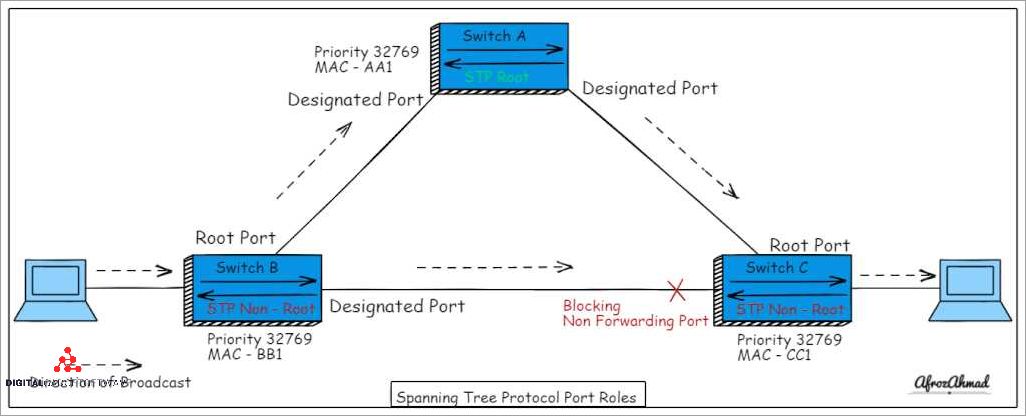
In the world of networking, the process of communication between devices is crucial to ensure the smooth transmission of data throughout a network. One important aspect of this communication is the exchange of Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDU) between bridges or switches. BPDU is a special type of data unit that is used in the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) to establish a loop-free topology in a network.
BPDU frames are a key component in the Ethernet technology. When a bridge or switch receives a BPDU frame, it analyzes the information contained within the frame to determine the most efficient path for data transmission. This analysis is often referred to as the bridge’s decision-making process, and it plays a vital role in ensuring that data is transmitted in the most optimal way possible.
The BPDU frames contain important information about the bridge’s identity, the bridge’s priorities, and the ports that the bridge is connected to. This information is used by the switches to build a network topology and to identify the best paths for data transmission. By analyzing the information contained within the BPDU frames, the switches are able to create a loop-free network, thus preventing any potential network issues or data loss.
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is responsible for managing and exchanging the BPDU frames between bridges or switches. The main goal of STP is to prevent loops in a network by disabling redundant links between switches. The STP algorithm determines the most optimal path for data transmission, and it does so by calculating a cost value for each possible route. This cost value is based on factors such as bridge priorities and port costs.
In conclusion, the Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDU) are an essential part of networking as they enable the smooth functioning of a network by creating a loop-free topology. By exchanging BPDU frames, bridges and switches are able to make informed decisions about the best paths for data transmission, ensuring optimal network performance.
Contents
- 1 The Basics of BPDU
- 2 The BPDU Format
- 3 BPDU Transmission and Exchange
- 4 BPDU Filtering and Filtering Databases
- 5 FAQ about topic “Understanding BPDU in Networking: How Bridge Protocol Data Units Work”
- 6 What is a BPDU?
- 7 How does BPDU guard work?
- 8 What is the purpose of BPDU filtering?
- 9 How does a switch choose the root bridge?
- 10 What is the purpose of BPDU timers?
The Basics of BPDU
BPDU, or Bridge Protocol Data Unit, is a fundamental component in network topology for spanning tree protocol (STP). It is a specialized frame format used by bridges or switches to exchange information about network topology and maintain the stability of the spanning tree. BPDU packets are carried within Ethernet frames and contain important data that helps switches make decisions to prevent loops and optimize network performance.
When a switch receives a BPDU, it analyzes the information contained in the data frame to determine the role it will play in the network. The BPDU carries information such as the bridge ID, port ID, and cost associated with each bridge. This information is used to calculate the shortest path to the root bridge, which is the central bridge in the network. The spanning tree protocol uses the information exchanged through BPDU to construct a loop-free tree that connects all the bridges in the network.
Each bridge in the network generates and sends BPDU packets periodically, ensuring that the network is constantly updated with the latest information about the spanning tree. The BPDU frames are sent out on all designated ports of a switch, allowing neighboring switches to receive and process the information. This constant exchange of BPDU frames helps the network dynamically adapt to changes in the topology, such as link failures or new bridges being added.
By using BPDU, switches are able to intelligently select the best paths in the network, avoid loops, and optimize traffic flow. The spanning tree protocol, with the help of BPDU, ensures that there is only one active path between any two network nodes, preventing redundant paths that can cause network congestion or broadcast storms. BPDU plays a vital role in maintaining the stability and efficiency of Ethernet networks by allowing switches to exchange crucial network information and make informed decisions about forwarding data frames.
Why Bridge Protocol Data Units are Important
The Bridge Protocol Data Unit (BPDU) plays a crucial role in networking as it allows switches to exchange information and establish the network topology. A BPDU is a frame or unit of data that is used by switches to communicate with each other and create a loop-free network environment.
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a network protocol that uses BPDU to prevent loops in Ethernet networks. When switches exchange BPDU messages, they can identify redundant links and create a logical tree structure to ensure data is forwarded along the most efficient path.
By exchanging BPDU messages, switches can determine the best path for data transmission and avoid loops that could result in network congestion and broadcast storms. The BPDU contains information about the switch’s identity, the port it is connected to, and the cost or priority of the path. This helps switches make informed decisions about how to forward data packets.
The BPDU also enables switches to detect changes in the network, such as the addition or removal of switches or changes in link status. When a switch receives a BPDU with new information, it can update its forwarding tables and adapt to the new network topology.
In summary, the Bridge Protocol Data Unit (BPDU) is essential in networking as it enables switches to exchange information, establish the network topology, prevent loops, and ensure efficient data transmission. Without BPDU and the Spanning Tree Protocol, network performance and stability could be compromised.
The BPDU Format
The Bridge Protocol Data Unit (BPDU) is a data unit used by network switches to exchange information about the network topology. It is a fundamental part of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and is used by switches to elect a root bridge and determine the best path to reach the root bridge.
A BPDU is encapsulated in an Ethernet frame and contains various fields that convey important information. The fields of a BPDU include the priority, the MAC address of the sending bridge, the sequence number, and other information specific to the STP implementation being used.
The BPDU format is standardized and ensures compatibility between different network switches. It allows switches to exchange information about their roles, such as root bridge or designated bridge, and their current state, such as forwarding or blocking. This information is crucial for maintaining a loop-free topology and preventing network loops, which can cause broadcast storms and degrade network performance.
When a switch receives a BPDU, it analyzes the information within the unit to make decisions about its role within the network. It determines whether it should become the root bridge or a designated bridge based on the priority and MAC address values. The received BPDU also contains a topology change flag, which allows switches to quickly react to any topology changes in the network.
In summary, the BPDU format is a crucial aspect of networking, specifically in Ethernet-based networks. It allows switches to exchange information about the network topology and make decisions that ensure a loop-free and efficient network. Understanding the BPDU format is essential for network administrators and engineers to properly configure and manage their switches.
Understanding the Components of a BPDU
A Bridge Protocol Data Unit (BPDU) is a special data unit used in networking to manage the spanning tree protocol. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the topology of a network by exchanging information between switches. A BPDU is a frame-based unit that is encapsulated within the Ethernet frame format.
The main components of a BPDU include the bridge ID, port ID, and the root bridge ID. The bridge ID uniquely identifies each switch in the network and is used to determine the root switch. The port ID represents the port on the switch through which the BPDU is sent. The root bridge ID is the ID of the root switch in the network.
The BPDU also contains other important information like the path cost and the bridge priority. The path cost is the cumulative cost of sending a packet from one switch to another, and it helps in determining the best path for forwarding packets. The bridge priority is a value assigned to each switch and is used to elect the root bridge in the network.
When a switch receives a BPDU, it compares the bridge ID, port ID, root bridge ID, and other information with its own values. Based on the comparison, the switch makes decisions on forwarding or blocking ports to prevent loops in the network. This process helps in establishing a loop-free network topology.
In summary, a BPDU is a crucial component of the spanning tree protocol in networking. It contains information about the switch, port, root bridge, path cost, and bridge priority. By exchanging and analyzing BPDUs, switches can determine the best path for packet forwarding and prevent loops in the network.
The Different Types of Bridge Protocol Data Units
In networking, the Bridge Protocol Data Unit (BPDU) is a frame-based protocol that is used to establish and maintain a loop-free network topology. It is primarily used in Ethernet networks, where multiple switches are interconnected to create a spanning tree network. The BPDU carries information about the network topology and is exchanged between switches to ensure that the network operates efficiently and without any loops.
There are two main types of BPDU: Configuration BPDU (CBPDU) and Topology Change Notification (TCN) BPDU. The CBPDU is used to exchange information about the spanning tree configuration, such as the root bridge, bridge priorities, and port roles. It is sent periodically by the root bridge to all other switches in the network. The TCN BPDU, on the other hand, is used to notify switches of a change in the network topology, such as a switch or port becoming unavailable.
The CBPDU contains important data that is used by switches to calculate the spanning tree. It includes fields such as the switch’s MAC address, bridge priority, port priority, and port roles. The MAC address is used to identify the sender of the BPDU, while the bridge priority determines the root bridge in the spanning tree. The port priority and port roles determine the forwarding behavior of each switch port.
The TCN BPDU, as the name suggests, is used to notify switches of a topology change in the network. This could be a result of a switch or port going down, or a new switch or port being added to the network. When a switch receives a TCN BPDU, it will trigger a process called the topology change notification process. This process involves the switch flushing its MAC address table and recalculating the spanning tree. It ensures that the network adapts to the topology change quickly and efficiently, without disrupting the communication between devices.
In summary, the BPDU is a crucial part of the spanning tree protocol in Ethernet networks. The different types of BPDUs, including the Configuration BPDU and Topology Change Notification BPDU, carry important data about the network topology and changes in the topology. They are exchanged between switches to establish a loop-free network and ensure efficient communication within the network.
BPDU Transmission and Exchange
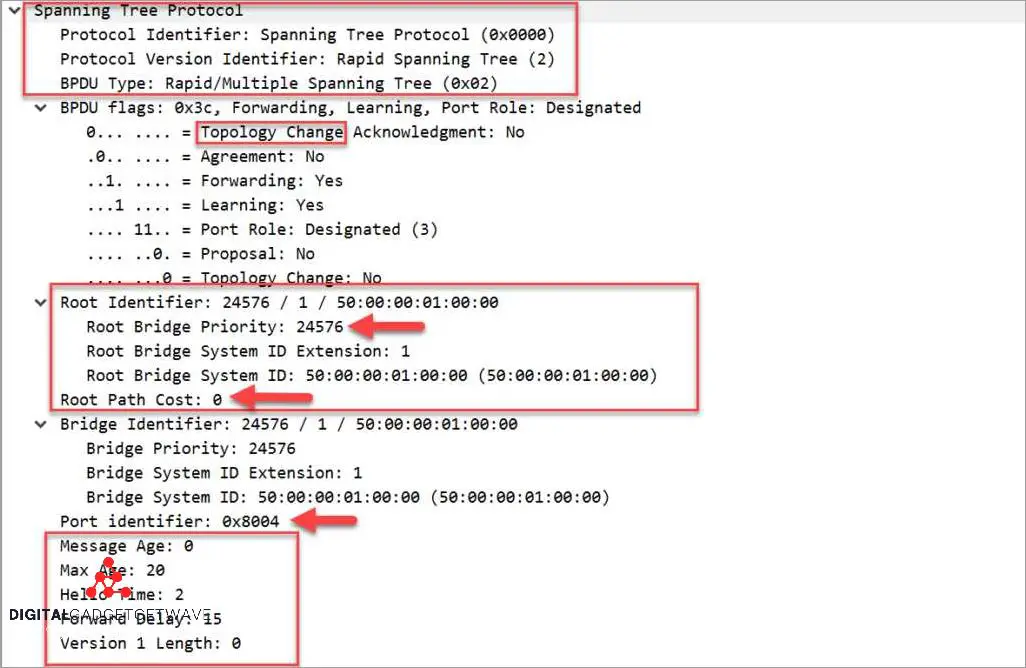
BPDU (Bridge Protocol Data Unit) transmission and exchange is a critical aspect of networking protocols. A BPDU is a special type of frame that carries information about bridge and network topology. It is used by switches in a network to communicate and establish a loop-free topology using the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP).
When a switch sends out a BPDU, it includes information about the switch’s identity, priority, and the status of its ports. The BPDU frames are transmitted periodically to ensure that all switches in the network have up-to-date information about the network topology. This allows switches to collectively determine the best path to forward data packets and avoid loops that can cause network congestion and disruptions.
During the BPDU exchange process, switches compare the information in the received BPDU frames with their own bridge ID and port information. They use this information to elect a root bridge and to determine the best paths to reach the root bridge. This process helps in creating a loop-free tree-like structure known as the spanning tree. The spanning tree ensures that redundant paths are blocked, preventing loops and ensuring efficient data transmission within the network.
Ethernet switches are primarily responsible for transmitting and exchanging BPDU frames in a network. They use a designated BPDU multicast address to send the frames to all other switches in the network. The BPDU frames are encapsulated in Ethernet frames and transmitted according to the network’s physical and data link layer procedures.
In summary, BPDU transmission and exchange play a crucial role in establishing and maintaining a loop-free network topology. It allows switches to coordinate and make informed decisions about the forwarding of data packets within the network. By exchanging BPDU frames, switches create the spanning tree, which ensures efficient and reliable data transmission in a network.
How BPDU Messages are Sent
BPDU (Bridge Protocol Data Unit) messages are an essential part of the spanning tree protocol (STP) in networking. These messages are sent by network switches to communicate information about the network topology and ensure the creation of a loop-free spanning tree.
When a switch is first powered on or connected to the network, it starts sending out BPDU messages. These messages are encapsulated in Ethernet frames and are sent to a special multicast address called the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Bridge Group Address.
The BPDU frames contain information about the bridge’s priorities, bridge identifiers, and port costs. They also include information about the root bridge and the sender’s position in relation to the root bridge. This information is used by switches to make decisions on which ports to block or forward traffic on, in order to prevent loops in the network.
When a switch receives a BPDU message, it compares the information in the received message with its own STP information. If the received message contains better or more up-to-date information, the switch updates its STP information accordingly. If the received message contains inferior information, the switch simply discards the BPDU.
BPDU messages are sent periodically by switches to ensure that the network topology remains updated. The frequency of BPDU transmission is determined by the value of the hello-time parameter, which is configurable on switches. By default, switches send BPDU messages every two seconds in most networking protocols.
In summary, BPDU messages are the data units used by bridges and switches to exchange information about the network topology. These messages are encapsulated in frames and are sent periodically to ensure the creation of a loop-free spanning tree. By exchanging BPDU messages, switches are able to determine the root bridge, calculate the best path to the root bridge, and prevent loops in the network.
Receiving and Processing BPDU Messages
When a bridge is connected to a network and is running the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), it actively participates in the process of creating and maintaining a loop-free topology. This is achieved through the exchange of Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) with other bridges in the network.
When a bridge receives a BPDU message, it first checks the information contained within the BPDU to determine if it is a superior bridge. If the receiving bridge has a lower priority or bridge ID, it will update its own priority and bridge ID to that of the superior bridge.
The bridge then examines the flags and timers in the BPDU to determine the state of the network. For example, the Topology Change flag indicates if there has been a recent change in the network’s topology, while the Root Bridge ID identifies the bridge that is currently the root of the spanning tree. By analyzing these values, the bridge can make informed decisions about its role in the network.
Once the bridge has processed the information in the BPDU, it can take appropriate actions. For example, if the bridge determines that it is a designated bridge, it will proceed to forward the BPDU out of all its designated ports. On the other hand, if the bridge determines that it is the root bridge, it will send its own BPDU with the Root Bridge ID set to its own bridge ID.
In summary, the receiving and processing of BPDU messages is a crucial component of networking protocols like STP. By analyzing the information contained within BPDUs, bridges can determine their role in the network and take appropriate actions to ensure a loop-free topology.
BPDU Filtering and Filtering Databases
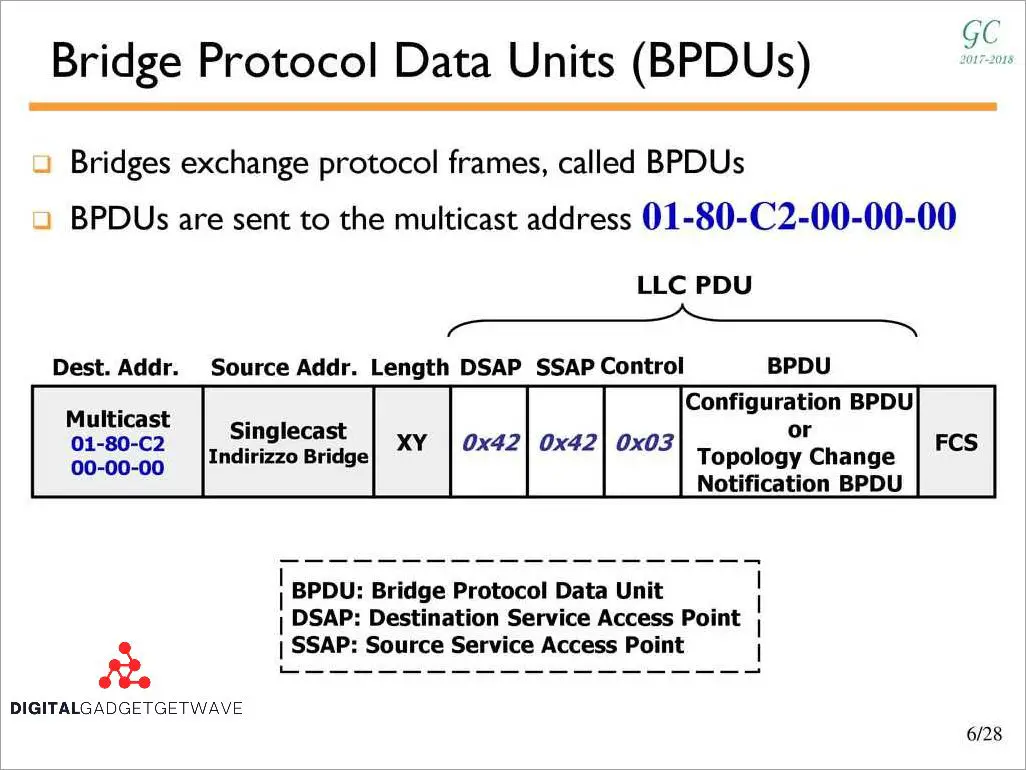
BPDU Filtering
BPDU Filtering is a feature in network switches that allows you to control the forwarding of Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) on a particular port. BPDUs are protocol messages used by Ethernet switches to communicate and establish the network topology. By enabling BPDU Filtering on a switch port, you can prevent the transmission and reception of BPDUs, effectively disabling Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on that port.
Filtering Databases
In the context of BPDU Filtering, a filtering database is a table or record that keeps track of the configured state of BPDU filtering on each switch port. This database is used by the switch to determine whether BPDUs should be forwarded or filtered on a specific port.
When BPDU Filtering is enabled on a switch port, the port is added to the filtering database and marked as a BPDU-filtered port. As a result, BPDUs received on that port are not sent out to other ports in the network, and BPDUs from other switches are not received on that port.
The filtering database can be accessed and modified through the switch’s management interface or command-line interface. It allows network administrators to selectively enable or disable BPDU filtering on specific ports, based on their understanding of the network topology and requirements.
By configuring the filtering database, administrators can effectively control the behavior of the switch and the network in terms of BPDU forwarding and filtering. This ensures that the network topology remains stable and that loop-free paths are established through the spanning tree algorithm.
The Role of BPDU Filtering in Network Maintenance
In computer networking, the bridge protocol data unit (BPDU) plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and efficiency of network topology. BPDU filtering is a feature that helps to manage and control the distribution of BPDU frames within a network.
BPDU frames are used by bridges and switches to exchange information about network topology and to prevent loops from occurring in the network. These frames contain data such as the bridge ID, the port ID, and the path cost to reach a particular bridge. By analyzing this data, the switches can determine the most optimal path for forwarding Ethernet frames within the network.
However, in certain situations, it may be necessary to filter out or discard some BPDU frames. One common scenario is when there are multiple switches connected to the same network segment. Without filtering, each switch would receive and process every BPDU frame, which can cause unnecessary overhead and consume network resources.
By implementing BPDU filtering, network administrators can reduce the amount of BPDU frames that are processed by switches. This can help to improve network performance and reduce congestion, especially in large and complex networks with multiple switches.
BPDU filtering can be configured on individual switch ports or globally on a switch. When a switch port is configured with BPDU filtering, it will not process incoming BPDU frames and will not participate in the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) calculations. This can be useful in scenarios where a switch port is connected to an end device, such as a server, that does not need to participate in STP or where the switch port is connected to a non-STP aware device.
Overall, BPDU filtering is an important tool for network maintenance as it helps to optimize the distribution of BPDU frames and reduce unnecessary processing by switches. By properly configuring BPDU filtering, network administrators can ensure the stability and efficiency of their network infrastructure.
Managing BPDU Filtering Databases
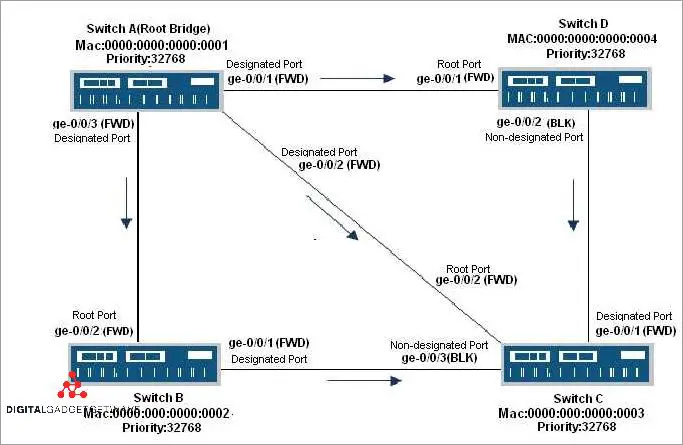
When it comes to managing BPDU filtering databases in Ethernet bridging networks, it is important to understand how bridge protocol data units (BPDUs) work. BPDUs are frames that are used by switches to exchange information about the network topology and establish a spanning tree protocol. These BPDUs contain important information such as the switch ID, the switch priority, and the port ID.
In a BPDU filtering database, each entry corresponds to a specific bridge port. The database keeps track of which BPDUs are allowed or blocked on each port. The filtering database is responsible for determining if a received BPDU should be processed or discarded. This process is crucial for maintaining the integrity and stability of the network.
Managing the BPDU filtering database involves configuring the specific rules for each bridge port. These rules determine whether BPDUs received on a particular port should be passed through or filtered out. By carefully configuring the filtering database, network administrators can control the flow of BPDUs and ensure that only necessary information is processed.
It is important to note that in certain scenarios, such as when implementing a redundancy protocol like Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP), the BPDU filtering database may need to be adjusted to allow specific BPDUs to be processed. This is because RSTP relies on BPDUs to detect and respond to changes in the network topology.
In summary, managing the BPDU filtering databases in Ethernet bridging networks is essential for maintaining a stable and efficient network. By configuring the filtering rules for each bridge port, network administrators can control the flow of BPDUs and ensure that the network operates according to the desired topology and protocol.
FAQ about topic “Understanding BPDU in Networking: How Bridge Protocol Data Units Work”
What is a BPDU?
A BPDU stands for Bridge Protocol Data Unit. It is a data packet used in networking to ensure the loop-free operation of bridges and switches in a spanning tree network.
How does BPDU guard work?
BPDU guard is a feature in networking that protects against the misconfiguration of switch ports. When BPDU guard is enabled on a port, it will automatically shut down the port if it receives a BPDU packet, indicating a misconfiguration or potential looping in the network.
What is the purpose of BPDU filtering?
BPDU filtering is a feature in networking that allows a switch port to ignore or filter out BPDU packets. This is useful in certain scenarios where a switch port should not participate in the spanning tree protocol, such as when connecting to a non-switch device.
How does a switch choose the root bridge?
A switch chooses the root bridge based on the Bridge ID, which is a combination of the Bridge Priority and the MAC address of the switch. The switch with the lowest Bridge ID becomes the root bridge in a spanning tree network.
What is the purpose of BPDU timers?
BPDU timers are used in networking to control the frequency at which BPDU packets are sent and received. They help ensure the stability and efficiency of the spanning tree protocol by regulating the exchange of information between switches and preventing unnecessary network traffic.

