
Digitalization has revolutionized the industrial sector, enabling more efficient and precise control over various processes. Industrial control systems play a vital role in this digital transformation, ensuring seamless communication and data management between different components. Two key automation solutions commonly used in industrial applications are Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) and Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs).
RTUs and PLCs serve as the central control units in an industrial control system, but they have distinct differences in terms of functionality and communication protocols. PLCs are digital devices designed to control and monitor specific processes. They utilize a specialized programming language to execute commands and perform calculations. RTUs, on the other hand, are analog devices that acquire data from field devices and transmit it to a central control system.
Communication plays a crucial role in industrial control systems, and both RTUs and PLCs support various protocols for efficient data exchange. PLCs often use protocols such as Modbus or Ethernet for communication with other devices within the network. RTUs, on the other hand, commonly support wireless communication protocols like GSM or Ethernet for remote monitoring and control.
When it comes to choosing the right automation solution for a particular application, several factors need to be considered. The choice between an RTU and a PLC depends on the specific requirements of the industrial process, such as the type of control needed, the complexity of the system, and the availability of communication infrastructure. Additionally, the integration with other components, such as SCADA systems or gateways, should also be taken into account.
Contents
- 1 Key Differences between RTU and PLC
- 2 Factors to Consider when Choosing between RTU and PLC
- 3 Real-World Examples of RTU and PLC Applications
- 4 Making the Right Choice: RTU or PLC?
- 5 FAQ about topic “RTU vs PLC: Understanding the Difference and Choosing the Right Automation Solution”
- 6 What is the difference between RTU and PLC?
- 7 Can I use a PLC instead of an RTU?
- 8 What are the advantages of using an RTU over a PLC?
- 9 What are the advantages of using a PLC over an RTU?
- 10 Which automation solution is better for my application: RTU or PLC?
Key Differences between RTU and PLC

1. Ethernet Communication: One of the major differences between RTU and PLC is the type of communication used. RTUs typically use Ethernet for communication, allowing for faster and more reliable data transfer between devices in the field and the central control system.
2. Device and Data Handling: RTUs are primarily designed for handling data from various devices in the field, such as sensors and actuators. They typically have a higher capacity for handling a large number of devices and data points compared to PLCs.
3. Control System Integration: PLCs, on the other hand, are specifically designed for industrial control systems. They excel at tasks such as process control, automation, and sequential control. PLCs are often utilized in manufacturing and production environments.
4. Modbus Protocol: RTUs commonly use the Modbus protocol for communication with other devices and systems. This protocol allows for the transfer of both digital and analog data, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
5. SCADA Compatibility: RTUs are commonly used in SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems. They act as a gateway between the field devices and the SCADA system, collecting and transmitting data for monitoring and control.
6. Industrial Network Integration: RTUs are designed to integrate into industrial networks, providing connectivity to various devices and systems. They often serve as a bridge between different protocols and communication standards.
7. Automation Capability: PLCs are known for their advanced automation capabilities. They can perform complex logical and mathematical operations, making them suitable for demanding control and automation tasks.
8. Digital and Analog Inputs: RTUs typically have a higher number of analog inputs compared to PLCs. This allows them to monitor and control a wider range of field devices that require analog signals for accurate measurement and control.
In summary, RTUs and PLCs have different strengths and applications in the field of automation. RTUs excel at handling large amounts of data from diverse devices, while PLCs are specifically designed for industrial control systems and automation tasks.
Functions and Applications
The functions and applications of RTUs (Remote Terminal Units) and PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) are essential in industrial automation and control systems. Both devices play a crucial role in collecting, processing, and transmitting data for monitoring and controlling various processes and equipment.
Analog and digital inputs and outputs are common functions of both RTUs and PLCs. These devices can receive and process signals from sensors and transmitters, and then activate actuators or alarms accordingly. This allows for precise monitoring and control of variables such as temperature, pressure, level, flow, and more.
RTUs and PLCs are also equipped with robust communication capabilities. They can support various protocols such as Modbus, Ethernet, and wireless networks, allowing them to seamlessly integrate with other devices and systems. RTUs often act as gateways, enabling communication between field devices and the SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) system, while PLCs are commonly used for local control and automation tasks.
When it comes to applications, RTUs are widely used in industries such as oil and gas, water and wastewater treatment, energy, and transportation. They are typically deployed in remote and harsh environments, where reliable communication and data acquisition are essential. RTUs can connect to a wide range of field devices, including sensors, pumps, valves, and motors, establishing a robust network for real-time monitoring and control.
On the other hand, PLCs are mainly utilized in manufacturing and industrial processes that require precise control and automation. They are often used in applications such as assembly lines, robotics, packaging, and material handling systems. PLCs offer high-speed processing capabilities and flexibility, allowing for efficient and accurate control of complex processes and machinery.
In summary, both RTUs and PLCs have their specific functions and applications in industrial automation and control systems. While RTUs focus on remote data acquisition, communication, and integration with field devices and SCADA systems in challenging environments, PLCs excel in local control and automation tasks, offering fast processing capabilities and flexibility in manufacturing and industrial processes.
Programming and Control Capabilities
The primary function of both RTUs and PLCs is to provide a system for controlling and monitoring various industrial processes. However, there are important differences in their programming and control capabilities.
PLCs, or Programmable Logic Controllers, are widely used in industrial automation. They are specifically designed for controlling digital and analog devices in a wide range of applications. PLCs allow for the creation of complex control programs using ladder logic, function blocks, or structured text. These programs can be easily modified or updated to accommodate changes in the control process.
On the other hand, RTUs, or Remote Terminal Units, are primarily used for data acquisition and remote monitoring in field devices. They are designed to collect data from various sensors and equipment and transmit it to a central control system. RTUs typically use protocols such as Modbus, DNP3, or OPC to communicate with the control system. They are also capable of performing basic control functions, such as opening or closing valves or turning on or off pumps.
In terms of networking capabilities, PLCs are often used in local control systems, where they can communicate with other PLCs on the same network or with a central control system via Ethernet or other industrial protocols. They can also be integrated with SCADA systems to provide a centralized monitoring and control solution. RTUs, on the other hand, are often used in remote locations where wired network connections are not feasible. They can operate in wireless networks, such as cellular or satellite networks, and act as gateways between the field devices and the central control system.
Overall, while both PLCs and RTUs have programming and control capabilities, their primary focus is different. PLCs are ideal for controlling and monitoring digital and analog devices in an industrial setting, while RTUs are more suited for remote data acquisition and monitoring in field devices. The choice between the two depends on the specific requirements of the automation system.
Communication and Connectivity
In industrial automation systems, communication and connectivity play a crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation and control of various devices and processes. RTUs (Remote Terminal Units) and PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) are both commonly used for this purpose, as they provide reliable and efficient communication between different components of an industrial system.
One of the most widely used communication protocols in industrial automation is the Modbus protocol, which allows for the exchange of data between different devices in a SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) system. This protocol enables the control and monitoring of various parameters, such as temperature, pressure, and flow rate, in an industrial process.
RTUs and PLCs are capable of collecting and processing data from various field devices, such as sensors and actuators, and sending control signals to these devices. They can communicate with devices using different types of communication interfaces, including analog and digital signals, as well as wireless communication technologies.
In addition to their communication capabilities, RTUs and PLCs can also serve as gateways to connect different networks together. For example, an RTU or PLC can act as a bridge between an Ethernet network and a field bus network, allowing for seamless communication between devices in different parts of the industrial system.
Overall, communication and connectivity are indispensable aspects of industrial automation. RTUs and PLCs provide the necessary infrastructure and protocols to enable efficient and reliable communication between different devices and components in an industrial system, ensuring smooth and accurate control of industrial processes.
Factors to Consider when Choosing between RTU and PLC
When it comes to choosing between Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) and Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) in an industrial automation system, several factors need to be taken into consideration. These factors include the type of control required, the network protocols used, connectivity options, and the specific needs of the application.
Digital and Analog Control: The first factor to consider is the type of control required for the automation system. RTUs are designed for both digital and analog control, making them suitable for applications that require a combination of both. PLCs, on the other hand, excel in digital control and are ideal for applications that primarily involve discrete logic.
Network Protocols and Connectivity: Another important factor is the compatibility of the automation devices with the existing network infrastructure. RTUs typically support a wide range of protocols, including Modbus, DNP3, and IEC 60870-5, making them compatible with various SCADA systems. PLCs, on the other hand, often use proprietary protocols and may require additional gateways or converters to integrate with the existing network.
Data Acquisition and Processing: The ability to capture and process data is crucial in an automation system. RTUs are designed to collect data from field devices and sensors and then transmit it to a central control center or SCADA system. PLCs, on the other hand, focus more on local control and process data at a faster rate, making them suitable for applications that require real-time control and processing.
Wireless Connectivity: In some applications, wireless communication may be required, especially in remote or hard-to-reach locations. RTUs often offer built-in wireless capabilities, allowing for easy connectivity to the network. In contrast, PLCs typically require additional wireless modules or communication devices to establish wireless connections.
Industrial Environment: The specific requirements of the industrial environment should also be taken into account. RTUs are designed to operate reliably in harsh industrial environments, with features such as rugged construction and wide temperature ranges. PLCs, on the other hand, are more commonly used in control cabinet installations and may require additional protective measures in harsh environments.
In conclusion, when choosing between RTUs and PLCs for an industrial automation system, it is essential to consider factors such as the type of control required, network protocols and connectivity, data acquisition and processing capabilities, wireless connectivity, and the industrial environment. By carefully assessing these factors, the right automation solution can be selected to meet the specific needs of the application.
System Complexity and Scalability
The complexity of an industrial automation system is determined by the number of devices and the level of control required. Both RTUs and PLCs play a crucial role in managing this complexity.
A PLC, or Programmable Logic Controller, is typically used for controlling a specific process or machine. It is designed to interface with various sensors, actuators, and other devices, and execute a set of predetermined instructions. PLCs excel at handling digital signals and discrete control systems.
On the other hand, an RTU, or Remote Terminal Unit, is primarily used for monitoring and controlling multiple devices over a network. RTUs are often employed in SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems, which require a high degree of scalability and remote communication. RTUs can interface with a wide range of protocols, such as Modbus, and handle both analog and digital signals.
The versatility of an RTU makes it a suitable choice for applications that involve complex networking, such as industrial control systems that require communication between different field devices and a central control center. With an RTU acting as a gateway, devices in the field can transmit data wirelessly or through Ethernet communication to the central control system.
It’s important to consider scalability when choosing between an RTU and a PLC. If your automation needs are expected to expand in the future, an RTU may be a better option. RTUs can easily integrate additional devices and handle a larger network compared to PLCs, which are typically designed for individual machines or processes.
In summary, the complexity and scalability of an industrial automation system determine whether an RTU or a PLC is the better choice. If you require a high degree of networking, remote communication, and the ability to interface with a variety of devices, an RTU is the optimal solution. However, if you need discrete control of a specific process or machine, a PLC may be more suitable.
Environmental Conditions and Reliability
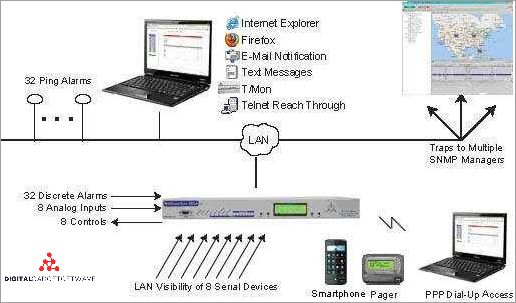
When it comes to choosing an automation solution for industrial systems, one of the key factors to consider is the environmental conditions in which the devices will be operated. Both RTUs and PLCs are designed to withstand harsh industrial environments, but they have different capabilities and limitations.
RTUs (Remote Terminal Units) are commonly used in applications where there is a need for wireless communication and remote monitoring. They are capable of connecting to various types of sensors and devices, such as digital and analog inputs, to gather data from the field. RTUs often support protocols like Modbus, which allows them to communicate with other devices in the system, including SCADA systems.
On the other hand, PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) are typically used in applications where precise control and automation are required. PLCs are commonly used in manufacturing and process industries to control machines and processes. They are designed to operate in harsh environments and can handle high-speed communication and control tasks.
When it comes to reliability, both RTUs and PLCs are known for their robustness and durability. They are designed to operate 24/7 in harsh industrial environments, where temperature fluctuations, humidity, and electromagnetic interference are common. Both devices are built with protective measures to ensure their reliability and durability over time.
In terms of communication options, RTUs often support wireless technologies such as Ethernet, GSM, and satellite, which allow for remote monitoring and control over large distances. PLCs, on the other hand, typically use wired communication protocols such as Ethernet or serial communication (RS-485), which are more suitable for short distances and high-speed communication.
In conclusion, when choosing between an RTU and a PLC for an industrial automation system, it is important to consider the environmental conditions in which the devices will operate. Both devices are reliable and robust, but their capabilities and communication options differ. If wireless communication and remote monitoring are essential, an RTU may be the better choice. If precise control and automation are required, a PLC would be more suitable.
Cost and Maintenance

In terms of cost, both RTUs and PLCs have their own advantages and considerations. PLCs generally have a higher upfront cost compared to RTUs, as they are typically more complex and robust devices designed for industrial automation. However, PLCs often have a longer lifespan and require less frequent maintenance, which can ultimately reduce their overall cost of ownership.
On the other hand, RTUs are generally less expensive and more compact, making them suitable for smaller-scale applications or remote sites with limited space. They are also easier to install and integrate into existing systems, which can further reduce costs. However, RTUs may require more frequent maintenance and have a shorter lifespan compared to PLCs.
When it comes to maintenance, both RTUs and PLCs require regular monitoring and diagnostics to ensure optimal performance and prevent failures. This includes checking for hardware issues, troubleshooting communication problems, and updating firmware or software as needed.
In terms of communication, both RTUs and PLCs are capable of digital and analog data acquisition and control. They can communicate with various devices and systems through protocols such as Modbus, Profibus, or Ethernet/IP. RTUs typically have built-in communication interfaces, while PLCs often require additional communication modules. Both can also support wireless communication through cellular networks or Wi-Fi, allowing for remote monitoring and control.
In summary, the choice between an RTU and a PLC for automation largely depends on the specific requirements of the application, including cost, maintenance, communication capabilities, and scalability. While PLCs generally offer more advanced features and long-term reliability, RTUs can be a cost-effective solution for smaller-scale or remote applications with limited space. Proper maintenance and regular monitoring are essential for both types of devices to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Real-World Examples of RTU and PLC Applications
RTUs (Remote Terminal Units) and PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) are widely used in various industrial automation applications. They provide control and monitoring capabilities for different systems and processes. Here are some real-world examples of their applications:
- Modbus Control System: RTUs and PLCs are commonly used in Modbus control systems. Modbus is a widely used communication protocol in the industrial automation field. RTUs and PLCs can act as Modbus masters or slaves, allowing for the communication and control of devices connected to the system.
- SCADA Systems: SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems rely on RTUs and PLCs for data collection, monitoring, and control. RTUs and PLCs gather and transmit data from sensors and field devices to a central SCADA system, allowing operators to visualize and manage the industrial processes.
- Industrial Ethernet Networks: RTUs and PLCs are essential components of modern industrial Ethernet networks. They provide the bridge between the field devices and the network, allowing for seamless communication and control. RTUs and PLCs equipped with Ethernet interfaces can transmit data and receive instructions over the network.
- Wireless Sensor Networks: RTUs equipped with wireless communication capabilities are used in wireless sensor networks for industrial monitoring and control. These RTUs can collect data from wireless sensors deployed in the field and transmit it wirelessly to a centralized control system, eliminating the need for physical wiring.
- Control of Field Devices: RTUs and PLCs play a vital role in controlling various field devices in industrial automation. Whether it’s controlling pumps, valves, motors, or other devices, RTUs and PLCs are responsible for executing the necessary control logic and generating control signals to ensure proper operation.
- Digital Input/Output Devices: RTUs and PLCs often interface with digital input/output (I/O) devices. These devices can include sensors that detect the state of a physical variable, such as temperature or pressure. RTUs and PLCs receive inputs from these devices and generate outputs accordingly to control the process.
- Gateway Functionality: RTUs and PLCs with gateway functionality can bridge different communication protocols and networks. They can convert between different protocols, such as Modbus, Ethernet/IP, or Profinet, allowing devices using different protocols to communicate with each other.
These are just a few examples of how RTUs and PLCs are used in real-world industrial automation applications. Their versatility and flexibility make them essential components in controlling and monitoring various systems and processes.
RTU Application: Remote Monitoring and Control of Oil and Gas Pipelines
Oil and gas pipelines are critical infrastructure for transporting valuable resources over long distances. To ensure smooth operations and prevent accidents, remote monitoring and control are essential. This is where RTUs (Remote Terminal Units) come into play.
An RTU is an industrial automation device that acts as a gateway between the field and control systems. It collects data from various sensors and equipment, both digital and analog, along the pipeline. Using the Modbus protocol, the RTU ensures seamless communication with other devices, such as SCADA systems or PLCs.
With the help of wireless or Ethernet connectivity, RTUs establish a network that enables real-time data transmission and control. The industrial RTUs are designed to withstand harsh field conditions, including extreme temperatures, humidity, and vibrations. They are typically installed at strategic locations along the pipeline to monitor pressure, flow, temperature, and other parameters.
The remote monitoring and control capabilities of RTUs allow operators to detect and respond promptly to any abnormalities or potential threats. For example, if the pressure exceeds safe levels, the RTU can trigger an alarm and initiate measures to mitigate the risk. Similarly, in the event of a leak or rupture, the RTU can automatically shut off the flow and notify the appropriate personnel.
By continuously collecting and analyzing data, RTUs provide valuable insights into pipeline performance and enable predictive maintenance. By identifying patterns and trends, operators can optimize operations, reduce downtime, and maximize efficiency. Additionally, RTUs play a crucial role in ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and safety protocols.
PLC Application: Automated Assembly Line in Manufacturing
An automated assembly line is a vital component of modern manufacturing processes that use advanced technologies, such as industrial robots and conveyor systems, to streamline production and improve efficiency. In such a system, a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) plays a crucial role in controlling and coordinating various steps of the assembly process.
PLC is an industrial digital computer that utilizes both analog and digital input/output modules to control machinery on the assembly line. It receives data from sensors and other devices, processes it using a built-in microprocessor, and then sends control signals to actuators and motors based on predefined logic and instructions.
PLC systems are commonly connected in a network architecture using Ethernet or wireless communication protocols, such as the Modbus protocol, to enable seamless data exchange and coordination between different devices. This network also allows a Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) system to monitor and supervise the assembly line operation in real-time.
One of the key advantages of using PLCs in automated assembly lines is their flexibility and scalability. PLCs can be easily programmed and reprogrammed to accommodate changes in the manufacturing process or to add new functionalities. Additionally, PLCs can integrate with other automation devices, such as Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) or gateways, to extend their capabilities and enhance communication within the network.
RTUs are specialized devices that interface between the analog and digital field devices and the PLC system. They can translate analog signals, such as temperature or pressure readings, into digital data that can be processed by the PLC. RTUs also often provide additional communication protocols, such as Modbus TCP/IP, to enable communication between the PLC system and external devices.
In summary, a PLC-based automation system is an essential component of an automated assembly line in manufacturing. With its ability to process analog and digital data, its network connectivity, and its flexibility, the PLC forms the backbone of the system, ensuring seamless control and coordination of the various elements in the assembly process.
Making the Right Choice: RTU or PLC?
When it comes to industrial automation, the choice between Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) and Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) is crucial. Both RTUs and PLCs play a significant role in the automation system, but they serve different purposes and have distinct characteristics.
An RTU, or Remote Terminal Unit, is a digital device used in the field of automation. It acts as a gateway between the field and the central control system, collecting data from various sensors and equipment. RTUs are commonly used in industries such as oil and gas, utilities, and manufacturing. They are designed to handle digital and analog signals and can communicate wirelessly or through Ethernet.
A PLC, or Programmable Logic Controller, on the other hand, is a computer-based device used for controlling industrial processes. PLCs are widely used in automation systems to control machines and equipment. They can receive inputs from sensors, make decisions based on predefined logic, and provide outputs to control actuators. PLCs are highly flexible and can be programmed to execute complex tasks.
RTUs and PLCs are often used together in an automation system. The RTUs collect data from the field and transmit it to the central control system, while the PLCs analyze the data and make control decisions. The communication between the RTUs and PLCs is typically done using industrial protocols such as Modbus. This allows for seamless integration and efficient data exchange between the two systems.
When choosing between an RTU and a PLC, it is important to consider the specific requirements of the automation system. If the system requires extensive data collection from the field, such as monitoring multiple sensors and equipment, an RTU is the preferred choice. On the other hand, if the focus is more on control and decision-making, a PLC would be the better option.
In summary, RTUs and PLCs are both essential components of an automation system. While RTUs are designed for data collection and communication in the field, PLCs are used for control and decision-making. Understanding the specific needs of the system and the desired functionality will help in making the right choice between an RTU and a PLC.
Assessing Your Automation System Needs and Objectives
When it comes to implementing an automation system, it is important to assess your specific needs and objectives. This will help determine whether you should use a Remote Terminal Unit (RTU) or a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC). Understanding the difference between these two industrial control devices is crucial in making the right choice for your automation system.
Firstly, you need to consider the scope of your automation system. RTUs are typically used in large-scale applications where multiple devices need to be monitored and controlled. They act as gateways between the field devices and the SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) system, providing communication and protocol conversion capabilities.
On the other hand, PLCs are ideal for smaller-scale applications that require precise control over one or a few devices. PLCs are designed to perform logic functions and execute specific tasks, often in real-time. They are commonly used in manufacturing and process control systems.
Next, you should evaluate the type of data that needs to be collected and processed. RTUs are capable of handling both analog and digital data, making them suitable for applications that require monitoring and control of various parameters. They can also support various communication protocols such as Modbus and Ethernet, enabling seamless integration with different devices and systems.
PLCs, on the other hand, excel in handling digital data and executing control functions. They are known for their reliability and ability to perform complex logical operations. PLCs are often equipped with inputs and outputs that can be directly connected to sensors and actuators.
Additionally, you should consider the communication requirements of your automation system. RTUs are typically used in wired communication networks, utilizing protocols such as Ethernet and Modbus TCP/IP. However, there are also wireless RTUs available for applications where wired connections are not feasible.
PLCs, on the other hand, can be integrated into both wired and wireless networks. They offer flexibility in terms of communication options, allowing for seamless integration with other devices and systems.
In conclusion, assessing your automation system needs and objectives is crucial in determining whether an RTU or a PLC is the right choice for your industrial control system. Consider the scope of your system, the type of data you need to handle, and the communication requirements. This will ensure that you select the appropriate device to meet your automation needs and optimize your industrial processes.
Consulting with Automation Experts

When it comes to selecting the right automation solution for your system, consulting with automation experts can be invaluable. These experts have a deep understanding of the different options available, including RTUs and PLCs, and can help you make an informed decision based on your specific needs and requirements.
Automation experts can provide guidance on the various protocols and communication options that are relevant to your system. For example, they can help you understand the differences between RTUs and PLCs in terms of their ability to communicate with SCADA systems. They can also advise you on the best data gateway options, such as Modbus or wireless, to ensure seamless integration with your existing network.
Field experts can also assist in determining the most appropriate device for your industrial environment. For example, if you have a system that requires a high level of control over analog signals, they can recommend a PLC that is capable of handling these requirements. Alternatively, if your system requires digital control and communication, they may suggest an RTU that is compatible with Ethernet or other digital networks.
By consulting with automation experts, you can benefit from their extensive knowledge and experience in the field. They can help you navigate the complexities of automation systems and ensure that you choose the right solution for your specific needs. Whether you require advanced control capabilities, reliable communication protocols, or seamless integration with existing systems, automation experts can provide the expertise needed to make the best decision for your system.
In summary, consulting with automation experts is crucial when considering the different automation solutions available for your system. They can guide you through the various options, including RTUs and PLCs, and help you evaluate the pros and cons based on your specific requirements. By leveraging their expertise, you can make an informed decision that maximizes the efficiency and effectiveness of your automation system.
Future-Proofing Your Automation Solution

In order to future-proof your automation solution, it is important to consider the use of wireless technology. Wireless gateways and devices can provide a more flexible and scalable automation system by eliminating the need for physical connections. This can be particularly beneficial in industrial settings where field devices are spread out across large areas.
Another key aspect to consider is the ability to gather and analyze data. SCADA systems, with the help of RTUs (Remote Terminal Units), are capable of collecting and transmitting large amounts of data from various devices within an industrial network. This data can be used for real-time monitoring, control, and decision-making.
Industrial automation systems also require efficient and reliable communication protocols. The Modbus protocol, for example, is widely used in RTU and PLC systems. It allows for seamless communication between devices, ensuring that data is transmitted accurately and efficiently.
With the advancement of technology, Ethernet has become a popular choice for industrial automation. Ethernet-based communication offers high-speed connectivity and can easily integrate with existing networks. This makes it possible to connect multiple devices, such as RTUs and PLCs, to a single network for centralized control.
Furthermore, future-proofing your automation solution involves considering the type of data that will be collected and processed. In addition to digital data, analog data is also crucial in many industrial processes. Therefore, the automation system should support both digital and analog signals.
Lastly, when choosing an automation solution, it is important to select a system that can adapt to future technologies and industry standards. This includes compatibility with emerging communication protocols, support for advanced analytics, and the ability to integrate with emerging technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT).
FAQ about topic “RTU vs PLC: Understanding the Difference and Choosing the Right Automation Solution”
What is the difference between RTU and PLC?
RTU stands for Remote Terminal Unit, while PLC stands for Programmable Logic Controller. The main difference between them is their function and application. RTUs are typically used in remote monitoring and control systems, where they gather data from sensors and send it to a central control center. On the other hand, PLCs are used in industrial automation systems to control and monitor manufacturing processes. So, while both RTUs and PLCs are used for automation, their specific applications and functionality differ.
Can I use a PLC instead of an RTU?
Yes, in some cases you can use a PLC instead of an RTU. However, it depends on the specific requirements of your automation system. RTUs are often preferred for remote applications where they need to be able to withstand harsh environments and communicate over long distances. PLCs, on the other hand, are more suited for industrial environments where they need to control and monitor various processes. So, while it is possible to use a PLC instead of an RTU, careful consideration should be given to the specific needs of your automation system.
What are the advantages of using an RTU over a PLC?
There are several advantages of using an RTU over a PLC. Firstly, RTUs are designed to handle remote applications, which means they are often built to withstand extreme temperatures, humidity, and other environmental factors. They also have built-in communication capabilities, allowing them to transmit data over long distances. Additionally, RTUs are usually equipped with a variety of input and output options, making them suitable for a wide range of sensors and actuators. Finally, RTUs typically have lower power consumption compared to PLCs, making them more energy-efficient.
What are the advantages of using a PLC over an RTU?
Just as there are advantages to using an RTU, there are also advantages to using a PLC. One major advantage of PLCs is their flexibility and programmability. PLCs can be easily customized to meet the specific requirements of different automation systems. They also offer a wide range of communication options, allowing for seamless integration with other devices and systems. Additionally, PLCs often have faster processing speeds and higher memory capacity compared to RTUs, making them suitable for complex automation tasks. Finally, PLCs are often more cost-effective than RTUs, especially for applications where a large number of inputs and outputs are required.
Which automation solution is better for my application: RTU or PLC?
The choice between an RTU and a PLC depends on several factors, including the specific requirements of your application, the environmental conditions, and the budget. If your application is located in a remote area with harsh environmental conditions and requires long-distance communication, an RTU may be the better choice. On the other hand, if your application is in an industrial setting and requires customization, flexibility, and fast processing speeds, a PLC may be more suitable. It is important to carefully evaluate your requirements and consult with automation experts to determine the best solution for your specific application.


