optic technology has further expanded service coverage, with both ILECs and CLECs making investments in fiber infrastructure. Fiber-optic networks provide high-speed broadband access and enable the delivery of advanced services like video streaming and cloud computing. This has led to increased competition in the telecom industry and improved service coverage for customers.
Overall, service coverage is a critical factor to consider when choosing a telecom provider. Whether you opt for an ILEC or a CLEC, their service coverage will determine the availability and quality of the telephone and broadband services you can access in your area. Understanding the differences between ILECs and CLECs and how they impact service coverage can help you make an informed decision about your telecom services.
Pricing and Competition
When it comes to telecom services, pricing and competition play a crucial role in the industry. ILECs and CLECs, as providers of telecom services, operate in a regulated environment where pricing is based on certain factors and competitive dynamics.
Under regulation, ILECs have the responsibility to provide essential telephone services to the public. They are granted the right to access and use local exchange facilities, which include the network infrastructure and telephone lines. ILECs have the advantage of owning the local infrastructure, such as copper wires and the traditional telephone network, giving them a significant market advantage.
On the other hand, CLECs are the competitors in the market. They do not own the local facilities or network infrastructure like ILECs do. Instead, CLECs lease access to ILEC-owned facilities on a wholesale basis, which allows them to offer their telecom services to customers without having to invest in building their own infrastructure.
Competition between ILECs and CLECs is not limited to traditional telephone services. With the rise of broadband and VoIP technologies, CLECs can also offer these services, competing directly with ILECs. This has created a more competitive market landscape, with both ILECs and CLECs striving to attract customers by offering competitive pricing packages and innovative services.
In order to promote competition, regulatory bodies have introduced interconnection and unbundling agreements. These agreements require ILECs to provide CLECs with access to their local network infrastructure, enabling CLECs to offer their services to customers. This ensures that CLECs can compete on a level playing field with ILECs, fostering a more competitive market.
Additionally, the availability of fiber optic networks has further intensified the competition between ILECs and CLECs. Fiber offers higher speeds and more reliable connections, making it an attractive option for both residential and business customers. ILECs and CLECs are investing in expanding their fiber networks to offer faster and more advanced telecom services.
How ILEC and CLEC Impact Your Telecom Services

ILEC (Incumbent Local Exchange Carrier) and CLEC (Competitive Local Exchange Carrier) play a significant role in shaping the telecom services available to consumers and businesses. These two types of carriers differ in terms of their infrastructure, competition, and regulatory obligations, ultimately impacting the quality and availability of telecom services offered to customers.
ILECs are traditional providers that own the local exchange networks and have established a significant presence in the market. They possess the necessary facilities and network infrastructure to deliver various services like voice, broadband, and data to customers. ILECs are subject to specific regulations due to their status as the incumbent carriers. They are responsible for providing universal access and maintaining the communication infrastructure within their service areas.
CLECs, on the other hand, are carriers that entered the market to challenge the dominance of ILECs. They rely on leasing or unbundling the ILEC’s facilities to provide telecom services to customers. CLECs often focus on offering competitive pricing, innovative services, and superior customer support to differentiate themselves from ILECs. They have contributed significantly to the expansion of broadband services by deploying fiber-optic networks and adopting advanced technologies like Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP).
Competition between ILECs and CLECs has spurred advancements in telecom services. CLECs enhance customer choice by providing alternative options to ILEC services, fostering competitive pricing and improved service quality. Additionally, CLECs facilitate interconnection agreements with ILECs, ensuring seamless communication across different networks. This cooperation enables both ILECs and CLECs to offer comprehensive telecom solutions to customers.
Regulation also plays a role in shaping the impact of ILECs and CLECs. Regulatory bodies govern various aspects, such as ensuring fair access to ILEC infrastructure for CLECs, interconnection agreements, and quality of service. These regulations aim to maintain a level playing field in the telecom market and encourage competition, ultimately benefiting customers with improved services and innovative solutions.
Ownership and Control

Ownership and control of telecommunications networks play a critical role in the competitive landscape of the telecom industry. These networks are the backbone that enables access to telephone and broadband services. In the United States, ownership and control are divided between Incumbent Local Exchange Carriers (ILECs) and Competitive Local Exchange Carriers (CLECs).
ILECs, also known as traditional telephone companies, own and operate the infrastructure and facilities that make up the telephone network. They were given this ownership through historical regulation and have a monopoly over the local exchange services in their designated regions. ILECs typically have extensive infrastructure, including copper and fiber-optic lines and switching equipment.
CLECs, on the other hand, are new entrants in the market and provide competition to ILECs. Unlike ILECs, CLECs do not own their own network infrastructure. Instead, they lease or “unbundle” portions of the ILEC’s network to provide service to customers. This practice is regulated to ensure fair interconnection and access to the local network for CLECs.
The competition between ILECs and CLECs has been fueled by the Telecommunications Act of 1996, which aimed to foster competition in the telecom industry. This legislation required ILECs to allow access to their network for competitive providers, promoting a more level playing field for CLECs. Today, CLECs can provide a wide range of telecom services, including local and long-distance telephone, broadband, and data services, to customers in ILEC territories.
While ILECs still maintain a significant advantage due to their ownership of the network infrastructure, CLECs have made significant strides in providing competitive telecom services. CLECs often focus on using the latest technologies, such as fiber-optic networks, to offer faster and more reliable broadband service to their customers. As a result, consumers now have more choices when it comes to selecting a telecom service provider, and competition continues to drive innovation and improvements in the industry.
Service Quality and Reliability
In the telecommunications industry, service quality and reliability are crucial factors for both ILECs and CLECs. ILECs, or incumbent local exchange carriers, are the established providers that own and operate the local telephone infrastructure. They have invested heavily in building and maintaining facilities and networks, ensuring a high level of service quality and reliability.
One reason for the ILECs’ superior service quality and reliability is their access to extensive network infrastructure. They have built a robust and reliable network that can handle a large volume of telephone calls and provide broadband access. This infrastructure includes copper lines, fiber optic cables, and other technologies that enable them to deliver high-speed and dependable services.
CLECs, on the other hand, typically rely on the ILECs’ infrastructure and facilities to provide their services. Through interconnection agreements, CLECs gain access to the ILECs’ local exchange facilities, allowing them to offer competitive telecom services. However, this reliance on the ILEC’s infrastructure can sometimes pose challenges in terms of service quality and reliability.
Competition in the telecom industry has led to regulatory requirements, such as local loop unbundling, which allows CLECs to lease portions of the ILEC’s network and provide their own services. This has increased competition and spurred innovation, but it can also result in inconsistencies in service quality and reliability. CLECs may face limitations in accessing certain network elements or may rely on outdated infrastructure, impacting the overall service provided to customers.
With the advent of new technologies, such as Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) and fiber-optic networks, both ILECs and CLECs are striving to improve their service quality and reliability. These technologies offer higher capacity and faster speeds, enabling more reliable voice and data transmission. Both ILECs and CLECs are investing in upgrading their infrastructure to provide a better customer experience.
In conclusion, while ILECs generally have a reputation for superior service quality and reliability due to their ownership and control of local exchange facilities, CLECs can also offer reliable services by leveraging the ILEC’s infrastructure through interconnection agreements. However, the level of service quality and reliability may vary depending on the specific CLEC and its access to the ILEC’s network. Ongoing investment in modern technologies and infrastructure is essential for both ILECs and CLECs to meet the increasing demands of customers in the telecom industry.
Flexibility and Innovation
The competition between ILECs and CLECs has led to increased flexibility and innovation in the telecommunications industry. One of the key factors driving this is the unbundling agreement, which allows CLECs to access the local exchange facilities and infrastructure of ILECs. This enables CLECs to provide services that are not only competitive with those offered by ILECs, but also innovative and tailored to meet the needs of their customers.
One area where this flexibility and innovation is particularly evident is in the deployment of fiber optic networks. Both ILECs and CLECs have been investing heavily in fiber optic infrastructure to support high-speed broadband services. This investment is driven by the growing demand for faster and more reliable internet connections, as well as the increasing reliance on internet services for business and personal use.
In addition to fiber optic networks, another area of innovation is in the development of Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) services. VoIP allows users to make telephone calls over the internet, bypassing traditional telephone networks. This technology has paved the way for new service providers, including CLECs, to enter the telecommunications market and offer competitive voice services.
The regulatory framework that governs the interconnection of ILECs and CLECs also plays a role in fostering flexibility and innovation. Regulations ensure that CLECs have fair and non-discriminatory access to ILEC infrastructure and services, enabling them to compete on a level playing field. This promotes healthy competition and encourages both ILECs and CLECs to continuously improve their services and develop new technologies.
Overall, the competition between ILECs and CLECs has fueled flexibility and innovation in the telecommunications industry. Both types of providers are investing in new infrastructure, developing innovative services, and competing to offer the best broadband and telephone services to their customers. This competition benefits consumers by driving down prices, improving service quality, and expanding choices in the telecommunications market.
Choosing Between ILEC and CLEC for Your Telecom Services
When it comes to choosing a telecommunications service provider, you may come across the terms ILEC and CLEC. ILEC stands for Incumbent Local Exchange Carrier, while CLEC stands for Competitive Local Exchange Carrier. Understanding the differences between these two options is crucial for making an informed decision about your telecom services.
Interconnection Agreements:
One key difference between ILECs and CLECs lies in their interconnection agreements. ILECs have existing agreements with other carriers that allow them to access the public switched telephone network (PSTN), enabling them to provide traditional telephone services. CLECs, on the other hand, need to negotiate specific interconnection agreements to gain access to the same network.
Access to Exchange Networks:
ILECs typically have a well-established infrastructure in place, including access to exchange networks, which are essential for routing telephone calls and providing other telecom services. CLECs, on the other hand, may need to rely on the infrastructure of ILECs or build their own facilities to have access to exchange networks.
VoIP and Broadband Services:
While both ILECs and CLECs can provide traditional telephone services, CLECs often have an advantage when it comes to offering Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) and broadband services. CLECs can leverage their independence from legacy telephone networks to provide more innovative and cost-effective solutions in these areas.
Regulation and Unbundling:
The telecom industry is subject to regulations aimed at promoting fair competition. In many cases, ILECs are required to unbundle their infrastructure and allow CLECs to use some of their facilities, such as copper lines or fiber optic cables. This unbundling requirement gives CLECs the opportunity to offer competitive local service options.
When choosing between an ILEC and CLEC for your telecom services, it’s important to assess your specific needs and evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each type of provider. Consider factors such as the type of service you require, the infrastructure available in your area, and the level of innovation you desire in your telecom solutions. By carefully weighing these factors, you can make an informed decision that best suits your business or personal requirements.
Considerations for Business Customers
When it comes to choosing a telecom service provider, business customers should take into account several key considerations. One of the first factors to consider is whether the provider is an ILEC or a CLEC.
An ILEC, or incumbent local exchange carrier, refers to the dominant telecom provider in a particular geographic area. They generally have an established telecom infrastructure and often offer a wide range of services, such as voice, data, and broadband.
A CLEC, or competitive local exchange carrier, on the other hand, is a telecom provider that competes with the ILEC in a specific market. CLECs typically rely on the ILEC’s infrastructure to provide services but also have the ability to offer additional services such as VoIP or fiber-optic connections.
Regulation is another important consideration for business customers. ILECs often have more strict regulatory requirements compared to CLECs. This can impact pricing, service agreements, and access to certain network facilities. CLECs, on the other hand, may have more flexibility in terms of pricing and service offerings.
Business customers should also consider the level of competition in their area. In markets with high competition, both ILECs and CLECs may offer competitive pricing and service options. Conversely, in areas with limited competition, ILECs may have a stronger market position, which could result in higher prices and fewer choices for business customers.
Another consideration for business customers is the availability of broadband services. ILECs typically have a more extensive network infrastructure, which may translate to greater broadband coverage. CLECs, however, may offer more innovative and advanced broadband technologies, such as fiber-optic connections.
Finally, business customers should also consider the interconnection and unbundling agreements between ILECs and CLECs. These agreements determine the terms and conditions for CLECs to access and use ILEC’s network facilities. Understanding these agreements can help businesses assess the quality and availability of services from both ILECs and CLECs in their area.
Considerations for Residential Customers
When it comes to choosing a telecom service provider for your residential needs, there are several important considerations to keep in mind. One of the main factors to consider is whether the provider is an ILEC or a CLEC.
An ILEC, or Incumbent Local Exchange Carrier, is a telecommunications company that owns and operates the infrastructure and telephone network in a particular geographic area. They have an established infrastructure, including copper and fiber optic cables, which provide access to services like broadband internet, voice over IP (VoIP), and local telephone services. As the incumbent provider, they generally have the advantage of having a well-developed network and extensive coverage.
On the other hand, a CLEC, or Competitive Local Exchange Carrier, is a telecom provider that operates in competition with the ILEC. CLECs typically lease or purchase network facilities from ILECs and use them to provide their own services. This allows for increased competition and choice for residential customers. The CLECs may offer different pricing plans, features, and customer service options compared to the ILEC.
One advantage of choosing a CLEC is the possibility of accessing advanced services, such as fiber optic broadband, that may not be available from the ILEC. CLECs may invest in upgrading their infrastructure to provide high-speed internet and other innovative services that can enhance the residential customer experience.
In some cases, residential customers may have the option to choose an ILEC and a CLEC for different services. For example, a customer may choose to use the ILEC for their local telephone service, while opting for a CLEC for their broadband internet or VoIP services. This can allow customers to take advantage of competitive pricing and service options from different providers.
Another consideration for residential customers is interconnection. Both ILECs and CLECs must enter into interconnection agreements to establish the terms and conditions for the exchange of traffic between their networks. These agreements ensure that customers can communicate with each other regardless of the telecom provider they are using. It’s important for residential customers to choose a provider that has established interconnection agreements to ensure seamless communication with others.
In conclusion, residential customers have several considerations to keep in mind when choosing a telecom service provider. Understanding the differences between ILECs and CLECs, the available services, competition, infrastructure, and interconnection agreements can help customers make informed decisions that best suit their individual needs.
FAQ about topic “ILEC vs CLEC: Understanding the Differences and How They Impact Your Telecom Services”
What is the difference between an ILEC and a CLEC?
An ILEC, or incumbent local exchange carrier, is a telecommunications company that operates in a specific geographic area and generally has a monopoly in that area. A CLEC, or competitive local exchange carrier, is a telecommunications company that competes with the ILEC in providing local phone services. The main difference between the two is that ILECs have a long-established presence and infrastructure in a particular area, while CLECs are newer and often rely on leasing or purchasing access to the ILEC’s infrastructure.
Why are there ILECs and CLECs?
The existence of both ILECs and CLECs is a result of deregulation in the telecommunications industry. In the past, ILECs had a monopoly in their respective areas, but with deregulation, competition was introduced to promote innovation and lower prices for consumers. CLECs emerged as competitors to ILECs, offering alternative options for local phone services.
What are the advantages of using an ILEC?
Using an ILEC for telecommunications services has some advantages. Firstly, ILECs often have well-established infrastructure and networks in place, which can provide a stable and reliable connection. Additionally, ILECs may have a wider coverage area compared to CLECs, particularly in rural or remote areas where CLECs may not have a presence. Lastly, ILECs may offer bundled services, such as phone, internet, and TV, which can be convenient for customers.
What are the advantages of using a CLEC?
Using a CLEC for telecommunications services has its advantages as well. CLECs may offer more competitive pricing compared to ILECs, as they are often newer entrants and can offer lower rates to attract customers. CLECs may also be more flexible in terms of service offerings, as they are not tied to legacy systems and can adapt to changing technologies more quickly. Additionally, CLECs may provide more personalized customer service and be more responsive to customer needs.
Can I switch from an ILEC to a CLEC or vice versa?
Switching from an ILEC to a CLEC or vice versa is possible in some cases, depending on the availability of services in your area. However, it is important to note that the process may involve changing phone numbers and other logistical considerations. It is recommended to contact both the ILEC and CLEC providers to discuss your options and determine the feasibility of switching.


