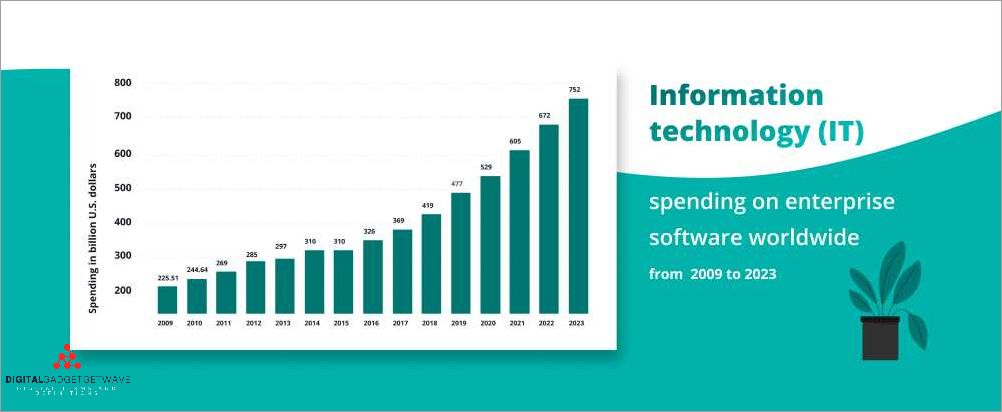
Enterprise applications play a crucial role in modern businesses. These applications provide security, customization, and integration to enable efficient and productive operations. With the increasing reliance on mobile devices and the need for flexibility, enterprise applications have become even more important.
A key aspect of enterprise applications is their data-driven nature. These applications enable businesses to gather, store, and analyze data, which can be used for informed decision-making and improved performance. Collaboration is another significant feature of enterprise applications. These applications facilitate teamwork and communication within an organization, enhancing productivity and efficiency.
Implementation and scalability are vital considerations in enterprise applications. Businesses need applications that can be easily implemented across their organization and can scale as the business grows. Compatibility is also crucial, as enterprise applications need to work seamlessly with existing systems and technologies.
Cloud-based enterprise applications have gained popularity due to their reliability and user-friendly interface. These applications can be accessed from anywhere, anytime, providing maximum flexibility to users. Additionally, cloud-based applications enable interoperability, allowing different systems to work together smoothly.
Analytics is another essential feature of enterprise applications. These applications provide valuable insights into business operations, helping organizations make data-driven decisions. Upgradeability is also crucial, as enterprise applications need to keep pace with evolving technologies and business needs.
Overall, enterprise applications are essential tools for businesses to increase efficiency, productivity, and performance. By leveraging the capabilities of these applications, organizations can streamline processes, improve collaboration, and achieve their business goals.
Contents
- 1 Top Enterprise Application Examples Increasing Efficiency and Productivity
- 2 What are enterprise applications?
- 3 Importance of enterprise applications
- 4 Enterprise Application Examples
- 5 Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- 6 Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
- 7 Supply Chain Management (SCM)
- 8 Human Resources Management (HRM)
- 9 FAQ about topic “Top Enterprise Application Examples for Increasing Efficiency and Productivity”
- 10 What are some popular enterprise applications?
- 11 How do enterprise applications increase efficiency and productivity?
- 12 Can enterprise applications be customized to meet specific business needs?
- 13 What are the benefits of using enterprise applications?
- 14 Are enterprise applications suitable for small businesses?
Top Enterprise Application Examples Increasing Efficiency and Productivity
In today’s fast-paced and competitive business environment, enterprises need robust and user-friendly applications to stay ahead. These applications provide a range of benefits, including increased efficiency and productivity. Here are some top examples of enterprise applications that are known for their ability to increase efficiency and productivity:
- Security: Enterprise applications prioritize the security of sensitive data and protect it from unauthorized access. With strong security measures in place, businesses can ensure the confidentiality and integrity of their information.
- Automation: Enterprise applications automate repetitive tasks, allowing employees to focus on more strategic and value-added activities. This improves efficiency and reduces the risk of human errors.
- Mobile: Mobile enterprise applications enable employees to access important information and perform tasks on the go. This flexibility increases productivity by allowing work to be done anytime, anywhere.
- Collaboration: Enterprise applications with collaboration features enable teams to work together more effectively. They can share documents, communicate in real-time, and coordinate their efforts, leading to better outcomes and higher productivity.
- Flexibility: Enterprise applications that are flexible and customizable can adapt to the specific needs of a business. This allows organizations to tailor the application to their unique workflows, improving efficiency and productivity.
- Interoperability: Enterprise applications that can seamlessly integrate with other systems and tools enhance efficiency by enabling smooth data exchange and streamlining processes.
- Integration: Integration with existing enterprise systems and third-party applications is crucial for maximizing productivity. Enterprise applications that offer easy integration capabilities allow businesses to leverage their existing tools and workflows.
- Reliability: Reliable enterprise applications ensure smooth and uninterrupted operations. They minimize downtime, improve productivity, and provide a hassle-free user experience.
- Customization: Customizable enterprise applications enable businesses to adapt the software to their specific requirements. This customization enhances efficiency by aligning the application with the organization’s unique processes and workflows.
- Efficiency: Enterprise applications are designed to optimize business processes and workflows, resulting in improved efficiency and productivity. They automate tasks, eliminate bottlenecks, and provide real-time visibility into operations.
- Upgradeability: Enterprise applications that are easily upgradable allow businesses to stay current with the latest features and functionality. Upgrades often bring efficiency improvements, ensuring that the application continues to support the organization’s productivity goals.
- Compatibility: Compatibility with different operating systems and devices is essential for maximizing productivity. Enterprise applications that support a wide range of platforms and devices ensure that employees can work seamlessly regardless of their preferred technology.
- Implementation: Smooth and efficient implementation is crucial for realizing the benefits of an enterprise application. A well-planned implementation process minimizes disruption and ensures that employees can quickly start using the application to its full potential.
- Data-driven: Enterprise applications that leverage data analytics enable businesses to make informed decisions and optimize processes. By analyzing data, organizations can identify areas for improvement and take proactive measures to increase efficiency and productivity.
- Cloud-based: Cloud-based enterprise applications offer scalability, accessibility, and cost-effective deployment. With data and software stored in the cloud, businesses can easily scale their operations and provide remote access to employees, further improving efficiency and productivity.
- Scalability: Scalable enterprise applications can handle growing data volumes, user numbers, and transaction loads without sacrificing performance. This scalability ensures that the application remains efficient and productive even as the business expands.
What are enterprise applications?
Enterprise applications are software systems that are designed to support and enable the complex business processes and operations of organizations.
These applications provide the flexibility and collaboration needed to streamline and improve business processes. They allow employees to work together efficiently and effectively, whether in the same office or remotely.
Enterprise applications often offer customization options, allowing organizations to tailor the software to their specific needs. This can include creating workflows, designing user interfaces, and integrating with other systems.
Enterprise applications are designed to be user-friendly, with intuitive interfaces that require minimal training. They are often mobile-friendly, allowing employees to access and use the applications on their smartphones or tablets.
Upgradeability is an important feature of enterprise applications, as technology continually evolves. These applications allow organizations to easily update and upgrade their software to take advantage of new features and improvements.
Data-driven decision-making is another key aspect of enterprise applications. They provide organizations with the ability to collect, analyze, and report on data, enabling them to make informed decisions and optimize their operations.
Implementing enterprise applications requires interoperability with existing systems and processes. They need to seamlessly integrate with other software and hardware to ensure a smooth transition and minimize disruptions.
Analytics capabilities are often built into enterprise applications, allowing organizations to gain insights from their data and identify trends, patterns, and opportunities. This enables them to make data-driven decisions and drive business growth.
Security is a critical aspect of enterprise applications. They need to protect sensitive data and intellectual property from unauthorized access and cyber threats. This includes robust authentication, encryption, and access control mechanisms.
Enterprise applications aim to increase productivity by automating and streamlining repetitive tasks and processes. This frees up employees’ time to focus on more value-added activities and improves overall efficiency.
Scalability and performance are important considerations for enterprise applications. They need to be able to handle growing data volumes and user loads without significant degradation in performance. This ensures that the applications can keep up with the organization’s growth.
Compatibility with different operating systems, browsers, and devices is essential for enterprise applications. They need to work seamlessly across various platforms to provide a consistent and optimal user experience.
Many enterprise applications are now cloud-based, allowing organizations to access and use the software over the internet. This provides the flexibility of remote access, reduces infrastructure costs, and ensures that the software is always up-to-date.
Importance of enterprise applications

Enterprise applications play a crucial role in modern businesses, providing the foundation for efficient and productive operations. They enable interoperability between different departments and systems, allowing seamless exchange of data and information.
These applications are data-driven, capturing and analyzing vast amounts of information to provide valuable insights and support decision-making processes. Through automation, they streamline repetitive tasks, reducing manual errors and increasing efficiency.
Enterprise applications offer flexibility, allowing organizations to customize and adapt them to their specific needs. They can be implemented across various departments and integrated with existing systems, facilitating streamlined workflows and collaboration.
Moreover, they provide upgradeability, enabling businesses to stay up-to-date with the latest technologies and features. This ensures improved scalability and performance, allowing organizations to handle growing demands and support increased workloads.
Reliability is another important aspect of enterprise applications. They are designed to provide a stable and secure environment, protecting sensitive data and ensuring business continuity. With advanced analytics capabilities, these applications enable organizations to gain valuable insights from their data and make informed decisions.
Integration is key, as enterprise applications seamlessly connect different systems and platforms, facilitating smooth data transfer and collaboration. Additionally, enterprise applications now have mobile compatibility, enabling employees to access and interact with data on the go, leading to improved productivity.
Cloud-based enterprise applications are becoming increasingly popular, providing organizations with the benefits of scalability, accessibility, and cost-efficiency. They can be customized to suit specific business needs and offer a secure and reliable environment for data storage and management.
In conclusion, enterprise applications are vital for businesses as they promote efficiency, productivity, and security. With their customizable and scalable nature, they empower organizations to adapt and grow in a rapidly changing business landscape.
Enterprise Application Examples
Enterprise applications play a crucial role in increasing efficiency and productivity within companies. These applications range from customization cloud-based tools to reliable and upgradeable software options that enhance performance and integration among teams. Implementing these enterprise applications enhances security and collaboration, allowing for data-driven and automated processes.
One example of an enterprise application is analytics software, which provides businesses with insights into their data. This data-driven approach enables companies to make informed decisions and identify areas for improvement. By analyzing trends and patterns, companies can streamline operations and increase efficiency.
Another example of an enterprise application is mobile applications that offer flexibility and compatibility across different devices. These user-friendly applications allow employees to access critical information and perform tasks while on the go. By providing a mobile platform, enterprises can improve productivity and responsiveness.
Additionally, automation software is an essential enterprise application that streamlines repetitive tasks, reducing the risk of errors and increasing efficiency. By automating processes, companies can save time and resources, allowing employees to focus on more strategic tasks. This not only improves productivity but also contributes to cost-saving measures.
Furthermore, collaboration software enables teams to work together seamlessly, regardless of their location. These applications facilitate real-time communication, file sharing, and project management. By promoting collaboration, enterprises can enhance teamwork, expedite decision-making processes, and increase productivity.
Overall, enterprise applications provide businesses with the tools needed to optimize their operations and achieve their goals. From increasing efficiency and productivity to improving performance and integration, these applications play a crucial role in modern enterprises across various industries.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)

Customer Relationship Management (CRM) refers to the automation and management of a company’s interactions with its current and potential customers. It plays a crucial role in enhancing productivity, efficiency, and overall business performance. CRM systems provide a data-driven approach, allowing businesses to gather and analyze customer information for better decision-making.
One of the key benefits of CRM is its compatibility and integration with other enterprise applications, such as sales and marketing automation tools. This allows for seamless data sharing and collaboration across different departments, resulting in improved customer service and streamlined processes.
CRM implementation offers customization options that enable businesses to adapt the system to their specific needs and workflows. This flexibility ensures that organizations can align the CRM solution with their unique requirements, making it more efficient and effective in managing customer relationships.
Furthermore, CRM systems provide a high level of reliability and performance, ensuring that customer data is secure and accessible at all times. With advanced analytics capabilities, businesses can gain valuable insights into customer behavior, preferences, and trends, enabling them to make informed decisions and personalize their interactions.
Modern CRM solutions are often cloud-based, providing additional benefits such as scalability and upgradeability. Businesses can easily scale their CRM systems as their customer base grows, and take advantage of regular updates and new features provided by the software vendor without the need for extensive IT resources.
Moreover, CRM solutions are increasingly mobile-friendly, allowing sales and customer service teams to access and update customer information on the go. This mobility empowers employees to provide real-time assistance and deliver a personalized experience, leading to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Security is another crucial aspect of CRM, as it involves handling sensitive customer data. Cloud-based CRM systems often offer robust security measures, such as data encryption, user authentication, and role-based access control, ensuring that customer information is protected from unauthorized access or data breaches.
In conclusion, CRM is a vital enterprise application that offers automation, productivity, efficiency, compatibility, data-driven insights, integration, performance, reliability, analytics, customization, collaboration, flexibility, interoperability, scalability, upgradeability, mobile access, and security to improve customer relationship management processes and drive business success.
Benefits of CRM applications
Compatibility: CRM applications are designed to work seamlessly with other software and systems, ensuring compatibility and easy integration.
Implementation: CRM applications can be implemented quickly and easily, allowing businesses to start utilizing their features and benefits in a timely manner.
Mobile: CRM applications provide mobile access, enabling employees to access important customer data and information from their smartphones or tablets while on the go.
Security: CRM applications offer robust security measures to protect sensitive customer information, ensuring data privacy and preventing unauthorized access.
Automation: CRM applications automate various tasks and processes, reducing manual work and streamlining operations to enhance productivity and efficiency.
Performance: CRM applications are designed to deliver high performance, allowing businesses to handle a large volume of customer data and interactions without any performance issues.
Interoperability: CRM applications can easily integrate with other enterprise systems, enabling seamless data sharing and collaboration across different departments.
Scalability: CRM applications can scale according to the changing needs of the business, accommodating an increasing number of users, customers, and data without any performance degradation.
Flexibility: CRM applications offer flexibility in terms of customization, allowing businesses to tailor the software to their specific requirements and workflows.
Data-driven: CRM applications provide businesses with actionable insights and analytics based on customer data, helping them make informed decisions and improve their overall strategy.
Customization: CRM applications can be customized to match the unique branding and requirements of the business, creating a personalized user experience.
Upgradeability: CRM applications regularly release updates and new features, ensuring that businesses can stay up to date with the latest advancements in CRM technology.
Efficiency: CRM applications streamline customer-related processes, allowing businesses to handle customer inquiries, orders, and support requests more efficiently, resulting in improved customer satisfaction.
Reliability: CRM applications are known for their reliability, providing businesses with a stable and robust platform for managing customer relationships and interactions.
Cloud-based: CRM applications can be deployed in the cloud, eliminating the need for on-premises infrastructure and providing businesses with anytime, anywhere access to customer information.
Productivity: CRM applications empower employees with the tools and information they need to effectively manage customer relationships, increasing overall productivity and performance.
Analytics: CRM applications offer advanced analytics capabilities, allowing businesses to analyze customer data and trends to gain valuable insights and make data-driven decisions.
Collaboration: CRM applications foster collaboration among different teams and departments, enabling them to work together towards a common goal of delivering exceptional customer experiences.
Integration: CRM applications can integrate with other business systems, such as marketing automation and ERP software, enabling seamless data exchange and a unified view of customer information.
Successful CRM implementation examples

CRM (Customer Relationship Management) systems have become a crucial tool for businesses to effectively manage customer interactions and improve overall sales and marketing efforts. Here are some examples of successful CRM implementations:
- Compatibility: A successful CRM implementation should be compatible with existing systems and technologies used by the organization, ensuring seamless integration and data exchange.
- Customization: A CRM system should be customizable to fit specific business needs and processes, allowing organizations to tailor it to their requirements and workflows.
- User-friendly: A user-friendly CRM interface is essential for ensuring quick adoption and ease of use by employees, reducing the learning curve and increasing productivity.
- Mobile: Mobile CRM applications enable sales representatives and other employees to access important customer data and perform key tasks on the go, enhancing efficiency and customer service.
- Reliability: A reliable CRM system ensures uninterrupted access to critical customer data and functionality, minimizing downtime and maximizing user satisfaction.
- Integration: CRM integration with other systems, such as ERP or marketing automation tools, enables data-driven decision-making and streamlines business processes.
- Data-driven: Successful CRM implementations leverage data analytics to derive valuable insights, enabling businesses to make informed decisions and better understand customer behavior.
- Performance: A high-performance CRM system enables quick response times, efficient data processing, and smooth user experience, ensuring optimal productivity and customer service.
- Efficiency: A well-implemented CRM system automates time-consuming tasks and provides centralized access to customer information, significantly improving efficiency and reducing manual effort.
- Interoperability: CRM systems that can seamlessly integrate with other applications and platforms allow businesses to leverage existing technologies and optimize workflows.
- Scalability: Successful CRM implementations are scalable, allowing organizations to accommodate growth and increasing customer data volumes without compromising performance.
- Analytics: CRM systems with robust analytics capabilities enable businesses to track and analyze key metrics, such as customer acquisition cost and customer lifetime value, improving decision-making and targeting strategies.
- Security: A secure CRM system protects sensitive customer data and ensures compliance with privacy regulations, fostering trust and loyalty among customers.
- Automation: CRM automation features, such as lead nurturing and email marketing automation, enable businesses to streamline repetitive tasks and improve marketing and sales processes.
- Collaboration: CRM systems that support collaboration and team coordination foster better communication and cooperation among employees, enhancing overall productivity.
- Cloud-based: Cloud-based CRM solutions offer scalability, accessibility, and cost-efficiency, allowing organizations to access their CRM data from anywhere and reduce infrastructure costs.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are software applications used by organizations to manage and integrate various business processes. ERP systems enable businesses to streamline their operations, increase efficiency, and improve productivity.
Implementation of an ERP system involves the integration of different modules, such as finance, human resources, supply chain management, and customer relationship management, into a single unified platform. This integration allows for seamless data flow across departments, making it easier for employees to collaborate and access the information they need.
ERP systems provide flexibility and scalability, allowing businesses to adapt and grow. These systems are user-friendly and provide a centralized platform for employees to access and manipulate data, enabling them to make data-driven decisions. Additionally, automation features within ERP systems automate repetitive tasks, reducing manual work and freeing up employees’ time for more value-added activities.
Cloud-based ERP solutions offer the advantage of being accessible from anywhere, allowing users to access information and perform tasks using a mobile device. This mobility enhances productivity, enabling employees to work remotely and collaborate efficiently.
Furthermore, ERP systems improve overall performance and interoperability within an organization. Customization options allow businesses to tailor the ERP system to their specific needs and requirements. These systems also offer easy upgradeability and compatibility with other software applications.
Analytics capabilities within ERP systems provide valuable insights into business operations, enabling organizations to make data-driven decisions. Moreover, ERP systems prioritize security, ensuring that sensitive company data is protected from unauthorized access and cyber threats. This enhances data security and protects the organization’s intellectual property.
In summary, ERP systems are powerful tools for organizations to increase efficiency, improve collaboration, automate processes, and enhance productivity. With their flexibility, scalability, and user-friendly interfaces, ERP systems enable businesses to manage and integrate various processes and data, leading to better decision-making and overall success.
How ERP systems streamline business processes
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have become essential tools for businesses looking to streamline their operations and increase efficiency. These software applications are designed to integrate and automate various business processes, allowing for better compatibility and data-driven decision making.
One of the key benefits of ERP systems is their scalability and upgradeability. As businesses grow and evolve, their ERP system can easily adapt and accommodate the changing needs. Additionally, ERP systems offer interoperability, allowing different departments and functions to share data and collaborate seamlessly.
ERP systems also provide flexibility in terms of implementation and customization. Businesses can choose to implement an ERP system that best suits their specific needs and requirements. They can also customize the system to match their workflows and processes, ensuring maximum efficiency.
In today’s mobile and remote work environment, ERP systems offer the advantage of accessibility. Employees can access the system from anywhere and collaborate in real-time. This mobile capability enables faster decision-making and increased productivity.
Integration and automation are two crucial aspects of ERP systems. These systems integrate various business functions, such as finance, human resources, and supply chain management, into a unified platform. By automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks, ERP systems reduce manual errors and increase productivity.
Modern ERP systems are often cloud-based, offering enhanced security and reliability. Data is stored in secure servers, ensuring protection against data breaches and unauthorized access. Additionally, automatic backups and disaster recovery options provide peace of mind to businesses.
ERP systems also prioritize user-friendliness and provide easy-to-use interfaces. Employees can quickly navigate through the system and access the information they need without extensive training. The availability of analytics and reporting features further enhances decision-making processes.
Overall, ERP systems are powerful tools that streamline business processes, improve efficiency, and boost productivity. Their compatibility, scalability, customization, integration, automation, and security features make them indispensable in today’s competitive business landscape.
Real-world examples of successful ERP implementations
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have become a crucial component for businesses to streamline their operations and enhance productivity. Several real-world examples demonstrate how ERP implementations have successfully addressed various challenges and brought about significant improvements.
1. Integration and analytics: Company XYZ implemented an ERP system that integrated all their departments and allowed for seamless data flow. By leveraging the system’s analytics capabilities, they gained valuable insights into their supply chain and were able to optimize their inventory management process.
2. Reliability and mobility: Organization ABC adopted a mobile ERP solution that provided real-time access to critical business information. This allowed their employees to make informed decisions on the go, resulting in improved efficiency and customer satisfaction.
3. User-friendly and upgradeable: Company DEF implemented an ERP system that was intuitive and easy to navigate, resulting in minimal training requirements for their employees. Additionally, the system’s upgradeability ensured that they could adapt to future business needs without disrupting their operations.
4. Scalability and collaboration: Organization GHI implemented a cloud-based ERP solution that offered scalability to accommodate their growing business needs. The system also facilitated collaboration between departments, enabling effective communication and efficient decision-making.
5. Automation and customization: Company JKL implemented an ERP system that automated several manual processes, such as invoice generation and inventory management, reducing human error and increasing productivity. The system’s customization capabilities allowed them to tailor it to their specific requirements.
6. Interoperability and performance: Organization MNO implemented an ERP system that seamlessly integrated with their existing software applications, eliminating the need for duplicate data entry. This improved data accuracy and overall system performance.
7. Data-driven and secure: Company PQR implemented an ERP system that leveraged data to drive decision-making and enhance operational efficiency. They also ensured data security by implementing robust security measures and encryption protocols.
8. Flexibility and compatibility: Organization STU implemented an ERP system that offered flexibility in terms of deployment options, allowing them to choose between on-premises and cloud-based solutions. The system’s compatibility with their existing infrastructure ensured a smooth transition and minimized disruptions.
These real-world examples highlight the diverse benefits of successful ERP implementations, ranging from increased efficiency and productivity to improved collaboration and data-driven decision-making. By leveraging the capabilities of ERP systems, businesses can optimize their operations and gain a competitive edge in the market.
Supply Chain Management (SCM)
Supply Chain Management (SCM) is a vital component of any business that involves the movement of goods or services. It encompasses the automation and integration of various processes involved in the production, distribution, and delivery of products.
In today’s fast-paced business environment, flexibility and customization are key factors in successful supply chain management. SCM solutions enable businesses to adapt to changing market demands and customize their processes to meet specific needs.
Efficiency is another crucial aspect of SCM. By streamlining processes and optimizing resource allocation, businesses can minimize costs, reduce waste, and improve overall production and delivery efficiency.
Security and compatibility are paramount in an increasingly connected world. SCM systems provide secure and compatible platforms for data sharing and collaboration among different stakeholders in the supply chain.
Upgradeability is important to ensure that SCM systems can adapt to new technologies and market trends. Mobile compatibility allows users to access and manage supply chain information on the go, increasing flexibility and efficiency.
Data-driven analytics provide insights into supply chain performance, helping businesses make informed decisions and improve overall efficiency. Interoperability allows different software systems to exchange data seamlessly, enhancing collaboration and efficiency.
Cloud-based SCM solutions offer scalability and reliability, as they can handle large volumes of data and provide uninterrupted service. They also facilitate collaboration among different stakeholders in real-time, regardless of their geographic location.
Implementing a user-friendly SCM system ensures that users can easily navigate and utilize its features, minimizing training time and increasing productivity. Additionally, a well-designed user interface enhances user satisfaction and adoption rates.
In conclusion, Supply Chain Management (SCM) solutions play a crucial role in optimizing business operations. They provide automation, integration, flexibility, customization, efficiency, security, compatibility, upgradeability, mobile access, data-driven analytics, interoperability, scalability, collaboration, cloud-based reliability, and user-friendly interfaces to improve efficiency and productivity throughout the supply chain.
Advantages of SCM applications
1. Implementation: SCM applications provide organizations with a streamlined process for implementing supply chain management strategies. They offer pre-built frameworks and modules that can be easily tailored to fit the specific needs of the business, reducing the time and effort required for implementation.
2. Efficiency: SCM applications automate various supply chain processes, such as inventory management, order fulfillment, and logistics, resulting in improved operational efficiency. By eliminating manual tasks and reducing human errors, these applications help organizations save time and resources.
3. Upgradeability: SCM applications often offer frequent updates and upgrades that incorporate the latest industry trends and technologies. This ensures that organizations can stay ahead of the competition and continue to improve their supply chain operations.
4. User-friendly: SCM applications are designed to be intuitive and user-friendly, making it easier for employees to navigate and use the software. This reduces training time and increases user adoption rates, leading to faster implementation and higher productivity.
5. Security: SCM applications provide robust security features to protect sensitive supply chain data from unauthorized access and cyber threats. This includes encryption, user authentication, and data backup and recovery mechanisms, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of the information.
6. Integration: SCM applications can integrate with other business systems, such as ERP and CRM software, to provide a seamless flow of information across different departments. This improves decision-making processes and facilitates collaboration among teams.
7. Flexibility: SCM applications offer flexibility in terms of customization, allowing organizations to tailor the software to their unique supply chain requirements. This ensures that the application can adapt to changing business needs and support future growth.
8. Reliability: SCM applications are built to handle large volumes of data and complex supply chain processes. Their robust architecture and scalability ensure that they can handle high transaction loads without compromising performance or system stability.
9. Cloud-based: Many SCM applications are cloud-based, allowing organizations to access and manage their supply chain data from anywhere, at any time. This enables remote work capabilities and improves collaboration among geographically dispersed teams.
10. Collaboration: SCM applications facilitate collaboration by providing features such as real-time messaging, task assignment, and document sharing. This enhances communication and coordination among supply chain stakeholders, leading to improved efficiency and productivity.
11. Mobile: SCM applications often have mobile versions or companion apps that enable users to access and manage supply chain data on the go. This allows for greater flexibility and responsiveness in decision-making and problem-solving.
12. Data-driven: SCM applications provide organizations with real-time and accurate data on various supply chain metrics, such as inventory levels, demand forecasts, and supplier performance. This enables data-driven decision-making and helps optimize supply chain operations.
13. Interoperability: SCM applications support interoperability with different software systems and technologies, allowing for seamless data exchange and integration with external partners and suppliers. This promotes collaboration and ensures a smooth flow of goods and information across the supply chain.
14. Performance: SCM applications are designed to optimize performance by automating repetitive tasks, eliminating bottlenecks, and improving resource utilization. This results in faster order fulfillment, reduced lead times, and improved customer satisfaction.
15. Productivity: SCM applications increase overall productivity by streamlining supply chain processes, reducing manual work, and improving data accuracy. This allows employees to focus on more value-added tasks and enhance their efficiency.
16. Compatibility: SCM applications are often compatible with various hardware platforms, operating systems, and databases, ensuring seamless integration with existing IT infrastructure. This reduces the need for additional investments and minimizes disruption to ongoing operations.
17. Scalability: SCM applications are scalable, allowing organizations to easily accommodate changes in business requirements and handle increased transaction volumes. This ensures that the software can grow alongside the organization and support future expansion plans.
18. Customization: SCM applications offer customization options that allow organizations to align the software with their specific supply chain processes and workflows. This ensures that the application can fully meet the unique requirements of the business.
Notable SCM implementation examples

Supply chain management (SCM) plays a crucial role in any organization’s success. By implementing SCM software and applications, businesses can streamline their processes, increase efficiency, and enhance productivity. Here are some notable examples of SCM implementations:
Upgradeability: Companies like XYZ Corporation have implemented SCM systems that offer regular updates and upgrades to keep up with changing business needs and technological advancements. This ensures that their SCM processes remain efficient and up-to-date.
Data-driven: Tech giant ABC Inc. utilizes a data-driven SCM system that collects and analyzes real-time data from various sources like sales, inventory, and customer feedback. This helps them make informed decisions and optimize their supply chain operations.
Reliability: DEF Manufacturing implemented a reliable SCM solution that focuses on minimizing disruptions in the supply chain. By integrating advanced tracking and monitoring technologies, they ensure timely delivery of products and maintain customer satisfaction.
Interoperability: Company GHI has implemented an SCM system that seamlessly integrates with their existing ERP and CRM systems. This interoperability allows for smooth data flow and improved communication between different departments, optimizing their supply chain operations.
Cloud-based: Organization JKL utilizes a cloud-based SCM solution that provides flexibility and scalability. This allows them to access critical supply chain data from anywhere and easily scale their operations as their business grows.
Security: MNO Corporation implemented an SCM system with robust security measures to protect sensitive supply chain information. This ensures that their data remains secure, minimizing the risk of breaches or unauthorized access.
Analytics: PQR Inc. uses an SCM software equipped with advanced analytics capabilities. By leveraging data analytics, they gain valuable insights into their supply chain performance, identify bottlenecks, and implement strategies to improve efficiency.
Efficiency and flexibility: Company STU has implemented an SCM system that focuses on automating routine tasks and workflows. This streamlines their supply chain processes, improves efficiency, and enables flexibility to adapt to changing market demands.
Collaboration: Organization VWX utilizes an SCM solution that promotes collaboration among different stakeholders, such as suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors. This fosters better communication, coordination, and synchronization throughout the supply chain network.
Mobile and user-friendly: Company YZ Corp. utilizes a mobile SCM application that allows their workforce to access supply chain information on-the-go. This mobile-friendly solution improves productivity and enables real-time decision-making even when employees are not in the office.
Overall, these notable SCM implementations highlight the importance of upgrading to modern, data-driven, and integrated SCM systems to enhance efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness in today’s fast-paced business environment.
Human Resources Management (HRM)
Human Resources Management (HRM) is an essential aspect of running a successful enterprise. HRM encompasses various processes and activities aimed at managing and optimizing the workforce within an organization. With the advancement of technology, enterprise applications have been developed to support HRM functions, improving collaboration and efficiency within HR departments.
Enterprise HRM applications offer a range of benefits, including improved security and data protection. These applications implement robust security measures to safeguard sensitive employee information, ensuring compliance with privacy regulations and protecting against data breaches.
Flexibility and performance are key features of modern HRM applications. These applications allow HR professionals to adapt and customize workflows and processes to meet the specific needs of their organization. With automation and streamlining of manual tasks, HRM applications enhance efficiency and productivity within the HR department.
Integration and interoperability are crucial for HRM applications to effectively communicate and exchange data with other systems within the organization. This facilitates seamless information flow and eliminates data silos, enabling HR professionals to make more informed, data-driven decisions.
The implementation of HRM applications can be tailored to suit the organization’s requirements, whether it’s a small business or a large enterprise. These applications can be customized to align with the company’s existing HR policies and practices.
HRM applications are often cloud-based and mobile-friendly, allowing employees and HR professionals to access and manage HR-related tasks and information from anywhere, at any time. This mobility and accessibility enhance the overall user experience and convenience.
Furthermore, cloud-based HRM applications offer scalability and upgradeability, enabling organizations to easily accommodate growth and evolve their HR processes as needed. These applications provide a centralized platform for managing employee data, performance evaluations, training, and more.
In summary, the use of HRM enterprise applications offers organizations a wide range of benefits, including increased efficiency, improved collaboration, and enhanced productivity. These applications provide a secure, flexible, and user-friendly solution for managing the human resources within an organization.
Benefits of HRM software
HRM software offers numerous benefits to organizations, helping them enhance their human resources processes and streamline their operations. Some of the key benefits include:
- Upgradeability: HRM software allows organizations to easily upgrade their systems as per their growing needs and changing requirements.
- Compatibility: HRM software is designed to be compatible with various operating systems and platforms, ensuring seamless integration into existing systems.
- Flexibility: HRM software provides flexibility and adaptability, allowing organizations to customize the solution according to their specific needs and workflow.
- Customization: HRM software enables organizations to customize the features and functionalities based on their unique HR processes and policies.
- Implementation: HRM software supports smooth implementation and onboarding, minimizing disruption and ensuring a quick return on investment.
- Productivity: HRM software automates various HR tasks and processes, enhancing overall productivity and efficiency across the organization.
- Interoperability: HRM software integrates seamlessly with other systems and applications, enabling smooth data exchange and collaboration.
- User-friendly: HRM software is designed with a user-friendly interface, making it easy for HR professionals and employees to navigate and use the system effectively.
- Automation: HRM software automates repetitive and time-consuming HR tasks, freeing up HR professionals to focus on strategic activities.
- Scalability: HRM software can easily scale as the organization grows, accommodating additional users, departments, and functionalities.
- Collaboration: HRM software enables better collaboration and communication among HR teams and employees, enhancing overall HR processes.
- Cloud-based: HRM software offers the benefits of cloud computing, providing access to HR data and functionalities from anywhere and at any time.
- Reliability: HRM software ensures reliable data storage and retrieval, reducing the risk of data loss or errors in HR records.
- Performance: HRM software enhances performance tracking and evaluation, enabling organizations to measure and improve employee performance effectively.
- Data-driven: HRM software provides valuable insights and analytics, enabling data-driven decision making for better HR strategies and policies.
- Mobile: HRM software offers mobile accessibility and compatibility, allowing HR professionals and employees to access HR functionalities on the go.
- Security: HRM software ensures the security of sensitive HR data with robust security measures, protecting it from unauthorized access or breaches.
- Analytics: HRM software leverages advanced analytics capabilities to analyze HR data and generate meaningful reports and insights for informed decision making.
- Integration: HRM software integrates with other essential business systems, such as payroll and accounting software, for seamless information exchange and holistic HR management.
In conclusion, HRM software offers a wide range of benefits, from automation and increased productivity to enhanced collaboration and data-driven decision making. Implementing an HRM software solution can significantly improve an organization’s HR processes, efficiency, and overall performance.
Leading HRM system examples

Performance: Top HRM systems offer high performance and fast response times to ensure efficient HR processes.
Compatibility: Leading HRM systems are compatible with various operating systems, allowing users to access and use the system on different devices.
Efficiency: HRM systems streamline and automate HR processes, increasing efficiency and reducing manual workloads.
Interoperability: These systems can seamlessly integrate with other enterprise applications, improving data sharing and collaboration between different departments.
Cloud-based: Many HRM systems are cloud-based, allowing access to HR information from anywhere, anytime, and eliminating the need for on-premises servers.
Mobile: Leading HRM systems offer mobile applications, enabling HR professionals to access and manage HR data on the go.
Automation: HRM systems automate repetitive tasks such as employee onboarding, leave management, and performance reviews.
Data-driven: These systems provide analytics and reporting capabilities, allowing HR professionals to make data-driven decisions.
Productivity: HRM systems improve productivity by streamlining processes, reducing paperwork, and providing self-service options for employees.
Reliability: Top HRM systems are reliable and ensure data integrity, so HR professionals can trust the accuracy of the information.
Analytics: These systems provide advanced analytics and reporting features to help HR professionals gain insights into workforce trends and make informed decisions.
Upgradeability: Leading HRM systems offer regular updates and upgrades to ensure they stay up to date with the latest features and technology.
Flexibility: HRM systems are flexible and can be customized to meet the specific needs of an organization.
Integration: These systems can integrate with other business applications such as payroll and attendance systems, further streamlining HR processes.
User-friendly: Top HRM systems have intuitive interfaces and user-friendly designs, making it easy for HR professionals to navigate and use the system.
Collaboration: HRM systems enable collaboration between HR professionals and employees, facilitating communication and fostering a collaborative work environment.
Security: Leading HRM systems prioritize data security and employ robust security measures to protect sensitive employee information.
Scalability: These systems can scale to accommodate the growing needs of an organization as it expands.
FAQ about topic “Top Enterprise Application Examples for Increasing Efficiency and Productivity”
What are some popular enterprise applications?
Popular enterprise applications include customer relationship management (CRM) systems, enterprise resource planning (ERP) software, supply chain management (SCM) systems, human resource management (HRM) software, and business intelligence (BI) tools.
How do enterprise applications increase efficiency and productivity?
Enterprise applications increase efficiency and productivity by automating processes, streamlining workflows, improving communication and collaboration, providing real-time data and analytics, and reducing manual tasks and human errors. They help organizations optimize their operations and make informed decisions.
Can enterprise applications be customized to meet specific business needs?
Yes, most enterprise applications can be customized to meet specific business needs. They often have flexible configurations and integrations options that allow organizations to tailor the software to their specific requirements and processes. This customization ensures that the application aligns with the unique needs of the business.
What are the benefits of using enterprise applications?
Some benefits of using enterprise applications include improved efficiency and productivity, enhanced data accuracy and consistency, better decision-making through real-time insights, increased collaboration and communication among teams, streamlined business processes, and cost savings through automation and optimization.
Are enterprise applications suitable for small businesses?
Yes, enterprise applications can be suitable for small businesses. While some applications may be more robust and geared towards larger enterprises, there are also scaled-down versions or cloud-based solutions available that cater to the needs and budgets of small businesses. These applications can still provide benefits such as improved efficiency, better data management, and streamlined workflows for small organizations.


