
High Availability (HA) is a critical aspect of any virtualization environment. It ensures that applications and services remain available and accessible even in the event of hardware or software failures. VMware HA is a technology that provides fault-tolerant and load balancing capabilities to enhance the availability of virtual resources.
VMware HA allows virtual machines (VMs) to be automatically restarted on another server in a cluster in the event of a hardware or software failure. This ensures that applications and services running on these VMs can quickly recover and continue serving users without interruption.
By implementing a HA cluster, organizations can ensure that downtime is minimized and that critical applications and services are always available. In a HA cluster, multiple servers are connected through a network, and resources are distributed across these servers. This allows for load balancing and optimal utilization of resources.
In the event of a server failure, VMware HA automatically detects the failure and initiates a failover process, where the affected VMs are quickly restarted on another server in the cluster. This failover process is seamless to the users, and they experience minimal disruption in service.
VMware HA also provides additional benefits such as backup and disaster recovery capabilities. It allows organizations to easily create backups of VMs and replicate them to another location for disaster recovery purposes. This ensures that data is protected and can be quickly recovered in the event of a disaster.
Contents
- 1 Overview of VMware HA
- 2 Importance of High Availability in Virtualization
- 3 Benefits of VMware HA
- 4 How VMware HA Works
- 5 Implementing VMware HA
- 6 Fault Tolerance and VMware HA
- 7 FAQ about topic “Understanding VMware HA: High Availability in Virtualization”
- 8 What is VMware HA and how does it work?
- 9 What are the benefits of using VMware HA?
- 10 Can VMware HA protect against application failures?
- 11 What are the requirements for setting up VMware HA?
- 12 Can VMware HA protect against network failures?
Overview of VMware HA
VMware HA, short for VMware High Availability, is a high-availability feature provided by VMware, a leading virtualization technology provider. It ensures the uninterrupted availability of virtual machines (VMs) by providing automatic failover in case of server failures.
High availability is essential for businesses to ensure continuous operation and minimize downtime. VMware HA achieves this by creating a cluster of servers, known as an HA cluster, where the virtual machines are distributed. This distribution ensures load balancing, as the virtual machines are spread across multiple physical servers, reducing the load on each server. In case of a server failure, the VMs are automatically restarted on another server within the cluster, ensuring redundancy and minimizing disruption.
VMware HA also provides network redundancy by monitoring the network health and automatically moving the virtual machines to another server if there is a network failure. This ensures that the virtual machines remain accessible and functional even if there are network issues.
In addition to providing failover and redundancy, VMware HA also allows for scheduled backup and recovery of virtual machines. This feature ensures that regular backups are taken and can be used for quick and efficient recovery in case of any software or hardware issues.
The main benefit of VMware HA is the increased uptime and reliability it provides. By distributing virtual machines across multiple servers and automatically performing failover in case of failures, VMware HA ensures that virtualized applications and services remain available and provide uninterrupted service to users.
In summary, VMware HA is a fault-tolerant and highly reliable solution that enhances the availability and resilience of virtualized environments. By utilizing this technology, organizations can ensure that their critical applications and services have minimal downtime and can quickly recover from any unforeseen failures.
Importance of High Availability in Virtualization
High Availability (HA) is a crucial component of virtualization technology, ensuring that virtual machines (VMs) and applications remain operational in the event of failures or disruptions. HA provides a level of redundancy and fault tolerance, allowing for seamless recovery and minimizing downtime in a virtual environment.
One of the key benefits of HA is its ability to automatically detect and respond to hardware or software failures. By clustering multiple virtual servers together, HA enables failover to occur, where the workload is automatically shifted from a failed server to a healthy one. This ensures continuity of operations and avoids any disruptions in service.
By implementing HA, organizations can also achieve improved resource utilization and load balancing. HA monitors the performance and capacity of virtual machines and, based on predefined rules, automatically redistributes the workload across the cluster. This helps to optimize the utilization of resources and prevents any single server from being overloaded, ensuring better performance and scalability.
Moreover, HA plays a critical role in data protection and disaster recovery. With HA, organizations can ensure that critical data is backed up and replicated across multiple servers, reducing the risk of data loss. In the event of a server failure, the virtual machines can be quickly and efficiently recovered, minimizing the impact on the business.
Additionally, HA provides a high level of uptime and availability for virtualized applications. By eliminating single points of failure, HA ensures that the virtual environment remains highly available, even in the event of network outages or hardware failures. This increases the overall reliability and accessibility of applications, enhancing the user experience.
In summary, high availability is a fundamental component of virtualization, offering redundancy, fault tolerance, and automated failover capabilities. It provides organizations with improved resource utilization, load balancing, and data protection. By implementing HA, organizations can achieve higher uptime, better performance, and enhanced reliability for their virtual infrastructure.
Benefits of VMware HA
VMware HA, or High Availability, is a powerful technology that provides various benefits in a virtualized environment. This software-based solution ensures high uptime and fault-tolerant operations by automatically monitoring the health of virtual machines and responding to any failures or issues.
One of the main advantages of VMware HA is its ability to provide network and data redundancy. In the event of a server failure or other network issues, HA can automatically transfer the workload to other available servers in the cluster. This means that even if one server goes down, the virtual machines will continue to run on other servers without any interruption, ensuring seamless operation.
Another benefit of VMware HA is its ability to ensure resource availability. HA continuously monitors resource usage and can automatically distribute the workload among multiple servers in order to prevent overloading a single server. This load balancing feature helps to optimize resource utilization and improve overall system performance.
VMware HA also provides failover and recovery capabilities. In the event of a virtual machine failure, HA can automatically restart the virtual machine on another server in the cluster. This ensures that critical applications and services remain available even in the event of a failure, minimizing downtime and improving business continuity.
Moreover, VMware HA simplifies the backup and recovery process. By automatically moving virtual machines to healthy servers, HA allows for easier backup and recovery operations. This eliminates the need for manual intervention and ensures that virtual machines are always protected and available.
In summary, VMware HA offers numerous benefits in a virtualized environment. It provides high availability, network and data redundancy, load balancing, and fault-tolerant operations. With HA, organizations can achieve improved uptime, enhanced resource utilization, and simplified backup and recovery processes.
How VMware HA Works
VMware HA (High Availability) is a technology that ensures the availability of virtual machines in a VMware cluster. It is designed to provide fault tolerance and automatic recovery from hardware or software failures. This ensures that the virtual machines remain up and running, minimizing downtime and ensuring high availability of resources.
When a VMware HA cluster is configured, multiple physical servers, known as hosts, are grouped together to form a cluster. These hosts pool their resources, such as memory, CPU, and storage, to create a virtual infrastructure that can support multiple virtual machines.
In the event of a hardware or software failure on one of the hosts, VMware HA detects the failure and automatically restarts the affected virtual machines on another available host within the cluster. This process, called failover, ensures that the virtual machines continue to run without any disruption.
VMware HA also provides load balancing capabilities. It monitors the resource utilization of each host in the cluster and dynamically allocates virtual machines to ensure an even distribution of workload. This helps optimize the performance and efficiency of the virtual infrastructure.
Another important feature of VMware HA is data redundancy. It uses shared storage to store the virtual machine data, allowing it to be easily accessed and recovered in case of host failures. This eliminates the risk of data loss and provides a reliable platform for data recovery.
Overall, VMware HA is a technology that brings high availability to virtualization environments. By combining fault-tolerant design, automatic failover, load balancing, and data redundancy, it ensures that virtual machines remain accessible and operational, maximizing uptime and minimizing the impact of hardware or software failures.
Cluster Configuration
In the world of virtualization, a cluster configuration is a critical component for ensuring high availability and fault tolerance. A cluster consists of multiple virtual machines running on different physical servers, working together to provide redundancy and load balancing. By distributing the virtual machines across multiple servers, the cluster ensures that if one server fails, the virtual machines can failover to another server, minimizing downtime and ensuring continuous availability.
To configure a cluster, the first step is to install and configure the VMware software. This software provides the necessary tools and resources to manage the cluster and its virtual machines. Once the software is installed, the physical servers can be added to the cluster, creating a pool of resources that can be shared among the virtual machines. This pooling of resources allows for efficient use of hardware and ensures that each virtual machine has access to the necessary computing power and storage.
The cluster configuration also includes configuring the network and storage infrastructure. The network needs to be properly configured to provide connectivity to the virtual machines and allow for communication between the servers. The storage infrastructure should be designed with redundancy in mind, using technologies such as RAID or SAN, to ensure data availability and reliability.
One of the key features of a cluster configuration is the ability to provide automatic failover and recovery in the event of a server failure. This is achieved through the use of VMware High Availability (HA) technology. HA monitors the health and status of the servers in the cluster, and in the event of a failure, it automatically restarts the virtual machines on a different server. This failover process is seamless to the user and ensures minimal disruption to the virtual machines.
In addition to High Availability, the cluster configuration can also include other technologies such as fault-tolerant virtual machines and backup and recovery solutions. Fault-tolerant virtual machines provide continuous uptime by replicating the virtual machine across multiple servers, so that if one server fails, the replica takes over without any interruption. Backup and recovery solutions ensure data protection by regularly backing up the virtual machine data and allowing for easy recovery in case of data loss or system failure.
Overall, a well-configured cluster is essential for ensuring high availability and uptime in a virtualized environment. By leveraging the power of virtualization software and technologies such as VMware HA, organizations can ensure that their virtual machines are always up and running, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity.
Heartbeat Mechanism
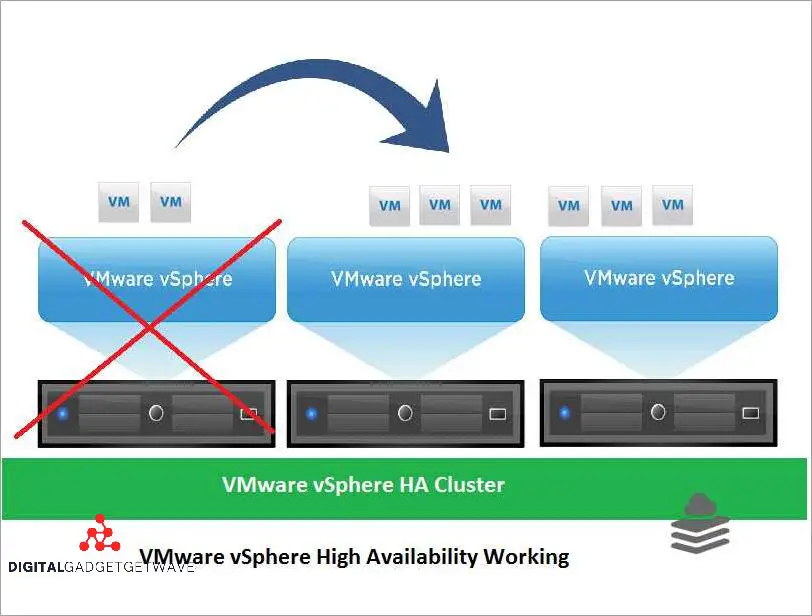
The heartbeat mechanism is a crucial component of a high availability (HA) system in virtualization technology such as VMware. It plays a vital role in ensuring the uptime and recovery of virtual servers within a cluster.
At its core, the heartbeat mechanism is a network communication between the servers within the cluster. It serves as a constant monitoring tool, allowing each server to check the status and availability of other servers in real-time.
By continuously exchanging heartbeat messages, the servers establish a reliable and fault-tolerant system. If a server fails to receive a heartbeat from another server within a specified timeframe, it assumes that the other server has encountered an issue or failure.
The heartbeat mechanism acts as a trigger for failover, a process in which the virtual machines running on the failed server are automatically migrated to another available server in the cluster. This failover process ensures the uninterrupted availability of critical applications and data.
The heartbeat mechanism also provides redundancy and load balancing capabilities. In a HA cluster, multiple servers share the workload, and if one server becomes overloaded or experiences a hardware failure, the workload can be redistributed to other available servers.
Overall, the heartbeat mechanism is a software-based technology that enables high availability and fault tolerance in virtualized environments. It helps to ensure the continuous operation of critical applications and the efficient utilization of resources within a cluster.
Virtual Machine Monitoring
Virtual machine monitoring is a crucial aspect of ensuring the uptime and availability of virtualized servers in a VMware environment. With the increasing reliance on virtualization technology, it is essential to have robust monitoring mechanisms in place to detect and address any potential issues that may arise.
One of the primary areas of concern is ensuring data backup and redundancy. Virtual machines store critical data and applications, and any loss or downtime can have severe consequences. Through effective monitoring, administrators can track the health and performance of virtual machines and ensure that regular backups are being performed to safeguard against data loss.
In addition to data backup, virtual machine monitoring also helps in ensuring the availability of resources. Monitoring tools can provide insights into resource utilization, such as CPU and memory usage, allowing administrators to identify any bottlenecks or potential overloads. This information can then be used to make informed decisions about resource allocation and load balancing.
Another important aspect of monitoring is detecting and responding to failures. In a high availability (HA) cluster, where multiple virtual machines are deployed across multiple physical hosts, monitoring tools can detect any faults or failures and trigger automatic failover mechanisms. This ensures seamless continuity in case of server or network failures, minimizing downtime and maximizing availability.
High availability and fault-tolerant systems rely on effective monitoring for quick recovery. By continuously monitoring the health and performance of virtual machines and their underlying infrastructure, administrators can proactively address any issues that may impact availability. This may include identifying and resolving performance bottlenecks, detecting and mitigating security threats, and ensuring proper configuration of network and storage resources.
In conclusion, virtual machine monitoring is an essential component of any virtualization environment. It helps ensure uptime, backup, and redundancy of critical data and resources, enables failover and recovery in case of failures, and facilitates effective load balancing and resource allocation. By leveraging monitoring tools and technologies, administrators can optimize the performance and availability of their virtualized infrastructure.
Implementing VMware HA

Implementing VMware High Availability (VMware HA) is a critical step in ensuring high availability and fault tolerance in a virtualized environment. VMware HA is a technology that provides automatic restart and recovery of virtual machines in the event of a host failure.
By configuring a VMware HA cluster, multiple hosts are grouped together to form a high availability cluster. This cluster provides redundancy and load balancing, ensuring that virtual machines can be automatically moved to healthy hosts in the event of a failure, thus minimizing downtime and maximizing uptime.
VMware HA relies on a network monitoring mechanism to detect host failures. The cluster continuously monitors the heartbeat of each host, ensuring that they are operational. In the event of a failure, the virtual machines running on the failed host are automatically restarted on other hosts in the cluster. This failover process occurs seamlessly, ensuring minimal disruption to business operations.
To further enhance availability and protect against data loss, it is recommended to combine VMware HA with other technologies such as VMware Fault Tolerance and backup software. VMware Fault Tolerance provides continuous availability by creating a secondary virtual machine that mirrors the primary virtual machine, ensuring uninterrupted operation even in the event of a host failure.
Additionally, implementing backup software in the virtual environment ensures that critical data and virtual machines are protected. Regular backups help prevent data loss and provide a means for recovery in the event of a disaster. By combining VMware HA, Fault Tolerance, and backup software, organizations can achieve a comprehensive high availability strategy.
Prerequisites
In order to understand VMware HA and its benefits, it is important to have a basic understanding of virtualization technology and high availability concepts.
First and foremost, it is crucial to have a high uptime requirement for your virtual environment. This means that your applications and services cannot afford to have long periods of downtime, and any interruptions must be minimized.
Next, you should have a cluster of physical servers or hosts that are running VMware software, such as VMware vSphere. This cluster will provide the necessary resources for running your virtual machines (VMs) and enabling high availability.
It is also important to have redundant and fault-tolerant network connectivity within your cluster. This ensures that if one network connection fails, there is another one available for the VMs to communicate.
Data backup and recovery mechanisms should be in place to protect your virtual infrastructure and ensure that critical data is not lost in the event of a failure. This can be achieved through regular backups and implementing proper disaster recovery strategies.
Finally, load balancing and resource management techniques should be implemented to distribute the workload evenly among the servers in the cluster. This ensures that no single server becomes overloaded and helps to improve overall performance and availability.
Configuration Steps

To configure high availability (HA) in VMware, follow these steps:
- Deploying a Cluster: Start by creating a cluster, which is a logical group of virtualization hosts. The cluster provides a unified view of the resources available across the hosts. It enables load balancing and fault tolerance.
- Enabling HA: Once the cluster is created, enable HA for the cluster. This ensures that virtual machines (VMs) running on the cluster are protected against host failures. HA monitors the health of the hosts and automatically restarts the VMs on another host in the cluster if a host fails.
- Configuring Admission Control: Admission control ensures that sufficient resources are available in the cluster to support VM restarts in case of host failures. Configure admission control to specify how much failover capacity should be reserved.
- Setting Up Network Redundancy: Configure networking to ensure redundancy and availability. Use multiple physical network interfaces on each host and set up redundant network paths to ensure that VMs remain connected even if a network link or interface fails.
- Configuring VM Monitoring: Enable VM monitoring to ensure the availability of individual VMs. VM monitoring monitors the heartbeat of VMs and automatically restarts them if they become unresponsive.
- Configuring Datastore Heartbeating: Datastore heartbeating is used to monitor the connectivity between hosts and shared datastores. It helps prevent false host failure detections and improves the overall reliability of HA.
- Testing and Monitoring: Test the HA configuration by simulating host failures and verifying that VMs are successfully restarted on other hosts in the cluster. Monitor the HA functionality regularly to ensure continuous availability and uptime.
- Backups and Disaster Recovery: While HA provides high availability within a cluster, it is important to implement backup and disaster recovery strategies to protect data and ensure business continuity. Use backup software and disaster recovery technology to create regular backups and implement recovery plans.
By following these configuration steps, organizations can leverage VMware HA to ensure high availability and fault-tolerant virtualization environments, reducing downtime and minimizing the impact of host failures.
Best Practices
In order to ensure high availability and fault-tolerant operation in a virtualized environment, there are several best practices that organizations can follow:
1. Load Balancing: Distribute the workload evenly across multiple virtual servers to optimize resource utilization and avoid bottlenecks.
2. Network Redundancy: Implement redundant network connections to ensure continuous connectivity in case of network failures.
3. Server Redundancy: Set up multiple physical servers in a cluster to provide failover capability in case of hardware failures.
4. Backup and Recovery: Regularly back up virtual machine data to ensure quick recovery in case of data loss or system failure.
5. Virtual Machine High Availability (HA): Enable VMware HA feature to automatically restart virtual machines on other hosts in the event of host failures.
6. Fault-Tolerant Cluster: Configure a fault-tolerant cluster using VMware technology to provide uninterrupted operation even in the event of a host or hardware failure.
7. Resource Monitoring: Monitor resource usage regularly to identify and resolve any performance issues or potential bottlenecks.
8. Software Patching and Upgrades: Keep the virtualization software and virtual machine operating systems up to date with the latest patches and upgrades to ensure security and performance improvements.
9. Uptime Monitoring: Continuously monitor the uptime and availability of virtual machines to ensure ongoing business operations.
10. Data Replication: Implement data replication technologies to replicate virtual machine data across multiple storage devices or locations for enhanced data protection and disaster recovery.
Fault Tolerance and VMware HA
Fault tolerance is a critical aspect of any high availability (HA) solution in virtualization. VMware HA leverages the industry-leading technology to provide fault tolerance for virtualized environments.
VMware HA uses software-based recovery mechanisms to ensure that the virtual machines (VMs) run continuously and without interruption, even in the event of hardware failures. This technology provides automatic failover of VMs to other servers in the cluster, ensuring minimal downtime and maximum availability.
One of the key features of VMware HA is its ability to distribute the VMs across multiple servers in a cluster. This load balancing technique ensures that the resources are evenly distributed and that each server operates within its capacity. In the event of a server failure, the VMs are automatically moved to another server in the cluster, allowing for seamless failover and uninterrupted operation.
In addition to load balancing, VMware HA also provides redundancy for critical data and resources. By replicating the data and resources across multiple servers, it ensures that there is no single point of failure. This redundancy is crucial for maintaining high uptime and availability.
When a VM is running in a fault-tolerant mode, VMware HA continuously monitors the VM for any signs of failure or abnormal behavior. If any issue is detected, VMware HA automatically activates a failover process, transferring the VM’s workload to another server. This ensures uninterrupted operation and minimal impact on the user experience.
VMware HA not only provides fault tolerance for individual VMs, but it also ensures high availability for the entire virtual environment. By utilizing clustering and failover mechanisms, VMware HA ensures that the virtualized infrastructure remains resilient and responsive, even in the face of hardware failures or other disruptions.
Understanding Fault Tolerance
Fault tolerance is a critical aspect of ensuring high availability in virtualization. It refers to the ability of a system or technology to continue functioning without interruption even in the event of a failure or error. In the virtualization context, fault tolerance enables the system to automatically switch to a backup or redundant resource in case of a failure, without experiencing any downtime or loss of data.
One of the key technologies that enable fault tolerance in virtualization is failover. Failover allows virtual machines or servers to automatically switch to a secondary or backup resource when the primary resource becomes unavailable. This ensures that critical services and applications can continue running without any disruption to the user experience.
Fault tolerance requires the availability of redundant resources to ensure seamless operation. This typically involves deploying multiple virtual machines or servers in a cluster or an infrastructure that can support the workload. The use of redundant resources provides backup and recovery options in case one resource fails, ensuring continuity of operations and minimizing any potential downtime.
Another important technology contributing to fault tolerance is load balancing. Load balancing distributes the workload across multiple resources, ensuring that no single resource becomes overloaded and causing a failure. This helps maintain optimal performance and minimizes the risk of a single point of failure.
In addition to hardware redundancy and load balancing, fault tolerance can also be implemented at the software level. For example, high availability (HA) software can monitor the health and availability of virtual machines or servers and automatically initiate failover processes when needed. This ensures that critical services and applications are always accessible, even in the event of a failure.
Data redundancy and backup strategies are also crucial for fault tolerance. By replicating data across multiple locations or storage devices, organizations can ensure that data remains accessible and recoverable even in the event of a failure. This helps prevent data loss and enables quick recovery in case of a disaster.
Network redundancy is another important aspect of fault tolerance. By having multiple network connections or paths, organizations can ensure that network connectivity remains available even if one connection fails. This helps maintain continuous access to critical services and resources.
In summary, fault tolerance plays a crucial role in ensuring the availability and reliability of virtualized environments. By implementing strategies such as hardware and software redundancy, load balancing, and data backup, organizations can minimize downtime, improve uptime, and ensure uninterrupted access to critical resources and services.
Integration with VMware HA
VMware HA (High Availability) technology allows for the automatic recovery of virtual machines and their applications in the event of a server or software failure. This integration with VMware HA ensures high availability and minimizes disruptions by providing quick failover and recovery options.
By utilizing VMware HA, businesses can ensure that their critical data and applications are protected through real-time monitoring and automatic failover. When a server or software failure is detected, VMware HA automatically restarts the failed virtual machines on alternate servers within the cluster. This allows for continuous availability and minimal downtime.
In the event of a failure, VMware HA redistributes the virtual machines and their associated workloads across the remaining available servers in the cluster. This load balancing feature ensures that resources are efficiently utilized and minimizes the impact on performance.
VMware HA also provides network and storage redundancy to further enhance availability. By utilizing multiple network connections and storage paths, the virtual machines can continue to operate even if one or more connections fail. This fault-tolerant approach ensures that data is accessible and the virtual machines remain operational.
Additionally, VMware HA integrates with backup and recovery software, allowing for the automatic backup and restoration of virtual machines in the event of a failure. This integration ensures that critical data is protected and can be quickly restored, minimizing the risk of data loss and downtime.
In summary, VMware HA provides high availability for virtualized environments by enabling quick failover and recovery, load balancing of resources, and integration with backup and recovery software. This integration ensures minimal disruptions and ensures that critical applications and data remain accessible in the event of a failure.
Enhancing High Availability with Fault Tolerance
In virtualized environments, ensuring high availability is crucial to avoid downtime and maintain the continuous operation of critical services. VMware HA (High Availability) provides a solution by automatically restarting virtual machines on different servers in the event of a host failure. However, to further enhance availability, organizations can implement fault tolerance.
Fault tolerance goes beyond HA by providing continuous availability without any interruption in service. It achieves this by creating a duplicate copy, or a secondary virtual machine, that runs in parallel with the primary virtual machine. Any changes made to the primary virtual machine, such as data or configuration modifications, are instantly replicated to the secondary virtual machine.
This redundancy eliminates single points of failure, ensuring that even if the primary virtual machine fails, the secondary virtual machine seamlessly takes over with no downtime or disruption in user experience. This level of fault-tolerant protection is especially critical for applications that cannot tolerate any loss of data or downtime.
To ensure effective fault tolerance, the fault-tolerant (FT) feature requires that the virtual machines be homogenous, meaning they should have the same hardware and software configurations. Additionally, the network must be fault-tolerant, meaning it should have redundant interfaces and switches to prevent any disruptions.
By combining HA with fault tolerance, organizations can achieve a highly available and fault-tolerant virtual environment. HA provides load balancing, automatically redistributing virtual machines across servers to optimize resource utilization and prevent overloading. In the event of a server failure, HA enables quick failover and recovery, minimizing downtime.
Fault tolerance, on the other hand, provides an additional layer of protection by ensuring instant failover with no interruption in service. With both HA and fault tolerance implemented, organizations can achieve maximum uptime, data protection, and disaster recovery capabilities within their virtualization environments. Regular backups of virtual machines should also be performed to further enhance availability and provide a fallback option in case of data corruption or other issues.
FAQ about topic “Understanding VMware HA: High Availability in Virtualization”
What is VMware HA and how does it work?
VMware HA, or High Availability, is a feature in virtualization that ensures business continuity by automatically restarting virtual machines on another host in the event of a host failure. It works by monitoring the health of hosts using a heartbeat mechanism, and when a failure is detected, it triggers a virtual machine restart on another healthy host in the cluster.
What are the benefits of using VMware HA?
Using VMware HA provides several benefits, including increased uptime and improved availability of virtual machines. It helps to minimize downtime by automatically restarting virtual machines on different hosts, reducing the impact of host failures on critical workloads. Additionally, it simplifies the management of virtualized environments by automating the process of detecting and recovering from host failures.
Can VMware HA protect against application failures?
No, VMware HA is designed to protect against host failures and not application failures. While it can help to reduce the impact of a host failure on virtual machines, it does not provide any guarantees for the availability of individual applications running within those virtual machines. Organizations should implement additional measures, such as application-level high availability solutions, to protect against application failures.
What are the requirements for setting up VMware HA?
To set up VMware HA, you need a VMware vSphere cluster with at least three hosts. The hosts must be running the same version of ESXi and be part of the same network and storage configuration. Additionally, the hosts must have shared storage, such as a SAN or NAS, to store the virtual machine files. VMware HA also requires a vCenter Server to manage the cluster and configure the HA settings.
Can VMware HA protect against network failures?
Yes, VMware HA can help to mitigate the impact of network failures on virtual machines. When a host loses network connectivity, VMware HA detects this as a failure and triggers a virtual machine restart on another host. However, it’s important to note that VMware HA cannot protect against complete network outages or network partitioning scenarios, as it relies on network connectivity for host communication and cluster management.


