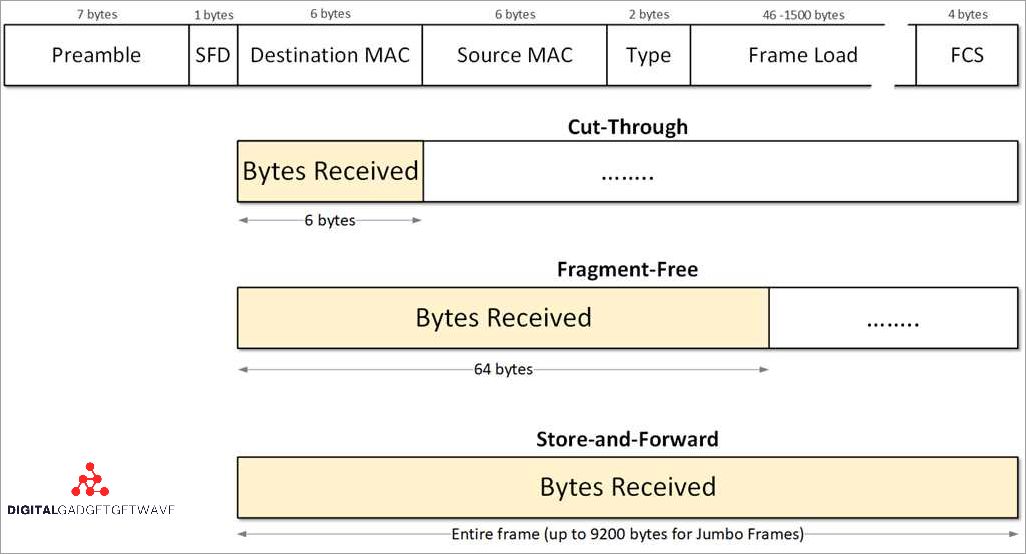
A cut-through switch is a networking device that plays a crucial role in forwarding traffic efficiently and quickly within a local area network (LAN). Unlike traditional switches, which utilize the store-and-forward method, a cut-through switch forwards packet frames as soon as they are received, leading to significant improvements in network performance.
At its core, a cut-through switch operates at the data link layer of the network protocol stack. By analyzing the packet header information, the switch can quickly determine the destination port for the incoming frame and immediately begins forwarding it. This eliminates the need for the switch to buffer the entire frame before forwarding, resulting in reduced latency and increased throughput.
One of the key advantages of a cut-through switch is its ability to facilitate the efficient transmission of data across the network. Traditional switches utilize the spanning tree protocol (STP) to prevent network loops, but this can introduce additional delays. In contrast, a cut-through switch does not rely on the STP, allowing for faster network performance and more efficient use of available bandwidth.
In addition, a cut-through switch can support virtual LANs (VLANs), allowing for the segmentation and isolation of network traffic. This helps to optimize network traffic flow and enhance security by isolating different user groups or departmental networks. By defining specific VLANs, a cut-through switch can prioritize and route traffic accordingly, improving overall network performance and ensuring a better user experience.
Contents
- 1 What is a cut through switch?
- 2 Importance of a cut-through switch
- 3 Efficiency of a cut through switch
- 4 Reduced latency
- 5 Speed of a cut through switch
- 6 Faster data transmission
- 7 Advantages of using a cut through switch
- 8 Future prospects
- 9 FAQ about topic “Understanding the Benefits of a Cut Through Switch: Efficiency and Speed”
- 10 What is a cut through switch?
- 11 How does a cut through switch increase efficiency?
- 12 What are the benefits of using a cut through switch?
- 13 Are there any drawbacks to using a cut through switch?
- 14 How does a cut through switch compare to a store and forward switch?
What is a cut through switch?
A cut through switch is a type of Ethernet switch that performs the packet forwarding based on the destination MAC address without waiting for the entire packet to be received. This type of switch operates at the data link layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model and utilizes a flow control mechanism known as cut-through forwarding.
Unlike a hub or a router, which process packet headers such as the IP or TCP header before forwarding them, a cut-through switch starts forwarding the packet as soon as it reads the destination MAC address. This allows for faster forwarding of traffic and reduces latency in the network.
A cut-through switch helps to ensure efficient and speedy transmission of data within a local area network (LAN) or a virtual LAN (VLAN). It offers improved performance and minimizes the delay caused by processing and analyzing packet headers.
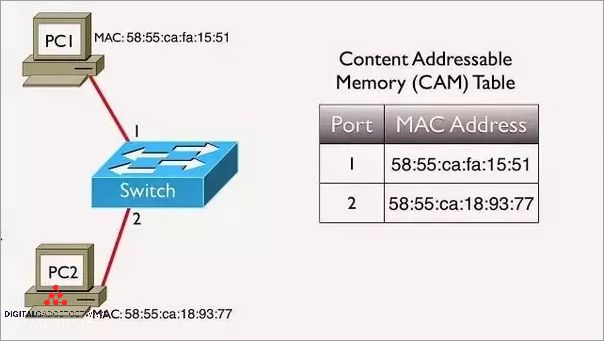
When a packet enters a cut-through switch, the switch reads the destination MAC address and searches its forwarding table to determine the appropriate port to send the packet. It then starts forwarding the packet immediately, without waiting for the entire frame to arrive. This process helps to reduce packet delay and optimize network performance.
In addition to its fast packet forwarding capabilities, a cut-through switch may also provide features such as port mirroring, VLAN support, and management interfaces for network configuration and monitoring. It can be a valuable tool in optimizing network traffic and improving overall network efficiency.
Importance of a cut-through switch
A cut-through switch is an important component in a network as it plays a crucial role in the efficient and speedy transmission of data. Unlike a router that operates at the network layer and examines each packet before forwarding it, a cut-through switch operates at the data link layer and forwards the frame without fully examining its contents.
By quickly forwarding the frames, a cut-through switch reduces the overall latency in the network. This is particularly important in high-traffic LAN environments where delays can negatively impact the performance of applications and user experience. The cut-through switch is designed to handle large volumes of network traffic efficiently.
Another benefit of a cut-through switch is its ability to manage network bandwidth. It can prioritize certain types of traffic, such as voice or video data, to ensure smooth and uninterrupted communication. This is achieved through the use of VLANs (virtual local area networks) which allow the switch to separate and prioritize different types of traffic.
In addition, a cut-through switch supports various protocols, such as Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and Ethernet. These protocols enable the switch to provide a reliable and stable network connection by preventing loops and ensuring proper forwarding of packets. This helps in maintaining the integrity and flow of data within the network.
Overall, the use of a cut-through switch in a network infrastructure is essential for achieving optimal network performance. Its ability to quickly forward frames, manage network traffic, support various protocols, and prioritize important data makes it an indispensable component in modern network management.
Efficiency of a cut through switch
In a network, a cut through switch plays a crucial role in improving the efficiency and speed of data transmission. Unlike other switches, which process an entire packet before forwarding it, a cut through switch only examines the packet header and begins forwarding the data as soon as it is received. This allows for significantly reduced latency and faster transmission times.
By cutting through the packet and forwarding it immediately, a cut through switch minimizes the amount of time it takes for data to travel from the source port to the destination port. This is especially beneficial in high-bandwidth networks where a delay in forwarding can bottleneck the flow of data.
Cut through switches are also able to handle different types of network traffic more efficiently. For example, a cut through switch can easily handle VLAN traffic, as it does not need to analyze the entire data frame of each packet. This makes it ideal for managing traffic in large LAN environments where data flows from multiple VLANs.
Furthermore, a cut through switch can also improve performance and efficiency in spanning tree networks. By forwarding packets immediately, the switch can bypass the usual spanning tree protocol delays, resulting in faster network convergence and reduced downtime.
It is important to note that while a cut through switch offers significant speed improvements, it does come with some drawbacks. For example, since the switch forwards packets without fully examining their contents, it cannot detect or correct errors. Additionally, cut through switches may not be suitable for networks with mixed traffic types or for environments that require advanced network management features.
In conclusion, the efficiency of a cut through switch lies in its ability to quickly and effectively forward packets based on their headers, resulting in reduced latency and improved network performance. However, it is essential to consider the specific network requirements and traffic types before deploying a cut through switch.
Reduced latency
Latency refers to the delay or time it takes for data to travel from its source to its destination in a network. In traditional networks, data often experiences latency due to various factors such as network congestion, processing delays, and queuing delays. However, a cut-through switch can help reduce latency significantly.
One way a cut-through switch reduces latency is by forwarding data at the data link layer, specifically at the Ethernet frame level. Unlike a network router that operates at the network layer and makes packet-level decisions, a cut-through switch operates at a lower layer and can quickly examine only the necessary information from the frame header before forwarding the data.
Another factor that contributes to reduced latency is the absence of VLAN tagging and protocol verification, which are usually required in traditional forwarding methods. With a cut-through switch, these additional checks are not performed, allowing for faster forwarding of data.
The port-based forwarding in a cut-through switch also helps decrease latency. Each port in the switch is dedicated to forwarding traffic to a specific destination, reducing the time it takes to determine the appropriate port for forwarding.
Cut-through switches are also designed to handle flows of traffic more efficiently. They can quickly identify and prioritize high-priority flows, ensuring that these flows experience minimal delays compared to low-priority traffic. This ability to handle flows efficiently contributes to overall reduced latency in the network.
In addition to reducing latency, cut-through switches also help improve network performance and throughput, making them an excellent choice for environments where speed and efficiency are critical.
Improved performance
Implementing a cut-through switch can greatly improve the performance of a network. By using a cut-through switch, packet forwarding can be done more efficiently and quickly. Cut-through switches operate at the layer 2 level of the OSI model, which means they can make forwarding decisions based on the destination MAC address in the Ethernet frame header.
One of the main benefits of a cut-through switch is its ability to process packets without having to wait for the entire packet to be received. Instead, cut-through switches start forwarding the packet as soon as the destination MAC address is identified. This eliminates the need for the switch to buffer and store the packet, resulting in reduced latency for time-sensitive applications, such as real-time video streaming or online gaming.
Additionally, cut-through switches can be configured to prioritize certain flows or protocols, allowing for better management of network traffic. By implementing VLANs (Virtual LANs), a cut-through switch can separate different types of traffic and prioritize them accordingly. For example, voice over IP (VoIP) traffic can be given higher priority over other data traffic to ensure crisp and clear communication.
Another advantage of a cut-through switch is its ability to handle a high volume of traffic. With its efficient packet forwarding capabilities, a cut-through switch can handle a large number of packets simultaneously, making it suitable for environments with heavy network traffic, such as data centers or enterprise networks.
In comparison to older network devices like hubs or bridges, which operate at the layer 1 level and forward entire frames, cut-through switches offer significant performance improvements. A hub, for example, forwards all incoming traffic to all ports, resulting in unnecessary traffic and decreased network efficiency. Cut-through switches, on the other hand, analyze and forward only the necessary portions of the frame, resulting in improved overall network performance.
Enhanced user experience
The use of a cut through switch can greatly enhance the user experience in a Local Area Network (LAN) environment. By utilizing cut through switching, data can be forwarded at an extremely high speed, resulting in minimal latency and a seamless network experience for users.
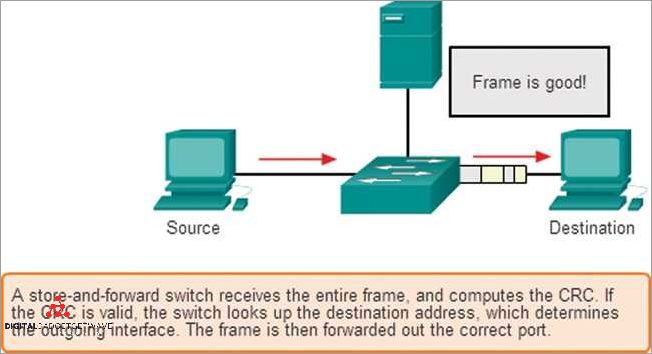
Unlike traditional store-and-forward switching, where the switch needs to receive the entire frame or packet before forwarding it, a cut through switch starts forwarding data as soon as it receives the destination address. This allows for faster data transmission and reduces delay in sending and receiving information.
In addition to speed, a cut through switch also allows for efficient management of network traffic. With the support of Ethernet and other network protocols, a cut through switch can intelligently prioritize certain types of data, such as voice or video, over others. This ensures that critical data flows smoothly without interruption, improving overall network performance and user experience.
Furthermore, a cut through switch can support VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) and Spanning Tree Protocol, enabling the segmentation of a network into different virtual LANs. This allows for the isolation of traffic and the prevention of broadcast storms, which can significantly improve network stability and security.
In summary, the implementation of a cut through switch can provide an enhanced user experience by increasing the speed and efficiency of data forwarding, prioritizing critical data flows, and ensuring network stability and security through VLAN and spanning tree support.
Speed of a cut through switch
A cut through switch is a type of network switch that is designed to forward data packets at a very high speed. It differs from other switch types, such as a store and forward switch, in that it begins forwarding a packet before the entire packet has been received. This allows for faster transmission of data and reduces the overall latency of the network.
Unlike a spanning tree protocol (STP) or a router, which must process the entire frame or packet before making a forwarding decision, a cut through switch immediately starts forwarding the packet as soon as it has received the destination MAC address. This process is also known as cut through forwarding. By bypassing the traditional packet analysis and CRC checks, a cut through switch minimizes processing time and improves the overall speed of data transmission.
One of the reasons why a cut through switch is so fast is due to its operation at the data link layer, specifically at the Ethernet level. By working at this layer, the switch does not need to process higher-layer protocols, such as IP or routing protocols. It simply focuses on forwarding Ethernet frames based on their MAC addresses.
In addition to the speed benefits, a cut through switch also offers other advantages, such as support for virtual LANs (VLANs). VLANs allow for the segmentation of network traffic, which can improve performance and security. A cut through switch can allocate different VLANs to different ports, allowing for efficient management of network traffic.
Overall, the speed of a cut through switch is a major benefit for networks that require fast and efficient data transmission. By minimizing the processing time and bypassing unnecessary checks, a cut through switch can significantly improve the speed and efficiency of a network.
Faster data transmission
Faster data transmission is a crucial factor in today’s technology-driven world. One of the key components that contributes to faster data transmission is the use of a cut-through switch.
A cut-through switch is a type of network switch that operates at the data link layer of the OSI model. Unlike traditional network switches that use a store-and-forward mechanism, a cut-through switch forwards traffic at a much faster rate by only reading the destination MAC address of a packet and then immediately sending it out through the appropriate port. This process eliminates the need to wait for the entire frame to be received, reducing latency and improving overall network performance.
In addition to faster data transmission, a cut-through switch also enhances the efficiency of the network by efficiently managing traffic flow. It can prioritize certain types of traffic, such as voice or video data, by using VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) and assigning different levels of priority to each VLAN. This allows for smoother data transmission and prevents data congestion or bottlenecks.
Moreover, a cut-through switch can also improve the overall speed of the network by efficiently handling Ethernet frames. It can quickly analyze the headers of incoming frames and determine the appropriate port for forwarding, reducing the time it takes for the data to reach its destination. This makes it an ideal choice for high-speed LAN (Local Area Network) environments where speed and efficiency are paramount.
Furthermore, a cut-through switch can also help in reducing network complexity by replacing older network devices such as routers and hubs. It eliminates the need for routers by directly forwarding data packets to the appropriate ports, and it replaces hubs by allowing for simultaneous data transmission to multiple ports. This simplifies network management and reduces the overall network infrastructure required.
In conclusion, a cut-through switch offers numerous benefits, including faster data transmission, efficient traffic management, enhanced network speed, and reduced network complexity. By utilizing a cut-through switch, organizations can achieve faster and more efficient data transmission, leading to improved productivity and overall network performance.
High-speed data transfer
In today’s digital world, the demand for high-speed data transfer has significantly increased. The ability to transmit large amounts of data quickly and efficiently is crucial in various industries, such as finance, healthcare, and telecommunications. To meet these demands, organizations rely on advanced network technologies, and one of the key components in achieving high-speed data transfer is a cut-through switch.
A cut-through switch operates at the data link layer of the OSI model, providing efficient packet forwarding. Unlike traditional hub-based networks that simply broadcast all received traffic to every connected device, a cut-through switch intelligently examines the destination MAC address of each incoming frame and directs it only to the appropriate port. By doing so, it minimizes the processing time and eliminates the need for unnecessary data transmission, resulting in faster data transfer.
Management of data traffic is another feature that contributes to high-speed data transfer in cut-through switches. These switches utilize various protocols, such as Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network), to optimize network performance. STP avoids loops in a network by designating one switch as the root bridge, ensuring that data packets are forwarded along the shortest path. VLANs, on the other hand, separate network traffic into different virtual networks, enabling better control and prioritization of data flow.
Furthermore, the architecture of a cut-through switch enables efficient forwarding of data within a network. Unlike routers that examine the entire packet before making a forwarding decision, a cut-through switch only examines the destination MAC address. This streamlined process reduces latency and allows for faster data transfer. Additionally, cut-through switches operate at the Ethernet layer, making them compatible with most networks and facilitating seamless integration with existing infrastructure.
In conclusion, high-speed data transfer is an essential requirement for modern organizations. Cut-through switches offer several benefits in achieving this goal, including efficient packet forwarding, traffic management through protocols like STP and VLAN, and streamlined data forwarding at the Ethernet layer. By leveraging these capabilities, organizations can optimize their network performance, reduce latency, and ensure fast and reliable data transfer.
Quick response time
One of the key benefits of using a cut through switch is its quick response time. When it comes to processing network traffic, traditional routers can be quite slow due to their complex routing algorithms. On the other hand, a cut through switch operates at the data link layer (Layer 2) of the Ethernet network, which allows it to forward packets at much faster speeds.
By analyzing and forwarding data frames at the Ethernet port level, a cut through switch is able to provide a much more efficient packet forwarding process. This is because it only needs to look at the destination MAC address of a packet in order to determine the appropriate port to forward it to. This streamlined approach cuts down on unnecessary processing and reduces latency in the network, resulting in a quicker response time.
Furthermore, a cut through switch also benefits from the use of VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) technology, which allows for the segmentation of a physical LAN into multiple logical LANs. This segmentation helps to manage network traffic more efficiently by isolating different types of traffic and reducing congestion. With the ability to prioritize and assign different levels of service to VLANs, a cut through switch can ensure that critical data flows smoothly and without delays.
In addition, a cut through switch supports the use of spanning tree protocol, which helps to prevent loops in the network by blocking redundant links. This enhances network stability and improves overall performance by reducing the chance of packet collisions and retransmissions.
In summary, the quick response time of a cut through switch can greatly benefit network management by increasing efficiency and reducing latency. With its streamlined packet forwarding process and support for VLANs and spanning tree protocol, a cut through switch is an excellent choice for organizations seeking to optimize their network performance.
Advantages of using a cut through switch
1. Increased efficiency: Cut through switching allows for faster data transmission compared to other methods, such as store and forward switching. This is because cut through switches start forwarding a frame as soon as the destination address is read, without waiting for the entire frame to be received. This results in lower latency and improved network efficiency.
2. Reduced network congestion: Cut through switches can help reduce network congestion by quickly forwarding frames through the network, minimizing the chances of bottlenecks. This is particularly important in high-traffic environments where a delay in the network can significantly impact performance.
3. Layer 2 functionality: Cut through switches operate at the layer 2 (data link layer) of the OSI model, allowing for efficient switching of Ethernet frames. They can read the destination MAC address of a frame and determine the appropriate port to forward it to, making them suitable for LAN environments.
4. Improved switch management: Cut through switches typically come with advanced management features, such as VLAN support, flow control, and port mirroring. These features allow for better control of network traffic, ensuring that packet forwarding is optimized and network resources are used efficiently.
5. Faster packet forwarding: When compared to routers, cut through switches offer faster packet forwarding. Routers typically analyze the entire packet, including the network and transport layer headers, before making forwarding decisions. Cut through switches, on the other hand, only need to read the destination MAC address, allowing for faster forwarding of packets.
6. Spanning multiple network segments: Cut through switches can be used to connect multiple network segments, expanding the reach of a LAN. By connecting different segments using cut through switches, organizations can create larger networks without sacrificing performance.
Overall, the use of cut through switches can bring significant advantages, such as increased efficiency, reduced network congestion, improved switch management, faster packet forwarding, and the ability to span multiple network segments. These benefits make cut through switches a valuable tool for organizations looking to optimize network performance and speed.
Future prospects
The future prospects for cut-through switches are extremely promising. As data networks continue to expand and handle larger volumes of traffic, the need for efficient forwarding mechanisms becomes crucial. Cut-through switches provide a solution that improves network performance by significantly reducing latency and increasing data throughput.
One of the key areas where cut-through switches show great potential is in the field of routing. Traditional routers often suffer from performance issues due to the processing overhead involved in examining every header of a packet and making forwarding decisions at the network layer. With cut-through switches, the forwarding decision is made based on the destination MAC address in the Ethernet frame, enabling faster and more efficient routing.
In addition to routing, cut-through switches also offer advantages in local area networks (LANs) where there is a high demand for speedy data transmission. For example, in a VLAN environment, where traffic is segmented into separate virtual networks, cut-through switches can effectively handle inter-VLAN communication by quickly forwarding packets between VLANs without unnecessary delays.
Furthermore, with the increasing popularity of real-time applications such as video conferencing and online gaming, the need for low latency becomes critical. Cut-through switches excel in reducing latency by immediately forwarding packets as they arrive, bypassing the time-consuming process of examining and verifying the entire packet.
As network technology continues to evolve and new protocols are developed, cut-through switches have the potential to adapt and enhance their capabilities. They can improve the flow and handling of various types of data, including multimedia and voice packets, by prioritizing and expediting the transmission of these time-sensitive packets.
FAQ about topic “Understanding the Benefits of a Cut Through Switch: Efficiency and Speed”
What is a cut through switch?
A cut through switch is a type of network switch that forwards data packets as soon as they are received, without buffering or storing them. This helps to reduce latency and increase network efficiency.
How does a cut through switch increase efficiency?
A cut through switch increases efficiency by immediately forwarding data packets without waiting for the entire packet to be received. This reduces the amount of time it takes for the packet to reach its destination, minimizing latency and improving overall network performance.
What are the benefits of using a cut through switch?
There are several benefits of using a cut through switch. Firstly, it improves network efficiency by reducing latency. Secondly, it provides faster data transmission, resulting in quicker response times. Lastly, it allows for better utilization of available bandwidth, increasing overall network capacity.
Are there any drawbacks to using a cut through switch?
While cut through switches offer many advantages, they do have some drawbacks to consider. One potential drawback is that they may forward corrupt or erroneous packets more readily than other types of switches. Additionally, they may have limited support for features such as flow control or error checking.
How does a cut through switch compare to a store and forward switch?
A cut through switch differs from a store and forward switch in the way it handles data packets. While a cut through switch immediately forwards packets as soon as they are received, a store and forward switch buffers the entire packet before forwarding it. This difference in handling can affect latency, network efficiency, and the ability to detect and handle errors in the data.


