
When it comes to choosing a RAID configuration for data protection, there are many factors to consider. Two popular options are RAID 1 and RAID 10. Each of these arrays offers different levels of performance, data backup, security, redundancy, and mirroring.
RAID 1, also known as disk mirroring, is a configuration that involves duplicating data across multiple drives. This provides excellent data protection, as the information is stored on two or more drives simultaneously. In the event of a drive failure, the data is still available on the remaining drives, ensuring reliability and redundancy. However, RAID 1 does not provide the same capacity as other configurations, as half of the storage is used for mirroring.
On the other hand, RAID 10 combines the benefits of RAID 1 and RAID 0 (disk striping). This configuration involves mirroring two separate RAID 0 arrays, providing both data redundancy and improved performance. RAID 10 offers the best of both worlds, with fast read and write speeds, high reliability, and excellent data protection. However, it requires a larger number of drives to implement, making it more expensive in terms of cost per gigabyte.
In summary, RAID 1 is a great choice for small-scale data protection, ensuring reliability and redundancy, but at the cost of reduced capacity. RAID 10, on the other hand, provides both high performance and data protection, making it suitable for larger-scale storage needs. Ultimately, the choice between these RAID configurations depends on the specific needs and requirements of the user.
Contents
- 1 Overview
- 2 Raid 1: Mirroring for Data Redundancy
- 3 Raid 10: Combining Mirroring and Striping
- 4 FAQ about topic “Raid 1 vs Raid 10: Which RAID Configuration is Best for Data Protection?”
- 5 What is RAID 1?
- 6 What is RAID 10?
- 7 Which RAID configuration provides better data protection?
- 8 Which RAID configuration offers better performance?
- 9 Can RAID 10 be considered as a backup solution?
Overview
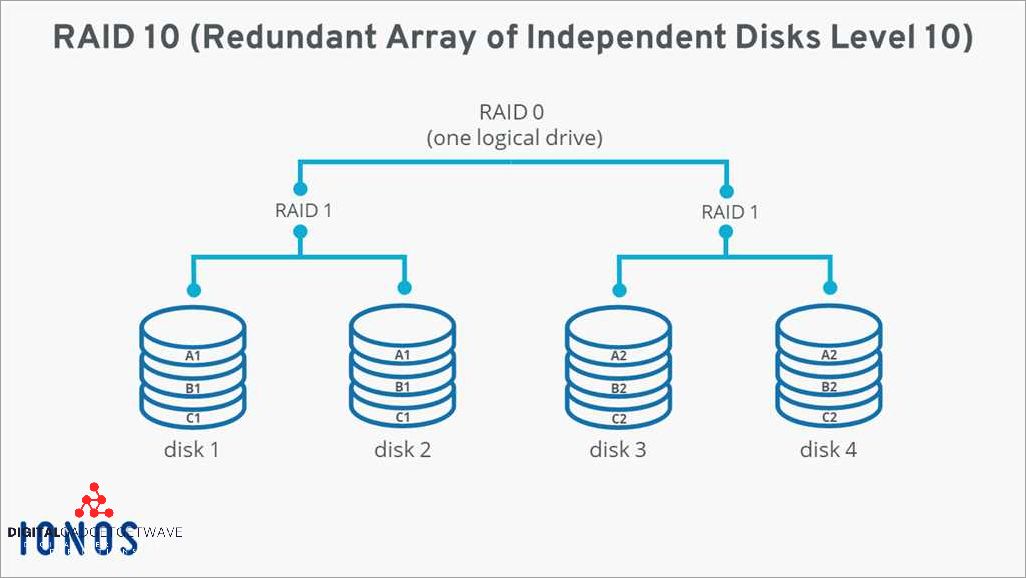
The choice between RAID 1 and RAID 10 configuration is crucial for data protection and storage. Both RAID levels provide mirroring and redundancy to ensure the safety and accessibility of data. However, there are differences in terms of fault tolerance, performance, security, and capacity.
In RAID 1, also known as mirroring, two drives are used to store identical copies of data. This level offers excellent reliability and fault tolerance as the data remains accessible even if one drive fails. However, RAID 1 has the trade-off of reduced storage capacity since half of the drives are used for mirroring.
Raid 10, on the other hand, combines the benefits of RAID 1 and RAID 0 (striping). It uses at least four drives and is formed by mirroring two RAID 1 arrays. The data is striped across the mirrored pairs, providing both redundancy and improved performance. Raid 10 offers high fault tolerance and performance, but also requires more drives.
When it comes to data security, both RAID 1 and RAID 10 provide excellent protection against drive failures. In the event of a drive failure, the remaining drives in the array can continue operating without any loss of data or service interruption.
Overall, RAID 1 is a good option for those primarily concerned with data redundancy and maximum fault tolerance, especially for smaller storage capacities. RAID 10, on the other hand, is more suitable for users who require a balance between performance, capacity, and reliability.
Understanding RAID and its Importance for Data Storage
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a technology that combines multiple physical drives into a single logical unit to enhance the security, performance, and reliability of data storage systems. RAID configurations, such as RAID 1 and RAID 10, play a vital role in ensuring data integrity and protection against drive failures.
RAID 1, also known as mirroring, involves the duplication of data on two separate drives. This redundancy provides enhanced security and fault-tolerance since if one drive fails, the data is still accessible on the other drive. However, RAID 1 has a significant drawback in terms of capacity utilization, as it requires the use of twice as many drives as the desired storage capacity.
On the other hand, RAID 10, also known as RAID 1+0, combines the benefits of RAID 1 and RAID 0 (striping) to achieve both redundancy and performance improvements. RAID 10 involves the creation of mirrored pairs, with each pair being striped to enhance read and write speeds. This configuration offers a higher level of fault-tolerance as it can withstand the failure of multiple drives within each mirrored pair.
In terms of data storage capacity, RAID 1 is more efficient as it utilizes only 50% of the total drive capacity for redundancy. In contrast, RAID 10 requires at least four drives and utilizes only 50% of the total capacity for mirroring and striping, resulting in higher storage overhead.
When it comes to performance, RAID 10 shines due to its striping feature, which allows simultaneous read and write operations across multiple drives. This striping improves I/O speed, making it optimal for applications that require high-performance data access.
Choosing the best RAID configuration depends on the specific requirements of your data storage needs. RAID 1 is ideal for applications that prioritize data security and require minimal capacity. On the other hand, RAID 10 is suitable for applications that demand both redundancy and performance, even at the cost of higher storage overhead.
In summary, RAID configurations play a crucial role in data storage by providing security, fault-tolerance, redundancy, and improved performance. Whether you choose RAID 1 or RAID 10, it is essential to weigh the trade-offs between capacity utilization and performance to make an informed decision that suits your specific needs.
Importance of Data Protection in Modern Computing
In the modern computing era, data protection is of utmost importance. With the ever-increasing reliance on digital storage and the growth of big data, ensuring the safety and integrity of data has become a critical task for businesses and individuals alike.
One of the key aspects of data protection is ensuring the availability and reliability of data. This is where RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) configurations come into play. RAID is a data storage technique that combines multiple physical drives into a single logical unit, providing enhanced fault-tolerance, capacity, and performance.
Raid 1 and Raid 10 are two common RAID configurations used for data protection. Raid 1, also known as disk mirroring, involves creating an exact copy of data on two or more drives. This redundancy ensures that if one drive fails, the data is still accessible from the other drive. It provides a high level of reliability and data redundancy.
Raid 10, on the other hand, combines the features of Raid 1 and Raid 0. It involves mirroring data across multiple pairs of drives and striping data across those mirrored pairs. This configuration offers both fault-tolerance and improved performance. Even if one drive in a pair fails, the data can still be accessed from the mirrored drive, providing a higher level of data redundancy and availability.
Another important aspect of data protection is data backup. While RAID configurations offer a level of redundancy and fault-tolerance, they are not a substitute for regular backups. Backing up data to external storage or cloud services ensures that even in the event of a catastrophic failure or data corruption, a recent copy of the data is available for recovery.
In conclusion, data protection is crucial in modern computing. RAID configurations like Raid 1 and Raid 10 provide improved fault-tolerance, capacity, performance, and redundancy. However, it is important to remember that RAID is not a substitute for regular backup practices. Employing both RAID configurations and regular backup strategies ensures comprehensive data protection and reduces the risk of data loss, improving the overall security and integrity of stored data.
Raid 1: Mirroring for Data Redundancy
Raid 1 is a RAID configuration that focuses on data redundancy and reliability. It is achieved through the process of mirroring. In a Raid 1 setup, data is duplicated across a pair of drives, creating an exact copy or mirror of the data on both drives. This redundant setup provides a high level of data protection, making it an ideal choice for critical systems or environments where data loss is unacceptable.
The mirroring process in Raid 1 involves writing the same data to two separate drives simultaneously. This ensures that if one drive fails, the other drive contains an exact copy, allowing for seamless access to the data and minimizing downtime. The mirrored drives work in parallel, meaning that performance is not improved compared to a single drive setup. However, the redundancy of the Raid 1 configuration provides great peace of mind, knowing that data is safe even in the event of drive failure.
One of the advantages of Raid 1 is its simplicity. Since the data is duplicated across drives, there is no complex striping or parity calculations involved. This makes the setup process straightforward and easy to understand. Additionally, the mirroring technique provides excellent fault-tolerance, as it allows for immediate failover to the unaffected drive in case of drive failure.
Raid 1 is often used for applications that require high data reliability, such as storage systems for critical files or backup servers. It provides a strong level of data security and redundancy, ensuring that even in the case of a drive failure, the data remains accessible and intact. While Raid 1 does not offer the same capacity or performance benefits as Raid 10, its focus on data redundancy and reliability makes it a valuable choice for data protection.
What is RAID 1 and How Does it Work?
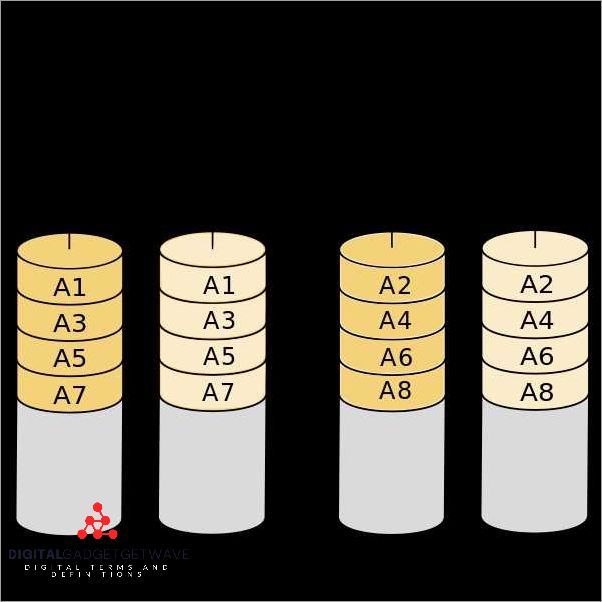
RAID 1, also known as disk mirroring, is a popular RAID configuration that provides fault-tolerance and data protection. In RAID 1, data is duplicated on multiple drives to ensure redundancy and prevent data loss.
The basic idea behind RAID 1 is to create an exact copy, or mirror, of the data on two or more drives. This means that if one drive fails, the data can still be accessed and retrieved from the mirrored drive. RAID 1 offers a high level of reliability and ensures that even if one drive fails, the system can continue to operate with minimal interruption.
In a RAID 1 configuration, each drive in the array contains the same data. Every piece of data is written to both drives simultaneously, creating an identical copy. This mirroring process provides excellent data security and backup since all the data is stored in duplicate. If one drive becomes unavailable, the system can immediately switch to the other drive without any interruption or loss of data.
In terms of performance, RAID 1 does not offer any performance benefits like RAID 10, which uses striping and parity for improved performance. However, RAID 1 does provide faster read speeds because data can be read from multiple drives simultaneously. Write speeds, on the other hand, are slower as data must be written to both drives at the same time.
When it comes to storage capacity, RAID 1 does not provide as much capacity as RAID 10. In RAID 1, the total capacity of the array is equal to the capacity of a single drive. For example, if you have two 1TB drives in a RAID 1 array, the total usable capacity will be 1TB. This is because the data is mirrored on both drives, resulting in a redundancy factor of 1:1.
In summary, RAID 1 offers excellent data reliability, capacity, and security through disk mirroring. While it may not provide the same performance benefits as RAID 10, RAID 1 is a solid choice for users who prioritize data protection and fault-tolerance over performance.
Advantages of Raid 1 for Data Protection
Raid 1, also known as mirroring, is a popular RAID configuration for data protection. It provides fault-tolerance by creating an exact copy of data on two or more drives. This means that if one drive fails, the other drives in the array can still provide the necessary backup.
The main advantage of Raid 1 is its high level of data security. With each drive mirroring the other, there is redundancy in the storage array. This redundancy ensures that even if one drive fails, the data remains intact on the other drive.
In terms of capacity, Raid 1 offers less storage capacity compared to Raid 10. This is because the capacity is limited to the size of a single drive. However, this limitation is offset by the reliability and data protection that Raid 1 provides.
Another advantage of Raid 1 is its simplicity. It is easy to set up and maintain, making it an ideal choice for individuals or small businesses with limited technical expertise. Additionally, Raid 1 does not require any special hardware or software, making it cost-effective.
Raid 1 also offers good performance for read operations as data can be read simultaneously from multiple drives. However, write performance may be slightly slower compared to Raid 10 due to the need to write data to multiple drives simultaneously.
In conclusion, Raid 1 provides a reliable and secure data protection solution with its fault-tolerance, mirroring, and redundancy features. While it may have limitations in terms of storage capacity and write performance compared to Raid 10, it offers simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and good read performance.
Limitations and Considerations of Raid 1
Raid 1, also known as mirroring, is a popular RAID configuration that provides a high level of data redundancy and fault-tolerance. However, it also has some limitations and considerations that need to be taken into account when choosing this RAID array option for data protection.
1. Reduced capacity: One of the main limitations of Raid 1 is the reduced capacity compared to other RAID configurations like Raid 10. In Raid 1, the capacity of the array is limited to the size of a single drive since data is mirrored on each drive. This means that if you have two 1TB drives in a Raid 1 array, you will only have 1TB of usable storage capacity.
2. Lower performance: While Raid 1 offers high data redundancy and reliability, it may not provide the same level of performance as other RAID configurations like Raid 10. This is because Raid 1 does not offer the striping feature that allows data to be split across multiple drives for improved read and write speeds.
3. No parity or backup: Another limitation of Raid 1 is that it does not provide any parity or backup capabilities. In case of a drive failure, the mirrored drive can take over seamlessly, but there is no protection against data corruption or accidental deletion. This means that if data is corrupted or deleted on one drive, it will be replicated on the other drive as well.
4. Limited security: Raid 1 does not offer any additional security features beyond mirroring. While it can protect against drive failures and ensure data availability, it does not provide any measures for data protection against unauthorized access or data breaches.
5. Higher cost: Raid 1 requires the use of multiple drives in a mirrored setup, which can result in higher costs compared to other RAID configurations that offer similar levels of data protection. The cost of purchasing and maintaining additional drives should be considered when choosing Raid 1.
In conclusion, while Raid 1 offers a high level of data redundancy and fault-tolerance, it does have limitations in terms of capacity, performance, backup, security, and cost. It is important to consider these factors and evaluate the specific requirements of your data protection needs before choosing Raid 1 or considering alternatives like Raid 10.
Raid 10: Combining Mirroring and Striping
Raid 10, also known as RAID 1+0, is a combination of mirroring and striping techniques to provide enhanced data protection and performance. It combines the best features of RAID 1 and RAID 0 to deliver a robust and efficient storage solution.
In a RAID 10 configuration, multiple drives are used, usually in pairs. The data is mirrored across these drives, providing redundancy and reliability. Additionally, the data is striped, which means it is divided into blocks and distributed across the mirrored drives. This striping technique enhances the performance of the storage system.
The combination of mirroring and striping in RAID 10 offers several benefits. Firstly, it provides excellent fault tolerance. If one drive fails, the mirrored copy ensures that the data remains accessible without interruption. This redundancy ensures high levels of data availability and minimizes the risk of data loss.
Furthermore, RAID 10 offers improved performance compared to other RAID configurations. The striping technique distributes data across multiple drives, allowing for simultaneous read and write operations. This parallelism enhances the overall performance of the storage system, making it ideal for applications requiring high I/O operations.
Raid 10 also provides enhanced security for stored data. The mirroring feature ensures that data is duplicated and stored on separate drives. In case of a drive failure or data corruption, the mirrored copy can be used to restore the data, reducing the risk of permanent data loss.
In summary, RAID 10 is an excellent choice for data protection, combining the benefits of mirroring and striping. It offers increased capacity, improved performance, fault-tolerance, and security. The redundancy provided by mirroring ensures data reliability, while the striping enhances storage system performance. Whether for backup, data storage, or high-performance applications, RAID 10 is a reliable configuration for data protection.
Explaining the Concept of RAID 10
RAID 10, also known as RAID 1+0 or mirrored stripes, is a RAID configuration that combines the features of RAID 1 and RAID 0 to provide both data protection and performance.
In RAID 10, the drives are divided into multiple pairs, wherein each pair has a mirrored copy of the same data. This mirroring ensures redundancy and fault-tolerance, as if one drive fails, the other drive in the mirrored pair can continue to function without any data loss.
To further enhance the performance, the mirrored pairs are then striped together into a RAID 0 array. This striping allows for data to be split across multiple drives simultaneously, increasing the read and write speeds. It also provides a higher storage capacity as the total capacity is the sum of all the drives in the array.
The combination of mirroring and striping in RAID 10 offers both data protection and performance benefits. The mirroring provides redundancy and security against drive failures, ensuring that data is always available even in the event of a drive failure. The striping enhances the read and write speeds, allowing for faster data access and improved overall performance.
RAID 10 is commonly used for applications that require high levels of both data security and performance, such as databases, file servers, and virtualization environments. Its reliability, fault tolerance, and capacity make it an ideal choice for businesses that prioritize data protection and need fast and efficient access to their data.
Benefits of RAID 10 for Data Protection
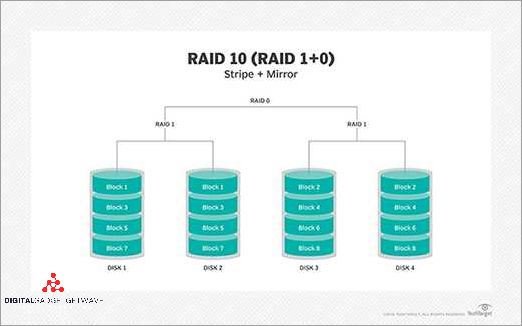
RAID 10, also known as RAID 1+0, combines the benefits of striping and mirroring to provide enhanced data protection. This configuration offers improved fault-tolerance and reliability compared to other RAID levels.
One of the key advantages of RAID 10 is its high level of redundancy. By mirroring data across multiple drives, RAID 10 ensures that if one drive fails, the data can be easily rebuilt from the other mirrored drive. This redundancy minimizes the risk of data loss and provides a reliable backup system.
With RAID 10, the data is striped across multiple drives, which enhances performance. This striping technique allows for faster data access and read/write speeds compared to other RAID configurations. By distributing the workload across multiple drives, RAID 10 improves overall system performance.
In terms of capacity, RAID 10 offers a good balance. The usable capacity of a RAID 10 array is approximately half of the total capacity of the drives in the array. However, this reduction in capacity is offset by the enhanced data protection and performance benefits provided by RAID 10.
Another advantage of RAID 10 is its simplicity. Unlike other RAID configurations that involve complex calculations for parity data, RAID 10 does not require parity calculations. This simplicity makes RAID 10 easier to manage and maintain.
In summary, RAID 10 provides several benefits for data protection. Its combination of striping and mirroring offers fault-tolerance, reliability, and redundancy. Additionally, RAID 10 improves system performance and is relatively simple to manage. These advantages make RAID 10 a popular choice for organizations seeking robust data protection.
Considerations and Drawbacks of Raid 10
When considering the best RAID configuration for data protection, Raid 10 has several considerations and drawbacks that should be taken into account.
1. Capacity Efficiency: Raid 10 is not as efficient in terms of capacity compared to Raid 1. This is because Raid 10 requires a minimum of four drives to operate, and half of the total drives in the array are used for mirroring. Therefore, if your goal is to maximize storage capacity, Raid 10 may not be the best choice.
2. Performance Impact: While Raid 10 offers improved read and write performance compared to Raid 1, it may not be as performant as other RAID configurations, such as Raid 0. This is because Raid 10 involves both striping and mirroring, which adds some overhead to the data access process.
3. Cost: Implementing Raid 10 requires a minimum of four drives, which can make it a more expensive option compared to Raid 1. Additionally, since half of the drives are used for mirroring, the cost per unit of usable storage capacity is increased.
4. Backup and Redundancy: While Raid 10 provides redundancy and fault-tolerance, it is not a substitute for regular data backup. In the event of multiple drive failures or other catastrophic events, data loss can still occur. Therefore, it is important to have a proper backup solution in place to ensure data integrity.
5. Security: Raid 10 does not provide any additional security features compared to Raid 1. It is primarily focused on data protection and fault-tolerance but does not offer advanced security capabilities such as encryption or access controls. Therefore, if data security is a priority, additional measures should be implemented.
In conclusion, Raid 10 offers a good balance between performance, redundancy, and fault-tolerance. However, it is important to consider the capacity efficiency, performance impact, cost, backup and redundancy requirements, and overall security needs before deciding on the best RAID configuration for data protection.
Comparing Raid 1 and Raid 10 for Data Protection
When it comes to data protection, two RAID configurations that are often compared are RAID 1 and RAID 10. Both configurations offer different levels of performance, storage capacity, redundancy, and security.
Raid 1, also known as disk mirroring, creates an exact copy of data on two or more drives. This ensures that even if one drive fails, the data can still be accessed from the remaining drives, providing a high level of fault-tolerance. However, the capacity of the RAID array is limited to the size of a single drive, as each drive in the array holds a duplicate copy of the data.
Raid 10, on the other hand, combines the features of both Raid 0 and Raid 1. It requires a minimum of four drives and provides both striping and mirroring. The data is striped across multiple drives, improving performance, while also being mirrored to provide redundancy. Raid 10 offers higher capacity compared to Raid 1, as it combines the capacity of multiple drives.
When it comes to reliability, Raid 1 is considered to be more reliable as it provides an exact copy of data on each drive. In the event of a drive failure, the mirrored drive can immediately take over, minimizing downtime and ensuring data integrity. Raid 10, while still offering redundancy, relies on striping and parity for data protection, which can be more complex and potentially prone to errors.
While both Raid 1 and Raid 10 offer data protection, the choice between them depends on specific requirements. If performance is a priority and capacity can be sacrificed, Raid 10 is a suitable choice. On the other hand, if data redundancy and reliability are the main concerns, Raid 1 is a more appropriate option. It is also worth noting that Raid 10 requires a minimum of four drives, while Raid 1 can be implemented with just two drives.
In conclusion, Raid 1 and Raid 10 are both viable options for data protection, with their own strengths and limitations. Understanding the differences and evaluating specific needs can help in making the right choice for ensuring the safety and integrity of data.
Which RAID Configuration is Better for Your Needs?
When it comes to data protection, deciding on the best RAID configuration for your needs can be a challenge. Two popular options are RAID 1 and RAID 10, each with its own advantages and considerations.
RAID 1:
In a RAID 1 configuration, also known as mirroring, data is duplicated across two drives. This offers a high level of fault-tolerance, as if one drive fails, the other drive contains an exact copy of the data. RAID 1 provides excellent data reliability and security, as both drives have identical information.
However, RAID 1 also has some drawbacks. One is that it requires double the storage capacity, as each drive must store the same data. This can be costly if you need a large amount of storage. Additionally, while RAID 1 offers redundancy and data protection, it does not provide the same performance benefits as other RAID configurations.
RAID 10:
RAID 10 combines the benefits of both RAID 1 and RAID 0 (striping with parity). It utilizes a minimum of four drives, where data is mirrored across two sets of drives, and then these sets are striped for improved performance. RAID 10 offers both redundancy and performance, making it a suitable choice for those who require both high fault-tolerance and speed.
One of the advantages of RAID 10 is that it offers better performance compared to RAID 1. This is because data can be accessed from multiple drives simultaneously, resulting in faster read and write speeds. However, RAID 10 does require more drives compared to RAID 1, which may increase the overall cost and complexity of the array.
In conclusion, the best RAID configuration for your needs depends on your specific requirements. If data reliability and security are paramount, RAID 1 may be the better choice. On the other hand, if you need a balance of redundancy and performance, RAID 10 may be more suitable. Assess your storage capacity, performance needs, and budget to determine which RAID configuration is the right fit for you.
Final Thoughts on Data Protection and Raid Configurations
When it comes to data protection and choosing the right RAID configuration, there are several important factors to consider. RAID is a technology that provides redundancy and fault tolerance by combining multiple drives into a single storage array.
Raid 10, also known as RAID 1+0, offers both mirroring and striping. It is considered to be the most fault-tolerant RAID level, as it combines the advantages of RAID 1 and RAID 0. With Raid 10, data is mirrored across multiple drives, ensuring that if one drive fails, the data can still be accessed from the other mirrored drives. This provides an extra layer of protection against drive failure and data loss.
On the other hand, Raid 1, also known as mirroring, duplicates data onto multiple drives. While it offers the highest level of redundancy, it has a lower capacity compared to Raid 10. Since data is mirrored, Raid 1 requires twice the amount of storage space. However, it provides a higher level of reliability and can sustain multiple drive failures without losing data.
When considering performance, Raid 10 outperforms Raid 1. Since data is both mirrored and striped, Raid 10 offers higher read and write speeds compared to Raid 1. This makes it a better choice for applications or systems that require fast data access and high-performance.
While both Raid 1 and Raid 10 provide data redundancy and fault-tolerance, it is important to note that RAID is not a substitute for regular backups. RAID protects against drive failures, but it does not protect against other types of data loss such as accidental deletion, file corruption, or physical damage to the entire storage array. Therefore, it is crucial to have a separate backup strategy in place to ensure the safety and recoverability of important data.
In conclusion, when it comes to data protection, both Raid 1 and Raid 10 have their own advantages and limitations. If storage capacity and cost are not a major concern, Raid 10 provides the highest level of data protection and performance. However, if budget and capacity are a consideration, Raid 1 can still offer a reliable and resilient solution. Additionally, it is important to have a regular backup strategy regardless of the RAID configuration chosen, to safeguard data from other potential risks.
FAQ about topic “Raid 1 vs Raid 10: Which RAID Configuration is Best for Data Protection?”
What is RAID 1?
RAID 1, also known as mirroring, is a RAID configuration that duplicates data across two or more drives. This ensures that if one drive fails, the data can be accessed from the remaining drive(s).
What is RAID 10?
RAID 10, also known as RAID 1+0, combines RAID 1 and RAID 0. It mirrors the data across multiple drives, like RAID 1, and then stripes the mirrored sets, like RAID 0. This provides both data redundancy and improved performance.
Which RAID configuration provides better data protection?
Both RAID 1 and RAID 10 provide data protection, but RAID 10 offers better protection due to its combination of mirroring and striping. In RAID 10, even if one drive fails, the remaining drives can still maintain the redundancy and ensure data integrity.
Which RAID configuration offers better performance?
RAID 10 generally offers better performance compared to RAID 1. This is because RAID 10 combines the striping of RAID 0, which improves read and write speeds, with the redundancy of RAID 1. However, the performance improvement may vary depending on the number of drives and the specific workload.
Can RAID 10 be considered as a backup solution?
No, RAID 10 should not be considered a backup solution. While it provides data redundancy and can protect against drive failure, it does not protect against other forms of data loss such as accidental deletion, data corruption, or natural disasters. It is always recommended to have a separate backup system in place, even when using RAID 10.


