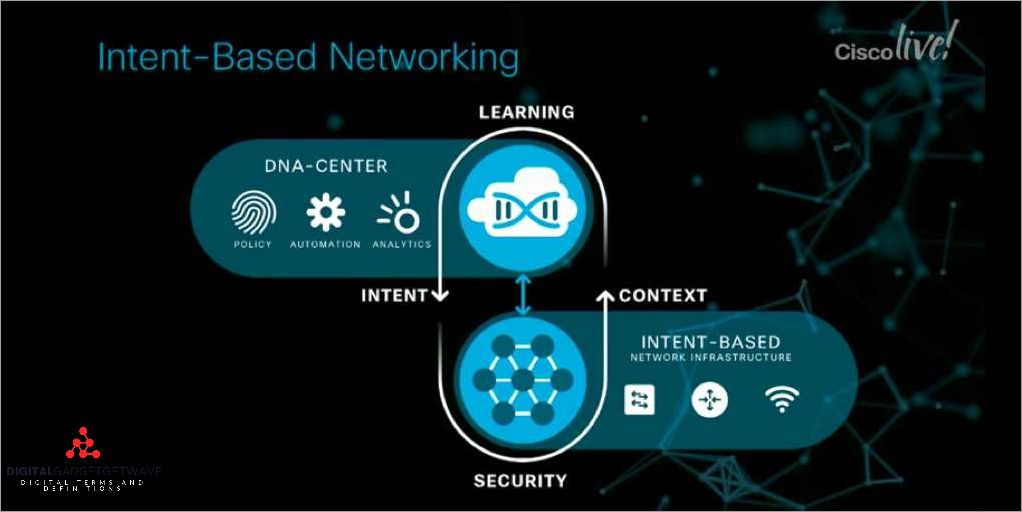
Modern networks are becoming increasingly complex, with a multitude of devices, applications, and data flowing through them. To meet the demands of this complexity, organizations are turning to intent based networking. This revolutionary approach to network management combines the power of analytics, virtualization, and automation to simplify network operations.
With intent based networking, organizations can achieve greater scalability, as networks can be easily expanded or contracted to meet changing needs. The management of network policies and configurations is greatly simplified, allowing for faster and more efficient deployment and troubleshooting. This ensures that networks are always optimized for performance and can quickly adapt to new demands.
One of the key benefits of intent based networking is its intelligence. By translating high-level business goals into specific network instructions, organizations can ensure that their networks are aligned with their overall objectives. This allows for more agile and responsive operations, as networks can automatically adjust their configurations based on changing conditions.
Additionally, intent based networking enhances security by enabling a proactive approach to threat detection and response. By continuously monitoring network activity and applying machine-learning algorithms, potential security threats can be identified and mitigated before they can cause harm. This increases network resilience and helps organizations stay ahead of emerging threats.
Furthermore, intent based networking enables greater efficiency through policy-driven orchestration. By automating routine network operations, organizations can minimize human error and reduce the time and effort required to manage networks. This allows IT professionals to focus on more strategic tasks and frees up resources for other business-critical initiatives.
In conclusion, intent based networking is a powerful solution for modern networks. By leveraging the capabilities of analytics, software-defined networking, and automation, organizations can enhance their network performance, security, and efficiency. With the ability to easily scale and adapt to changing needs, intent based networking is revolutionizing network management and enabling organizations to meet the demands of today’s digital world.
Contents
- 1 Understanding the Power of Intent Based Networking in Modern Networks
- 2 What is Intent Based Networking?
- 3 Benefits of Intent Based Networking
- 4 Implementation of Intent Based Networking
- 5 The Future of Intent Based Networking
- 6 FAQ about topic “Unlocking the Potential of Intent Based Networking in Today’s Networks”
- 7 What is Intent Based Networking (IBN) and how does it work?
- 8 What are the benefits of Intent Based Networking?
- 9 How does Intent Based Networking simplify network troubleshooting?
- 10 Can Intent Based Networking be used in any type of network environment?
- 11 Are there any challenges or limitations with implementing Intent Based Networking?
Understanding the Power of Intent Based Networking in Modern Networks
Intent Based Networking (IBN) is a revolutionary approach to network management that brings scalability, optimization, and efficiency to modern networks. It is designed to understand the intent of the users and automatically configure the network to meet those requirements. By focusing on intent, IBN enables agile and intelligent network management, ensuring that the network operates in a way that aligns with the goals and objectives of the organization.
One of the key benefits of IBN is its ability to provide simplified and automated network operations. By leveraging software-defined networking (SDN) principles, IBN allows for the virtualization of network functions and the automation of many repetitive tasks. This not only reduces the complexity of network management but also improves the overall efficiency and performance of the network.
IBN also integrates advanced analytics and intelligence to provide enhanced network security. By monitoring network traffic and identifying potential threats, IBN can proactively take actions to protect the network and ensure data privacy. This proactive approach to security helps organizations stay one step ahead of cyber threats and minimizes the risk of data breaches.
Another advantage of IBN is its ability to provide centralized network orchestration. By having a single interface to manage and control the entire network, organizations can streamline their network management processes and improve overall operational efficiency. This centralized approach also enables faster troubleshooting and problem resolution, reducing downtime and improving user experience.
In conclusion, the power of Intent Based Networking lies in its ability to bring scalability, optimization, efficiency, and security to modern networks. By leveraging advanced analytics, automation, and software-defined principles, IBN simplifies network management, enhances network performance, and improves security. With its agile and intelligent approach, IBN is shaping the future of network management and enabling organizations to meet the growing demands of modern networks.
What is Intent Based Networking?
Intent Based Networking is a revolutionary approach to networking that aims to simplify and optimize network operations. It is based on the idea of aligning network management and performance with the overall intent and goals of the organization.
By leveraging the power of automation, orchestration, and software-defined networking, Intent Based Networking enables IT teams to manage and control the network with greater efficiency and agility. It provides a centralized platform for network management, offering a simplified and scalable solution for handling complex network infrastructures.
The key features of Intent Based Networking include intelligence, virtualization, and analytics. The intelligence component allows the network to continuously learn and adapt to changing conditions, optimizing performance and security. Virtualization enables the creation of virtual network environments for better resource allocation and scalability. Analytics provide valuable insights into network performance and security, enabling proactive optimization.
With Intent Based Networking, organizations can achieve greater network efficiency, reliability, and security. It streamlines network operations, reduces manual configuration, and provides a more agile and responsive network infrastructure. The integration of automation and optimization empowers IT teams to focus on higher-level tasks and strategic initiatives, rather than mundane network management tasks.
Definition of Intent Based Networking
Intent Based Networking (IBN) is a networking approach that aims to automate and simplify network operations through the use of software-defined networking (SDN), analytics, and intelligent orchestration. IBN leverages advanced technologies and algorithms to optimize network management, improve security, and enhance performance and efficiency.
At its core, IBN is based on the principle of translating high-level business intent into network policies and configurations. This means that instead of manually configuring individual network devices, administrators can specify their desired outcomes, and the network infrastructure automatically implements and enforces the necessary configurations to achieve those outcomes.
IBN integrates various components to enable this automation and intelligence. It leverages advanced analytics to gather data from the network, analyze it, and extract meaningful insights. These insights are then used to dynamically adjust network policies and configurations to optimize performance and meet business requirements.
One of the key benefits of IBN is its ability to simplify network management and operations. By automating many routine tasks, administrators can focus on higher-level strategic initiatives and troubleshooting, rather than getting bogged down by manual configuration and maintenance.
IBN also provides enhanced security capabilities. With its intelligence and automation, the network can detect and respond to potential threats in real-time, proactively adjusting configurations to protect against attacks and unauthorized access.
Additionally, IBN enables scalability and agility in network infrastructure. With its software-defined approach, network resources can be easily virtualized and provisioned on-demand, allowing for flexible scaling and rapid deployment of new services.
In conclusion, Intent Based Networking is a powerful approach to networking that brings together automation, analytics, and intelligent orchestration to simplify operations, enhance security, and optimize performance.
Key Features of Intent Based Networking
Intent Based Networking (IBN) is a paradigm shift in network management, offering a wide range of features that revolutionize the way networks are designed, deployed, and operated. Some of the key features of Intent Based Networking include:
- Virtualization: IBN leverages virtualization technologies to abstract network resources, making the network more scalable and efficient. It allows for the allocation of resources on-demand and provides flexibility in managing network infrastructure.
- Efficiency: By automating various tasks and simplifying network operations, IBN improves overall network efficiency. It reduces manual configuration errors, enhances troubleshooting capabilities, and enables faster network provisioning.
- Agile: IBN enables networks to quickly adapt to changing business requirements. It provides the ability to define policies and rules that automatically configure the network based on the desired intent, resulting in a more agile and responsive network infrastructure.
- Performance: IBN utilizes software-defined networking (SDN) to optimize network performance. It allows for centralized control and management of network resources, enabling better traffic management, load balancing, and quality of service (QoS) enforcement.
- Security: IBN integrates security policies and protocols into the network fabric, ensuring that security is built into every aspect of the network. It provides real-time threat detection, network segmentation, and automated security enforcement based on predefined intent.
- Analytics: IBN leverages advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms to gather, analyze, and interpret network data. This allows for proactive monitoring, anomaly detection, and predictive maintenance, resulting in improved network performance and reliability.
- Integration: IBN can be seamlessly integrated with existing network infrastructure and management systems. It allows for interoperability between different vendors and technologies, providing a unified view and control of the network environment.
- Intelligence: IBN incorporates artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) capabilities to continuously learn from network data and user behavior. This intelligence enables the network to optimize itself, predict and prevent issues, and adapt to changing network conditions.
- Policy: IBN enables policy-based network management, where network configuration and behavior are driven by predefined policies and intent. It provides a declarative approach to network management, allowing administrators to define high-level policies rather than configuring individual network devices.
- Management: IBN simplifies network management by providing a centralized platform for configuration, monitoring, and control. It eliminates the need for manual configuration of individual devices and allows for network-wide management and orchestration.
These key features of Intent Based Networking make it a powerful and transformative approach to network management. By aligning network operations with business intent, IBN enables organizations to achieve greater network efficiency, agility, and security, ultimately leading to improved business outcomes.
Benefits of Intent Based Networking

Intent Based Networking (IBN) brings numerous benefits to modern networks by leveraging the power of orchestration, policy automation, and network virtualization. This new approach revolutionizes network operations and enables organizations to achieve higher levels of performance, scalability, and agility.
One of the key advantages of IBN is its ability to provide real-time analytics and intelligence, enabling IT teams to gain deep insights into network behavior and quickly identify any potential bottlenecks or security vulnerabilities. By using intent-based policy management, organizations can enforce security policies consistently across the network, ensuring a high level of protection against threats.
IBN also simplifies network management by abstracting network complexities and providing a unified view of the entire infrastructure. This simplification allows for easier integration of new services and applications, as well as improved troubleshooting and faster problem resolution. Additionally, the software-defined nature of IBN enables organizations to automate routine tasks and streamline network operations, leading to increased efficiency and cost savings.
With IBN, organizations can achieve greater network agility, as the network can dynamically adapt to changing business needs. Whether it’s scaling up or down, IBN allows for seamless provisioning and configuration of network resources, eliminating the need for manual intervention and minimizing the risk of human errors.
In conclusion, the benefits of Intent Based Networking are clear: improved performance, scalability, and agility; simplified network management; increased efficiency and cost savings; enhanced security and intelligence; and seamless integration and automation. To stay ahead in the modern networking landscape, organizations should consider adopting IBN as a strategic approach to their network operations.
Automated Network Provisioning
Automated network provisioning is a key component of intent based networking, as it allows for the automated configuration and deployment of network resources based on predefined policies and intents. This automated process simplifies network management and eliminates the need for manual intervention, resulting in improved efficiency and reduced operational costs.
By defining policies and intents, network administrators can specify the desired performance and security requirements for different applications and services. With automated provisioning, the network infrastructure can dynamically adapt and optimize its resources based on these policies, ensuring that the network is always aligned with the organization’s goals and objectives.
The agility provided by automated network provisioning allows for quick and seamless scaling of the network as the organization’s requirements evolve. This scalability is particularly important in modern networks that encompass various technologies such as virtualization, software-defined networking, and network function virtualization.
In addition to scalability, automated network provisioning also enables seamless integration with other network management tools and technologies such as orchestration, analytics, and intelligent software-defined networking platforms. These integrations further enhance the network’s efficiency and provide valuable insights into network performance and optimization.
Overall, automated network provisioning revolutionizes network operations by streamlining the deployment and management processes. With its simplified and intelligent approach, it empowers organizations to achieve greater agility, efficiency, and scalability in their networking infrastructure.
Enhanced Network Security
Network security is a critical aspect of modern networks, and with the adoption of intent-based networking, it has become more efficient and effective. Automation plays a significant role in enhancing network security by reducing manual errors and ensuring consistent policy enforcement. By automating security workflows, organizations can streamline security management and improve response times to potential threats.
Policy-based security is another key feature of intent-based networking. With policy-based security, organizations can define specific security rules and policies that govern network traffic and access. This enables the network to automatically detect and mitigate potential security breaches based on predefined policies, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or malicious activities.
Virtualization and scalability further enhance network security capabilities. With the software-defined nature of intent-based networks, security policies can be more easily applied and managed across a virtualized infrastructure. This allows organizations to scale their security measures effectively and adapt to changing network demands, ensuring consistent protection for the entire network environment.
The integration of security intelligence and analytics into intent-based networking enables proactive threat detection and prevention. By leveraging advanced analytics tools, organizations can gain insights into network behavior and identify potential security vulnerabilities or anomalies. This enables agile and preventive actions to be taken to secure the network and safeguard business operations.
The simplified management and orchestration capabilities of intent-based networking also contribute to enhanced network security. With centralized management and orchestration, organizations can more efficiently monitor and control security policies, ensuring that all network devices and components are configured correctly and are in compliance with security standards. This reduces the risk of misconfigurations or gaps in security measures.
In conclusion, intent-based networking brings significant advancements in network security by leveraging automation, policy-based enforcement, virtualization, scalability, intelligence, and simplified management. These capabilities work together to optimize the performance of security measures, protect against potential threats, and enable organizations to secure their networks effectively and efficiently.
Improved Network Performance and Reliability
With the advent of intent-based networking, the performance and reliability of networks have seen a significant boost. This is achieved through the use of intelligent software-defined networking solutions that prioritize network traffic and optimize network resources based on pre-determined policies and intents.
One of the key benefits of intent-based networking is its scalability and orchestration capabilities. With the ability to automate network management operations, organizations can scale their networks more efficiently and effectively. This means that as the network grows, the management of the network becomes more agile and simplified.
By utilizing virtualization technologies, intent-based networking can provide a higher level of network performance and reliability. Virtual networks allow for the creation of isolated network segments that can be optimized for specific workloads or applications. This enables organizations to allocate network resources more efficiently and ensure that critical applications receive the necessary bandwidth and priority.
Furthermore, intent-based networking incorporates advanced analytics and intelligence capabilities to enhance network performance. By collecting and analyzing network data in real time, organizations can gain valuable insights into network behavior and identify areas for optimization. This allows for proactive measures to be taken to improve network performance and reliability.
Overall, intent-based networking brings a new level of efficiency and reliability to network operations. By aligning network policies with business intent and automating network management tasks, organizations can optimize their network performance and ensure a more reliable and resilient network infrastructure.
Implementation of Intent Based Networking
Intent Based Networking (IBN) is a revolutionary approach to network management that is transforming the way networks are designed, implemented, and operated. It relies on the use of advanced software-defined networking (SDN) technologies to provide a highly scalable and agile infrastructure.
IBN implements a policy-based approach, where network operations are driven by the intent of the operator. This intent is expressed in the form of high-level instructions, which are then automatically translated into specific network configurations and actions. This simplifies network management and makes it more efficient, as it eliminates the need for manual configuration and troubleshooting.
One of the key elements of IBN is the integration of network virtualization and automation. By abstracting the underlying physical infrastructure, IBN enables the creation of virtual networks that can be easily provisioned, scaled, and optimized to meet specific performance and security requirements.
Another important aspect of IBN is its intelligence and analytics capabilities. IBN leverages advanced analytics and machine learning techniques to provide real-time insights into network performance, security, and operational issues. This enables proactive troubleshooting, optimization, and policy enforcement, resulting in improved network reliability and performance.
IBN also enhances network security by enabling the enforcement of security policies at the network level. It provides a centralized framework for monitoring and controlling network traffic, detecting and mitigating security threats, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
Overall, the implementation of Intent Based Networking brings significant benefits to modern networks. It simplifies network operations, enhances scalability and agility, improves network performance and security, and enables intelligent automation and orchestration. By leveraging the power of intent, IBN enables network administrators to create, manage, and optimize networks with greater ease and efficiency.
Components of an Intent Based Network
An Intent Based Network (IBN) is a modern approach to networking that focuses on automating and simplifying network operations based on the intent of the user. It involves the utilization of software-defined networking, virtualization, and automation to optimize network performance while ensuring enhanced scalability, security, and efficiency.
Key components of an Intent Based Network include:
- Intent: The user’s desired outcome or goal for the network, which is expressed in natural language.
- Orchestration: The process of automating and coordinating various network functions to achieve the intended outcome efficiently.
- Policy: Set of rules and guidelines that govern how the network should behave to align with the user’s intent and ensure security and compliance.
- Automation: The ability of the network to automatically configure, provision, and manage resources based on the user’s intent, reducing manual intervention and human errors.
- Software-defined networking (SDN): The separation of network control and forwarding functions, allowing for centralized control, agility, and programmability of the network.
- Virtualization: The abstraction of network resources to create virtual networks, enabling scalability, flexibility, and efficient resource utilization.
- Analytics: Gathering and analyzing network data to gain insights into network performance, user behavior, and security threats, allowing for proactive management and optimization of the network.
- Integration: Seamlessly incorporating different network components and technologies, such as switches, routers, firewalls, and software applications, to provide a unified and cohesive network infrastructure.
- Management: The centralized control and monitoring of the network, allowing for easy configuration, troubleshooting, and reporting.
An Intent Based Network adopts an agile and proactive approach to network management, ensuring that the network aligns with the user’s intent and dynamically adapts to changing requirements. By leveraging automation, optimization, and advanced analytics, organizations can streamline network operations, enhance security, and improve overall network performance.
Challenges in Implementing Intent Based Networking
Implementing intent based networking presents a number of challenges, but the benefits it brings make it a worthwhile endeavor for organizations.
1. Automation: One of the key challenges in implementing intent based networking is the need for automation. Intent based networking relies on software-defined policies to automate network operations, which requires a significant investment in infrastructure and personnel to manage and maintain.
2. Simplified Policy-Based Management: Another challenge is the complexity of defining and implementing policies. Intent based networking aims to simplify policy-based management by providing a more intuitive and user-friendly interface, but this requires organizations to carefully define their intent and ensure it is properly translated into network policies.
3. Agile Network Analytics: Intent based networking relies on network analytics to provide real-time insights into network performance and security. However, implementing effective network analytics requires organizations to integrate and analyze massive amounts of data, which can be a daunting task.
4. Intelligent Orchestration: Intent based networking also requires intelligent orchestration capabilities to dynamically allocate network resources and optimize network efficiency. Implementing intelligent orchestration requires organizations to invest in advanced technologies and integrate them into their existing network infrastructure.
5. Scalability and Virtualization: The scalability of intent based networking is a challenge, especially for organizations with large and complex networks. Implementing intent based networking requires organizations to ensure their network architecture is capable of handling the increased workload and supporting virtualization technologies.
In conclusion, while implementing intent based networking poses challenges, such as automation, policy management, analytics, orchestration, and scalability, the benefits it brings in terms of agility, intelligence, security, and efficiency make it a compelling option for modern networks. It is crucial for organizations to carefully evaluate these challenges and invest in the necessary resources and technologies to successfully implement intent based networking.
The Future of Intent Based Networking
Intent Based Networking (IBN) is revolutionizing the way networks are designed, operated, and managed. It offers enhanced efficiency, performance, and security through a simplified and automated approach. As the world becomes more connected, the need for agile and intelligent networks is growing, and IBN provides the solution.
One of the key advantages of IBN is its ability to align network operations with business intent. By leveraging policy-based automation and analytics, networks can dynamically adapt to meet changing business requirements. This integration of intent and network management enables organizations to optimize their network resources and ensure optimal performance.
IBN also brings virtualization and orchestration capabilities, enabling the creation of software-defined networks. This allows for greater flexibility and scalability, as well as easier deployment and management of network services. With IBN, IT teams can provision and configure network resources more efficiently, reducing the time and effort required for manual tasks.
Furthermore, IBN provides enhanced security through intent-based policy enforcement. By defining intent-based policies, organizations can ensure that security measures are consistently applied across the network. This proactive approach to security minimizes the risk of breaches and improves overall network resilience.
Looking ahead, the future of IBN holds even more promise. Advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning will further enhance the intelligence and automation capabilities of IBN. This will enable networks to learn and adapt in real-time, optimizing performance and troubleshooting network issues more effectively.
In conclusion, Intent Based Networking is set to shape the future of network management and operations. With its focus on intent, automation, and analytics, IBN enables organizations to build agile and intelligent networks that can adapt to meet evolving business needs. As technology continues to evolve, IBN will play a crucial role in driving network optimization and security.
Emerging Technologies and Trends
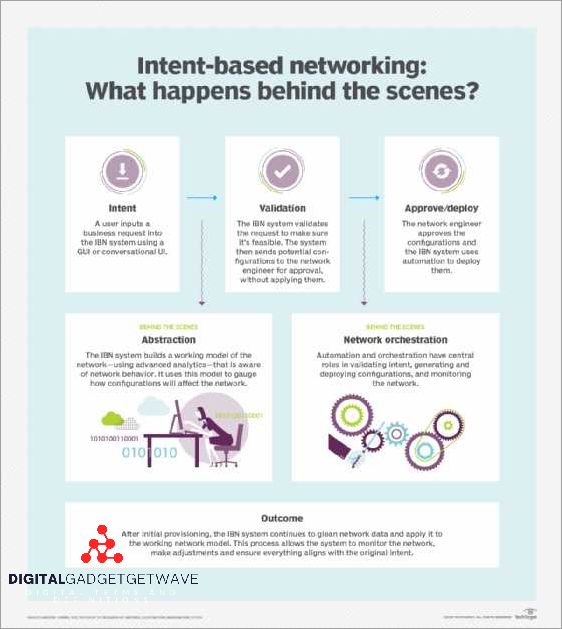
In today’s rapidly changing technology landscape, emerging technologies and trends are shaping the way networks are designed and managed. These new advancements, such as virtualization, policy-based networking, and software-defined networking (SDN), are revolutionizing the way businesses operate and interact with their networks.
Virtualization is one of the key emerging technologies that is transforming the networking industry. With virtualization, businesses can create multiple virtual network instances on a single physical hardware, leading to increased scalability, efficiency, and performance. It allows for the consolidation of network resources and the ability to quickly scale up or down based on demand.
Policy-based networking is another trend that is gaining traction in modern networks. By defining and enforcing policies, businesses can ensure that network resources are allocated based on predefined rules and requirements. This approach enables more granular control over network traffic and enables optimized resource allocation.
Software-defined networking (SDN) is a paradigm shift in network management. By separating the control plane from the data plane, SDN enables centralized management and orchestration of network resources. This centralized approach allows for greater automation, simplified operations, and improved network agility. SDN also enables the integration of advanced analytics and machine learning capabilities into network management, leading to improved performance, security, and optimization.
Another emerging trend is the use of intent-based networking. With intent-based networking, businesses can define their network requirements and goals using high-level policies and objectives. The network infrastructure then automatically translates these intentions into configuration changes and orchestration actions. This approach streamlines network management, reduces human errors, and allows for more proactive and automated network operations.
In conclusion, emerging technologies and trends are driving significant changes in the networking industry. Virtualization, policy-based networking, software-defined networking, and intent-based networking are just a few examples of the advancements that are reshaping the way networks are designed, managed, and operated. By embracing these technologies, businesses can unlock new levels of scalability, efficiency, performance, and security in their networks.
Potential Applications of Intent Based Networking
Intent Based Networking (IBN) is a revolutionary approach to network management that brings agility, efficiency, and automation to modern networks. The potential applications of IBN are vast and can greatly benefit various aspects of network operations and management.
1. Network Orchestration: IBN enables the orchestration of network resources based on intent, allowing for simplified management and configuration of complex network services. It provides a unified view of the network and automates the provisioning, deployment, and monitoring of network services.
2. Scalability and Efficiency: IBN improves network scalability by dynamically adjusting network resources based on intent. It optimizes network performance and resource allocation, leading to increased efficiency and better utilization of network infrastructure.
3. Security and Policy-based Management: IBN enhances network security by automatically enforcing security policies based on intent. It provides granular control over network access and simplifies security management by automatically detecting and responding to security threats.
4. Performance Optimization: IBN leverages advanced analytics and artificial intelligence to continuously monitor and analyze network performance. It identifies performance bottlenecks, predicts potential issues, and optimizes network configurations in real-time to ensure optimal performance.
5. Virtualization and Network Integration: IBN enables the virtualization of network resources, allowing for the creation of virtual networks that can be easily managed and configured based on intent. It also facilitates seamless integration with cloud and third-party platforms, enabling efficient multi-domain network management.
6. Simplified Network Operations: IBN simplifies network operations by providing a centralized management interface that abstracts the complexity of network infrastructure. It enables the automation of routine tasks, reduces human error, and streamlines network troubleshooting and maintenance.
7. Intelligent Analytics: IBN leverages advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms to extract insights from network data. It provides real-time visibility into network performance, user behavior, and application usage, enabling proactive network management and troubleshooting.
Overall, the potential applications of Intent Based Networking are diverse and can greatly enhance network management, performance, security, and scalability in modern networks. By leveraging intent and automation, IBN brings agility and intelligence to network operations, allowing organizations to meet the growing demands of digital transformation.
FAQ about topic “Unlocking the Potential of Intent Based Networking in Today’s Networks”
What is Intent Based Networking (IBN) and how does it work?
Intent Based Networking (IBN) is a networking approach that focuses on simplifying network management and operations by allowing administrators to define high-level business policies or intents, instead of manually configuring individual network devices. In IBN, network devices use automation and machine learning to interpret and implement the desired intent. This enables quick and accurate network provisioning, troubleshooting, and security enforcement.
What are the benefits of Intent Based Networking?
Intent Based Networking offers several benefits for modern networks. Firstly, it improves operational efficiency by automating manual network configuration and management tasks. It also enhances network agility, as administrators can quickly provision new services or make changes to the network based on high-level intents. IBN also enables better network security by automatically enforcing policies and detecting anomalies. Finally, IBN provides better visibility and analytics, allowing administrators to gain insights into network performance and make data-driven decisions.
How does Intent Based Networking simplify network troubleshooting?
Intent Based Networking simplifies network troubleshooting by providing a holistic view of the network and its intent. When an issue or anomaly occurs, network administrators can use IBN to quickly identify the root cause and take appropriate actions. IBN leverages automation and machine learning to correlate and analyze data from various network devices, making it easier to pinpoint and resolve problems. This saves time and effort compared to traditional manual troubleshooting methods.
Can Intent Based Networking be used in any type of network environment?
Yes, Intent Based Networking can be applied to various types of network environments, including data centers, campus networks, and wide area networks (WANs). IBN’s focus on high-level business intents makes it adaptable to different network architectures and requirements. Whether it’s a small-scale local network or a large-scale distributed network, IBN can provide the benefits of automation, agility, and security.
Are there any challenges or limitations with implementing Intent Based Networking?
While Intent Based Networking offers numerous benefits, there are some challenges and limitations to consider. One challenge is the initial setup and configuration of the intent policies. It requires a clear understanding of the network’s objectives and business requirements. Another challenge is the integration with existing network infrastructure, as IBN may require compatible hardware and software. Additionally, the deployment and management of IBN systems may require specialized skills and training. It’s important to carefully assess the network environment and plan the implementation of IBN accordingly.


