
Electricity is the essential form of energy used in modern society. It is generated through various means, including fossil fuels, nuclear power, and renewable sources such as solar and wind. The generation of electricity involves converting other forms of energy into electrical power.
The capacity to generate and transmit electricity is crucial for maintaining a reliable power grid. The transmission system allows electricity to be delivered from power plants to homes, businesses, and other utilities. It ensures that the energy reaches its destination with minimal losses.
Load electricity refers to the amount of power consumed by electrical devices and systems. The demand for electricity varies throughout the day, with peaks during certain times when usage is higher. Managing load electricity is essential to ensure the system can handle the demand without overloading or causing blackouts.
Understanding load electricity is particularly crucial in the context of smart grids and renewable energy sources. Smart grids enable more efficient management of electricity consumption, allowing for better demand response and optimization of resources. Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, have variable generation capacities, and load electricity management helps ensure a stable and reliable supply from these sources.
Contents
- 1 Understanding Load Electricity
- 2 Definition of Load Electricity
- 3 Types of Load Electricity
- 4 Importance of Understanding Load Electricity
- 5 FAQ about topic “Understanding Load Electricity: Definition, Types, and Importance”
- 6 What is load electricity?
- 7 What are the types of load electricity?
- 8 Why is it important to understand load electricity?
- 9 How can load electricity be reduced?
- 10 What are the potential risks of exceeding the electrical load?
Understanding Load Electricity
In the field of electricity, load refers to the amount of power consumed by an electrical system at any given time. It represents the demand for electricity from consumers, such as households, businesses, and industries. Understanding load electricity is crucial for utilities to effectively manage the capacity of the power grid and ensure reliable energy supply to meet the demand.
Electricity load can vary throughout the day, as different activities and appliances are used. To meet this variable demand, electricity is generated, transmitted, and distributed from various sources, including traditional power plants, renewable energy sources, and even distributed generation systems. The electricity grid connects these sources to consumers, ensuring a reliable and continuous supply of electricity.
In order to ensure the stability and reliability of the electricity system, load electricity management is essential. This involves monitoring and balancing the supply and demand of electricity in real-time. Utilities use advanced technologies, such as smart grid systems, to optimize load management and improve energy consumption.
Understanding load electricity also includes considering the different types of loads, such as residential, commercial, and industrial loads. Each type of load has its own characteristics and requirements, which must be taken into account when designing and operating the electricity system.
Overall, load electricity is a fundamental concept that plays a crucial role in the efficient and reliable operation of the electricity grid. With the increasing demand for electricity and the need to transition to cleaner energy sources, understanding and effectively managing load electricity is becoming even more important.
Definition of Load Electricity
Load electricity refers to the power or energy consumed by electrical devices and equipment. It is the amount of electric energy used by consumers to operate their appliances, machines, and systems.
In the context of electrical power systems, load electricity plays a crucial role in the generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity. It represents the demand for electricity by end-users and determines the capacity required to meet that demand.
The electricity load can vary throughout the day and is influenced by factors such as time of day, weather conditions, and consumer behavior. Utilities and grid operators need to anticipate and manage the load electricity to ensure the reliability and stability of the electrical system.
Load electricity can come from various sources, including conventional fossil fuel-based power plants, nuclear power plants, and renewable energy sources such as solar and wind. The shift towards utilizing more renewable energy sources has led to the development of smart grid technologies, which enable better monitoring and management of load electricity.
Understanding and managing load electricity is essential for utilities and grid operators to maintain a balance between supply and demand in the electrical grid. By accurately predicting and adjusting the load, they can optimize the use of available resources, reduce waste, and ensure a reliable and efficient distribution of electricity to consumers.
What is Load Electricity?
Load electricity refers to the amount of electric power consumed by various utilities and devices connected to the electrical grid. It represents the demand placed on the electrical system by consumers at a given time.
The load electricity can vary depending on factors such as time of day, weather conditions, and consumer behavior. During peak periods, when there is high demand for electricity, the load on the system is higher. Conversely, during off-peak periods, the load is lower.
The capacity of the electrical grid to meet the load electricity demand is an important aspect of the overall system reliability. The transmission and distribution infrastructure must be capable of handling the load and ensuring that electricity is delivered efficiently and reliably to consumers.
With the emergence of smart grid technologies, load electricity can be managed more effectively. Smart meters and advanced monitoring systems allow for real-time data collection and analysis, enabling utilities to optimize load management strategies and improve overall grid performance.
Understanding load electricity is crucial for utilities and energy providers. It helps them plan for future generation and distribution needs, as well as promote energy efficiency and renewable energy integration. By managing the load electricity efficiently, utilities can reduce strain on the grid, ensure reliable power supply, and meet the growing energy demand in a sustainable manner.
Types of Load Electricity
There are different types of load electricity that contribute to the overall power consumption and demand within an electrical system.
1. Residential Load: This type of load electricity refers to the power consumed by households for various purposes such as lighting, heating, cooling, and appliances. It is essential for utilities to understand and manage residential load electricity to ensure the reliable and efficient distribution of power to homes.
2. Commercial Load: Commercial load electricity is the power consumed by businesses, offices, and commercial establishments. This includes energy used for lighting, air conditioning, computers, and other equipment. Managing commercial load electricity is crucial for maintaining a stable and balanced electrical grid.
3. Industrial Load: Industrial load electricity refers to the power consumed by factories, manufacturing plants, and other industrial facilities. These loads are typically high in magnitude and require a reliable and robust power supply to support production processes and machinery.
4. Agricultural Load: Agriculture consumes a significant amount of electricity for activities such as irrigation, livestock farming, and crop processing. Ensuring a reliable supply of electricity to meet the agricultural load demand is important for sustaining agricultural production and minimizing disruptions.
5. Smart Load: With the advent of smart technologies, there is an increasing focus on optimizing energy consumption through smart load management systems. These systems enable households, businesses, and industries to monitor and control their electricity usage, thereby reducing overall demand and improving energy efficiency.
6. Renewable Load: As the world moves towards sustainable energy sources, an increasing portion of load electricity comes from renewable sources such as solar, wind, and hydropower. Integrating renewable load electricity into the grid requires proper coordination and balancing to ensure smooth and reliable power generation and distribution.
7. Transmission Load: Transmission load refers to the electricity that is lost during the transmission process from the generation source to the distribution system. Minimizing transmission load is crucial for maintaining the efficiency and reliability of the electrical grid.
8. Distribution Load: Distribution load electricity is the power consumed within the distribution system itself. This includes losses in transformers, distribution lines, and other equipment. Proper management of distribution load ensures the efficient delivery of electricity to end-users.
In conclusion, understanding the different types of load electricity and effectively managing their generation, transmission, and distribution is vital for maintaining the reliability and sustainability of the electrical grid while meeting the ever-increasing demand for power consumption.
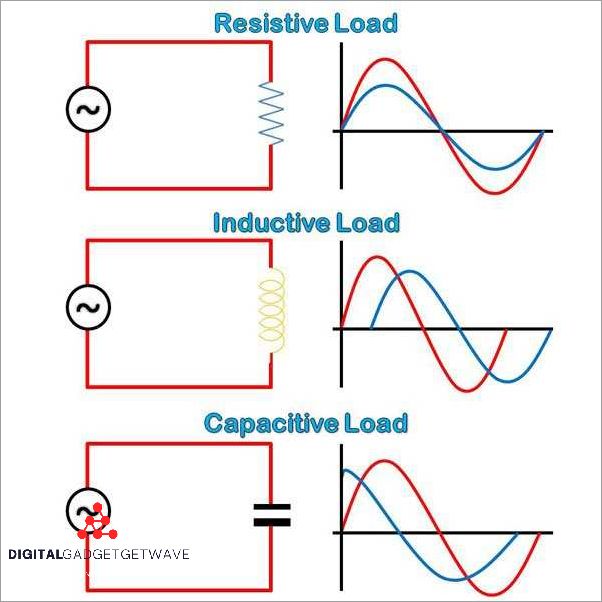
Resistive Load
A resistive load is a type of electrical load that consumes electricity by converting it into heat. It is a common type of load found in many electrical systems, such as household appliances, heaters, and incandescent light bulbs.
Unlike other types of loads, resistive loads do not change the frequency or waveform of the electricity. Instead, they simply resist the flow of current and convert the electrical energy into heat through electrical resistance.
Resistive loads are typically connected to power sources through transmission and distribution systems operated by utilities. These systems are designed to handle the capacity and demand for electricity and ensure its reliable delivery to consumers.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in using renewable energy sources to meet the electricity demand of resistive loads. This shift towards renewable energy generation aims to reduce the carbon footprint and reliance on fossil fuels for electricity production.
With the advancements in technology, smart grids are being developed to enable more efficient management of resistive loads. These smart grids can monitor and control the electricity consumption of different devices, optimizing their usage based on the supply and demand of electricity.
In conclusion, resistive loads play a crucial role in the consumption of electricity. They convert electrical energy into heat and are commonly used in various electrical systems. As the demand for electricity continues to grow, it is essential to explore renewable energy sources and develop smart grids to ensure the reliability and efficiency of the electricity distribution system.
Inductive Load
An inductive load is a type of electrical load that requires an electromagnetic field to operate. It is characterized by the presence of devices such as motors, transformers, and solenoids, which rely on the interaction between electric currents and magnetic fields. Inductive loads are commonly found in various systems and industries, including power generation, transmission, distribution, and utilitie
Capacitive Load
A capacitive load is a type of load that consumes reactive power from the electrical grid. It is characterized by its ability to store electric energy in an electric field. Capacitive loads are commonly found in a variety of electrical devices and systems, including power factor correction capacitors, AC motors, and electronic equipment.
The presence of capacitive loads on the electrical grid can affect its overall performance and reliability. Capacitive loads can lead to voltage fluctuations and power factor issues. However, when properly managed, capacitive loads can help improve the power factor of the grid and increase its capacity for transmitting and distributing electricity.
In modern smart grid systems, capacitive loads can be controlled and managed to optimize energy consumption. By using advanced technologies and algorithms, utilities can actively regulate and balance the reactive power demand of capacitive loads, ensuring a more efficient use of electrical energy.
Capacitive loads also play a significant role in renewable power generation. As renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power become more prevalent, the grid needs to accommodate their intermittent nature. Capacitive loads can help stabilize the grid by absorbing excess energy during peak generation periods and releasing it during low generation periods.
Overall, capacitive loads are an essential element of the electrical power system. They help balance the reactive power demand, improve grid reliability, and support the integration of renewable energy sources. By understanding and managing capacitive loads effectively, utilities can ensure a more efficient and sustainable use of electricity.
Importance of Understanding Load Electricity
Understanding load electricity is essential for the efficient consumption and management of power in electrical systems. Load refers to the amount of electrical energy consumed by various devices and appliances connected to the grid. By understanding the load, utilities and individuals can make informed decisions about energy usage, transmission, and distribution.
One of the key reasons why understanding load electricity is important is to ensure the reliability and stability of the power grid. By monitoring and managing the load, utilities can balance the demand and supply of electricity. This helps to avoid blackouts, brownouts, and other disruptions in the system.
Another crucial aspect of understanding load electricity is its impact on renewable energy sources. Renewable energy generation, such as from solar and wind, is variable and depends on natural factors. By understanding the load patterns, utilities can strategically integrate renewable energy sources into the grid to optimize their utilization and reduce dependence on traditional fossil fuel-based power generation.
Moreover, understanding load electricity is essential for the development and implementation of smart grid technologies. Smart grids utilize advanced sensors, meters, and communication systems to collect real-time data on electricity consumption. This data can help utilities and consumers identify patterns, trends, and inefficiencies in energy usage. By analyzing load data, consumers can adjust their energy consumption habits, reducing their carbon footprint and saving on utility bills.
Furthermore, understanding load electricity is crucial for managing peak demand periods. As electricity demand fluctuates throughout the day, utilities need to ensure that sufficient power generation and transmission capacities are available to meet the highest peak loads. By accurately forecasting load patterns, utilities can plan and optimize their power generation and distribution infrastructure, avoiding overloads and maximizing operational efficiency.
In conclusion, understanding load electricity is of utmost importance in the modern energy landscape. It enables utilities and consumers to make informed decisions about energy consumption, transmission, and distribution. By managing load effectively, reliability and stability of the power grid are ensured, renewable energy sources can be integrated optimally, and the development of smart grid technologies can be facilitated.
Safety Considerations
Electricity is an essential source of power for our society, but it also poses certain safety risks. It is important to understand and follow safety precautions when dealing with electrical load, both in terms of power generation and consumption.
Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, are gaining popularity due to their environmental benefits. However, it is crucial to ensure the safety of these installations. Proper maintenance and regular inspections of renewable energy systems are necessary to prevent accidents and ensure optimal performance.
Smart grids have become a key component of modern power distribution systems. These grids rely on advanced technologies to monitor and control the flow of electricity. However, the integration of smart grid technologies also introduces new safety considerations. It is important to ensure the reliability and security of these systems to prevent disruptions and protect against cyber threats.
Capacity planning is a critical aspect of electrical load management. Utilities and power generation companies need to ensure that the electricity supply can meet the demand of consumers. Adequate infrastructure and transmission capabilities are required to maintain a reliable and safe power distribution system.
When working with electricity, it is important to be aware of the risks involved. Electrical shock, fires, and other accidents can occur if proper safety procedures are not followed. It is crucial to use insulated tools, wear protective gear, and undergo regular training to minimize the risk of accidents and injuries.
In conclusion, safety considerations are of utmost importance when dealing with electrical load. Whether it is the generation, consumption, or distribution of electricity, it is imperative to follow safety guidelines and procedures to ensure the safety and reliability of the power grid.
Efficient Energy Usage
Efficient energy usage is a crucial aspect of the electricity system. It involves optimizing the generation, distribution, and consumption of electricity to meet the increasing demand and reduce wastage.
One way to achieve efficient energy usage is through the adoption of renewable energy sources. By diversifying the generation mix and relying more on solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, we can reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and lower the environmental impact of electricity production.
Another important aspect of efficient energy usage is the implementation of smart grid technologies. A smart grid integrates advanced communication and automation systems into the electricity infrastructure. It enables utilities to monitor and control the flow of electricity in real-time, optimizing transmission and load management.
Efficient energy usage also involves promoting energy conservation and demand response programs. These initiatives encourage consumers to reduce their electricity consumption during peak demand periods, helping to balance the load on the system and improve reliability.
Furthermore, effective metering and billing systems can play a significant role in promoting efficient energy usage. By providing consumers with real-time information about their electricity consumption and costs, they can make informed decisions and adjust their behavior accordingly.
In conclusion, efficient energy usage is essential for a sustainable and reliable electricity system. By transitioning to renewable energy sources, implementing smart grid technologies, promoting energy conservation, and providing consumers with accurate information, we can optimize the generation, distribution, and consumption of electricity.
FAQ about topic “Understanding Load Electricity: Definition, Types, and Importance”
What is load electricity?
Load electricity refers to the amount of electrical power consumed by devices or equipment connected to an electrical system. It represents the demand for electricity and can vary depending on the type and number of devices being used.
What are the types of load electricity?
There are two main types of load electricity: resistive load and reactive load. Resistive load includes devices like incandescent bulbs and electric heaters, which convert electrical energy into heat or light. Reactive load includes devices like motors and transformers, which require electrical energy to create a magnetic field.
Why is it important to understand load electricity?
Understanding load electricity is important for several reasons. Firstly, it allows for efficient use of electrical systems, as knowledge of the type and magnitude of loads can help in designing and sizing electrical installations. Secondly, it helps in managing electrical consumption, ensuring that the electrical load does not exceed the capacity of the system, which can lead to power outages or equipment failure. Lastly, understanding load electricity is essential for troubleshooting electrical problems and optimizing energy usage.
How can load electricity be reduced?
Load electricity can be reduced in several ways. One way is through energy-efficient practices, such as using energy-saving appliances, turning off lights and electronics when not in use, and optimizing heating and cooling systems. Another way is through load shedding, which involves selectively turning off certain electrical loads during high demand periods. Additionally, load electricity can be reduced by using smart technologies that enable better monitoring and control of electricity consumption.
What are the potential risks of exceeding the electrical load?
Exceeding the electrical load can lead to various risks. Firstly, it can cause overheating and damage to electrical equipment, leading to costly repairs or replacements. Secondly, it can result in power outages and disruptions to critical services, such as hospitals or data centers. Furthermore, exceeding the electrical load can increase the risk of electrical fires, posing a threat to life and property. It is essential to ensure that the electrical load is properly managed to mitigate these risks.


