
SME stands for Small and Medium-sized Enterprises. These are business enterprises that fall within a certain size range in terms of their assets, annual turnover, and number of employees. SMEs are key players in any national economy, contributing to the economic development and growth of a country. They are considered the backbone of the business sector, providing job opportunities and fostering entrepreneurship.
In general, small enterprises are defined as those that have fewer than 50 employees and a turnover of less than a certain amount, while medium-sized enterprises have between 50 to 249 employees and a higher turnover. SMEs can be found in various sectors, including manufacturing, services, and agriculture.
One of the main advantages of SMEs is their ability to adapt quickly to changing market conditions and customer demands. They are often characterized by their flexibility and innovative approach, which allows them to stand out in a competitive business environment. SMEs play a crucial role in fostering economic growth and development, as they contribute to job creation, promote local entrepreneurship, and stimulate technological advancement.
For individuals who aspire to start their own business, SMEs offer a viable option. Setting up a small or medium-sized enterprise allows entrepreneurs to fulfill their passion, create job opportunities for others, and contribute to the overall economic well-being of their community. SMEs are an essential part of the economic landscape, providing a solid foundation for business growth and development.
In conclusion, SMEs are small and medium-sized enterprises that play a crucial role in economic development and growth. They are characterized by their flexibility, innovation, and entrepreneurial spirit. SMEs provide job opportunities, promote local entrepreneurship, and contribute to the overall economic well-being of a country. Whether it is a small proprietorship or a medium-sized organization, SMEs have a significant impact on the business sector and the economic stability of a nation.
Contents
- 1 What does SME mean?
- 2 Definition of SME
- 3 Explanation of SME
- 4 Classification of SME
- 5 Benefits of SME
- 6 FAQ about topic “What does SME mean? – Definition and Explanation”
- 7 What does SME stand for?
- 8 What is the definition of SME?
- 9 What are the characteristics of a SME?
- 10 How do SMEs contribute to the economy?
- 11 What challenges do SMEs face?
What does SME mean?
SME stands for Small and Medium-sized Enterprises. It refers to micro, small, and medium-sized companies or organizations that play a significant role in economic development, entrepreneurship, and job growth.
SMEs are defined differently in various countries, but generally, they are characterized by the number of employees, annual revenue, and total assets. In the European Union, for example, micro-enterprises have up to 10 employees, small enterprises have up to 50 employees, and medium-sized enterprises have up to 250 employees.
SMEs encompass a wide range of business types, including sole proprietorships, partnerships, and limited liability companies. They can be found in various industries such as manufacturing, services, and technology.
The importance of SMEs lies in their contribution to the economy. They create jobs, foster innovation, and drive economic growth. SMEs often have more flexibility and adaptability than large corporations, allowing them to respond quickly to market changes and opportunities.
In addition to their economic impact, SMEs also play a vital role in local communities. They support local suppliers and service providers, contribute to social development, and provide goods and services tailored to the needs of their specific markets.
Definition of SME

An SME, which stands for Small and Medium-sized Enterprise, is a business organization that falls between the realms of a micro-enterprise and a large company. SMEs are characterized by their size, with a medium-sized enterprise typically having fewer than 250 employees, while a small enterprise has fewer than 50 employees. These enterprises play a significant role in the economic development of a country as they contribute to employment generation, innovation, and overall economic growth.
SMEs can take various organizational forms, including sole proprietorship, partnership, or corporation. They are generally privately owned and operate across different sectors, such as manufacturing, services, or retail. SMEs often display a dynamic and entrepreneurial spirit, constantly seeking opportunities for expansion, development, and growth.
What distinguishes SMEs from larger corporations is their ability to adapt quickly to market changes and their focus on niche markets. This flexibility allows SMEs to cater to specific customer demands, develop innovative products and services, and establish closer relationships with their customers.
SMEs face unique challenges compared to larger companies, such as limited financial resources, limited access to capital, and the need for effective management of resources. However, SMEs are often considered the backbone of economies worldwide, contributing to job creation, fostering innovation, and promoting competition in the marketplace.
What is SME?
SME stands for Small and Medium-sized Enterprises. SMEs are business organizations that fall within a certain size range. They are smaller than large corporations, but larger than micro enterprises or sole proprietorships.
The exact definition of an SME can vary depending on the country and industry, but generally, SMEs are defined by certain criteria, such as the number of employees, annual turnover, and total assets. These criteria can differ, but they typically indicate that SMEs have a limited scale of operations compared to larger companies.
SMEs play a crucial role in the economic development of a country. They contribute to job creation, innovation, and competition in the market. As such, SMEs are often seen as a driving force for entrepreneurship and economic growth.
SMEs can operate in various sectors, including manufacturing, services, technology, and others. They can be a family-owned business, a start-up company, or a small-scale organization. The size and structure of SMEs allow them to respond quickly to market changes and adapt more easily to new trends and opportunities.
In summary, SMEs are small and medium-sized enterprises that stand somewhere between micro enterprises and large corporations. They play a significant role in the economy, fostering entrepreneurship, and contributing to economic growth and development.
Meaning of SME
SME stands for Small and Medium Enterprises. It refers to businesses that fall within a certain size range, which varies from country to country. SMEs play a crucial role in the development and growth of economies around the world.
What does SME mean? The term SME encompasses both small and medium-sized enterprises, but the exact criteria for classifying a company as small or medium can vary. In general, SMEs are defined based on factors such as the number of employees, annual turnover, or total assets.
For example, in the European Union, a micro-enterprise is defined as a company with no more than 10 employees and an annual turnover of up to €2 million. A small enterprise has fewer than 50 employees and an annual turnover of up to €10 million, while a medium-sized enterprise has fewer than 250 employees and an annual turnover of up to €50 million.
SMEs are often seen as the backbone of economic growth and entrepreneurship. They contribute to job creation, innovation, and competition in the market. SMEs also play a significant role in supporting the local community and driving regional development.
Within the SME sector, there are various types of businesses, including sole proprietorships, partnerships, and limited liability companies. These enterprises operate in diverse industries and sectors, ranging from manufacturing and retail to services and technology.
In conclusion, SMEs are small and medium-sized enterprises that have a crucial role in economic development. The exact criteria for defining an SME can vary, but they generally refer to companies within a certain size range in terms of employees, turnover, or assets. SMEs contribute to entrepreneurship, job creation, and overall economic growth.
Explanation of SME
SME stands for small and medium-sized enterprises. It refers to a category of economic organizations that fall between micro-businesses and large corporations. In general, SMEs are defined based on their size, turnover, and number of employees.
In most countries, the definition of SMEs varies, but they are typically classified as small businesses if they have fewer than a certain number of employees or a low turnover. Medium-sized businesses, on the other hand, have more employees and a higher turnover than small businesses, but are still smaller than large corporations.
What does SME mean for economic development and growth? SMEs play a crucial role in driving economic growth, job creation, and innovation. They are often considered the backbone of the economy since they account for a significant portion of employment and contribute to the overall GDP. SMEs also foster entrepreneurship and provide opportunities for sole proprietorship and small business owners to thrive.
In addition, SMEs are known for their agility and flexibility, allowing them to adapt quickly to market changes and customer demands. They are often more innovative and responsive compared to larger organizations, as they can take risks and implement new ideas more easily. This makes SMEs a vital part of the business ecosystem, especially in industries that require constant innovation and adaptation.
Overall, understanding what SME means is important for policymakers, economists, and entrepreneurs alike. SMEs play a crucial role in the economy, driving development, growth, and job creation. They provide opportunities for individuals to start and grow their own businesses, contributing to the overall economic well-being of a country.
Overview of SME
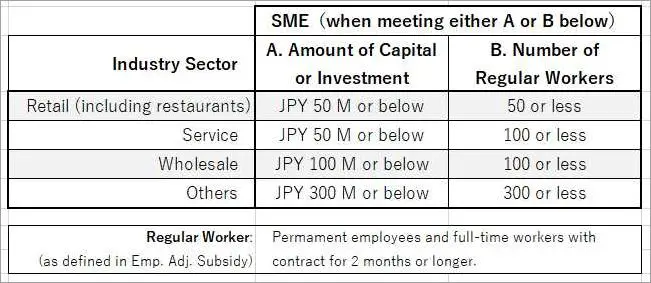
SME stands for Small and Medium-sized Enterprises. These are businesses that are characterized by their small size and limited resources. SMEs play a crucial role in the economic development of a country as they contribute to job creation, innovation, and overall economic growth.
SMEs include a wide range of enterprises, from sole proprietorships and micro companies to medium-sized organizations. They operate in various sectors, including manufacturing, services, and agriculture. SMEs are often driven by entrepreneurial individuals who have a passion for starting and growing their own business.
What does SME mean? SME is an acronym that stands for Small and Medium-sized Enterprises. It is a term used to refer to businesses that are smaller in size and have fewer resources compared to large corporations. SMEs are often characterized by their flexibility and ability to adapt quickly to changing market conditions.
Although the definition of SME may vary depending on the country and industry, it generally refers to businesses with a limited number of employees and revenue. For example, in the European Union, a small enterprise is defined as having less than 50 employees and a medium-sized enterprise has less than 250 employees.
SMEs are important for the growth of the economy as they create employment opportunities, foster innovation, and contribute to the overall productivity of a country. They also play a significant role in promoting regional development by supporting local communities and businesses.
In conclusion, SMEs are small and medium-sized enterprises that play a vital role in the economic development of a country. They are characterized by their small size, limited resources, and entrepreneurial spirit. SMEs contribute to job creation, innovation, and overall economic growth, making them an essential part of any economy.
Importance of SME
SME, which stands for Small and Medium Enterprises, plays a crucial role in the economic development of a country. These micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises are often seen as the backbone of an economy, contributing to job creation, innovation, and overall economic growth.
What makes SMEs important is their ability to adapt and respond quickly to market changes compared to larger organizations. SMEs are typically more agile and flexible, allowing them to seize business opportunities and drive economic growth.
SMEs also provide a platform for entrepreneurship and innovation. As small businesses, they can experiment with new ideas, products, and services that larger companies may be hesitant to explore. This culture of innovation fosters creativity and drives the development of new technologies and industries.
Furthermore, SMEs contribute significantly to job creation. They are often the primary source of employment in many countries, particularly for individuals who may not have the opportunity to work in larger corporations. SMEs provide jobs not only for skilled professionals but also for vulnerable groups such as youth, women, and persons with disabilities.
Another crucial aspect of SMEs is their contribution to the diversification of the economy. By operating in various sectors, SMEs reduce dependency on a single industry, creating a more stable and resilient economic landscape. This diversity of small businesses also ensures a healthy level of competition, benefiting consumers with greater choices and lower prices.
In conclusion, SMEs play a vital role in the economic development of a country. Their impact extends beyond job creation, fostering innovation, driving economic growth, and contributing to a more diverse and dynamic economy. Governments and policymakers recognize the importance of SMEs and often implement supportive measures to facilitate their growth and sustainability.
Classification of SME
In the field of business and economic development, SME stands for Small and Medium Enterprises. SMEs are a crucial part of any economy, as they play a significant role in driving growth, fostering innovation, and creating employment opportunities.
SMEs are typically classified based on the size and nature of their operations. The classification of SMEs can vary between countries, but there are common criteria that are widely used to determine the size of an enterprise.
One common classification criterion is the number of employees. Small enterprises are often defined as having fewer than 50 employees, while medium-sized enterprises may have between 50 and 250 employees. This criterion helps to differentiate SMEs from large corporations that have a significant workforce.
Another classification criterion is the annual turnover or revenue of the enterprise. Small enterprises generally have lower annual turnover compared to medium-sized enterprises. This criterion is often used to assess the financial strength and stability of an SME.
In addition to size, SMEs can be classified based on the legal structure of the organization. For example, proprietorships and sole proprietorships are small businesses owned and run by individuals, while companies are larger organizations with multiple owners or shareholders. This criterion helps to distinguish between different types of SMEs and their legal obligations.
Overall, the classification of SMEs is an important tool for policymakers, researchers, and entrepreneurs to understand the diversity and dynamics of small and medium-sized businesses. It helps in formulating appropriate policies and support mechanisms for the development and growth of the SME sector in the economy.
Types of SME
In the context of small business development and economic growth, SMEs can be classified into different categories based on their size and structure. Here are some common types of SMEs:
Micro-enterprises: Micro-enterprises are the smallest type of SMEs. They usually have fewer than ten employees and a low turnover. These small businesses are often run by a sole proprietorship or a small team of individuals.
Small enterprises: Small enterprises are slightly larger than micro-enterprises, with around ten to fifty employees. They have a higher turnover and may have more complex organizational structures. Small enterprises play a significant role in the economic growth of a country.
Medium-sized enterprises: Medium-sized enterprises have a larger scale than small enterprises, typically with fifty to two hundred employees. They have a higher turnover and often have more formalized management and operational structures. These businesses are considered to be in a transitional phase between small and large enterprises.
SMEs in specific industries: SMEs can also be categorized based on the specific industry they operate in. For example, there are SMEs in manufacturing, retail, agriculture, technology, and many other sectors. The classification based on industry helps to understand the unique challenges and opportunities faced by SMEs in different sectors.
Growth-oriented SMEs: Some SMEs are focused on rapid growth and expansion. These growth-oriented SMEs often have ambitious goals and invest heavily in innovation, entrepreneurship, and market expansion. They play a vital role in job creation and contribute significantly to the overall economic development of a country.
In conclusion, SMEs encompass a wide range of small and medium-sized businesses, each with its own unique characteristics and growth potential. Understanding the different types of SMEs is essential for policymakers, researchers, and entrepreneurs to develop targeted strategies and support mechanisms to foster their growth and success.
Criteria for SME classification
In the context of SME classification, there are certain criteria that are used to determine whether an enterprise can be considered as a small or medium-sized enterprise.
1. Size: The size of an SME is determined by various factors, including its number of employees, annual turnover, and balance sheet total. Generally, small enterprises have fewer employees and lower turnover compared to medium-sized enterprises.
2. Employment: SMEs are characterized by their relatively low number of employees. For example, small enterprises typically have fewer than 50 employees, while medium-sized enterprises can have between 50 and 250 employees.
3. Financial indicators: The financial indicators of an SME, such as its annual turnover and balance sheet total, are also taken into consideration for classification. Small enterprises usually have lower levels of turnover and balance sheet totals compared to medium-sized enterprises.
4. Legal structure: SMEs can have different legal structures, including sole proprietorship, partnership, or company. The legal structure can also play a role in determining the classification of an SME.
5. Sector: The sector in which an SME operates can also impact its classification. Different sectors may have different criteria for SME classification, as the economic characteristics and growth potential can vary.
Overall, the classification of an SME is determined by a combination of factors, including size, employment, financial indicators, legal structure, and sector. These criteria help define what an SME is and are used to support the development and growth of small and medium-sized enterprises, which play a crucial role in economic development and entrepreneurship.
Benefits of SME
SME stands for small and medium-sized enterprises. These types of businesses have a significant impact on the economic development of a country. SMEs play a crucial role in job creation, innovation, and driving economic growth. There are several benefits of SMEs for both the organization and the overall economy.
First, SMEs provide opportunities for entrepreneurship and business development. They allow individuals with innovative ideas to start their own small businesses and become self-employed. This fosters a culture of creativity and encourages individuals to take risks and pursue their entrepreneurial dreams.
SMEs also contribute to job creation. As these businesses grow, they require additional manpower to support their operations. They often provide employment opportunities for local communities, contributing to the reduction of unemployment rates. Additionally, SMEs often hire individuals with niche skills or specialized knowledge, which helps to develop a diverse and skilled workforce.
Another benefit of SMEs is their ability to support local economies. Unlike large multinational corporations, SMEs are often rooted in the communities they serve. They tend to source products and services from local suppliers, thus stimulating local economic activity. This creates a network of interdependent businesses, benefiting the overall economic development of the region.
SMEs also play a crucial role in fostering innovation. These companies are often more agile and flexible than larger corporations, allowing them to adapt and implement new ideas more quickly. SMEs are at the forefront of technological advancements and often contribute to industry innovation through their research and development efforts.
Lastly, SMEs offer opportunities for personal growth and development. In a small or micro company, individuals often have more diverse roles and responsibilities, allowing them to gain a wider range of skills and experiences. This can lead to personal and professional growth, as employees are exposed to various aspects of the business and have the opportunity to make a meaningful impact.
In conclusion, SMEs are essential for the economic development of a country. They provide opportunities for entrepreneurship, job creation, and innovation. SMEs also support local economies and offer opportunities for personal growth and development. Therefore, recognizing and supporting SMEs is vital for the overall growth and prosperity of a nation.
Economic benefits of SME
SME stands for Small and Medium Enterprises, which are the backbone of any economy. These enterprises play a crucial role in economic growth and development. They are typically smaller in size compared to larger companies, but they have a significant impact on job creation, innovation, and overall economic stability.
One of the economic benefits of SMEs is their contribution to job creation. Small and medium enterprises are often the main providers of employment opportunities, especially in developing countries. They create jobs not only for the business owners themselves but also for the local community. This helps in reducing unemployment rates and improving the standard of living for individuals.
SMEs also foster innovation and entrepreneurship. These enterprises are more flexible and adaptable compared to larger companies, which allows them to quickly respond to market changes and explore new opportunities. They are often the breeding ground for innovative ideas and technologies, driving economic growth and development.
Furthermore, SMEs promote regional development by decentralizing economic activities. They are usually located in smaller towns and rural areas, creating economic activities and opportunities outside of major cities. This helps in reducing regional inequality and promoting balanced economic growth across different regions.
Additionally, SMEs contribute to exports and trade. Many small and medium enterprises engage in international trade, exporting their products and services to different countries. This not only helps in increasing foreign exchange earnings but also contributes to the overall economic growth of the country.
In conclusion, SMEs have various economic benefits, including job creation, innovation, regional development, and contribution to exports and trade. They are an essential part of the economic fabric, and their growth and success are crucial for overall economic stability and prosperity.
Social benefits of SME
SME stands for Small and Medium Enterprises, which refer to small-sized companies or organizations. SMEs play a crucial role in the economic development of a country. They are the backbone of any economy, especially in promoting entrepreneurship and job creation.
One of the main social benefits of SMEs is their contribution to employment generation. These businesses provide opportunities for both skilled and unskilled workers, creating job opportunities for the local community. SMEs also promote inclusivity by employing individuals from different backgrounds, thus reducing unemployment rates and poverty levels.
SMEs also foster social cohesion within a community. They often operate at a local level, promoting interactions between individuals and fostering a sense of belonging. These businesses contribute to the development of local culture, traditions, and values, strengthening community ties.
Moreover, SMEs have a significant impact on the overall economic growth of a country. They stimulate innovation, creativity, and competition, leading to increased productivity. As a result, SMEs contribute to the GDP and help diversify the economy, reducing overreliance on a few large corporations.
Another social benefit of SMEs is their ability to support sustainable development. Being small in size, SMEs are more adaptable and flexible compared to larger companies. They are more likely to adopt sustainable practices and contribute to environmental conservation. SMEs can implement environmentally friendly technologies, reduce waste, and promote responsible consumption.
In summary, SMEs bring numerous social benefits to a society. They drive economic growth, create employment opportunities, foster social cohesion, and support sustainable development. Therefore, supporting and promoting SMEs is essential for the overall well-being of a community and its members.
FAQ about topic “What does SME mean? – Definition and Explanation”
What does SME stand for?
SME stands for Small and Medium-sized Enterprises.
What is the definition of SME?
The definition of SME varies depending on the country, but generally, SME refers to businesses that have a small or medium level of turnover, a limited number of employees, and operate independently.
What are the characteristics of a SME?
Some common characteristics of SMEs include having a smaller number of employees compared to larger corporations, being independently owned and operated, having a lower level of turnover, and often having a more localized customer base.
How do SMEs contribute to the economy?
SMEs play a vital role in the economy by driving innovation, creating jobs, and contributing to economic growth. They often serve as the backbone of many local economies and provide important services and products to their communities.
What challenges do SMEs face?
SMEs face a variety of challenges, including limited access to financial resources, intense competition from larger companies, difficulties in scaling up their operations, and navigating complex regulatory frameworks. They may also struggle with marketing their products or services and attracting and retaining skilled employees.


