
The Uda Yagi antenna, also known as the Yagi-Uda antenna, is a popular design for a directional antenna used in transmission and reception of wireless signals. Its design is based on the principles of radiation, gain, and alignment of multiple elements, making it a powerful tool for long-range communication.
The main structure of the Uda Yagi antenna consists of a driven element, one or more directors, and a reflector. The driven element is the active component that transmits or receives the signal. The directors are positioned in front of the driven element and help focus the radiation in the desired direction. The reflector is positioned behind the driven element and helps increase the gain by reflecting and re-radiating the signal.
Length of the elements of the Uda Yagi antenna is determined by the frequency of the signal being transmitted or received. Each element has a specific length that allows it to resonate at the desired frequency, ensuring efficient transmission or reception. The relative positioning and alignment of the elements play a crucial role in the overall performance of the antenna.
The Uda Yagi antenna is commonly used in television, wireless communication, and other applications where a strong and directional signal is required. Its directional properties make it highly suitable for long-range reception and transmission, allowing for improved signal quality and reduced interference. The beamwidth of the antenna can be adjusted by changing the number and arrangement of the directors, allowing for better control over the coverage area.
Contents
- 1 Understanding the Uda Yagi Antenna
- 2 What is the Uda Yagi Antenna?
- 3 History of the Uda Yagi Antenna
- 4 How Does the Uda Yagi Antenna Work?
- 5 Advantages of the Uda Yagi Antenna
- 6 Long Range Signal Reception
- 7 Excellent Directionality
- 8 Compact and Lightweight Design
- 9 Applications of the Uda Yagi Antenna
- 10 Amateur Radio
- 11 Television Broadcasting
- 12 Wireless Communication
- 13 FAQ about topic “Uda Yagi Antenna: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Directional Antenna Design”
- 14 What is a Uda Yagi antenna?
- 15 What are the advantages of a Uda Yagi antenna?
- 16 How does a Uda Yagi antenna work?
- 17 What are the applications of a Uda Yagi antenna?
- 18 Can a Uda Yagi antenna be used for satellite communications?
Understanding the Uda Yagi Antenna
The Uda Yagi antenna is a powerful directional antenna design commonly used in wireless communication systems. It is named after its inventors, Hidetsugu Yagi and Shintaro Uda, who developed the design in the early 1920s.
The Uda Yagi antenna operates by using a series of elements, including a driven element, reflector, and directors, to focus and transmit or receive wireless signals in a specific direction. The alignment and length of these elements are carefully designed to achieve a specific gain and beamwidth.
One of the key features of the Uda Yagi antenna is its high gain, which allows for increased transmission and reception range compared to other types of antennas. This gain is achieved by the collinear arrangement of the elements, which helps to enhance radiation in the desired direction.
The Uda Yagi antenna is known for its narrow beamwidth, meaning it can concentrate the signal in a specific direction rather than spreading it out uniformly. This directional ability makes it well-suited for applications such as television reception, where a focused signal is desired from a specific transmitter.
The Uda Yagi antenna is designed to work on a specific frequency or range of frequencies. The length and spacing of the elements are calculated based on the wavelength of the desired frequency, ensuring optimal performance for that particular frequency.
In summary, the Uda Yagi antenna is a directional antenna design that offers high gain and narrow beamwidth. Its unique array of elements and careful design allow for focused wireless transmission or reception. Whether used for television reception or other wireless communication systems, the Uda Yagi antenna provides a powerful solution for efficient signal transmission.
What is the Uda Yagi Antenna?
The Uda Yagi antenna is a type of directional antenna that is widely used in wireless communication and television reception. It is named after its inventors, Hidetsugu Yagi and Shintaro Uda, who developed the design in the 1920s. The Uda Yagi antenna is known for its high gain, which allows it to transmit and receive signals over long distances.
The Uda Yagi antenna consists of a driven element and a reflector, both of which are typically made of metal rods. The driven element is the main radiating and receiving element, while the reflector helps to focus the radiation and improve the antenna’s gain. Additional elements, such as directors, can be added to further enhance the antenna’s performance.
The length and alignment of the elements in the Uda Yagi antenna are critical for optimal transmission and reception. The length of the elements is determined by the desired frequency of operation, and the alignment is important for achieving the desired radiation pattern and beamwidth. By adjusting these parameters, the Uda Yagi antenna can be optimized for specific applications and operating frequencies.
One of the key advantages of the Uda Yagi antenna is its directional radiation pattern, which allows it to focus the signal in a specific direction and reject interference from other directions. This makes it ideal for point-to-point communication and long-range transmission. The antenna’s high gain and narrow beamwidth also contribute to its excellent performance in long-distance wireless communication.
History of the Uda Yagi Antenna
The Uda Yagi antenna, also known as the Yagi-Uda antenna, is a type of directional antenna that was first introduced in Japan in the 1920s by Hidetsugu Yagi and his assistant Shintaro Uda. The design of the Uda Yagi antenna was based on the earlier work of Shintaro Uda, who developed the concept of using collinear elements to create a directional radiation pattern.
The Uda Yagi antenna consists of a driven element, a reflector, and one or more directors. The elements are typically made of metal rods or wires and are arranged in a linear array. The reflector is placed behind the driven element, while the directors are positioned in front of the driven element. The length and spacing of the elements are carefully adjusted to achieve the desired radiation pattern and gain.
The Uda Yagi antenna gained popularity for its ability to transmit and receive wireless signals over long distances. It was initially used for high-frequency radio transmission, but it later found applications in television reception and other wireless communication systems. The Uda Yagi antenna’s directional design allows it to focus the transmitted or received signal in a specific direction, resulting in enhanced signal strength and reduced interference.
One of the key features of the Uda Yagi antenna is its beamwidth, which refers to the angular range within which the antenna can effectively transmit or receive signals. The beamwidth of the Uda Yagi antenna is determined by the alignment and spacing of the elements. A narrower beamwidth allows for greater signal concentration, while a wider beamwidth provides a larger coverage area.
The Uda Yagi antenna’s gain, which measures its ability to amplify the signal, is also an important characteristic. The gain of the Uda Yagi antenna is influenced by factors such as the number and length of the directors, the spacing between elements, and the frequency of the signal. By carefully selecting these parameters, the Uda Yagi antenna can achieve high gain and improve the overall performance of wireless communication systems.
How Does the Uda Yagi Antenna Work?
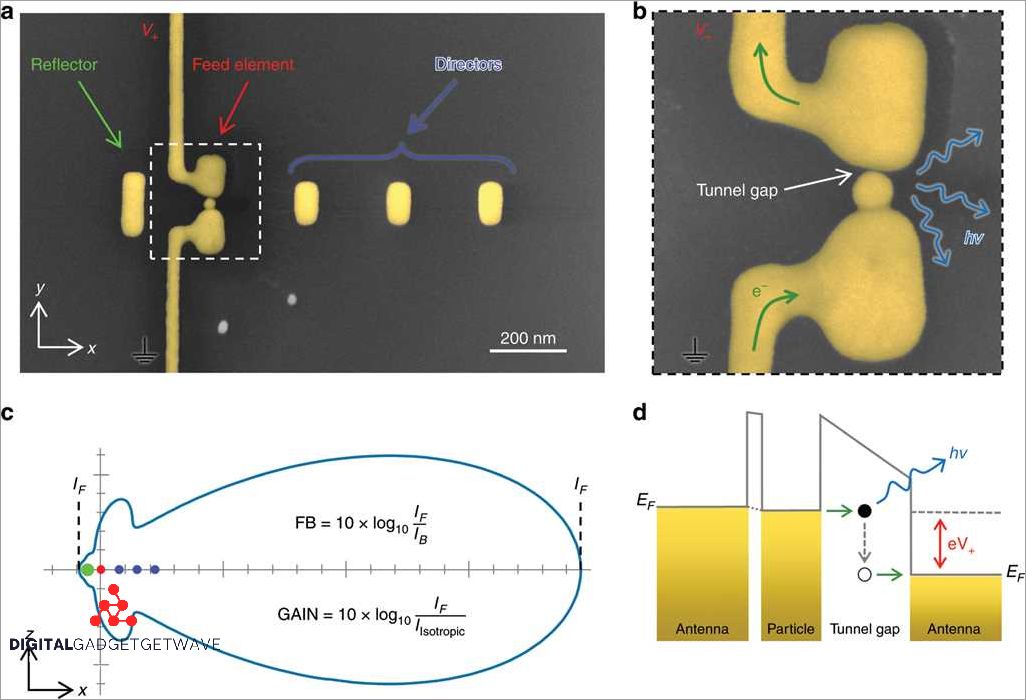
The Uda Yagi antenna is a powerful directional antenna design that is commonly used in wireless communication systems. It works by utilizing the principles of radiation and reception of electromagnetic waves.
The antenna consists of several elements, including a driven element, a reflector, and one or more director elements. The driven element is the main component responsible for transmitting and receiving signals. It is usually a dipole antenna, which consists of a wire or rod that is split in the middle and connected to a transmission line.
When a radio frequency signal is applied to the driven element, it generates an electromagnetic field. This field radiates away from the antenna in the form of electromagnetic waves. The length of the driven element is carefully designed to match the wavelength of the signal being transmitted or received.
The reflector element is positioned behind the driven element and is slightly longer than the driven element. It helps to reflect and focus the radiation from the driven element in a specific direction. This creates a directional beamwidth, allowing for better reception or transmission in that direction.
The director elements are positioned in front of the driven element and are slightly shorter than the driven element. They further narrow the beamwidth and improve the focus of the antenna’s radiation. The number and positioning of the director elements can vary depending on the desired beam direction and characteristics.
By carefully aligning the driven element, reflector, and director elements, the Uda Yagi antenna can effectively transmit or receive signals in a specific direction. The alignment is crucial for optimizing the antenna’s performance and maximizing the signal strength.
The Uda Yagi antenna is commonly used in various applications, including television reception, wireless communication systems, and even radio astronomy. Its design allows for a greater range and improved signal quality compared to other types of antennas, making it a popular choice in many industries.
The Role of the Driven Element
In a Uda Yagi antenna design, the driven element plays a crucial role in determining the reception capabilities of the antenna. It is the part of the antenna that is directly connected to the wireless transmission or reception system, such as a television or a wireless router.
The design of the driven element affects the overall performance of the antenna, including its gain, radiation pattern, and beamwidth. The length and alignment of the driven element are carefully determined to maximize the antenna’s ability to receive or transmit signals in a specific direction.
The driven element is typically positioned at the center of the antenna array, with other elements such as the reflector and director elements arranged around it. These additional elements help to shape the radiation pattern and increase the antenna’s directionality.
By carefully designing the driven element, the Uda Yagi antenna can achieve high gain and directional reception capabilities. The gain of the antenna refers to its ability to amplify signals, allowing for stronger reception of distant signals. The directional properties of the antenna enable it to focus its reception in a specific direction, reducing interference from other sources.
Overall, the driven element is a critical component in the Uda Yagi antenna design, responsible for the antenna’s reception capabilities, gain, and directional properties. By properly designing and positioning the driven element along with the other elements in the antenna array, it is possible to create a powerful directional antenna for wireless transmission and reception applications.
The Directors and Reflectors
A Uda Yagi antenna is a powerful directional antenna design that utilizes directors and reflectors to enhance its performance. The directors and reflectors are key elements of the antenna array, working together to shape the radiation pattern and increase the gain of the antenna.
In the Uda Yagi antenna design, the directors are shorter elements positioned in front of the driven element. They are aligned in a collinear manner and are slightly shorter in length compared to the driven element. The directors help to focus the transmission in a specific direction, reducing the beamwidth and increasing the forward gain of the antenna.
On the other hand, the reflector is positioned behind the driven element and is longer in length compared to the driven element. The reflector acts to reflect and redirect the transmitted signal, further enhancing the directional properties of the antenna. It helps to improve the reception of signals coming from the desired direction while reducing interference from other directions.
Together, the directors and reflector play a crucial role in the directional characteristics of the Uda Yagi antenna. By properly arranging these elements in the antenna design, it is possible to achieve a high degree of alignment and orientation towards the desired wireless transmission or television reception frequency. This results in enhanced signal quality and improved performance in long-range communication applications.
Advantages of the Uda Yagi Antenna
The Uda Yagi antenna design offers several advantages over other types of antennas. One of the main advantages is its directional nature. The Uda Yagi antenna is designed to focus the wireless signal in a specific direction, allowing for increased range and coverage. This makes it ideal for point-to-point transmission or reception of signals.
Another advantage of the Uda Yagi antenna is its high gain. The array of elements, including the reflector and director, work together to enhance the radiation and reception of the antenna. This results in a stronger, more focused signal, which can improve the overall performance of the wireless system.
The Uda Yagi antenna also offers a narrow beamwidth, which is the angular width of the main lobe of radiation. This means that the antenna has a highly focused radiation pattern, allowing for precise alignment and targeting of the wireless signal. This can be particularly beneficial in situations where interference needs to be minimized or where a specific point needs to be reached.
In addition, the Uda Yagi antenna has a relatively simple design, with a fixed length and minimal complexity. This makes it cost-effective and easy to manufacture, while still maintaining high performance. The simplicity of the design also allows for easy replication and scaling, making it suitable for various applications and frequency bands.
Overall, the Uda Yagi antenna is a powerful directional antenna that offers a range of advantages. Its high gain, narrow beamwidth, and simple design make it a popular choice for wireless communication systems that require focused and reliable transmission or reception of signals.
Long Range Signal Reception
The Uda Yagi antenna, also known as the Yagi-Uda antenna, is a highly efficient directional antenna that is designed to receive long range television signals. Its design utilizes a combination of elements, including reflectors and directors, to focus the incoming signal and reject interference from other sources.
Long range signal reception is achieved by the uda yagi antenna through its directional design. This means that it is able to receive signals from a specific direction while minimizing reception from other directions. The main element of the antenna is a driven element, which is connected to the television or other wireless transmission device.
The uda yagi antenna consists of a series of parallel elements arranged in a specific alignment. The length and spacing of these elements are carefully calculated to achieve the desired frequency response and beamwidth. The reflector element is positioned at a specific distance behind the driven element to reflect and amplify the signal, while the director elements are positioned in front of the driven element to focus and direct the signal.
By carefully adjusting the length and spacing of the elements, the uda yagi antenna is able to achieve a desired radiation pattern and beamwidth. The beamwidth determines the width of the reception angle, while the radiation pattern determines the strength and direction of the received signal. This allows the antenna to receive signals from a long range while filtering out unwanted interference.
In conclusion, the uda yagi antenna is a powerful and efficient antenna design that is ideal for long range signal reception. Its directional design and careful alignment of elements make it an excellent choice for receiving television signals and other wireless transmissions.
Excellent Directionality
The Uda Yagi antenna design is known for its excellent directionality, which allows for precise signal reception and transmission. The directional nature of this antenna is achieved through the use of additional elements such as directors and a reflector. These elements are strategically aligned with the driven element, which is the main part of the antenna that receives and transmits the wireless signals.
By arranging these elements in a collinear manner, the Uda Yagi antenna is able to focus the signal in a specific direction, resulting in a higher gain and improved reception. The gain of the antenna refers to the amplification of the signal, and the longer the length of the antenna, the higher the gain.
The alignment and size of the elements in the Uda Yagi antenna design are critical factors in achieving optimal directionality. The reflector, for example, is positioned slightly behind the driven element and helps to increase the reception of the desired signal while reducing interference from other directions.
The use of a directional antenna like the Uda Yagi is particularly beneficial for applications such as television reception, where a strong and focused signal is required. The radiation pattern of a directional antenna is characterized by a narrow beamwidth, which means that it provides a concentrated and focused signal in a specific direction rather than spreading the signal in all directions.
In summary, the Uda Yagi antenna design offers excellent directionality for wireless signal reception and transmission. Its collinear array of elements, including directors and a reflector, ensures a focused and amplified signal, resulting in improved signal strength and reception quality. Whether for television reception or other wireless applications, the Uda Yagi antenna design provides a powerful solution for achieving excellent directionality and enhanced signal performance.
Compact and Lightweight Design
The Uda Yagi antenna is known for its compact and lightweight design, making it an ideal choice for various wireless reception needs. It is designed to have a minimal size while still providing high gain and excellent radiation patterns. The use of a reflector and a yagi array allows for the antenna to achieve a more focused beamwidth, making it an efficient solution for long-distance transmission and reception.
The compact design of the Uda Yagi antenna also makes it easy to install and align. Its shorter length compared to other antenna designs allows for hassle-free installation on rooftops, masts, or other suitable mounting structures. With its lightweight construction, this antenna can be easily mounted and adjusted without requiring excessive manpower or equipment.
Despite its compact size, the Uda Yagi antenna offers impressive gain and signal reception capabilities. By utilizing multiple elements in the antenna array, it achieves directivity and gain in a specific direction, allowing for improved signal strength. This makes it especially beneficial for television and other wireless frequency reception, ensuring a better quality of reception for users.
In summary, the compact and lightweight design of the Uda Yagi antenna offers several advantages. It allows for easy installation and alignment, making it suitable for various applications. Moreover, it provides excellent gain and signal reception capabilities, making it an efficient solution for wireless communication needs.
Applications of the Uda Yagi Antenna
The Uda Yagi antenna, also known as the Yagi-Uda antenna, is a powerful directional antenna design that has found numerous applications in the field of wireless communication. Its unique collinear array design provides excellent reception and radiation characteristics, making it ideal for long-range transmission and reception of signals.
One of the most common applications of the Uda Yagi antenna is in television broadcasting. Due to its high gain and directional properties, it is often used to receive and transmit television signals in specific locations. Its alignment and directional characteristics help to enhance the signal strength and improve the overall quality of the television reception.
Another key application of the Uda Yagi antenna is in the field of wireless communication. It can be used for various frequency bands, including Wi-Fi, cellular, and satellite communication. The antenna’s high gain and beamwidth capabilities allow for efficient transmission and reception of wireless signals over long distances, enabling reliable and high-speed communication.
The Uda Yagi antenna also finds application in radar systems. Its directional properties and ability to provide a focused beamwidth make it ideal for radar applications, including weather radar, air traffic control radar, and military surveillance radar. The antenna’s reflector and director elements help to shape the transmitted and received signals, enabling accurate detection and tracking of targets.
Additionally, the Uda Yagi antenna can be used for point-to-point communication links. Its directional characteristics allow for precise alignment and targeting of the transmission signal, resulting in efficient and reliable data transmission. This makes it suitable for applications such as wireless backhaul, remote monitoring, and wireless networking.
In conclusion, the Uda Yagi antenna has diverse applications in various fields, including television broadcasting, wireless communication, radar systems, and point-to-point communication links. Its powerful directional design, high gain, and ability to shape signals make it a valuable tool for enhancing signal reception and transmission in these applications.
Amateur Radio
Amateur radio, also known as ham radio, is a popular hobby among individuals who are interested in radio communication. It involves the use of frequency bands allocated for non-commercial, non-governmental use. Amateur radio operators, or hams, make use of various equipment and antennas to communicate with others across different distances and frequencies.
One important aspect of amateur radio is reception. Hams use different types of antennas to receive signals from other radio stations. A commonly used design is the Yagi antenna, which is a directional antenna with one or more directors and a reflector. This design allows for efficient reception of signals from a specific direction, while reducing interference from other directions.
The length and number of elements in a Yagi antenna determine its frequency range and gain. By aligning the elements properly and adjusting their lengths, hams can optimize the antenna’s performance for a particular frequency band. The gain of a Yagi antenna refers to its ability to increase the strength of a signal in the desired direction. The narrower the beamwidth, the more directional the antenna.
Amateur radio enthusiasts can also use collinear arrays, which consist of multiple Yagi antennas stacked vertically. This arrangement enhances the gain and beamwidth, allowing for even greater directional reception. Another popular design is the Uda antenna, which is a simple wire antenna that can be easily constructed by hams for various frequencies.
The use of wireless technology, combined with the design and alignment of the antenna, enables amateur radio operators to communicate over long distances. The directional radiation pattern and gain of Yagi and Uda antennas play a significant role in improving the signal strength and reducing interference, making amateur radio a powerful and reliable means of communication.
Television Broadcasting

Television broadcasting is a method of transmitting television programs to viewers. It relies on the use of antennas and frequency modulation to transmit and receive signals. One important component of television broadcasting is the antenna, which is responsible for receiving the television signal from the transmission tower and converting it into a format that can be displayed on a television screen.
When it comes to television broadcasting, the gain of an antenna is crucial. Gain refers to the ability of an antenna to focus and amplify the received signal. A higher gain antenna is able to capture weaker signals and provide a clearer and more reliable reception. The gain of an antenna is determined by the design and alignment of its elements, which include a reflector and multiple director elements.
One popular design for a directional television antenna is the Yagi-Uda antenna. This antenna is made up of a driven element, reflector, and multiple director elements. The driven element is the main antenna that receives the signal, while the reflector and director elements help to focus and direct the signal. The length and spacing of these elements are carefully designed to maximize the antenna’s gain and beamwidth.
The Yagi-Uda antenna works by using constructive and destructive interference to direct the signal in a specific direction. The reflector element reflects the signal, while the director elements help to focus and amplify it. This directional radiation pattern allows for better reception of television signals from a specific transmission tower, while minimizing interference from other sources.
Television broadcasting relies on wireless transmission using specific frequency bands. Each television channel is assigned a specific frequency for transmission. These frequencies are carefully allocated to prevent interference between different television stations. The Yagi-Uda antenna is designed to work within a specific frequency range to ensure optimal reception of television signals.
In conclusion, television broadcasting relies on the use of antennas to transmit and receive signals. The Yagi-Uda antenna is a popular choice for directional reception, thanks to its design and alignment of elements. The gain and beamwidth of the antenna are important factors in the quality of reception. With proper antenna selection and alignment, viewers can enjoy clear and reliable television broadcasts.
Wireless Communication
Wireless communication refers to the transfer of information or data without the need for physical wires or cables. It uses electromagnetic waves to transmit and receive signals. One of the key components in wireless communication is the antenna, which plays a vital role in the transmission and reception of signals.
An antenna is a device that converts electrical energy into electromagnetic waves and vice versa. In wireless communication, antennas are used to transmit and receive signals. The design of an antenna determines its performance in terms of beamwidth, gain, and radiation pattern.
The Uda Yagi antenna is a popular directional antenna design used in wireless communication. It consists of a group of collinear elements arranged in a specific pattern to create a directional radiation pattern. The length and spacing of these elements are carefully calculated to optimize the antenna’s performance at a specific frequency.
The Uda Yagi antenna is widely used in various applications, including television broadcasting, where it is used to transmit and receive TV signals. Its directional design allows for better alignment with the transmission tower, resulting in improved reception quality. Additionally, the Yagi antenna’s gain helps amplify the signal, allowing for better long-distance wireless communication.
In conclusion, wireless communication relies on antennas for the transmission and reception of signals. The Uda Yagi antenna, with its directional design and optimized array of elements, is a powerful tool in wireless communication. Its beamwidth, gain, and radiation pattern contribute to improved signal quality and reception. Whether in television broadcasting or other wireless communication applications, the Uda Yagi antenna plays a crucial role in maintaining efficient and reliable communication.
FAQ about topic “Uda Yagi Antenna: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Directional Antenna Design”
What is a Uda Yagi antenna?
A Uda Yagi antenna, also known as a Yagi-Uda antenna, is a type of directional antenna design widely used in wireless communications. It consists of a dipole antenna with additional parasitic elements that help focus and direct the signal in a specific direction.
What are the advantages of a Uda Yagi antenna?
There are several advantages of using a Uda Yagi antenna. First, it has high gain, which means it can transmit and receive signals over long distances. Second, it has a narrow beamwidth, which helps in reducing interference from other sources. Third, it has a simple and compact design, making it easy to install and deploy. Lastly, it has good directivity and front-to-back ratio, which allows for better signal reception and rejection of unwanted signals.
How does a Uda Yagi antenna work?
A Uda Yagi antenna works based on the principle of electromagnetic radiation. The driven element, which is the dipole antenna, creates an electromagnetic field when the signal is applied. The parasitic elements, which are usually shorter or longer than the driven element, interact with this electromagnetic field and re-radiate it in a specific direction. This constructive interference helps in focusing the signal in the desired direction.
What are the applications of a Uda Yagi antenna?
Uda Yagi antennas are widely used in various applications. They are commonly used in television and radio broadcasting, where they help in transmitting and receiving signals over long distances. They are also used in wireless communication systems, such as Wi-Fi and cellular networks, to provide a strong and reliable signal. Additionally, Uda Yagi antennas are used in radar systems for detecting and tracking objects in the air and on the ground.
Can a Uda Yagi antenna be used for satellite communications?
Yes, a Uda Yagi antenna can be used for satellite communications. However, it is important to consider certain factors such as the frequency range and the pointing accuracy required for satellite tracking. Depending on the specific requirements, a Uda Yagi antenna can be designed and optimized to work effectively with satellite signals. It is also common to use a motorized rotator system with a Uda Yagi antenna for tracking and receiving signals from different satellites.


