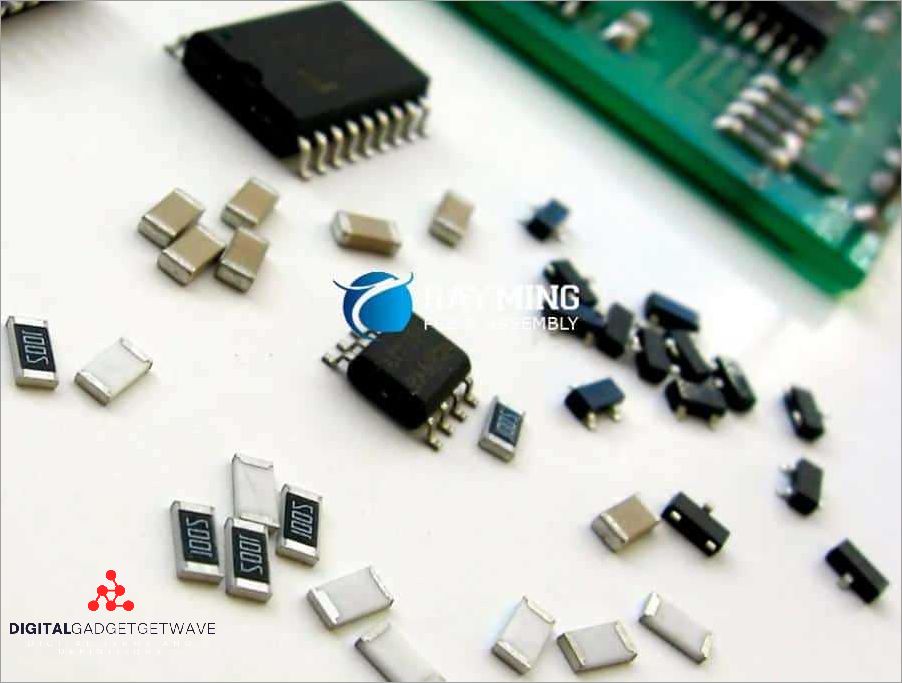
In the world of electronics, passive components play a crucial role in the design and functionality of circuits. These components include inductors, varistors, potentiometers, relays, fuses, capacitors, switches, oscillators, connectors, diodes, transformers, crystals, and resistors. Unlike active components like transistors, which require a power source to function, passive components do not require any external source of energy and can perform their designated tasks without any additional power supply.
Inductors are passive components that store energy in a magnetic field when an electric current flows through them. They are commonly used in circuits to control the flow of current or to store energy for later use. Capacitors, on the other hand, store electrical energy in an electric field. They are used in circuits for various purposes, such as filtering out certain frequencies or stabilizing voltage levels.
Resistors, another common passive component, restrict the flow of electric current. They are used to limit current, control voltage levels, and provide specific resistance values in a circuit. Diodes are also passive components that allow current to flow in only one direction. They are often used to convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) or to protect circuits from reverse polarity.
Transformers are passive components that transfer electricity between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. They are widely used for voltage conversion, isolation, and impedance matching in various electronic devices. Additionally, potentiometers are passive components used to vary the resistance in a circuit and adjust the desired output levels.
Varistors, relays, fuses, oscillators, crystals, and switches are other passive components commonly found in electronic circuits. Varistors protect circuits from voltage surges by diverting excess energy, while relays act as switches that control the flow of current between different circuit paths. Fuses, as their name suggests, protect circuits by breaking the flow of current when it exceeds a certain limit.
Oscillators generate periodic signals, which are essential for the functioning of many electronic devices. Crystals, often used in oscillator circuits, provide frequency accuracy and stability. Switches, on the other hand, are used for manual control of circuit connections or to enable/disable specific functions.
Understanding these passive components is crucial for any electronics engineer or hobbyist. By learning how they work and their respective applications, one can design and troubleshoot circuits with greater efficiency. Whether you are building an embedded system, repairing a device, or exploring the world of electronics, having a comprehensive understanding of passive components is essential for success.
Contents
- 1 What are Passive Components?
- 2 Why are Passive Components Important?
- 3 Common Types of Passive Components
- 4 How do Passive Components Work?
- 5 FAQ about topic “Understanding Passive Components in Electronics: A Comprehensive Guide”
- 6 What are passive components in electronics?
- 7 What is the purpose of resistors in electronic circuits?
- 8 How do capacitors work in electronic circuits?
- 9 What is the role of inductors in electronic circuits?
- 10 What types of switches are commonly used in electronic circuits?
What are Passive Components?

Passive components are fundamental building blocks in electronic circuits that do not require an external power source to function. These components are crucial for designing and constructing electronic devices and systems.
There are several types of passive components, each with its own unique characteristics and functions:
- Crystals and Oscillators: These components are used to generate precise frequencies and timing signals in electronic circuits.
- Inductors: Inductors store energy in a magnetic field and are commonly used in applications such as filters and power supplies.
- Resistors: Resistors limit the flow of electric current and are used in various applications, including voltage division, current sensing, and signal conditioning.
- Switches: Switches are passive components that control the flow of current in a circuit by opening or closing a connection.
- Varistors: Varistors are voltage-dependent resistors that protect electronic circuits from voltage spikes and transient events.
- Capacitors: Capacitors store electric charge and are commonly used for energy storage, coupling, and filtering purposes in circuits.
- Filters: Filters are passive components used to selectively pass or reject specific frequencies in a circuit.
- Diodes: Diodes are essential components that allow current to flow in one direction, commonly used in rectification and switching applications.
- Circuits, Transistors, and Components: Passive components are used in various types of circuits, including amplifiers, filters, and power supplies, and are also key elements in the operation of transistors.
- Embedded Systems and Potentiometers: Passive components play a crucial role in embedded systems, which are computer systems integrated into other devices or products. Potentiometers are variable resistors used for control and adjustment purposes in electronic circuits.
- Transformers and Connectors: Transformers are passive components used to transfer electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. Connectors provide physical connections between different components or devices.
- Passive Components in Electronics: Passive components are fundamental building blocks in the field of electronics. They are used in various applications and are essential for the proper functioning of electronic devices and systems.
- Fuses: Fuses are passive safety devices designed to protect circuits from excessive current by melting a wire or element and interrupting the flow of current.
Overall, passive components are essential elements in electronic circuits, providing specific electrical characteristics and performing vital functions in a wide range of applications.
Types of Passive Components
In the world of circuits and electronics, passive components play a crucial role. These components, unlike active components, do not require an external power source to function. They are used to control, filter, and manipulate electrical signals, making them an essential part of any electronic design. Let’s take a closer look at some common types of passive components.
Resistors

Resistors are perhaps the most fundamental passive component. They are used to limit or control the flow of current in a circuit. Resistors come in various values, allowing designers to tailor their circuits to specific requirements.
Capacitors
Capacitors store and release electrical energy. They are commonly used in circuits for various purposes, such as filtering out noise, coupling signals, and smoothing power supplies. Capacitors come in different types, including electrolytic capacitors, ceramic capacitors, and film capacitors.
Inductors
Inductors are passive components that store energy in a magnetic field. They are often used in circuits that require energy storage, such as filters and oscillators. Inductors can also be used to block or allow the flow of AC or DC signals.
Transformers
Transformers are vital components in electronics, especially in power supplies and communication systems. They enable voltage transformation and isolation between circuits, allowing signals or power to be transferred efficiently without direct electrical connection.
Diodes

Diodes are semiconductor components that allow current to flow in only one direction. They are commonly used in circuits as rectifiers, signal clippers, and voltage regulators. Diodes come in various types, such as Schottky diodes, Zener diodes, and light-emitting diodes (LEDs).
Switches and Relays

Switches and relays are passive components used to control the flow of current in a circuit. Switches provide a manual or mechanical means of opening or closing a circuit, while relays are electromechanical devices that use an electromagnetic coil to control the movement of switch contacts.
Potentiometers
Potentiometers, also known as variable resistors, are used for controlling the voltage or current in a circuit. By adjusting the resistance, potentiometers allow for precise control over parameters such as volume, brightness, or temperature.
Other passive components commonly found in electronics include crystals, varistors, connectors, filters, and fuses. Each component has its own unique characteristics and applications in designing and building electronic circuits.
Why are Passive Components Important?
Passive components play a crucial role in the field of electronics as they are the building blocks of various circuits and systems. They are called passive components because they do not require an external power source to operate. Instead, they respond to the electrical signals in the circuit and perform their specific functions.
Resistors are one of the most commonly used passive components in electronics. They control the flow of electrical current in a circuit, ensuring that the proper amount of current is delivered to each component. Capacitors, on the other hand, store and release electrical energy, making them ideal for use in filters, oscillators, and timing circuits.
Diodes are another important type of passive component. They allow current to flow in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction. This property is utilized in rectifiers, which convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) by only allowing the positive portion of the signal to pass through.
Inductors, also known as coils or solenoids, store electrical energy in the form of a magnetic field. They are used in various applications, such as filters and transformers, where they help in the transfer and conversion of electrical energy.
Other passive components include relays, fuses, potentiometers, connectors, crystals, switches, and varistors. Each of these components has a specific function and can be found in a wide range of electronic devices, from simple circuits to complex embedded systems.
Overall, passive components are essential for the proper functioning of electronic circuits. They provide stability, control, and protection, ensuring that electrical signals are processed accurately and efficiently. Without passive components, it would be challenging to build reliable and functional electronic devices.
Role of Passive Components in Electronics
Passive components play a crucial role in various electronic devices and circuits, providing specific functions to ensure their proper operation. These components, including capacitors, resistors, inductors, and diodes, do not generate or amplify electrical signals but rather control, limit, and store electrical energy.
Resistors are one of the most commonly used passive components in electronics. They are used to limit the flow of current, adjust signal levels, and provide stability in circuits. Capacitors, on the other hand, store electrical energy and are commonly used in filters, oscillators, and timing circuits.
Inductors, with their ability to store and release energy in the form of a magnetic field, are essential in transformers, relays, and oscillators. Diodes, which allow current to flow in one direction, are used in rectifier circuits, providing protection against reverse voltage.
Passive components also include varistors, which protect electronic circuits from voltage surges, and potentiometers, which enable manual adjustment of voltage levels. Connectors, switches, and embedded components, such as crystals, are also considered passive components, as they do not actively generate or amplify signals.
In summary, passive components are integral to the functionality and performance of electronic devices and circuits. They provide control, stability, energy storage, and protection, working alongside active components like transistors to ensure the smooth operation of various electronic systems.
Importance of Choosing the Right Passive Component

In the world of electronics, passive components play a crucial role in the overall functioning and performance of circuits. These essential components, such as resistors, capacitors, inductors, and more, are called “passive” as they do not require an external power source to function. However, choosing the right passive component is of utmost importance to ensure the optimal performance and reliability of electronic devices.
One key reason for selecting the appropriate passive component is its impact on circuit stability and functionality. For example, resistors are used to limit current flow and control voltage levels, while capacitors are utilized for energy storage and filtering. If the wrong resistance or capacitance value is chosen, it can lead to improper functioning of the circuit or the failure of crucial semiconductor components like transistors and diodes.
Inductors, on the other hand, are essential for energy storage and generation of magnetic fields. Embedding the wrong inductance value can result in inefficient circuit operation, affecting the overall performance of devices like oscillators and transformers. Furthermore, incorrect selection of components like relays, fuses, and switches can compromise the safety and reliability of circuits, potentially leading to short circuits or damage to sensitive electronic equipment.
Another important consideration in choosing the right passive component is its compatibility with the specific application and environmental conditions. For instance, electronic devices operating in high-frequency applications may require precise component values, such as crystals and filters, to achieve accurate frequency response and signal transmission. Similarly, components like varistors and potentiometers need to be chosen based on their ability to handle voltage surges and provide precise control over circuit parameters, respectively.
In summary, the importance of selecting the right passive component cannot be overstated. When choosing resistors, capacitors, inductors, transformers, diodes, and other passive components, it is crucial to consider their impact on circuit stability, functionality, safety, and compatibility with the intended application. By carefully evaluating the various capabilities and specifications of these components, one can ensure the successful operation and longevity of electronic devices and systems.
Common Types of Passive Components
Passive components are essential elements in electronics that do not require power to operate. They are used in various electronic circuits for their specific functions. Here are some common types of passive components:
- Resistors: These components provide resistance to the flow of electrical current in a circuit. They are used to control the current and voltage levels in electronic devices.
- Capacitors: Capacitors store and release electrical energy. They are used to filter out noise, stabilize voltage levels, and support timing functions in circuits.
- Inductors: Inductors store energy in a magnetic field. They are used in circuits to resist changes in current and filter out high-frequency noise.
- Diodes: Diodes allow current to flow in one direction and block it in the opposite direction. They are used in rectifiers, voltage regulators, and signal demodulation circuits.
- Transformers: Transformers are used to transfer electrical energy between circuits through electromagnetic induction. They are commonly used in power supplies, amplifiers, and communication systems.
- Switches: Switches control the flow of current in a circuit by opening or closing the circuit path. They are used to turn on or off electronic devices.
- Relays: Relays are electromagnetic switches that use a coil and contacts to control the flow of current in a circuit. They are often used in control circuits and automation systems.
- Connectors: Connectors are used to join different electronic components and devices together. They provide electrical and mechanical connections in circuits and systems.
- Fuses: Fuses are safety devices used to protect electronic circuits from excessive current. They melt when the current exceeds a certain threshold, breaking the circuit and preventing damage to other components.
- Varistors: Varistors are voltage-dependent resistors used to protect circuits from voltage spikes and transients. They are commonly used in power supplies and surge protection devices.
- Oscillators: Oscillators generate periodic waveforms or signals in electronic circuits. They are used in timing circuits, frequency synthesizers, and communication systems.
- Crystals: Crystals are used in oscillators and timing circuits to generate stable and precise frequencies. They are often used in digital clocks, microcontrollers, and communication devices.
- Potentiometers: Potentiometers, also known as variable resistors, are used to control the voltage and current levels in a circuit. They are often used as volume controls and variable voltage dividers.
These passive components play vital roles in electronic circuits and are the building blocks of various electronic devices.
Resistors
Resistors are one of the most common passive components in electronics. They are used to limit the flow of electric current in a circuit. Resistors come in different values, usually measured in ohms, and their purpose is to provide resistance to the flow of current.
Resistors are often used in combination with other passive components, such as capacitors, inductors, and transformers, to create various circuits. They are also used in conjunction with active components like transistors and oscillators to control the behavior of the circuit.
In addition to their basic function of limiting current, resistors can also be used for other purposes. They can be used as voltage dividers or in voltage regulator circuits to provide a stable output voltage. Resistors can also be used in filters to attenuate specific frequencies or in fuses to protect the circuit from excessive current.
There are different types of resistors available, each with its own characteristics and advantages. Some common types include carbon composition resistors, metal film resistors, and wirewound resistors. Each type has its own power rating, tolerance, and temperature coefficient, which need to be considered when choosing the right resistor for a specific application.
Resistors can be found in various electronic devices, from simple household appliances to complex embedded systems. They are used in a wide range of applications, including audio amplifiers, power supplies, radio receivers, and computer circuits.
In summary, resistors are essential passive components in electronics that play a crucial role in controlling the flow of current in a circuit. They are used in combination with other components to create various circuits and have a wide range of applications in different electronic devices. Understanding the characteristics and types of resistors is important in designing and troubleshooting electronic circuits.
Capacitors
Capacitors are one of the most common passive components used in electronics. They are widely used in various circuits for different purposes, such as energy storage, filtering, voltage regulation, and timing. Capacitors are essential for the smooth operation of electronic devices, as they store and release electrical energy when needed.
In electronics, capacitors are often used in conjunction with other passive components such as resistors, inductors, and diodes to create different types of circuits. These circuits can range from basic signal filtering circuits to complex oscillators or frequency generators. Capacitors are also used in voltage regulators, transistors, embedded systems, and transformers.
Circuits that contain capacitors can perform various functions. For example, capacitors can be used to smooth out voltage fluctuations in power supplies or to suppress noise in audio circuits. They can also be used as timing components in oscillators or as coupling capacitors in amplifier circuits. Additionally, capacitors can be used in filter circuits to remove unwanted frequencies from a signal or in motor control circuits to provide energy for starting and running motors.
There are different types of capacitors available, such as electrolytic capacitors, ceramic capacitors, film capacitors, and tantalum capacitors. Each type has its own characteristics and advantages, making them suitable for different applications. The choice of capacitor depends on factors such as capacitance value, voltage rating, tolerance, and temperature coefficient.
Capacitors play a crucial role in the functionality and reliability of electronic devices. Without capacitors, many electronic circuits would not function properly or would be more prone to malfunctioning. Therefore, it is important to understand the role and characteristics of capacitors when designing and troubleshooting electronic circuits.
Inductors
An inductor is a passive electronic component that stores energy in the form of a magnetic field. It is typically made up of a coil of wire. Inductors are commonly used in circuits for various purposes, such as controlling current flow, storing energy, and filtering out unwanted frequencies.
Inductors are often used in conjunction with other components, such as capacitors and resistors, to create different types of circuits. They can be found in a wide range of electronic devices, including transformers, filters, oscillators, and power supplies.
Inductors have the ability to resist changes in current flow. When a current is flowing through an inductor, it creates a magnetic field around the coil. This magnetic field stores energy, which is released when the current changes. This property makes inductors useful in applications where a stable current is needed, such as in power supplies or motor control circuits.
Inductors can also be used to filter out unwanted frequencies in a circuit. By combining an inductor with a capacitor, a low-pass or high-pass filter can be created. This allows specific frequencies to pass through the circuit while attenuating others.
There are different types of inductors available, including air-core inductors, iron-core inductors, and toroidal inductors. Each type has its own characteristics and is used in specific applications. Inductors are often labeled with a value in henries (H) or millihenries (mH), which indicates their inductance.
How do Passive Components Work?
Passive components are essential elements in electronic circuits that do not require any external source of power to function. They play a vital role in shaping and controlling electrical signals in a wide range of electronic devices.
Crystals are passive components that are widely used in electronic circuits for their ability to generate stable and precise frequencies. They are commonly found in oscillators and timing circuits where a specific frequency is required.
Diodes and transistors are another type of passive component that are used in electronic circuits for their ability to control the flow of electric current. Diodes allow current to flow in one direction and block it in the opposite direction, while transistors can amplify and switch electronic signals.
Filters are passive components that are used to remove or attenuate specific frequencies from an electrical signal. They are commonly used in audio circuits to remove unwanted noise or in power supplies to remove ripple voltage from a DC signal.
Transformers and inductors are passive components that are used to transfer electrical energy between circuits or to store energy in a magnetic field. Transformers are commonly used in power supplies to step up or step down voltage levels, while inductors are used to control current flow or build filters.
Oscillators are passive components that generate periodic signals, such as sine waves or square waves. They are widely used in electronic devices such as clocks, radios, and communication systems.
Capacitors are passive components that store electrical energy in an electric field. They are used in electronic circuits for various purposes, including smoothing power supplies, coupling signals between different stages of a circuit, and blocking direct current while allowing alternating current to pass.
Connectors, resistors, embedded fuses, switches, varistors, relays, and potentiometers are other examples of passive components that are commonly used in electronic circuits. Each of these components plays a specific role in shaping and controlling the behavior of the electrical signals passing through the circuit.
Basic Principles of Passive Components
Passive components are essential elements in the design and functionality of electronic circuits. They do not require an external power source to perform their function. Instead, they rely on the fundamental principles of electronics to manipulate or regulate electrical signals.
Some common passive components include resistors, capacitors, and inductors. Resistors are used to control the flow of current in a circuit by providing resistance. Capacitors can store and release electrical energy, while inductors resist changes in current flow. These components can be combined in different configurations to create filters, oscillators, and various other circuit functions.
Fuses are another type of passive component that are designed to protect electrical circuits from excessive current. When the current exceeds a certain threshold, the fuse melts and opens the circuit, preventing damage to other components. Connectors, on the other hand, are passive devices that provide physical connections between different components or circuits.
Transformers are passive components that are used to transfer electrical energy between different circuits at different voltage levels. They consist of two or more coils of wire, which are wound around a common magnetic core. Transformers are widely used in power supply circuits and audio systems.
Diodes are semiconductor devices that allow current to flow in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction. They can be used for rectification, voltage regulation, and signal modulation in circuits. Varistors, on the other hand, are passive components that are used to protect circuits from transient voltage spikes.
Relays are electromagnetic switches that are used to control the flow of current in a circuit. They consist of a coil and one or more contacts, which open or close depending on whether the coil is energized or not. Relays are commonly used in automation systems and control circuits.
Crystals are passive components used in electronic oscillators to generate precise frequency signals. They exhibit a phenomenon called piezoelectric effect, where mechanical stress produces an electric charge. Potentiometers are passive components that provide adjustable resistance, commonly used for volume control or voltage regulation.
Overall, passive components play a crucial role in the functionality of electronic circuits. They are embedded in various devices and systems, allowing for precise control and regulation of electrical signals. Understanding the basic principles of these components is essential for any electronics enthusiast or professional.
Interactions between Passive Components
Passive components play a crucial role in electronic circuits, and their interactions can greatly affect the overall performance of the system. Understanding how different passive components interact with each other is essential for designing reliable and efficient circuits.
Potentiometers, resistors, and capacitors are commonly used passive components in electronics. When connected in series, their interactions can determine the voltage division and can affect the behavior of the circuit. Additionally, potentiometers can be used as variable resistors to control current flow or voltage levels in a circuit.
Oscillators and crystals are passive components used in electronic circuits to generate precise and stable frequencies. The interactions between oscillators and crystals can ensure accurate timing and synchronization in various applications.
Transformers and relays are passive components that can be used to control the flow of power or signal in a circuit. Their interactions allow for voltage or current transformations, as well as switching operations in different parts of the circuit.
Filters can be created by combining different passive components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors. The interactions between these components determine the cutoff frequencies and the attenuation characteristics of the filter. Filters are commonly used to remove unwanted frequencies or noise from the signal.
Varistors, diodes, and fuses are passive components used to protect circuits from overvoltage or overcurrent conditions. Their interactions involve absorbing or redirecting excessive energy to prevent damage to the rest of the circuit.
Connectors are passive components that provide physical and electrical connections between different parts of a circuit. Their interactions ensure reliable interconnections and allow for easy maintenance or modification of the circuit.
Understanding the interactions between passive components is crucial for designing and troubleshooting electronic circuits. By considering the characteristics and behaviors of each component, engineers can create optimized circuits that meet the desired specifications.
FAQ about topic “Understanding Passive Components in Electronics: A Comprehensive Guide”
What are passive components in electronics?
Passive components in electronics are electronic components that do not require an external power source to function. They include resistors, capacitors, inductors, and various types of switches and connectors. These components are widely used in electronic circuits to control the flow of current and voltage.
What is the purpose of resistors in electronic circuits?
Resistors are passive components that are used to limit or control the flow of electric current in a circuit. They are primarily used to provide a specific amount of resistance, which can be used to reduce the current, divide the voltage, or adjust the gain of a circuit. Resistors can also be used to create voltage drops and dissipate heat in circuits.
How do capacitors work in electronic circuits?
Capacitors are passive components that store and release electrical energy in the form of an electric field. They consist of two conductive plates separated by a dielectric material. When a voltage is applied across the plates, the capacitor stores energy in the form of an electric field. This stored energy can then be released at a later time to perform various functions in electronic circuits.
What is the role of inductors in electronic circuits?
Inductors are passive components that store and release energy in the form of a magnetic field. They consist of a coil of wire wound around a core material. When a current flows through the coil, a magnetic field is created. This magnetic field stores energy, which can be released at a later time to perform functions such as filtering, energy storage, and impedance matching in electronic circuits.
What types of switches are commonly used in electronic circuits?
There are several types of switches commonly used in electronic circuits, including mechanical switches, push buttons, toggle switches, slide switches, and rotary switches. Mechanical switches are the most basic type and are operated manually. Push buttons are momentary switches that are pressed to make or break a connection. Toggle switches have a lever that can be flipped up or down to toggle the switch on or off. Slide switches have a sliding lever that can be moved to open or close a circuit. Rotary switches have multiple positions that can be selected by rotating the switch.


