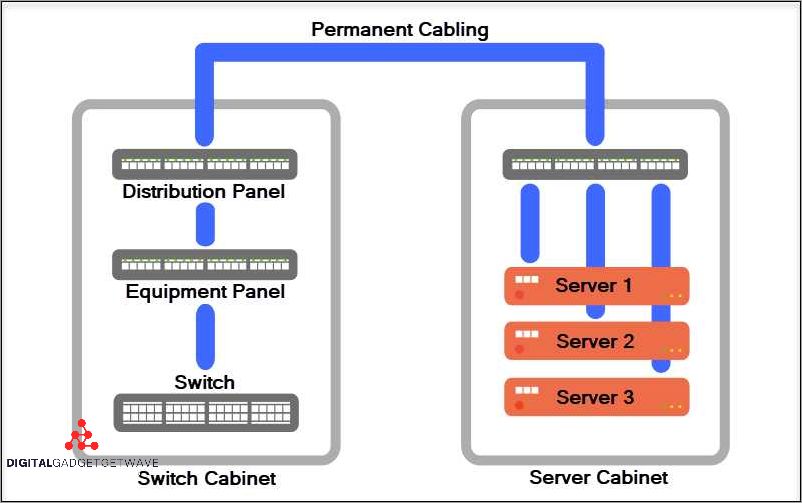
A cross connect is a critical element in the telecom industry that allows for the connection of different networks and equipment within a data center or colocation facility. It acts as a physical junction point where various communication paths can be established, enabling seamless data transfer and efficient network routing.
In simple terms, a cross connect is like a switchboard that connects different network resources together. It plays a crucial role in enabling fast and reliable communication between various devices, such as servers, routers, switches, and storage devices, within a data center. This connectivity is achieved through the use of physical cables, typically in the form of fiber optic cables or Ethernet cables.
One key aspect of cross connects is that they provide a direct, point-to-point connection between two devices or networks, without the need for additional routing or processing by intermediate equipment. This direct connection ensures low latency and high bandwidth, making cross connects an ideal choice for applications that require reliable and fast data transfer, such as cloud computing or large-scale data analysis.
Cross connects are typically implemented as physical connections within a data center or colocation facility. They are often organized in racks or cabinets, with each cross connect represented by a port on a patch panel. These ports serve as the interface between the cross connect and the connected equipment, allowing for easy management and troubleshooting.
In conclusion, cross connects are an essential component of modern data centers and telecommunication infrastructure. They serve as the physical backbone that enables efficient and reliable communication between different devices, networks, and services. Whether it is for connecting servers within a data center, establishing direct links between data centers, or providing direct access to the internet, cross connects play a pivotal role in ensuring seamless and robust connectivity.
Contents
- 1 What is a Cross Connect?
- 2 How Do Cross Connects Work?
- 3 FAQ about topic “Understanding Cross Connects: What They Are and How They Work”
- 4 What is a cross connect?
- 5 Why are cross connects important in data centers?
- 6 How do cross connects work?
- 7 What are the benefits of using cross connects?
- 8 Can cross connects be easily modified or reconfigured?
What is a Cross Connect?
A cross connect is a physical connection that allows two or more communication networks, systems, or devices to connect and exchange information or data. Cross connects are commonly used in telecom and network infrastructure, and they play a crucial role in enabling reliable and efficient communication between different network components.
A cross connect can be made using various types of cables, such as fiber optic cables, and it requires specialized equipment, such as switches, routers, and servers. These connections are typically made in a dedicated area, often called a cross connect or meet-me room, which is equipped with racks and panels to manage and organize the various cross connects.
Within a cross connect, individual connections or ports from different equipment or network components, such as servers or switches, are physically connected to establish a direct link between them. This allows for the transmission of data, voice, or video signals between the connected devices.
Cross connects are crucial for managing and routing network traffic effectively. They provide a high bandwidth connection and ensure efficient data flow within a network or data center. By directly connecting devices or systems, cross connects minimize latency and bottlenecks in data transmission, leading to improved overall network performance.
In addition to enabling local communication within a data center or network infrastructure, cross connects also play a crucial role in facilitating connections to external networks, including the internet. By establishing direct connections to internet service providers (ISPs) or other networks, cross connects provide a reliable and fast connection to the global network, enabling seamless and efficient communication with the outside world.
Definition of Cross Connect
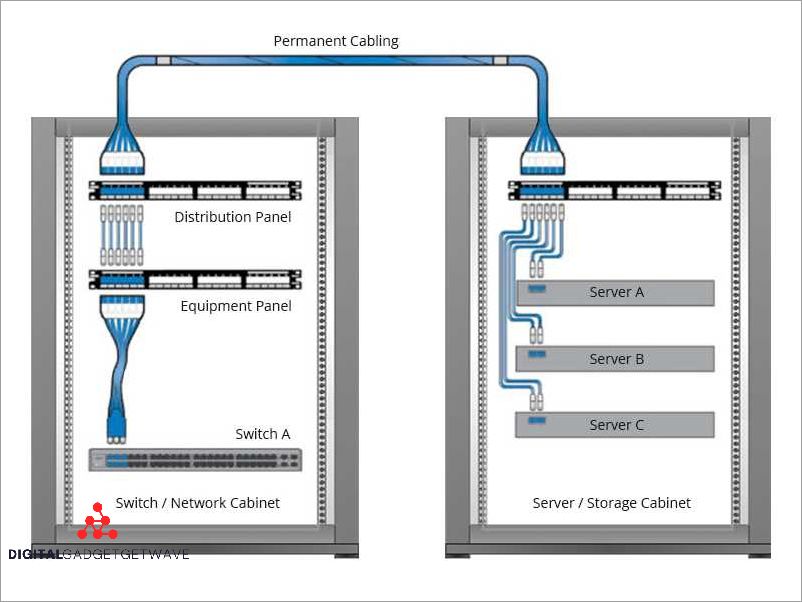
A cross connect is a physical connection that allows for the interconnection of different network components within a telecom or data center environment. It can be thought of as a switch or routing device that enables the flow of communication between various pieces of equipment.
Typically, cross connects are used to connect servers, switches, or other network equipment to facilitate the transfer of data. They provide a way to establish a direct and dedicated connection between devices, bypassing the need for routing through the entire network.
A cross connect is typically made using physical cables, such as fiber optic or Ethernet cables, and is often housed within a rack or cabinet specifically designed for this purpose. This centralized location allows for easy access and management of the cross connect connections.
One of the main benefits of a cross connect is its ability to provide reliable and high-speed communication between devices. By establishing a direct connection, data can be transferred quickly and efficiently, without experiencing the delays or congestion that can occur in a shared network environment.
Furthermore, cross connects are often used to connect to the internet or other external networks, providing access to a larger bandwidth and expanding the capabilities of the local network. This can be particularly beneficial for companies that require a fast and stable internet connection for their operations.
In summary, a cross connect is a physical connection that allows for the direct and dedicated interconnection of network equipment within a telecom or data center environment. It enables fast and reliable data transfer and provides access to a larger bandwidth for enhanced connectivity.
Types of Cross Connects
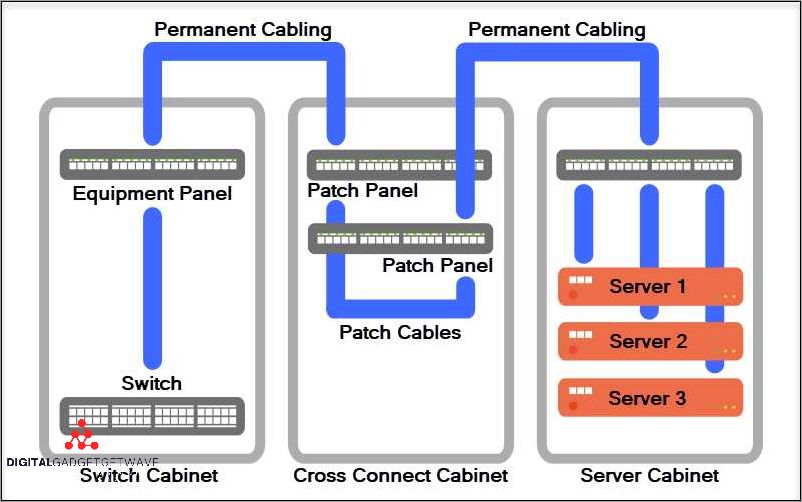
In the world of networking, cross connects play a crucial role in establishing reliable connections between different pieces of equipment. There are various types of cross connects available, each designed to cater to specific needs and requirements.
1. Copper Cross Connects: These cross connects utilize copper cables to establish connections between devices. They are commonly used in traditional data centers and telecom networks. Copper cross connects are cost-effective and provide sufficient bandwidth for basic communication needs.
2. Fiber Cross Connects: Fiber cross connects use fiber optic cables for data transmission. They are known for their high bandwidth capabilities and low latency. Fiber cross connects are ideal for high-speed networking applications, such as connecting servers, switches, and routers in data center environments.
3. Ethernet Cross Connects: Ethernet cross connects use Ethernet technology to establish connections. They are commonly used in local area networks (LANs) and wide area networks (WANs) to connect devices and enable efficient data transfer. Ethernet cross connects can support high-speed communication and are compatible with various network equipment.
4. Virtual Cross Connects: Virtual cross connects, also known as virtual private lines, provide a virtual connection between two endpoints over a shared physical network infrastructure. They are commonly used in cloud computing environments to establish secure and reliable connections between remote servers and data centers.
5. Rack-mounted Cross Connects: Rack-mounted cross connects are designed to be installed within server racks. They provide convenient connectivity options for multiple devices within the same rack. Rack-mounted cross connects help organize cable management and simplify network configuration.
6. Wireless Cross Connects: Wireless cross connects use wireless technology, such as Wi-Fi or Bluetooth, to establish connections between devices. They are commonly used for mobile devices, IoT devices, and wireless communication applications. Wireless cross connects provide flexibility and mobility in establishing connections without the need for physical cables.
Overall, cross connects are essential components in establishing physical connections within a network infrastructure. The choice of cross connect type depends on the specific requirements of the network, including the desired bandwidth, communication medium, and network equipment compatibility.
Importance of Cross Connects
A cross connect is a physical connection between two or more cables, allowing for direct communication between different telecom or data center equipment. Cross connects play a crucial role in ensuring efficient and reliable communication and data transfer within a network.
Cross connects are commonly used in data centers to interconnect servers, switches, routers, and other networking equipment. These connections help establish direct routes for data transfer, improving overall network performance and reducing latency. Without cross connects, data would have to be routed through multiple ports and switches, causing delays and bottlenecks.
In terms of telecom infrastructure, cross connects are essential for connecting carriers and service providers. They enable the exchange of voice and data traffic between different networks, allowing for seamless communication between customers of different telecom providers. Cross connects also play a critical role in facilitating internet connectivity, as they allow internet service providers to connect their networks to the larger internet backbone.
Cross connects are typically made using fiber optic cables, which can transmit large amounts of data at high speeds. The use of fiber optics ensures high bandwidth and low signal loss, enabling faster and more reliable communication between connected devices. In addition to fiber optic cross connects, Ethernet cross connects are also common, particularly for connecting customer equipment within a data center.
Proper management of cross connects is crucial to maintain an organized and efficient network infrastructure. This includes labeling and documenting each cross connect, specifying the devices or ports they connect and the purpose of the connection. Clear documentation helps network administrators easily identify and troubleshoot any issues or changes that may arise in the network.
In summary, cross connects are vital components of telecom and data center infrastructure. They facilitate direct and efficient communication between different devices, networks, and carriers, improving overall network performance and ensuring seamless connectivity. With the ever-increasing demand for data and faster communication, cross connects continue to play a crucial role in enabling reliable and high-speed data transfer.
How Do Cross Connects Work?
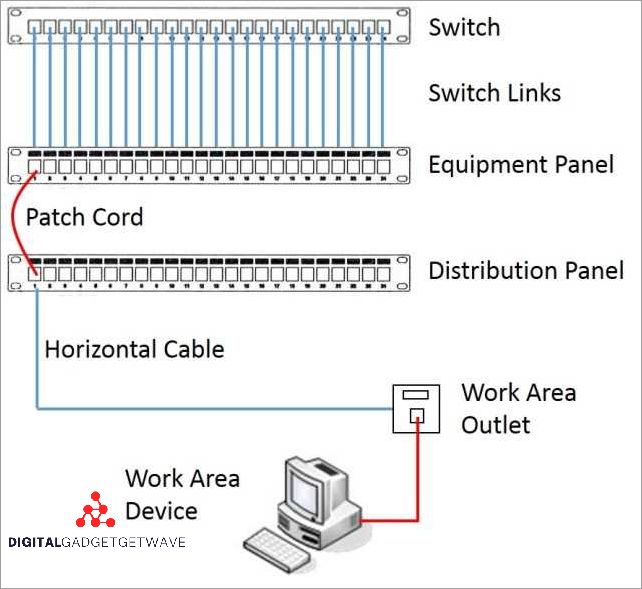
A cross connect is an essential component in a network communication system. It ensures seamless and efficient transfer of data between different equipment and network connections. At its core, a cross connect is a physical connection that links various communication devices, such as servers, switches, and routers, to establish direct connections.
The physical infrastructure of a cross connect involves the use of cables, ports, and racks. It can be implemented using various technologies, including Ethernet, fiber optic, and telecom. Each connection is made with precision, ensuring optimal routing and minimal signal loss.
When a cross connect is established, data can flow directly from one device to another without going through additional network nodes. This direct connection provides high bandwidth and low latency, which is crucial for applications that require real-time data transmission, such as video streaming and online gaming.
Cross connects are commonly found in data centers, where they facilitate connectivity between different servers, storage systems, and network switches. By eliminating the need for intermediate routing, a cross connect allows for faster and more efficient data transfers within the data center environment.
In addition to simple point-to-point connections, cross connects can also be utilized to create complex networks connecting multiple devices. This can be achieved by combining multiple cross connects to form a larger, interconnected network. This flexibility and scalability make cross connects an essential tool in modern network infrastructure.
Physical Connection
A physical connection refers to the actual connection between two devices or pieces of equipment in a network. It involves the use of ports, cables, and physical infrastructure to establish a direct link for data communication.
In a telecom or data center environment, a physical connection is established using cross connects. Cross connects are physical connections that allow different devices, such as servers, switches, and routers, to be connected directly to each other without going through a network or the Internet.
These physical connections are often made using Ethernet cables, which are capable of carrying large amounts of data. The bandwidth of the connection is determined by the capabilities of the cable, as well as the routing and networking equipment used.
The physical connection between devices is typically established by connecting one end of the cable to a port on one device, and the other end to a port on another device. This can be done using patch panels or other types of connectivity solutions.
Physical connections are crucial for ensuring reliable and high-speed data transfer between devices. They play a vital role in maintaining the overall performance of the network and enable efficient communication between different parts of a network infrastructure.
In a data center, physical connections are often organized and managed using racks. Racks provide a structured and organized way to connect and manage various devices, allowing for easy troubleshooting and maintenance.
Overall, physical connections form the foundation of any network or data center infrastructure. They enable devices and equipment to be connected directly, facilitating seamless communication and efficient data transfer.
Network Routing
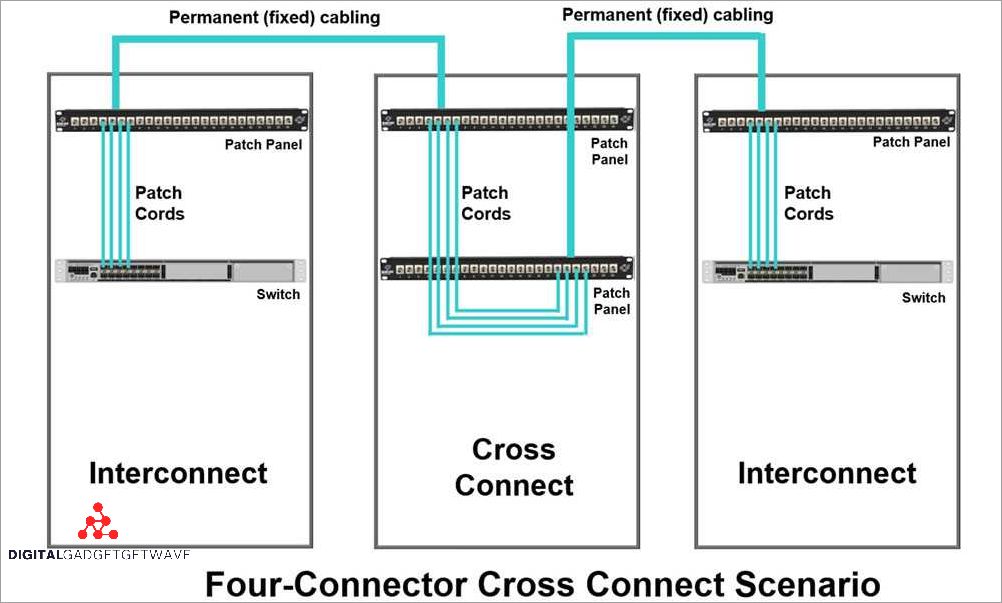
Network routing is an essential process in the telecommunications industry that enables data to travel efficiently across a network. It involves determining the best path for data packets to be transmitted from one network to another, by considering factors such as network congestion, bandwidth availability, and network topology.
In a data center or telecom facility, network routing is facilitated by various physical equipment, such as network switches, routers, and cross connects. These devices are connected using fiber optic cables and allow for the efficient transfer of data between different networks or network segments.
The routing process begins when a data packet arrives at a network port or interface. The packet contains information about its destination, and this information is used by the network devices to determine the optimal path for the data to reach its destination.
Routing decisions are typically made based on the shortest path or the path with the least network congestion. Network routers use routing tables, which contain information about the available network connections and the corresponding next hop for each destination, to make these decisions.
One common type of routing used in data centers and telecom facilities is layer 3 routing, also known as IP routing. In layer 3 routing, packets are forwarded based on their IP addresses. Layer 3 switches and routers are used to perform this type of routing.
In addition to routing data packets within a network, network routing also involves connecting multiple networks together. This is done through the use of cross connects, which provide physical connections between network switches, routers, and other network equipment. Cross connects allow for the exchange of data between different networks, enabling communication across the internet.
Overall, network routing is a critical aspect of network communication. It ensures that data is transmitted efficiently and reliably across networks, allowing for seamless communication between devices and users.
Data Transmission
Data transmission is the process of sending and receiving digital information across a network. It involves the connection and communication between various devices, such as servers, switches, and routers, in order to exchange data. This transmission of data is crucial for the functioning of any network, whether it is a local area network (LAN), wide area network (WAN), or the internet.
In data transmission, a physical connection is established between devices using cross connects. Cross connects are ports or patch panels that allow the interconnection of different equipment within a data center or network. These cross connects provide a means for the exchange of data between servers, switches, and other networking devices.
One common type of cross connect is an Ethernet cross connect, which utilizes Ethernet cables to establish connections between devices. Ethernet cables are widely used for data transmission due to their ability to transmit data at high speeds and over long distances. These cables are typically made of copper or fiber optic materials, depending on the specific requirements of the network.
The data transmitted through a cross connect is routed through the network using switches and routers. Switches are devices that connect multiple devices within a local network, enabling the exchange of data between them. Routers, on the other hand, connect networks together, allowing for communication between different networks, such as LANs and the internet.
Telecom and data centers play a vital role in data transmission. Telecom companies provide network infrastructure and services that enable the transmission of data over long distances, while data centers house the equipment and servers necessary for data storage and processing. These facilities ensure the efficient transmission of data by providing high-speed internet connections and ample bandwidth.
In conclusion, data transmission is a critical component of any network. It relies on the physical connection of devices through cross connects, the use of Ethernet cables for high-speed data transmission, and the routing of data through switches and routers. With the advancement of technology and the increasing demand for faster and more reliable data transmission, the telecom and data center industries continue to play a significant role in enabling seamless communication and connectivity.
FAQ about topic “Understanding Cross Connects: What They Are and How They Work”
What is a cross connect?
A cross connect is a physical connection that enables the transfer of data between two different networks or devices. It is typically made by connecting cables to the ports of network equipment, such as routers or switches.
Why are cross connects important in data centers?
Cross connects play a crucial role in data centers as they allow for the efficient and reliable transfer of data between various network systems and equipment. They help ensure fast and secure communication between servers, storage devices, and other network resources.
How do cross connects work?
Cross connects work by physically connecting the ports of two network devices or systems using cables. This creates a direct and dedicated link between them, allowing for the transmission of data without the need for intermediate equipment or routing.
What are the benefits of using cross connects?
Using cross connects offers several benefits, including reduced latency and improved network performance. They provide a dedicated and direct connection, which eliminates the need for data to travel through multiple devices or networks, resulting in faster data transfer speeds and lower latency.
Can cross connects be easily modified or reconfigured?
Yes, cross connects can be easily modified or reconfigured as per the changing network requirements. They are usually implemented using patch panels or cross connect panels, which allow for easy cable rearrangement or reconnection without the need for altering the network infrastructure.


