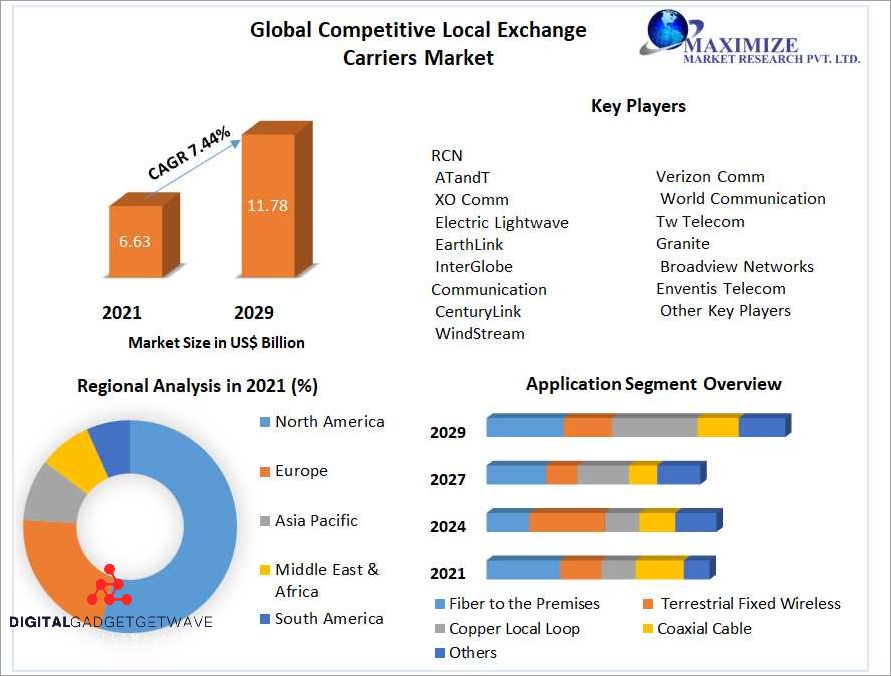
A Competitive Local Exchange Carrier (CLEC) is a telecommunications company that competes with traditional local telephone companies (Incumbent Local Exchange Carriers or ILECs) in providing various communication services to customers in a specific geographic area.
CLECs play a vital role in the telecom industry by offering alternative options to consumers and businesses for voice, data, and broadband services. They typically use their own network infrastructure, including fiber optic cables, switches, and routers, to provide these services.
Competition in the local telecom market is essential for consumers and businesses alike, as it offers greater choice and drives innovation. CLECs bring competition to areas that were previously monopolized by ILECs, leading to improved service quality, lower prices, and advancements in technology.
One of the key advantages of choosing a CLEC over an ILEC is the ability to access a wider range of services, such as advanced telecommunications solutions, wireless connectivity, and high-speed internet. CLECs often specialize in delivering reliable and cost-effective solutions tailored to the specific needs of their customers.
In order to operate, CLECs must comply with various regulations and guidelines set by regulatory bodies. These regulations ensure fair competition between CLECs and ILECs, and help maintain a level playing field in the telecom industry.
Contents
- 1 Definition and Purpose
- 2 Regulation and Market Competition
- 3 Services and Offerings
- 4 Key Players and Examples
- 5 FAQ about topic “Understanding Competitive Local Exchange Carriers (CLECs)”
- 6 What is a Competitive Local Exchange Carrier?
- 7 How do CLECs compete with ILECs?
- 8 What are some advantages of using a CLEC?
- 9 Do CLECs provide the same quality of service as ILECs?
- 10 Can I switch from my current ILEC to a CLEC?
Definition and Purpose
A Competitive Local Exchange Carrier (CLEC) is a telecom company that competes with traditional local exchange carriers (LECs) to provide telecommunication services within a specific geographic area. CLECs typically focus on offering alternative telephony and broadband services to residential and business customers.
The purpose of a CLEC is to provide competition in the telecommunications industry, which was historically dominated by large incumbent carriers. By offering competitive pricing, innovative services, and a focus on customer satisfaction, CLECs aim to challenge the monopoly or duopoly power of the incumbent carriers in the local exchange market.
CLECs often invest in their own infrastructure, including the deployment of fiber-optic networks, to offer high-speed broadband services and reliable telecommunication connections. This allows them to compete with incumbent carriers by offering a choice to customers who may have limited options in the market.
Regulation plays a significant role in shaping the operations of CLECs. They must adhere to certain regulatory requirements, such as obtaining licenses and complying with regulations related to the provision of telecommunications services. However, regulatory frameworks also aim to promote fair competition and protect consumers by preventing anti-competitive practices in the market.
With the advancement of technology, CLECs have expanded their offerings to include internet services, wireless telecommunication options, and various communication solutions. They strive to differentiate themselves through innovative products, exceptional customer service, and efficient operations to gain a competitive edge in the market.
In summary, a CLEC is a competitive telecommunications carrier that operates in the local exchange market to provide alternative telephony, internet, and broadband services. By offering choice and promoting competition, CLECs aim to provide customers with more options, better services, and competitive pricing compared to incumbent carriers.
Understanding the Competitive Local Exchange Carrier (CLEC)
A Competitive Local Exchange Carrier (CLEC) is a company that operates in the telecommunications industry as a competitive provider of communication services. These services include broadband internet, telephony, and data services. Unlike traditional local exchange carriers which operate in a regulated market, CLECs operate in a competitive environment.
CLECs typically own and maintain their own infrastructure, which includes networks and facilities for delivering these services. They often invest in technologies such as fiber optic cables to provide high-speed broadband connections to customers. This infrastructure allows CLECs to compete with other companies in the industry, including incumbent local exchange carriers (ILECs).
The CLEC industry has emerged as a result of competition and deregulation in the telecommunications market. In the past, local exchange carriers held a monopoly on providing communication services in their designated areas. However, with the introduction of competition, CLECs were able to enter the market and provide alternative options to consumers.
Regulation plays a significant role in the CLEC industry. CLECs must comply with regulations set by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) and other regulatory bodies to ensure fair competition and protect consumer rights. These regulations govern various aspects of the industry, such as pricing, interconnections with other carriers, and access to essential facilities.
As CLECs compete in the local exchange market, they strive to provide reliable and efficient communication services to businesses and consumers. They offer a range of services, including voice, data, and internet services, to meet the diverse needs of their customers. CLECs often differentiate themselves from ILECs by offering more competitive pricing, innovative service packages, and enhanced customer support.
In conclusion, CLECs are competitive providers in the local exchange market, offering a range of communication services to businesses and consumers. They operate in a deregulated environment and invest in their own infrastructure to provide reliable and high-speed broadband connections. Despite the challenges of competition and regulation, CLECs continue to play a significant role in the telecommunications industry.
Role and Importance of CLECs
CLECs, or Competitive Local Exchange Carriers, play a fundamental role in the communication industry, especially in the telephony market. These companies operate in local areas, providing competitive alternatives to incumbent local exchange carriers (ILECs) in terms of voice and broadband services.
The presence of CLECs is vital to foster competition and innovation in the telecommunications market. By offering alternative services and pricing to customers, CLECs create a more competitive environment, which benefits consumers and encourages technological advancements.
Furthermore, CLECs contribute to the development of a robust infrastructure by building and maintaining their own networks. These networks typically consist of both wireline and wireless connections, using technologies such as fiber optics and other high-speed transmission mediums.
Regulations also play a significant role in ensuring fair competition between CLECs and ILECs. The government imposes certain rules and requirements to promote a level playing field and prevent unfair practices. This regulation fosters competition, as well as ensures that all providers adhere to certain standards of service quality and reliability.
By offering a variety of services, such as voice, data, broadband, and internet connectivity, CLECs enhance customer choice and provide additional options compared to traditional ILECs. These services can be delivered through various platforms, including conventional landlines, wireless connections, or even through the internet.
Overall, CLECs are essential players in the communication industry, facilitating competition, technological innovation, and customer choice. Their contributions help drive the industry forward and improve the quality and affordability of communication services for local communities.
Regulation and Market Competition
In the telecommunications industry, competition among carriers is regulated by government bodies to ensure fair market practices and protect consumer interests. The emergence of Competitive Local Exchange Carriers (CLECs) has played a significant role in promoting competition in the local communication market.
CLECs are alternative providers of local telephony and data services, competing directly with the incumbent local exchange carriers. They utilize their own network infrastructure, including fiber-optic cables and wireless technologies, to offer competitive communication services such as voice, data, and broadband internet.
Regulation in the telecom sector involves setting rules and guidelines that govern the behavior of carriers and encourages fair competition. Regulatory bodies ensure that incumbent providers, as well as CLECs, adhere to these rules and operate in a manner that promotes a level playing field.
Market competition stimulates innovation and drives carriers to improve their services and offer competitive pricing. With a competitive market, consumers have more options to choose from and can benefit from better-quality services and affordable pricing. This has led to rapid advancements in technology and has made high-speed internet and other advanced communication services more accessible to a broader range of consumers.
Furthermore, competition in the local exchange market has incentivized carriers to invest in network infrastructure and expand their coverage. The proliferation of fiber-optic networks and wireless technologies has enabled CLECs and incumbent carriers to provide high-speed internet connections, contributing to the growth of the broadband industry.
Overall, regulation and market competition in the telecom industry create a balanced environment where carriers can offer innovative and cost-effective communication solutions. This allows consumers to have access to a wide variety of providers and services, ultimately benefiting from improved communication infrastructure and competitive pricing.
Regulatory Environment for CLECs
Operating as a Competitive Local Exchange Carrier (CLEC) in the telecommunications industry requires complying with a complex regulatory environment. CLECs are subject to regulations that aim to promote competition, protect consumers, and ensure fair market practices.
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) plays a crucial role in regulating CLECs and overseeing the industry. The FCC sets rules and guidelines that CLECs must adhere to, including requirements for interconnection, unbundling of network elements, and access to essential facilities.
One key area of regulation for CLECs is ensuring fair competition in the market. CLECs must demonstrate that they can offer services that are comparable to those of incumbent local exchange carriers (ILECs), the dominant providers in a given market. This includes providing competitive options for voice telephony, internet connectivity, and broadband services.
The regulatory environment also addresses issues related to network infrastructure. CLECs may deploy their own fiber optic networks or lease capacity on existing networks. The FCC regulates the terms and conditions of network access, ensuring that CLECs have fair and reasonable opportunities to compete in the market.
In addition to FCC regulations, CLECs must also comply with state-level regulations. State public utility commissions oversee the activities of CLECs within their jurisdictions and enforce compliance with state-specific rules. These regulations may include licensing requirements, consumer protection measures, and local service quality standards.
The evolving nature of the telecom industry and the increasing demand for new services, such as wireless and IP-based technologies, pose additional challenges for CLECs. As technology advances, regulatory bodies must adapt to address emerging issues, such as the regulation of Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) services or the transition to all-IP networks.
Competition in the Local Exchange Market
The local exchange market, which refers to the provision of telephony and communication services within a specific geographical area, has become increasingly competitive in recent years. This is due to deregulation and the emergence of competitive local exchange carriers (CLECs) alongside traditional incumbent carriers.
CLECs are telecommunications companies that compete with incumbent carriers by providing alternative voice, broadband, and wireless services. This competition has been facilitated by regulatory measures aimed at promoting a more open and competitive telecom industry.
With the advancement of technology, CLECs have been able to leverage modern infrastructure, such as fiber-optic networks, to deliver high-speed internet and communication services to customers. This has allowed for increased choice and diversity in the local exchange market.
One key advantage of CLECs is their ability to offer innovative services and pricing models, often at a lower cost than incumbent carriers. This has forced traditional providers to adapt and improve their own offerings to stay competitive.
In addition, the entrance of CLECs has stimulated investment in local telecom infrastructure, as companies seek to expand and enhance their service offerings. This has resulted in improved network quality and coverage, benefiting both residential and business customers.
Overall, the increasing competition in the local exchange market has led to a more dynamic and customer-centric industry. Consumers now have access to a wider range of service providers and can choose the option that best suits their needs and budget. This competition has also spurred innovation and advancement in the telecom industry, driving the development of new technologies and services.
Services and Offerings
A Competitive Local Exchange Carrier (CLEC) offers a variety of services and offerings to meet the communication needs of local businesses and consumers.
One of the main services provided by a CLEC is internet connectivity. They offer high-speed internet access through their telecom network infrastructure, including fiber and wireless technologies. This allows businesses and consumers to access the internet with fast and reliable connections, enabling them to transmit data, communicate, and access online services.
In addition to internet services, a CLEC also provides local telephony services. They offer competitive local and long-distance calling plans, allowing businesses and consumers to make and receive calls within their local exchange area as well as to other regions. These telephony services can be tailored to meet the specific needs of different customers, whether it is a small business with a few phone lines or a large corporation with extensive telecommunication requirements.
Furthermore, a CLEC may offer a range of other communication services, such as hosting, cloud-based solutions, and virtual private networks. These services enable businesses to enhance their communication capabilities and facilitate efficient collaboration and data sharing.
Being a competitive player in the telecom industry, CLECs strive to differentiate themselves by offering unique features, competitive pricing, and superior customer support. They aim to provide alternative options in the market, driving competition and ensuring that businesses and consumers have a choice in selecting their telecom service provider.
In summary, a CLEC offers a comprehensive range of services and offerings, including internet connectivity, local and long-distance telephony services, and additional communication solutions. By leveraging their network infrastructure and competing in the market, CLECs contribute to the availability of competitive and reliable telecom services for businesses and consumers.
Types of Services Provided by CLECs
CLECs, or Competitive Local Exchange Carriers, provide a variety of services in the telecommunications industry. These companies specialize in offering competitive alternatives to traditional telecom providers in the local market.
One of the main services provided by CLECs is internet broadband. CLECs use their own network infrastructure, including fiber optic cables, to deliver high-speed internet services to businesses and residential customers. This competition in the broadband market helps drive innovation and improve service quality.
CLECs also offer communication services such as telephony, both traditional landline and internet-based voice services. By utilizing their own network infrastructure, CLECs are able to provide cost-effective and reliable telephone services to customers, often with additional features such as voicemail and call forwarding.
Furthermore, CLECs may provide wireless services in addition to their wired offerings. They can act as wireless carriers, providing mobile phone services and wireless data connectivity. This allows customers to have more options and choices when it comes to their wireless service provider.
In summary, CLECs play a crucial role in the telecom industry by offering competitive services in the local market. They provide internet broadband, telephony, and wireless services, utilizing their own network infrastructure to deliver reliable and cost-effective solutions. Their presence helps drive competition and innovation, benefitting customers and the industry as a whole.
Benefits of Choosing a CLEC
Choosing a Competitive Local Exchange Carrier (CLEC) for your telecommunication needs can offer several benefits.
- Competition: The presence of a CLEC in the market promotes competition, which can lead to better service quality and competitive pricing. This competition encourages providers to continually improve their offerings to attract and retain customers.
- Expanded Coverage: CLECs often have their own infrastructure, including fiber optic networks, which allows them to provide broadband and wireless services in areas where traditional carriers may not have a strong presence. This expanded coverage can benefit businesses and consumers in underserved areas.
- Choice of Services: CLECs offer a range of services beyond traditional voice telephony, including high-speed internet access, cloud-based communication solutions, and managed services. This variety of offerings allows customers to choose the services that best fit their needs and budget.
- Regulatory Flexibility: CLECs are subject to different regulations compared to traditional carriers. This regulatory flexibility enables CLECs to quickly adapt to changes in the industry and offer innovative services that meet the evolving demands of customers.
- Local Expertise: CLECs often have a deep understanding of the local market and infrastructure, which can be beneficial when it comes to troubleshooting issues and providing personalized solutions to customers. Their local presence allows for quicker response times and more personalized customer service.
In conclusion, choosing a CLEC as your telecom provider can offer benefits such as increased competition, expanded coverage, a wider choice of services, regulatory flexibility, and local expertise. These advantages make CLECs a compelling option for businesses and consumers looking for reliable and innovative communication solutions.
Market Trends and Future Outlook for CLECs
The market trends and future outlook for Competitive Local Exchange Carriers (CLECs) are influenced by various factors. The increasing demand for faster and more reliable communication services has fueled the growth of telephony and internet providers. With the advent of new technologies such as fiber optic networks and wireless communication, CLECs have a unique opportunity to capture a larger share of the market.
In recent years, CLECs have been investing heavily in infrastructure to expand their networks and provide better services to customers. The deployment of fiber optic cables has enabled CLECs to offer high-speed broadband internet services, which are essential for businesses and individuals in today’s digital age.
Furthermore, CLECs are now moving beyond traditional telephony services and venturing into the wireless market. With the increasing popularity of mobile devices and the demand for seamless connectivity, CLECs are partnering with wireless carriers to provide integrated communication solutions to their customers.
One of the key advantages of CLECs is their ability to compete with traditional telecom companies in the local market. By leveraging their advanced network infrastructure, CLECs can offer competitive pricing and innovative services to customers, challenging the dominance of incumbent providers.
However, the future outlook for CLECs is not without challenges. The regulatory environment and government policies play a crucial role in shaping the market dynamics. CLECs need to navigate through complex regulations and ensure compliance to stay competitive.
Overall, the market for CLECs is expected to grow steadily in the coming years. As businesses and consumers increasingly rely on communication services, CLECs have the opportunity to capture a significant share of the market by providing reliable and advanced solutions.
Key Players and Examples
There are several key players in the competitive local exchange carrier (CLEC) market, providing a variety of broadband and telecom services. These providers operate at the local level, offering alternatives to traditional telephone companies in terms of service and pricing. Some of the major CLECs include:
- AT&T: One of the largest CLECs in the market, AT&T offers a wide range of telecommunication services, including local and long-distance calling, internet connectivity, and wireless communication.
- Verizon: Known for its extensive network infrastructure, Verizon is a leading CLEC with a strong presence in both the local and national markets. It offers a range of services, including internet, telephony, and fiber optic connectivity.
- CenturyLink: Operating across multiple states, CenturyLink is a competitive player in the CLEC market. It provides a range of telecom services, including local phone lines and internet access.
- Frontier Communications: Frontier Communications is another prominent CLEC, offering services in rural and urban areas. It specializes in providing broadband internet and telephone services to residential and business customers.
These CLECs compete with traditional telephone companies, such as AT&T and Verizon, in the local market. They have invested in their own network infrastructure, including wireless and fiber optic communication networks, to provide reliable and high-speed services to their customers.
Competition in the CLEC market is regulated by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the United States. The FCC sets rules and guidelines to ensure fair competition and protect consumers’ interests. CLECs must comply with these regulations and maintain a high standard of service quality.
In addition to the key players mentioned above, there are numerous other CLECs operating in the market, ranging from regional providers to niche companies that offer specialized telecom services. The CLEC market continues to evolve as new technologies and innovations emerge, shaping the future of local telecommunication services.
Leading CLECs in the Industry
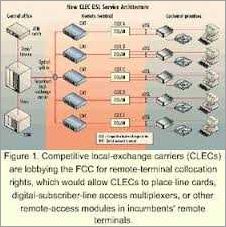
A Competitive Local Exchange Carrier (CLEC) is a telecom company that competes with traditional local exchange carriers (ILECs) by using its own infrastructure to provide communication services in a specific market. These CLECs have emerged as strong players in the industry, challenging the dominance of ILECs and offering innovative solutions to customers.
One of the leading CLECs in the industry is XYZ Telecom, which has built a robust fiber optic network that covers a wide geographic area. This network allows XYZ Telecom to offer high-speed internet and telephony services to businesses and residential customers. By leveraging their extensive network infrastructure, XYZ Telecom is able to provide competitive pricing and reliable service to their customers.
Another company leading the CLEC market is ABC Carrier. With a focus on wireless communication, ABC Carrier offers innovative solutions for mobile telephony and data services. Their advanced network technology ensures fast and reliable connectivity, making them a popular choice among customers. ABC Carrier’s strong presence in the local market has made them a formidable competitor to traditional ILECs.
Regulation has played a significant role in shaping the CLEC industry. The Telecommunications Act of 1996 allowed CLECs to enter the market and compete with ILECs, fostering competition and innovation. This regulatory environment created opportunities for CLECs to build their own networks and provide services that challenge the status quo.
In summary, leading CLECs in the industry are making significant strides in the telecom market. Through their competitive pricing, innovative services, and robust network infrastructure, these CLECs are providing customers with reliable communication options and challenging the dominance of traditional ILECs. As technology continues to evolve, CLECs will likely play an even bigger role in shaping the future of the telecommunications industry.
Success Stories of CLECs
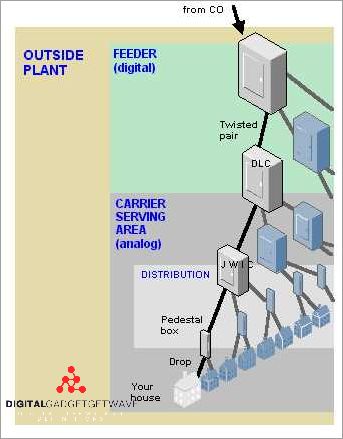
CLECs (Competitive Local Exchange Carriers) play a vital role in the communication industry, providing alternative local exchange services to traditional telecom companies. These companies have achieved significant success by leveraging their competitive advantage and innovative infrastructure.
One success story is a CLEC that focuses on providing high-speed internet services to underserved areas. By deploying broadband infrastructure and wireless networks, they have bridged the digital divide and brought reliable internet access to rural communities. This has not only improved connectivity but also opened up new opportunities for education, healthcare, and entrepreneurship.
Another success story is a CLEC that has revolutionized the telephony market by offering feature-rich services at competitive prices. They have leveraged their advanced network infrastructure to provide superior voice quality, enhanced call features, and cost-effective communication solutions. This has attracted a large customer base, including businesses and residential users, who have benefited from the company’s reliable and affordable telephony services.
One CLEC success story involves a company that specializes in fiber optic network deployment. By investing in fiber optic infrastructure, they have built a robust network that delivers ultra-fast and reliable broadband services. This has positioned them as a leading provider of high-speed internet, attracting customers who demand high bandwidth for streaming, gaming, and other data-intensive applications.
Furthermore, a successful CLEC has emerged as a key player in the telecommunications market by focusing on niche segments. They have tailored their services to meet the unique needs of specific industries or regions, providing specialized communication solutions. This targeted approach has enabled them to offer customized services, gain a competitive edge, and capture a significant market share.
In conclusion, CLECs have achieved remarkable success by offering competitive and innovative communication services. By leveraging their advanced network infrastructure, these companies have brought affordable broadband, reliable telephony, and specialized communication solutions to the market. Their success stories demonstrate the importance of competition and innovation in driving the growth and development of the telecom industry.
Comparing CLECs to Traditional Telecom Providers
When it comes to the local exchange carrier (LEC) industry, there are two main types of providers: traditional telecom providers and competitive local exchange carriers (CLECs). While both provide telephony and communication services, there are several key differences between the two.
Traditional telecom providers, also known as incumbent local exchange carriers (ILECs), are the established companies that have historically dominated the telecom industry. They have built extensive infrastructure, such as copper wire networks, to provide telephone and broadband services to customers.
CLECs, on the other hand, are newer players in the market that entered the industry as a result of the Telecommunications Act of 1996, which opened up competition in the telecom industry. They focus on providing local exchange services and often use more advanced technologies, such as fiber-optic networks, to deliver high-speed internet and other communication services.
One of the main advantages of CLECs is their ability to compete with traditional telecom providers. The deregulation of the industry has allowed CLECs to enter the market and offer competitive pricing and innovative services. This competition has led to lower prices, increased choice, and improved service quality for consumers.
CLECs also often specialize in specific areas of the telecom industry, such as business services or wireless communication. This specialization allows them to tailor their offerings to the needs of specific customer segments and provide more targeted solutions.
However, CLECs face challenges in competing with traditional telecom providers. They often lack the same level of infrastructure and network coverage as incumbent carriers, which can limit their ability to reach customers in certain areas. Additionally, CLECs must navigate complex regulatory frameworks to operate in the industry, which can add costs and administrative burdens.
In conclusion, while traditional telecom providers have long dominated the industry, CLECs have emerged as strong competitors in the market. They offer innovative services, competitive pricing, and specialization, but face challenges in terms of infrastructure and regulatory compliance. The ongoing competition between these two types of carriers is driving advancements in the telecom industry and benefiting consumers.
FAQ about topic “Understanding Competitive Local Exchange Carriers (CLECs)”
What is a Competitive Local Exchange Carrier?
A Competitive Local Exchange Carrier (CLEC) is a telecommunications company that competes with traditional local telephone companies, also known as Incumbent Local Exchange Carriers (ILECs). CLECs provide various services such as local and long-distance phone service, broadband internet, and data services to businesses and residential customers. Unlike ILECs, CLECs do not own the physical infrastructure of the telecommunications network, but instead lease it from ILECs or build their own network.
How do CLECs compete with ILECs?
CLECs compete with ILECs by offering alternative and often more competitive pricing plans, better customer service, and innovative services. They can negotiate lower rates for leasing network infrastructure from ILECs, which allows them to offer competitive pricing to their customers. Additionally, CLECs are often more flexible and responsive to customer needs compared to ILECs, which can be large and bureaucratic organizations. CLECs also have the advantage of being able to leverage new technologies and offer services that may not be available from ILECs.
What are some advantages of using a CLEC?
Using a CLEC can have several advantages. First, CLECs often offer more competitive pricing plans compared to ILECs, which can result in cost savings for businesses and individuals. Second, CLECs may offer more flexible and customizable service options, allowing customers to choose the services that best fit their needs. Third, CLECs are generally more responsive to customer service requests and provide better support compared to large ILECs. Finally, CLECs often have the latest technological advancements, allowing them to offer innovative services and features that may not be available from ILECs.
Do CLECs provide the same quality of service as ILECs?
CLECs strive to provide high-quality service to their customers, but the quality of service can vary depending on the specific CLEC and their network infrastructure. Some CLECs may have invested in high-quality network infrastructure that can deliver reliable and consistent service, while others may rely on leased infrastructure from ILECs, which could impact the quality of service. It is important for customers to research and compare the service quality of different CLECs before making a decision.
Can I switch from my current ILEC to a CLEC?
Yes, in most cases, you can switch from your current ILEC to a CLEC. However, the availability of CLEC services can vary depending on your location. Before switching, you should research and compare the services, pricing, and customer reviews of different CLECs in your area. You may also need to check if there are any contractual obligations or penalties associated with terminating your service with the ILEC. It is recommended to contact the CLEC directly for more information on the switching process and to ensure a smooth transition.


