![Intro to Wave Table Synthesis: How it Works and its Key Features - [Website Name] Intro to Wave Table Synthesis: How it Works and its Key Features - [Website Name]](/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/intro-to-wave-table-synthesis-how-it-works-and-its.jpg)
Wave Table Synthesis is a powerful digital audio synthesis technique that has revolutionized the world of electronic music. It is based on the manipulation of waveform samples, which are pre-recorded snippets of sound that can be seamlessly looped and modulated to create complex and dynamic musical textures.
At the core of wave table synthesis is the wave table, a digital representation of a musical waveform. This wave table acts as a sort of “ingredient” for creating sounds. By combining multiple wave tables, each with its own unique sonic characteristics, wave table synthesis is able to generate a wide range of sounds, from simple tones to complex and evolving textures.
Wave table synthesis relies on a specialized oscillator known as a wave table oscillator. This oscillator is responsible for reading the wave table and generating the audio signals. By modulating the playback speed and position within the wave table, the oscillator is able to create a variety of harmonic and timbral variations.
One of the key features of wave table synthesis is its flexibility and versatility. Unlike traditional analog synthesis techniques, wave table synthesis allows for precise control over the frequency and formant characteristics of a sound. This makes it ideal for creating realistic instrument sounds, as well as experimental and futuristic electronic tones.
Another important element in wave table synthesis is the wave table filter. This filter allows for further shaping and manipulation of the generated sound. By applying various filtering techniques, such as low-pass, high-pass, and band-pass filters, the wave table synthesis can create a range of tonal colors and textures.
In conclusion, wave table synthesis is a powerful and versatile technique that has become an essential tool in the world of electronic music production. Its ability to accurately reproduce and manipulate waveforms, combined with its flexible modulation and filtering capabilities, make it a popular choice among musicians and sound designers.
Contents
- 1 Understanding Wave Table Synthesis
- 2 How Wave Table Synthesis Works
- 3 Key Features of Wave Table Synthesis
- 4 Applications of Wave Table Synthesis
- 5 FAQ about topic “Introduction to Wave Table Synthesis: Understanding its Mechanism and Essential Features”
- 6 What is wave table synthesis?
- 7 How does wave table synthesis work?
- 8
- 9 What types of sounds can be created with wave table synthesis?
- 10
Understanding Wave Table Synthesis
Wave Table Synthesis is a technique used in electronic music synthesis to produce sounds. It involves the manipulation and generation of waveforms using a wave table oscillator. This method is commonly used in analog and digital synthesizers and has become an essential tool for musicians and sound designers.
The wave table oscillator is an electronic instrument that generates different waveforms, such as sine, square, triangle, and sawtooth waves. These waveforms can be used to create various musical tones and sounds. The oscillator’s waveform generator is capable of synthesizing complex waveforms by combining multiple basic waveforms or using advanced techniques like wavetable scanning.
One of the key features of wave table synthesis is its ability to produce different formant wavelengths. Formants are the resonant frequencies that give each sound its unique character. By manipulating the wave table and adjusting the formant frequencies, musicians can create a wide range of sound effects and timbres.
Another important aspect of wave table synthesis is modulation. Modulation refers to the process of dynamically altering the properties of a sound over time. With wave table synthesis, modulation possibilities are extensive, allowing for the creation of evolving and dynamic sounds. Modulation can be applied to parameters such as wave shape, pitch, amplitude, and filter settings, resulting in a rich and versatile sound palette.
Wave table synthesis also offers advantages in terms of sampling rate and filter capabilities. Since the waveforms are stored in a digital table, they can be sampled at high frequencies, allowing for a more accurate reproduction of the original sound. Additionally, wave table synthesis can apply complex filtering techniques, such as resonance and cutoff, to shape the sound further.
In conclusion, wave table synthesis is a powerful and versatile technique in the world of musical synthesis. It allows for the creation of a wide range of sounds, from simple waveforms to complex and evolving textures. Whether in analog or digital form, wave table synthesis has become an essential tool for musicians and sound designers in shaping the sonic landscape of contemporary music.
What is Wave Table Synthesis?
Wave Table Synthesis is a technique in electronic sound synthesis that involves the manipulation and creation of waveforms to produce sounds. It is a popular method used in both digital and analog musical instruments.
At its core, wave table synthesis involves a wave table, which is a table of stored waveforms that can be accessed and combined to create new sounds. Each waveform represents a specific sound or timbre, and by selecting and combining different waveforms, a wide range of sounds can be generated.
A key feature of wave table synthesis is the ability to morph between waveforms in real-time, creating smooth transitions between different sounds. This allows for dynamic and expressive musical performances, as the sound can be continuously shaped and modulated.
In wave table synthesis, a filter can be applied to the waveforms to alter their frequency characteristics. This can be used to mimic the natural timbre of various instruments, add formant-like qualities, or create unique and unconventional sounds.
Wave table synthesis can also incorporate techniques such as sampling and algorithmic modulation to further expand its sonic possibilities. By adding sampled sounds or applying mathematical algorithms to the waveforms, new and complex sounds can be created.
Overall, wave table synthesis is a versatile and powerful method for sound creation, offering a wide range of possibilities for musicians and sound designers. It is a fundamental technique in electronic music production and has been used to shape the sounds of countless songs and compositions.
History of Wave Table Synthesis
Wave Table Synthesis is a technique used in electronic music synthesis for generating and manipulating waveforms. It was developed in the late 1970s and early 1980s as an alternative to traditional analog synthesis techniques.
Prior to the advent of digital wave table synthesis, synthesizers used analog oscillators to produce different waveforms. These analog oscillators were limited in their ability to generate complex waveforms, and often required the use of external filters and modulation techniques to shape the sound.
With the rise of digital technology, wave table synthesis emerged as a new approach to sound generation. Instead of using analog oscillators, wave table synthesis uses digital oscillator banks or tables to store and retrieve pre-recorded samples of waveforms.
By playing back these stored waveforms at different frequencies, wave table synthesis allows for the creation of a wide range of sound textures and timbres. The table can be programmed to interpolate between different waveforms, resulting in smooth transitions and dynamic changes in the sound.
One of the key features of wave table synthesis is the ability to manipulate the composition of the table itself. This can be done through various modulation techniques, such as frequency modulation, amplitude modulation, and phase modulation. These modulations can dramatically alter the sound produced by the wave table, allowing for the creation of unique and expressive musical tones.
Wave table synthesis has been used in a variety of musical instruments and synthesizers, from hardware synthesizers to software plugins. Its versatility and flexibility have made it a popular choice for sound designers and musicians looking to explore new sonic possibilities.
Advantages of Wave Table Synthesis
Wave table synthesis offers several advantages that make it a valuable technique in electronic music synthesis:
- Wide range of waveforms: Wave table synthesis allows for the use of a wide variety of waveforms, including both analog and digital waveforms. This flexibility enables musicians to create unique sounds and experiment with different timbres.
- Real-time modulation: With wave table synthesis, it is possible to modulate various parameters of the waveform in real-time. This means that users can create dynamic and evolving sounds by modulating the frequency, amplitude, and other properties of the waveforms.
- High-quality sound: Wave table synthesis can produce high-quality sound due to its ability to accurately reproduce complex waveforms. This makes it suitable for creating realistic instrument sounds and capturing the nuances of musical performances.
- Efficient memory usage: Wave table synthesis uses a technique called wavetable scanning, which allows for efficient memory usage. Instead of storing individual samples, wave table synthesis stores a small number of waveforms and scans through them at different speeds to create a variety of tones.
- Filter and formant shaping: Wave table synthesis allows for the application of filters and formant shaping, which can further shape the sound and create interesting timbral effects. This adds depth and character to the synthesized sounds.
- Sampling and resynthesis: Wave table synthesis can also incorporate sampling and resynthesis techniques. This allows for the integration of real-world sounds into the synthesis process, opening up endless possibilities for sound design and musical expression.
Overall, wave table synthesis offers a powerful and versatile approach to sound synthesis, enabling musicians to create unique and expressive music. Its advantages in waveform flexibility, real-time modulation, sound quality, memory efficiency, and integration of sampling make it a valuable tool in electronic music production.
How Wave Table Synthesis Works
Wave table synthesis is a technique used in digital electronic music synthesis to create complex sounds that mimic real-world analog instruments. It involves the use of wave tables, which are essentially large tables of pre-recorded sound samples.
A wave table is a collection of sample waveforms, each representing a specific frequency and waveform shape. These waveforms can be manipulated and combined to create a wide range of sounds. The samples in the wave table are typically recorded or generated using various methods, such as sampling an analog instrument or using digital oscillators.
The wave table synthesis process involves modulating the waveform samples in real-time to create a musical instrument’s sound. This modulation can be done using various techniques, such as altering the playback speed of the samples or applying filters to change the frequency content.
One of the key features of wave table synthesis is the ability to smoothly transition between different waveforms within the table. This allows for seamless changes in sound characteristics, such as shifting from a pure sine wave to a complex waveform with harmonics. The transitions between waveforms can be controlled using modulation sources, such as envelope generators or LFOs (low-frequency oscillators).
Wave table synthesis is also capable of creating complex sounds by combining multiple waveforms from different positions in the wave table. This technique, known as wavetable scanning, allows for the creation of evolving sounds with dynamic timbral changes.
In addition to the basic waveforms, wave table synthesis can also utilize advanced techniques, such as formant synthesis and granular synthesis. Formant synthesis involves emphasizing specific frequency regions to simulate the resonant characteristics of the human voice or other musical instruments. Granular synthesis, on the other hand, involves dividing the waveforms into small, short-duration grains and recombining them to create new sounds.
Overall, wave table synthesis is a versatile and powerful tool in the realm of digital music synthesis. It allows for the creation of a wide range of sounds, from simple tones to complex and evolving timbres. With its ability to manipulate and combine waveforms in real-time, wave table synthesis offers endless possibilities for musicians and sound designers alike.
Generation of Wave Tables
In digital waveform synthesis, a wave table is a collection of precalculated values that represent a single cycle of a waveform. These wave tables are used by oscillators to generate musical tones and sounds in various types of synthesis, such as wavetable synthesis.
The generation of wave tables involves using algorithms to create a digital representation of different waveforms. These algorithms can be designed to mimic the behavior of analog electronic circuits or to generate unique and complex waveforms that are not easily achievable using analog methods.
One common technique for generating wave tables is through sampling. This involves capturing a sound using an audio recording and then breaking it down into small segments, called samples. Each sample represents the amplitude of the sound wave at a specific point in time.
Once the samples are obtained, they can be organized in a table format, with each sample being assigned to a specific position in the table. The table can then be accessed by a wave table oscillator, which reads the samples in sequence to generate the desired waveform.
Wave tables can also be generated using mathematical functions and algorithms, which can create complex waveforms with specific frequency and modulation characteristics. These algorithms can generate a wide range of waveforms, including classic waveforms such as sine, square, triangle, and sawtooth, as well as more unique and abstract waveforms.
Wave tables are a powerful tool in digital synthesis as they allow for precise control over the frequency, shape, and characteristics of the generated waveforms. They can also be used in conjunction with filters, modulation techniques, and formant shaping to further shape and sculpt the sound. With the advancement of digital music technology, wave table synthesis has become an integral part of modern music production and synthesis.
Playback and Manipulation of Wave Tables
Wave table synthesis is a powerful technique used in digital music production to create a wide range of sounds. It involves the manipulation and playback of wave tables, which are collections of carefully crafted waveforms. These waveforms can be combined and modulated to form complex sounds that can imitate real instruments or create entirely new sonic landscapes.
The manipulation of wave tables allows for the creation of unique sound textures and tones. One common technique is the use of formant tables, which contain specific frequency bands that can be used to shape the timbre of a sound. By modulating the playback speed and position within the wave table, musicians can create sweeping filter effects and dynamic changes in the sound.
Wave table synthesis also offers the ability to seamlessly transition between different waveforms, creating smooth and continuous changes in the sound. This is achieved by crossfading between adjacent waveforms in the table, creating a seamless blend of frequencies. This technique can be used to create evolving pads, dynamic textures, or realistic instrument articulations.
Another advantage of wave table synthesis is its efficient use of memory. Instead of storing individual samples for every frequency and pitch, wave tables store a single cycle of a waveform. This allows for more efficient memory usage while maintaining high-quality sound. Additionally, wave table synthesis benefits from advanced algorithms that can interpolate between waveforms, providing smooth transitions and avoiding artifacts.
With the advancements in digital technology, wave table synthesis has become a standard feature in many electronic musical instruments and software plugins. It offers a vast palette of sounds and textures, giving musicians and producers the ability to craft unique sonic landscapes. Whether it’s creating realistic instrument sounds, experimenting with abstract textures, or designing complex soundscapes, wave table synthesis provides endless possibilities for sound creation and manipulation in the world of music production.
Key Features of Wave Table Synthesis
Wave table synthesis is a digital musical technique that allows for the creation of complex sounds by manipulating and combining pre-recorded waveforms. It offers several key features that set it apart from other methods of synthesis.
1. Frequency Manipulation: Wave table synthesis allows for precise control over the frequency of the generated sound. By manipulating the playback rate of the stored waveforms, it is possible to create a wide range of tones and pitches.
2. Analog-like Waveforms: While wave table synthesis is inherently digital, it can produce waveforms that closely resemble those found in analog synthesis. This means that it can replicate the warm and rich tones typically associated with analog oscillators.
3. Waveform Selection and Cycling: Wave table synthesis provides the ability to select and cycle through different waveforms in real-time. This allows for dynamic variations in the sound and the creation of evolving timbres.
4. Filter and Modulation Options: Wave table synthesis offers various filter and modulation options to shape and modulate the generated waveforms. Filters can be used to alter the frequency content, while modulation can add movement and depth to the sound.
5. Formant and Sound Design: Wave table synthesis enables the creation of complex formant structures and detailed sound design. By combining multiple waveforms and applying modulation techniques, it is possible to create unique and expressive sounds.
6. Sampling and Instrument Replication: Wave table synthesis can sample real instruments and replicate their sounds. This makes it a powerful tool for recreating realistic instrument sounds in electronic music production.
Overall, wave table synthesis is a versatile and powerful technique that offers a wide range of possibilities in electronic music production and sound design. Its key features allow for precise control over frequencies, analog-like waveforms, waveform selection, filter and modulation options, formant and sound design, as well as sampling and instrument replication.
Dynamic Wave Table Scanning
Dynamic wave table scanning is a technique used in music synthesis and sound design that allows for the generation of complex and evolving waveforms. It involves the manipulation and interpolation of different waveforms stored in a wave table to create a rich and dynamic sound.
Wave tables are essentially collections of waveforms that are stored electronically or digitally. Each waveform represents a specific musical sound or frequency, and they can be of various types such as sine, square, or sawtooth waves. In dynamic wave table scanning, these waveforms are scanned or traversed in a non-linear or cyclical manner using an algorithm.
This scanning process allows for real-time manipulation and morphing of the waveforms. By modulating the scanning speed and direction, sound designers and musicians can create a wide range of timbres and textures in their musical compositions. It is a powerful technique that can give electronic instruments a more organic and expressive quality.
Dynamic wave table scanning can be used in both analog and digital synthesis. In analog synthesis, waveforms are typically stored in actual hardware wave tables, while in digital synthesis, they are stored in memory or on hard drives, allowing for greater flexibility and accessibility.
One of the key features of dynamic wave table scanning is its ability to create realistic and natural-sounding musical instruments. By carefully selecting and scanning different waveforms, it is possible to recreate the complex tonal characteristics of acoustic instruments, such as the formants of a human voice or the timbre of a violin.
In addition, dynamic wave table scanning can be combined with other synthesis techniques, such as filtering and modulation, to further shape and sculpt the sound. For example, by applying a low-pass filter to the scanned waveform, high-frequency content can be attenuated, resulting in a softer and more mellow sound.
In summary, dynamic wave table scanning is a powerful technique in music synthesis that allows for the creation of complex and evolving waveforms. It offers sound designers and musicians the ability to create a wide range of sounds and textures, and can be used to generate realistic and natural-sounding musical instruments.
Interpolation Techniques
In the realm of wave table synthesis, interpolation techniques play a crucial role in creating smooth and realistic waveforms. Interpolation refers to the process of estimating values between two known data points. It is an algorithmic method used to generate intermediate values based on the available data points.
Interpolation is particularly important for oscillators, which are the sound generators in wave table synthesis. Oscillators produce waveforms at different frequencies, which form the basis of the sound produced by a synthesizer or electronic musical instrument. To create a continuous and smooth waveform, interpolation is used to fill in the gaps between the sampled data points.
One common interpolation technique used in wave table synthesis is linear interpolation. This method calculates intermediate values by taking a weighted average of the surrounding data points. Linear interpolation provides a simple and efficient way to approximate the waveform between two adjacent samples. However, it can result in a loss of detail and introduce artifacts, especially when generating complex waveforms with fast frequency modulation or sharp changes in amplitude.
To address the limitations of linear interpolation, more advanced interpolation techniques have been developed. One such technique is cubic spline interpolation, which uses a mathematical curve-fitting approach. Cubic spline interpolation provides smoother and more accurate waveforms by using a higher-order polynomial function to estimate the intermediate values. This technique minimizes distortion and better captures the nuances of the original waveform.
Another important interpolation technique used in wave table synthesis is wavetable scanning. This method involves dynamically changing the playback speed and position within the wave table to create different timbral variations. By modulating the playback speed and applying interpolation algorithms, wavetable scanning allows for the creation of rich and evolving sounds. It can be used to simulate natural instrument sounds, such as the varying formants in a human voice or the timbral changes in a bowed string instrument.
In conclusion, interpolation techniques are essential in wave table synthesis as they enable the generation of smooth and realistic waveforms. They play a crucial role in creating the sound produced by oscillators, and different algorithms are used to interpolate the intermediate values between sampled data points. From linear interpolation to more advanced methods like cubic spline interpolation and wavetable scanning, these techniques contribute to the richness and complexity of electronic music.
Modulation and Filtering Capabilities
In wave table synthesis, modulation and filtering capabilities play a crucial role in shaping the waveform and creating unique musical sounds. Modulation refers to the process of altering the characteristics of a waveform over time, while filtering involves selectively attenuating or emphasizing specific frequencies within a sound.
Modulation techniques in wave table synthesis can include frequency modulation (FM), amplitude modulation (AM), and phase modulation (PM). These techniques allow for the creation of complex harmonic and timbral variations, adding depth and richness to the sound produced by the synthesizer.
Filters, on the other hand, are used to sculpt the frequency content of a waveform. They can be analog or digital, and they help to shape the overall tonal quality of the sound. Common types of filters used in wave table synthesis include low-pass, high-pass, band-pass, and notch filters.
One unique filtering technique used in wave table synthesis is formant filtering. Formants are resonant frequencies that give different musical instruments their characteristic timbre or “color.” By manipulating and emphasizing specific formants, wave table synthesizers can create sounds that resemble real instruments or generate entirely new and unique timbres.
Another powerful feature of wave table synthesis is the ability to modulate the wave table itself. By varying the position within the wave table, the sound produced by the oscillator can be continuously altered. This creates dynamic and evolving sounds that can mimic complex acoustic phenomena or generate otherworldly textures.
Overall, the modulation and filtering capabilities of wave table synthesis provide musicians with a wide range of possibilities for sound design and musical expression. Whether recreating traditional instruments or exploring new sonic territories, wave table synthesis offers a versatile and powerful tool for electronic music production.
Applications of Wave Table Synthesis
Wave table synthesis is a versatile digital synthesis technique that can be applied in various musical instruments and devices. It offers a wide range of applications in the world of music production, thanks to its ability to generate and manipulate complex waveforms.
One common application of wave table synthesis is in the creation of digital oscillators. By using a table of pre-recorded waveforms, these oscillators can produce a variety of unique and intricate sounds. This allows musicians and sound designers to explore new sonic possibilities and create rich and textured music.
Wave table synthesis is also used in the development of electronic musical instruments such as synthesizers. By utilizing this technique, these instruments can generate a wide range of waveforms, including traditional analog sounds as well as more complex and futuristic tones. This enables musicians to experiment with different timbres and create unique musical compositions.
In addition to creating and manipulating waveforms, wave table synthesis can also be used for audio processing. By applying filters, modulation techniques, and other algorithms to the wave table data, it is possible to shape and modulate the sound in various ways. This allows for the creation of dynamic and expressive musical performances.
Another application of wave table synthesis is in the field of formant synthesis. By using wave tables that contain vocal formants, it is possible to produce realistic and expressive vocal sounds. This technique is often used in electronic music production and sound design to create artificial voices and vocal effects.
Overall, wave table synthesis is a powerful and flexible tool in the world of digital music production. Its ability to generate and manipulate complex waveforms opens up a world of creative possibilities for musicians, sound designers, and electronic music enthusiasts. Whether it is used in synthesizers, samplers, or other musical devices, wave table synthesis offers a unique and innovative approach to sound generation and manipulation.
Music Production
Music production is the process of creating and recording music using a variety of techniques and instruments. In the world of electronic music, producers often rely on technological tools such as samplers and synthesizers to create their desired sounds.
One important aspect of music production is synthesis. Synthesis involves generating sounds using electronic instruments, known as synthesizers. These instruments use different techniques, such as waveform oscillators and modulation, to create a wide range of sounds.
One popular form of synthesis is wave table synthesis. This technique involves using a wave table, which is a collection of pre-recorded waveforms that can be manipulated and combined to create unique sounds. Wave table synthesis allows producers to experiment with different waveforms and create complex and evolving sounds.
In addition to synthesis, producers often use filters to shape the frequency content of their sounds. Filters can be used to remove unwanted frequencies or emphasize certain frequencies, allowing producers to sculpt the sound and create a specific formant or timbre.
Another important aspect of music production is sampling. Sampling involves taking snippets of existing music or sound recordings and incorporating them into new compositions. Producers can manipulate and transform these samples using algorithms and effects to create unique and interesting musical elements.
Music production can be done in both analog and digital domains. Analog production involves using hardware instruments and equipment, while digital production relies on software-based tools and virtual instruments. Both approaches have their advantages and can be used to create high-quality music.
Overall, music production is a creative and technical process that combines elements of art and science. It allows producers to harness the power of technology to create innovative and captivating music.
Sound Design
Sound design is an essential aspect of music production and synthesis. It involves creating and manipulating sounds using various techniques and tools. One important element of sound design is formant synthesis, which focuses on controlling the resonant frequencies of a sound to create unique timbres and textures. This technique is commonly used in vocal synthesis and is achieved through manipulating filter settings.
Digital oscillators are another fundamental tool in sound design. These electronic devices generate various waveforms, such as sine, square, triangle, and sawtooth waves, at different frequencies. By modulating these oscillators, sound designers can create complex and evolving sounds that add movement and interest to their musical compositions.
Analog and digital modulation techniques are widely used in sound design to add depth and character to sounds. Modulation involves altering the frequency, amplitude, or phase of a waveform using an external signal or modulation source. By applying modulation to different parameters of a sound, sound designers can create evolving textures and dynamic movement.
Sampling is a popular technique in sound design, where snippets of recorded audio are used as the basis for creating new sounds. By manipulating and processing the sampled audio, sound designers can create unique and interesting timbres that add depth and richness to their compositions.
Synthesis is a key component of sound design, involving the creation of new sounds using electronic instruments or software. Various synthesis techniques, such as subtractive synthesis, granular synthesis, and additive synthesis, allow sound designers to shape and sculpt sound waves to create unique and expressive musical elements.
The use of algorithms in sound design has revolutionized the field, enabling sound designers to create complex and intricate sounds using mathematical equations and patterns. Algorithmic synthesis allows for the generation of highly detailed and evolving sounds that would be practically impossible to create manually.
Filters are essential in sound design, as they allow for the shaping and sculpting of sound waves by selectively attenuating or boosting specific frequencies. By adjusting the cutoff frequency and resonance settings of a filter, sound designers can create a wide range of timbres and textures, adding depth and character to their compositions.
Wave table synthesis is a powerful technique in sound design that involves the use of pre-recorded waveforms, or wave tables, to create new sounds. By combining different wave tables and modulating their playback parameters, sound designers can create dynamic and evolving sounds that add interest and movement to their musical compositions.
In conclusion, sound design is a creative process that involves the manipulation and creation of sounds using various techniques and tools. Whether it’s through synthesis, sampling, modulation, or filtering, sound designers have a wide range of options to explore and experiment with, allowing them to create unique and expressive musical elements.
Virtual Instrument Development
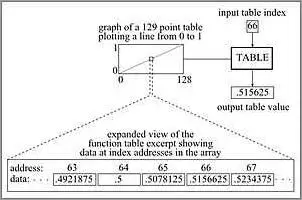
The development of virtual instruments has revolutionized the way musical instruments are created and played. Instead of relying on physical components like oscillators and filters found in traditional analog instruments, virtual instruments use software algorithms to generate and manipulate sounds.
The heart of a virtual instrument is the oscillator. This electronic generator produces waveforms with different shapes, such as sine, square, or sawtooth. These waveforms form the basis of the sound produced by the instrument. Virtual instruments have the advantage of being able to generate an unlimited number of oscillators, allowing for complex and layered sounds.
In addition to oscillators, virtual instruments often include filters. These filters shape the sound by manipulating the frequency content of the waveform. There are various types of filters, such as low-pass, high-pass, and band-pass filters, which can be used to achieve different effects and timbres.
One popular technique used in virtual instrument development is wave table synthesis. This technique involves using pre-recorded samples of real instruments or sounds and manipulating them using mathematical algorithms. This allows for realistic and expressive instrument emulation.
Another important aspect of virtual instrument development is modulation. Modulation techniques, such as amplitude modulation (AM) or frequency modulation (FM), can be used to add movement and dynamics to the sound. By modulating parameters such as volume, pitch, or filter cutoff, virtual instruments can create a wide range of expressive and evolving sounds.
Virtual instrument development also includes the creation of formant synthesis. Formants are harmonic peaks in the frequency spectrum of a sound. By manipulating these formants, virtual instruments can create sounds that resemble the human voice or various acoustic instruments.
Virtual instruments can be either digital or analog. Digital virtual instruments rely on software algorithms to generate and manipulate sounds, while analog virtual instruments use physical components to create and shape the sound. Both types have their own unique advantages and characteristics, allowing for a wide range of sonic possibilities.
In conclusion, virtual instrument development utilizes complex algorithms and techniques to create and manipulate sounds. From oscillators and filters to wave table synthesis and modulation, these instruments offer a vast palette of sounds for musicians and producers to explore and create with.
FAQ about topic “Introduction to Wave Table Synthesis: Understanding its Mechanism and Essential Features”
What is wave table synthesis?
Wave table synthesis is a type of sound synthesis that uses a collection of pre-recorded waveforms, called wave tables, to generate sound. These wave tables contain short audio snippets that can be played back at different speeds and pitches to create complex and evolving sounds.
How does wave table synthesis work?
Wave table synthesis works by cycling through a series of wave tables at a specific rate, known as the wavetable position. Each wave table contains a set of single-cycle waveforms, which are played back sequentially. By manipulating the wavetable position and applying various modulation techniques, such as frequency modulation and amplitude modulation, different timbres and textures can be achieved.
What types of sounds can be created with wave table synthesis?
Wave table synthesis is capable of producing a wide range of sounds, from realistic instrument sounds to abstract and futuristic textures. By manipulating the wavetable position, modulation parameters, and other synthesis parameters, it is possible to create digital versions of traditional instruments, as well as unique and otherworldly sounds that are not possible with traditional synthesis methods.


