If you have ever used a computer, chances are you have heard the term “Ethernet” before. It is the most commonly used connection protocol for transmitting data over the internet. One specific type of Ethernet technology is 100BASE-TX, which offers a fast and reliable means of data transmission.
At the heart of 100BASE-TX is the use of a switch, a device that allows multiple computers to be connected to a network. The switch acts as a central hub, directing data packets to their intended destinations. This technology allows for efficient and simultaneous communication between multiple devices.
One of the key advantages of 100BASE-TX is its high bandwidth. This refers to the amount of data that can be transmitted within a given amount of time. With 100BASE-TX, data can be transferred at speeds of up to 100 Megabits per second (Mbps). This makes it ideal for applications that require a fast and reliable internet connection, such as online gaming or video streaming.
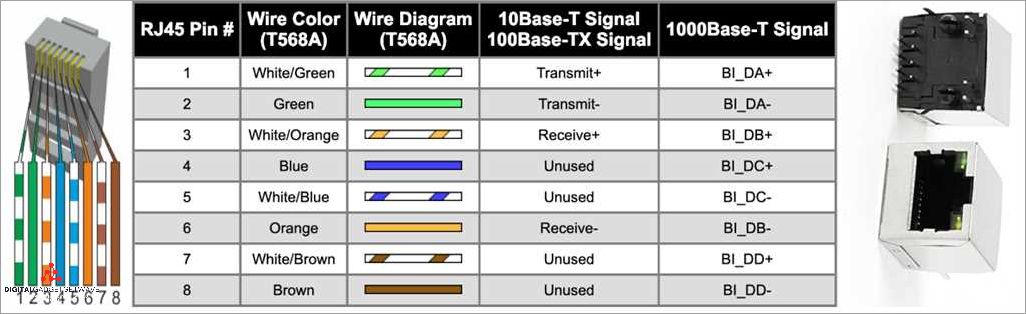
To connect devices to a 100BASE-TX network, a specific type of cable and connector are required. The cable used is typically a twisted pair cable, which consists of four pairs of wires twisted together to reduce interference. The connector used is known as an RJ-45 connector, which resembles a telephone plug, but with eight pins instead of four.
It’s worth noting that devices that do not have a built-in Ethernet port, such as older computers, can still be connected to a 100BASE-TX network using an Ethernet adapter. This adapter converts the device’s interface into one that is compatible with Ethernet technology.
In conclusion, 100BASE-TX is a highly efficient and reliable Ethernet technology that allows for fast data transmission over a network. With its high speeds, it is well-suited for applications that require high bandwidth, such as online gaming or video streaming. By understanding the basics of 100BASE-TX, you can make informed decisions when it comes to setting up and utilizing Ethernet networks.
Contents
- 1 What is 100BASE-TX?
- 2 How does 100BASE-TX Work?
- 3 Key Components of 100BASE-TX
- 4 Common Challenges and Troubleshooting
- 5 FAQ about topic “Understanding 100BASE-TX: A Guide to Ethernet Data Transmission”
- 6 What is 100BASE-TX?
- 7 How does 100BASE-TX achieve data transmission at 100 Mbps?
- 8 What are the advantages of using 100BASE-TX?
- 9 Can 100BASE-TX be used for long-distance data transmission?
- 10 Are there any limitations to 100BASE-TX?
What is 100BASE-TX?
100BASE-TX is a type of ethernet technology used for data transmission in computer networks. It is a Fast Ethernet standard that provides fast speeds and reliable connections for transferring data over a network.
With a speed of 100 megabits per second (Mbps), 100BASE-TX is ten times faster than the previous standard, 10BASE-T. This increase in speed allows for quicker data transfer and improved performance in a network environment.
100BASE-TX uses a twisted pair cable with an RJ-45 connector for its physical transmission. This type of cable, commonly known as an ethernet cable, is used to connect devices such as computers, switches, and routers in a network.
When connecting devices using 100BASE-TX, a network switch with 100BASE-TX ports is typically used. Each port on the switch can be connected to a device using an RJ-45 cable, allowing for multiple devices to be connected to the network simultaneously.
100BASE-TX is compatible with the internet protocol (IP) and supports the transmission of data packets using the Ethernet protocol. It is also backward compatible with slower ethernet standards, allowing for seamless integration into existing network infrastructures.
In recent years, ethernet technology has evolved further, with the introduction of gigabit ethernet, which offers even higher speeds for data transmission. However, 100BASE-TX continues to be widely used in various applications due to its reliability and cost-effectiveness.
Overview of Ethernet Data Transmission
Ethernet data transmission is a key component of computer networks, enabling the transfer of data between devices such as computers, switches, and routers. It utilizes a set of protocols and technologies to enable high-speed, reliable communication.
At the core of Ethernet data transmission is the use of cables, such as twisted pair cables, which are commonly referred to as Ethernet cables. These cables are equipped with RJ-45 connectors, which ensure a secure and reliable connection between devices.
When a computer or another device is connected to an Ethernet network, it is typically connected to a switch. The switch acts as a central device that directs and organizes the data transmission within the network.
The data transmission in Ethernet networks is conducted using a protocol known as the Ethernet protocol. This protocol sets the rules and standards for data transmission, ensuring that devices can communicate effectively and efficiently.
Ethernet data transmission offers various speeds and bandwidth capacities, including 10BASE-T, 100BASE-TX, and Gigabit Ethernet. These different speeds allow for different levels of data transfer, ranging from basic internet browsing to high-speed data-intensive applications.
In order for devices to connect to an Ethernet network, they require an Ethernet adapter. This adapter, also known as a network interface card (NIC), enables the device to send and receive data through the Ethernet network.
In summary, Ethernet data transmission is a crucial technology that enables the transfer of data between devices within a network. By utilizing Ethernet cables, switches, and protocols, devices can communicate efficiently and effectively, allowing for seamless internet connectivity and data sharing.
Benefits of 100BASE-TX

100BASE-TX Ethernet is a technology that provides reliable and high-speed data transmission over Ethernet cables. It offers numerous benefits for internet and computer networks, making it an essential component of modern technology infrastructure.
One of the main advantages of 100BASE-TX is its speed. With a bandwidth of 100 megabits per second, it allows for fast and efficient data transfer, making it suitable for various applications such as streaming media, online gaming, and large file transfers. This high-speed connection ensures a smooth and seamless user experience.
Furthermore, 100BASE-TX Ethernet provides a stable and reliable connection. It eliminates the need for wireless connections, which can be susceptible to interference and signal loss. With a physical cable connection, data transmission is more secure and less prone to disruptions, ensuring a consistent and uninterrupted internet experience.
Another benefit of 100BASE-TX is its compatibility. It is widely supported by various devices, including computers, laptops, servers, and network switches. This makes it easy to integrate into existing technology infrastructure without the need for additional adapters or converters. The standardized protocol of 100BASE-TX ensures seamless communication between devices and simplifies network setup and management.
Additionally, 100BASE-TX Ethernet uses a standard RJ-45 connector, which is widely used and readily available. This simplifies the installation process, as users can easily connect their devices to the network using standard Ethernet cables. The use of a common connector also ensures compatibility with a wide range of devices, further enhancing its convenience and usability.
In summary, the benefits of 100BASE-TX Ethernet include high-speed data transmission, stable connection, compatibility with various devices, and ease of installation. This technology is essential for modern networks, providing reliable and efficient data transfer that supports the increasing demand for bandwidth-intensive applications and services.
How does 100BASE-TX Work?
The 100BASE-TX is a type of Ethernet technology that provides high-speed data transmission in a network. It uses a twisted pair cable with an RJ-45 connector to carry data between devices. This technology is commonly used in local area networks (LANs) and is a popular choice for connecting computers, switches, and other network devices.
With 100BASE-TX, the network uses the Ethernet protocol, which is a set of rules and standards for transmitting data over a network. The protocol defines how data is packaged, addressed, and delivered between devices. It ensures that data is transmitted reliably and efficiently.
100BASE-TX operates at a speed of 100 megabits per second (Mbps), providing a high bandwidth for transferring data. This makes it suitable for transferring large files, streaming media, and other data-intensive tasks. The technology is also backward compatible, meaning it can work with slower Ethernet technologies, such as 10BASE-T.
In a 100BASE-TX network, data is transmitted using a full-duplex communication scheme. This means that devices can send and receive data simultaneously, improving the efficiency of data transmission. Each device is connected to a switch or a hub using an Ethernet port or adapter.
The data transmission in 100BASE-TX is achieved by sending electrical signals over the twisted pair cable. The cable consists of four pairs of wires, and each pair is used for transmitting and receiving data. The data is encoded into binary signals, which are then modulated onto the electrical signals.
Overall, the 100BASE-TX technology provides a reliable and high-speed method for transmitting data in a network. Its use of the Ethernet protocol, twisted pair cable, and RJ-45 connector makes it compatible with various devices and widely used in LANs and internet connections.
Physical Layer of 100BASE-TX

The physical layer of 100BASE-TX is an essential component of Ethernet data transmission. It defines the hardware and connection standards required for transmitting data over a network.
The 100BASE-TX protocol uses a standard RJ-45 connector, which is commonly found on Ethernet cables. This connector allows for a reliable and secure connection between devices, such as computers, switches, and routers.
With a transmission speed of 100 megabits per second (Mbps), 100BASE-TX offers a significant improvement over the older 10BASE-T Ethernet technology. This increase in speed allows for faster data transfers and a more efficient use of the network’s bandwidth.
One of the key advantages of 100BASE-TX is its compatibility with the existing infrastructure. It can be easily integrated into existing networks, making it an ideal choice for upgrading older systems without the need for extensive modifications.
Furthermore, 100BASE-TX is widely used in home and small office setups, as well as in larger enterprise networks. Its versatility and reliability make it a popular choice for connecting devices to the internet and other network resources.
In conclusion, the physical layer of 100BASE-TX plays a crucial role in Ethernet data transmission. With its standard RJ-45 connector, fast transmission speed, and compatibility with existing infrastructure, it provides a solid foundation for building efficient and reliable networks.
Data Transmission Process
The data transmission process is a crucial aspect of Ethernet technology and plays a significant role in the communication between devices and networks. It involves the transfer of data from one device to another through a physical connection or network.
At the heart of this process is the Ethernet port, which serves as the interface for data exchange between devices. The data, in the form of binary digits (bits), is transmitted through cables that connect the devices. These cables can vary in type and bandwidth, with options such as twisted-pair copper cables and fiber-optic cables.
In order to ensure efficient and reliable transmission, a protocol is followed. In the case of 100BASE-TX, which is a type of Ethernet technology providing data transmission at speeds of 100 megabits per second (Mbps), the data is transmitted using the RJ-45 connector. This connector is commonly used for Ethernet connections and provides a secure and reliable physical connection.
Once the data is transmitted through the cable and reaches the receiving device, it is processed and interpreted by the computer or network. This technology allows for the transmission of data packets, which are small units of data. The data packets contain not only the actual data being transmitted but also additional information such as the source and destination addresses.
To facilitate the transmission process, network switches are often used. These switches provide multiple ports that enable devices to be connected to the network. The switches also help manage and direct the data flow, ensuring that the data is transmitted efficiently and reaches the intended destination.
The data transmission process is a crucial component of modern technologies such as the internet, where fast and reliable communication is essential. With advancements in Ethernet technology, such as the introduction of gigabit Ethernet, the speed and capacity of data transmission have increased significantly, allowing for more efficient communication and data exchange between devices and networks.
Key Components of 100BASE-TX
The 100BASE-TX is a widely used Ethernet data transmission technology that provides high-speed connectivity over twisted-pair copper cables. This technology relies on several key components to ensure efficient and reliable data transmission.
RJ-45 Connector:
The RJ-45 connector is a standard connector used to establish a connection between the Ethernet cable and network devices such as computers, switches, and routers. It provides a secure and stable connection for data transmission.
Twisted-Pair Cable:
The twisted-pair cable is the medium through which the data is transmitted. It consists of pairs of insulated wires that are twisted together to reduce interference and crosstalk. This cable provides the necessary bandwidth for high-speed data transmission.
Network Adapter:
The network adapter, also known as a network interface card (NIC), is a hardware component that enables the computer to connect to the Ethernet network. It is responsible for transmitting and receiving data between the computer and the network.
Ethernet Switch:
An Ethernet switch is a device that connects multiple devices in a network, allowing them to communicate with each other. It acts as a central hub for data transmission, enabling fast and efficient communication between connected devices.
100BASE-TX Port:
The 100BASE-TX port is a specific port on a network device, such as a switch or computer, that supports 100BASE-TX Ethernet technology. It provides the interface for connecting the Ethernet cable and enables high-speed data transmission.
Internet Protocol (IP):
The Internet Protocol (IP) is a network protocol that is responsible for addressing and routing packets of data across the Internet. It ensures that data is correctly delivered to its intended destination.
Gigabit Ethernet:
Gigabit Ethernet is an Ethernet standard that supports data transmission rates of up to 1 gigabit per second (Gbps). It is an upgrade from 100BASE-TX and provides even faster speeds for high-bandwidth applications.
In conclusion, the key components of 100BASE-TX include the RJ-45 connector, twisted-pair cable, network adapter, Ethernet switch, 100BASE-TX port, Internet Protocol, and the possibility of upgrading to Gigabit Ethernet for faster data transmission. These components work together to establish a reliable and efficient Ethernet network for high-speed data communication.
Twisted Pair Cable
Twisted Pair Cable is a type of cable used for Ethernet data transmission. It consists of two pairs of twisted copper wires that are enclosed in a protective sheath. This type of cable is commonly used in networking, as it provides reliable and efficient data transmission.
Twisted Pair Cable is often terminated with a connector called RJ-45, which is compatible with most Ethernet devices. The RJ-45 connector allows for the connection of the cable to a computer, switch, or other network device.
One of the advantages of Twisted Pair Cable is its ability to support different Ethernet speeds, including 10 Mbps (megabits per second), 100 Mbps, and even gigabit speeds. This makes it a versatile and widely used cable in various networking environments.
The twisted pairs in the cable help to reduce interference and crosstalk, which can affect data transmission. This technology, known as twisted pair technology, enables reliable and high-speed data transmission over long distances.
Twisted Pair Cable is a key component in Ethernet networks, which are widely used for local area networks (LANs) and internet connections. It is compatible with the Ethernet protocol, which defines the rules and procedures for data transmission in a network.
When using Twisted Pair Cable in a network, it is important to consider the bandwidth requirements and the transmission speed needed. Higher bandwidth requirements may require the use of thicker cables or different cable categories, such as Cat 5e or Cat 6, to support faster data transmission.
Overall, Twisted Pair Cable is a reliable and widely used cable for Ethernet data transmission. Its compatibility with the RJ-45 connector and its ability to support different speeds make it a popular choice for computer networks and internet connections.
Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) vs Shielded Twisted Pair (STP)
Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) and Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) are two types of cables commonly used for data transmission in Ethernet networks. Both UTP and STP are based on twisted pair technology, which involves twisting pairs of wires together to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk.
UTP is the most widely used type of Ethernet cable and is commonly found in homes, offices, and other environments. It consists of four pairs of twisted copper wires and uses RJ-45 connectors to establish a connection between devices. UTP is affordable, easy to install, and can support data transmission speeds up to gigabit Ethernet.
STP, on the other hand, has an extra layer of shielding to provide additional protection against EMI and crosstalk. This shielding is usually made of metal foil or braided wire and helps to minimize the impact of external interference on the transmission. STP is commonly used in industrial environments or where there is a higher risk of electromagnetic interference.
While STP offers better protection against external interference, it is also generally more expensive and harder to install than UTP. Additionally, the shielding in STP can add to the bulk and weight of the cable, making it less flexible and more difficult to work with in tight spaces.
In terms of performance, both UTP and STP can support the same Ethernet protocols and have similar maximum data transmission speeds. The choice between UTP and STP depends on the specific requirements of the network and the level of interference present in the environment.
Network Interface Card (NIC)
A Network Interface Card (NIC) is a hardware component that allows a computer to connect to a local area network (LAN) or the internet. It provides the necessary interface between the computer and the network, enabling data transmission according to a predefined protocol, such as the Ethernet.
The NIC is connected to the computer via a port, typically a standard RJ-45 connector. This connector is used to attach an Ethernet cable, which is responsible for transmitting data between the network and the computer.
The NIC is responsible for managing the transmission of data between the computer and the network. It controls the flow of data, ensuring that it is sent and received correctly. Additionally, the NIC determines the speed and bandwidth at which data is transmitted, which can vary depending on the specific adapter and network technology used.
Modern NICs can support various network speeds, such as 10 Mbps (megabits per second), 100 Mbps, or even 1 Gbps (gigabit per second) for high-speed data transmission. These advancements in NIC technology have contributed to the increasing speed and efficiency of internet and network connections.
Furthermore, NICs may also include additional features such as the ability to support advanced network functionality like VLAN tagging or jumbo frames, or to offload certain network tasks from the computer’s CPU to improve overall performance. These additional features can enhance the capabilities and efficiency of the NIC.
In summary, the Network Interface Card (NIC) is an essential component in computer networking. It allows computers to connect to a network or the internet, manages data transmission, controls speed and bandwidth, and may offer additional features for improved network functionality and performance.
Common Challenges and Troubleshooting
When using 100BASE-TX technology, there can be several common challenges that can affect the data transmission and network connectivity. It is important to understand these challenges and be able to troubleshoot them effectively.
1. Poor connection: A poor connection between the Ethernet cable and the RJ-45 connector can result in unreliable data transmission. Make sure that the connector is securely plugged into the port on both the computer and the switch. Additionally, check for any damaged cables or connectors.
2. Limited bandwidth: 100BASE-TX offers a maximum bandwidth of 100 Mbps, which may not be sufficient for certain applications or large data transfers. Consider upgrading to a gigabit Ethernet adapter and cable for faster data transmission.
3. Network congestion: In a busy network, excessive data traffic can cause congestion, leading to slower speeds and dropped connections. To troubleshoot this issue, check for any devices or applications that may be using excessive bandwidth and consider implementing Quality of Service (QoS) protocols to prioritize critical data.
4. Protocol mismatch: Ensure that the devices on the network are configured to use the same Ethernet protocol. A mismatch in protocols can lead to communication issues and loss of connectivity. Check the settings on the computer, switch, and any other connected devices.
5. Faulty cable or adapter: A faulty Ethernet cable or adapter can cause intermittent connection issues. Replace the cable or adapter with a known working one to rule out any hardware faults.
6. Internet connectivity issues: If you’re experiencing connectivity issues with accessing the internet, check the network settings on your computer and ensure that the Ethernet connection is properly configured. Also, verify that your internet service provider is not experiencing any outages.
By addressing these common challenges and troubleshooting any issues, you can ensure smoother data transmission and a more reliable Ethernet network connection.
Interference and Signal Loss
When it comes to data transmission in an Ethernet network, interference and signal loss are common challenges that can affect the overall performance and reliability. Interference refers to any undesired electrical or electromagnetic disturbance that can disrupt the transmission of data. Signal loss, on the other hand, occurs when the strength or quality of the signal diminishes during transmission.
Interference and signal loss can be caused by various factors, such as electromagnetic radiation from nearby electronic devices, electrical noise from power lines, or even physical obstructions in the network environment. These factors can introduce errors and affect the integrity of the transmitted data.
Fortunately, Ethernet technology has evolved to mitigate the effects of interference and signal loss. The use of twisted-pair cables with proper shielding helps to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) by reducing the coupling of external signals with the transmission lines. Additionally, techniques like error detection and correction protocols, such as the cyclic redundancy check (CRC) used in Ethernet, help to detect and correct errors caused by signal loss or interference.
Another important aspect is the use of Ethernet switches. Switches play a crucial role in maintaining a stable and efficient connection within a network. They can isolate different segments of the network, minimizing the impact of interference and signal loss on the overall system. Switches also allow for the use of full-duplex communication, which enables simultaneous transmission and reception, further enhancing the reliability and speed of the Ethernet connection.
To ensure optimal performance and reduce the chances of interference and signal loss, it is important to use high-quality Ethernet cables, connectors, and adapters. The RJ-45 connector, commonly used in Ethernet connections, should be properly connected and secured to prevent signal loss due to loose or damaged connections. Additionally, upgrading to Gigabit Ethernet can provide higher data transfer speeds, reducing the time for which the connection is vulnerable to interference.
Compatibility Issues
When it comes to compatibility issues in Ethernet data transmission, there are several factors that can cause problems. One of the main factors is the type of connector used. Ethernet cables typically use RJ-45 connectors, which are the most common type. However, if you are trying to connect a device with a different type of port, such as a USB or HDMI port, you may encounter compatibility issues.
Another issue that can arise is with the network itself. Ethernet is a widely used technology, but different networks may have different specifications and requirements. For example, if you are using a switch or a router that does not support gigabit speed, you may experience slow transmission speeds. It is important to ensure that all the devices on your network are compatible with the Ethernet protocol and have the necessary bandwidth to support the transmission of data.
The type of cable used can also affect compatibility. Ethernet cables come in different categories, such as CAT5, CAT5e, and CAT6. Each category has different bandwidth capabilities, and using a lower category cable may limit the speed and performance of your network. It is recommended to use the highest category cable that is supported by your devices to ensure optimal performance.
Additionally, compatibility can be affected by the type of adapter or network interface card (NIC) used in your computer. If you are using an older computer that does not have an Ethernet port, you will need to use a USB Ethernet adapter. However, not all adapters are compatible with all devices, so it is important to check the specifications and compatibility of the adapter before making a purchase.
In conclusion, compatibility issues in Ethernet data transmission can arise from various factors, including the type of connector, port, network, cable, switch, gigabit speed, adapter, and computer. It is important to ensure that all the components of your network are compatible with each other to ensure smooth and efficient data transmission.
FAQ about topic “Understanding 100BASE-TX: A Guide to Ethernet Data Transmission”
What is 100BASE-TX?
100BASE-TX is a form of Fast Ethernet that uses two pairs of twisted-pair cables to transmit data at a rate of 100 Mbps. It is a popular standard for Ethernet data transmission.
How does 100BASE-TX achieve data transmission at 100 Mbps?
100BASE-TX achieves data transmission at 100 Mbps by using a combination of Manchester encoding and 4B/5B encoding. Manchester encoding ensures that the data is synchronized and has clear transitions, while 4B/5B encoding ensures that there is no DC bias.
What are the advantages of using 100BASE-TX?
There are several advantages of using 100BASE-TX. Firstly, it provides faster data transmission compared to earlier Ethernet standards. Secondly, it is compatible with existing Category 5 twisted-pair cables, making it easy to upgrade existing networks. Lastly, it is a widely adopted standard, which means that it is well-supported and compatible with a variety of devices.
Can 100BASE-TX be used for long-distance data transmission?
While 100BASE-TX is designed for short-distance data transmission, it is possible to extend its range using repeaters or switches. However, for longer distances, it is more common to use fiber optic cables or other Ethernet standards such as 1000BASE-T.
Are there any limitations to 100BASE-TX?
There are a few limitations to 100BASE-TX. Firstly, it is a half-duplex technology, which means that data can only be transmitted in one direction at a time. Secondly, the maximum distance for transmission is limited to 100 meters. Additionally, the use of multiple pairs of cables can increase the complexity and cost of the network infrastructure.


