
A bastion host is a dedicated and highly secure server or gateway that is used to authenticate, authorize, and control access to a private network from an external network, such as the internet. It acts as a point of defence and protection for the internal network, filtering and managing traffic to ensure only authorized and privileged users can access the resources within.
One of the key functions of a bastion host is to act as a secure entry point into the network. It is designed to withstand attacks and provide a secure connection for incoming connections, making it difficult for unauthorized users to gain access to sensitive data or resources. It acts as a gatekeeper, ensuring that only authenticated users with the necessary permissions can access the internal network.
By acting as a secure gateway, a bastion host helps to protect the network from external threats and unauthorized access attempts. It is often equipped with strong firewall rules and access control mechanisms, which allow it to inspect and control the traffic that flows through it. This ensures that only legitimate and authorized traffic is allowed to pass through to the internal network.
In addition to its security functions, a bastion host also often serves as a management endpoint for the network. It provides a secure platform for administrators to remotely manage and monitor the network, as well as troubleshoot any issues that may arise. It may also house specific tools and software that are used for network management and security purposes.
In summary, a bastion host plays a crucial role in securing a network by acting as a secure gateway and control point for incoming connections. It authenticates users, authorizes their access, and ensures that only authorized traffic is allowed through. It provides a layer of protection and control, making it an essential component of any secure network architecture.
Contents
- 1 Definition and Purpose of a Bastion Host
- 2 Key Features and Functionality
- 3 How Does a Bastion Host Work?
- 4 Secure Access Control
- 5 Firewall and Intrusion Detection
- 6 Benefits of Using a Bastion Host
- 7 Enhanced Security
- 8 Improved Compliance and Auditability
- 9 Best Practices for Implementing a Bastion Host
- 10 Hardening the Host
- 11 Limiting Access and Privileges
- 12 FAQ about topic “What is a bastion host: everything you need to know”
- 13 What is a bastion host?
- 14 Why is a bastion host important for network security?
- 15 What are the typical features of a bastion host?
- 16 How can a bastion host protect against cyber attacks?
- 17 Can a bastion host be compromised?
Definition and Purpose of a Bastion Host
A bastion host, also known as a jump server or pivot server, is a dedicated server designed to enhance the security of a network by providing secure access control. It acts as a gateway between an internal network and an external network such as the internet, allowing authorized users to access certain resources while keeping the network protected from potential threats. The main purpose of a bastion host is to monitor, authenticate, and secure the access of users.
One of the key functions of a bastion host is to serve as a point of entry for privileged users who need to remotely manage the network or servers. These privileged users, often administrators or system operators, can connect to the bastion host using secure protocols such as SSH (Secure Shell) or VPN (Virtual Private Network). The bastion host then verifies their identities and grants access to specific resources based on predefined permissions.
In addition to controlling user access, a bastion host also plays a crucial role in monitoring and logging network traffic. By analyzing incoming and outgoing connections, it can detect and alert administrators of any suspicious activities or attempted breaches. This monitoring capability makes the bastion host an essential component of an organization’s overall security infrastructure.
To ensure the highest level of security, bastion hosts are typically hardened and configured with strict security policies. This includes regularly patching and updating the server’s software, implementing firewalls and intrusion detection systems, and employing encryption techniques for secure communication. These measures collectively contribute to the defense of the network and protection of sensitive data.
In summary, a bastion host is a secure and authorized access point that provides controlled and monitored access to a network. Acting as a gateway, it allows privileged users to remotely manage the network while protecting it from unauthorized access and potential threats. By monitoring network traffic and implementing robust security measures, a bastion host helps organizations maintain a strong defensive posture against attacks.
Understanding the role of a bastion host
A bastion host plays a crucial role in the protection and management of a network. It serves as an endpoint for all incoming and outgoing traffic, monitoring and controlling access to a network.
Acting as a gateway, the bastion host acts as a defence mechanism against unauthorized access and ensures the security of the network. It is a privileged host that authenticates, controls, and monitors the connections made to and from the network.
The primary function of a bastion host is to secure the network by acting as a security barrier between the internal network and the outside world. It is equipped with firewalls and other security measures to prevent unauthorized access and protect sensitive data.
By allowing only authenticated and authorized users to access the network, the bastion host ensures that the network remains secure. It acts as a point of control where user access is managed and monitored.
Bastion hosts are commonly used to secure servers and other critical infrastructure components. It ensures that only legitimate users can access and make changes to these servers, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and potential security breaches.
In summary, a bastion host plays a crucial role in ensuring the security of a network. It acts as a gatekeeper, controlling access to the network and protecting it from unauthorized access. By monitoring and controlling the traffic, it acts as a security checkpoint, preventing potential threats and ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of the network.
Importance of secure remote access
Secure remote access is of utmost importance in today’s digital world, as it allows privileged users to access a secure network from a remote location. Firewalls serve as a crucial defense mechanism, filtering incoming and outgoing traffic and controlling access to the network.
Remote access enables authorized users to connect to a server or a network from anywhere, providing a flexible and convenient way to manage resources and perform necessary tasks. However, this convenience should not compromise security.
Secure remote access involves implementing strong security measures such as VPN (Virtual Private Network) connections, multi-factor authentication, and encryption. By using a host as a gateway, organizations can ensure that only authenticated users gain access to the network.
Monitoring and defense mechanisms are essential to protect against unauthorized access and potential security breaches. This includes real-time monitoring of network traffic, endpoint protection, and regular auditing of user access and activities.
To enhance security, secure remote access should include strict access controls, limiting access privileges for different user roles. Additionally, regular security updates and patch management is crucial to protect against known vulnerabilities and exploits.
In summary, secure remote access provides a way for authorized users to access resources and manage systems securely from a remote location. Implementing strong security measures, monitoring network traffic, and controlling access privileges are essential components of secure remote access.
Key Features and Functionality
A bastion host is a key management and security component in a network infrastructure. It serves as an authorized access point for users and acts as a gateway or endpoint for secure connections.
One of the key features of a bastion host is its ability to control and monitor incoming and outgoing network traffic. It acts as a secure entry point, allowing only authenticated users to connect to the network.
By authenticating users and authorizing their access, a bastion host enhances the overall security of the network. It acts a defense mechanism against unauthorized access attempts and provides a centralized point of control for regulating user access.
In addition to user authentication and access control, a bastion host also provides monitoring capabilities. It can monitor network traffic and log any suspicious or malicious activities. This allows network administrators to detect and respond to security threats in real-time.
To ensure a high level of security, a bastion host often incorporates firewalls and other security measures. It can be configured to allow or deny specific types of traffic, depending on the network’s security policies.
A bastion host is typically a dedicated server that is isolated from the rest of the network. It is specifically designed to handle privileged access requests and protect sensitive information. This separation helps prevent unauthorized users from gaining access to critical network resources.
Overall, a bastion host plays a crucial role in network security. It provides a secure entry point, controls user access, monitors network traffic, and acts as a defense mechanism against unauthorized access attempts. Its key features and functionality contribute to the overall security and integrity of the network infrastructure.
Network segmentation and isolation
Network segmentation and isolation is a crucial aspect of network security. It involves dividing a network into smaller, separate segments to enhance security and control access to sensitive resources.
By implementing network segmentation, organizations can limit the scope of unauthorized access to critical systems and confidential data. Access to segmented networks can be restricted to authorized individuals or systems, ensuring that only authorized users can access sensitive information.
Segmentation helps in managing and securing different parts of a network by using firewalls or other security devices. These devices monitor and control traffic between different segments, ensuring that only authenticated and authorized connections are allowed.
A bastion host, acting as a gateway server, is often used to provide secure access to segmented networks. It acts as an endpoint for remote connections and requires users to authenticate themselves before gaining access to the network. This adds an additional layer of security and helps defend against unauthorized access attempts.
Network segmentation also enables organizations to better monitor and control network traffic. By isolating different segments, it becomes easier to detect and respond to potential security threats or incidents. Monitoring and logging activities within each segment provide better visibility into potential vulnerabilities or suspicious activities.
In addition, network segmentation provides protection against lateral movement within a network. If an attacker manages to gain access to one segment, their ability to move laterally and compromise other segments is limited. This containment strategy helps prevent the spread of attacks and minimizes potential damage.
To summarize, network segmentation and isolation is a crucial aspect of network security. It helps secure sensitive resources, control access, and provides better defense against unauthorized access attempts. By implementing this approach, organizations can enhance their overall network security posture and better protect their valuable data and systems.
Monitoring and logging capabilities
A bastion host plays a crucial role in controlling and authenticating access to a network. It acts as a gateway for all incoming and outgoing network traffic to and from an organization’s internal network, allowing management of user access and enforcing security policies. With its enhanced security features, a bastion host acts as a fortress for the organization’s sensitive data and resources.
One of the key functions of a bastion host is to monitor and log all network traffic. By capturing and analyzing incoming and outgoing connections, it provides valuable insights into the security of the network. It logs events such as failed and successful login attempts, network traffic patterns, and unauthorized access attempts. These logs can be used to identify potential security threats and take appropriate action to mitigate them.
Monitoring the activities on a bastion host allows for real-time tracking of user actions, ensuring that all actions are authorized and comply with security policies. It helps to detect any abnormal behavior or suspicious activities that could pose a security risk. User activities such as file transfers, server administration, and system configurations can be monitored for any unauthorized or malicious actions.
With its logging capabilities, a bastion host provides a detailed record of all authorized user activities. These logs can be used for forensic analysis in the event of a security breach or incident. It helps in identifying the source of the breach, the extent of the damage, and the necessary steps to prevent future incidents.
To ensure the security of a network, it is essential to have a strong monitoring and logging system in place. A bastion host acts as the endpoint for all authorized connections, providing a defense layer against potential security threats. By monitoring and logging all activities, it allows organizations to maintain a secure environment and respond effectively to any security incidents.
How Does a Bastion Host Work?
A bastion host serves as a gateway for inbound traffic, acting as an endpoint for secure connections. It provides protection by monitoring and controlling access to the network, acting as a point of control for all incoming and outgoing traffic. The bastion host is typically implemented as a hardened server with specialized security features.
The main purpose of a bastion host is to provide a secure point of access for authorized users. It acts as a defensive layer, allowing only authenticated and authorized users to access the internal network. The bastion host restricts access to critical resources, such as servers with privileged information or management interfaces, ensuring that only trusted individuals can connect to them.
To achieve its security objectives, a bastion host typically employs a combination of security measures. These may include firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other security features that are configured to prevent unauthorized access and protect sensitive information. The bastion host is designed to be highly secure and resilient, with strict authentication and access controls in place to ensure that only authorized users can access its resources.
When a user attempts to access the network through a bastion host, they must authenticate themselves using secure credentials. This authentication process verifies the user’s identity and ensures that they are authorized to access the network. Once authenticated, the user is granted access only to the resources that they are allowed to access, based on their user permissions and the security policies that have been set up.
Overall, a bastion host plays a crucial role in securing a network by providing a controlled and secure entry point for authorized users. It helps prevent unauthorized access, protects valuable resources, and ensures that users adhere to security policies. By implementing a bastion host, organizations can significantly enhance their network security and protect against security threats.
Secure Access Control
Secure access control is a critical aspect of network security, especially when it comes to protecting sensitive data and resources from unauthorized access. Firewalls are often used as a first line of defense to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic. By implementing strong access control policies, firewalls can restrict access to the network and ensure that only authorized users are allowed in.
One common method of secure access control is through the use of bastion hosts. These highly secured hosts act as gateways to a network, allowing only authorized users to establish a connection. Bastion hosts are often equipped with additional security measures such as multi-factor authentication or privileged access management, further mitigating the risk of unauthorized access.
Secure access control also involves implementing strict password policies, requiring users to create strong and unique passwords. It is important to regularly update and monitor these passwords to prevent unauthorized access. Additionally, endpoint protection solutions, such as antivirus software or intrusion detection systems, can be implemented to provide an extra layer of defense against potential security threats.
Another important aspect of secure access control is the management and monitoring of user access rights. Network administrators should regularly review and update access privileges, ensuring that only the necessary permissions are granted to users. This helps prevent unauthorized access to critical resources and reduces the risk of insider threats.
In conclusion, secure access control is essential for maintaining the security of a network and protecting sensitive data. By implementing firewalls, bastion hosts, strong passwords, endpoint protection, and effective access rights management, organizations can establish a secure environment where authorized users can access resources and defend against potential security threats.
Authentication and Authorization
Authentication and authorization are crucial components of a secure bastion host. They provide protection and control access to the host’s resources.
Authentication is the process of verifying the identity of users or systems attempting to access the bastion host. This can involve various methods, such as passwords, biometrics, or multi-factor authentication. Strong authentication ensures that only authorized individuals or systems can establish a connection with the host.
Authorization, on the other hand, involves determining the actions or privileges that authorized users or systems have on the bastion host. It defines what resources they can access, what actions they can perform, and what level of control they have over the host. Effective authorization prevents unauthorized access and unauthorized activities on the host.
Bastion host authentication and authorization often leverage secure protocols and technologies to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of the connection. Firewalls are commonly used as a line of defense, monitoring and controlling inbound and outbound traffic to the bastion host. Additionally, privileged access management solutions can be implemented to manage and control the authentication and authorization processes.
The authentication and authorization mechanisms implemented in a bastion host also play a crucial role in network security. By securely authenticating users and authorizing their actions, the host becomes a secure gateway to other systems and resources within the network. This prevents unauthorized access and helps protect sensitive information from potential threats.
Implementing secure protocols
When it comes to securing an endpoint, implementing secure protocols is crucial. Secure protocols provide the necessary control to ensure that only authorized users can access the system. These protocols protect the sensitive data and information from unauthorized access.
One important aspect of implementing secure protocols is the protection of network traffic. Secure protocols ensure that all communication between the endpoint and other systems is encrypted, making it difficult for attackers to intercept or manipulate the data. This encryption helps to maintain the confidentiality and integrity of the information being transmitted.
Another vital aspect of implementing secure protocols is the authentication of users. Secure protocols require users to authenticate themselves before granting access to the system. This authentication process verifies the identity of the user and ensures that only authorized individuals can connect to the endpoint.
In addition to authentication, implementing secure protocols also involves the defense against unauthorized access and attacks. Secure protocols set up firewalls and gateways to monitor and control incoming and outgoing traffic, blocking any unauthorized attempts to access the system. This defense mechanism helps to protect the endpoint from malicious activities and prevents unauthorized access.
Implementing secure protocols also includes the management and monitoring of the endpoint’s security. Secure protocols establish security measures such as server monitoring and log analysis to detect any suspicious activities. These measures help in identifying and mitigating potential security breaches, providing an added layer of protection to the endpoint.
Furthermore, implementing secure protocols involves the concept of privileged access management. Secure protocols limit the privileged access given to users, ensuring that only authorized individuals have administrative control over the endpoint. This limitation reduces the risk of misuse or unauthorized access to critical system resources.
In summary, implementing secure protocols is essential for the protection and secure operation of an endpoint. These protocols help to control access, protect network traffic, authenticate users, defend against unauthorized access, and ensure the overall security of the system. By implementing secure protocols, organizations can strengthen their security posture and mitigate the risk of data breaches or unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Firewall and Intrusion Detection
Firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDS) are essential components of network security. They provide defense and protection against unauthorized access and malicious activities.
A firewall acts as a control point between a private network and the public internet. It filters network traffic, allowing authorized connections and blocking unauthorized access. Firewalls use a set of defined rules to authenticate and monitor incoming and outgoing traffic, ensuring that only legitimate users and services can access the network.
An IDS, on the other hand, is a network security system that monitors and analyzes network traffic for signs of malicious activities or potential attacks. It acts as a detective device, constantly scanning the network to identify and alert security personnel about any suspicious or malicious behavior.
Together, firewalls and IDS play a vital role in securing a network from external threats. They provide a secure gateway for authorized users, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive information and resources.
Furthermore, firewalls and IDS help protect the network from internal threats as well. They control and monitor the traffic between different endpoints within the network, ensuring that only authorized connections are established and preventing any unauthorized access or data breaches.
Network perimeter protection
Network perimeter protection is a crucial aspect of maintaining the security of a network. It involves implementing various security measures to protect the network from unauthorized access and potential threats. Firewalls play a vital role in network perimeter protection by acting as a barrier between the internal network and the external world. They filter and authenticate incoming and outgoing traffic, ensuring that only authorized users and connections are allowed.
Monitoring the network is another important component of network perimeter protection. By constantly monitoring network traffic and activities, potential security breaches can be identified and prevented. This can be achieved through the use of monitoring tools and intrusion detection systems.
A bastion host can also be utilized as part of network perimeter protection. This host acts as a gateway between the external network and the internal network. It provides an additional layer of security by controlling and managing access to internal resources. Only authorized users or connections are allowed through the bastion host, ensuring that any potential threats or attacks are filtered out.
Endpoint security is another essential aspect of network perimeter protection. By securing individual devices connected to the network, such as servers and workstations, the overall network security is strengthened. This can be achieved through the use of antivirus software, firewalls, and other security measures specifically designed for endpoint protection.
In summary, network perimeter protection encompasses various security measures such as firewalls, authentication mechanisms, monitoring tools, and bastion hosts. These measures work together to defend the network against unauthorized access and potential threats. By implementing a robust network perimeter protection strategy, organizations can ensure the security and integrity of their network and its resources.
Preventing unauthorized access attempts is a critical aspect of maintaining the security and integrity of a bastion host. To effectively manage this, several measures can be implemented:
Privileged access control: Limiting the number of users with privileged access to the bastion host significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access attempts. By carefully controlling who has administrative permissions, the chances of a malicious actor gaining control over the server are greatly minimized.
Endpoint authentication: Implementing strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication or smart cards, ensures that only authorized users can connect to the bastion host. This provides an additional layer of protection against unauthorized access attempts.
Monitoring and logging: Regularly monitoring and logging all activities on the bastion host allows for real-time detection and response to any suspicious or unauthorized access attempts. This can include monitoring for failed login attempts, unusual user behavior, or any other signs of unauthorized access.
Firewalls and secure gateways: Deploying firewalls and secure gateways at the network level can help prevent unauthorized access attempts by filtering incoming and outgoing traffic. Firewalls can be configured to allow only authorized connections to the bastion host, blocking any unauthorized attempts to access the server.
Regular security updates: Keeping the bastion host’s operating system and software up-to-date with the latest security patches and updates is crucial. These updates often include fixes for known vulnerabilities that could be exploited to gain unauthorized access.
Authorized user access control: Implementing stringent access control policies, such as role-based access control (RBAC), ensures that only authorized users can connect to the bastion host. This prevents unauthorized individuals or entities from gaining access to the server.
By implementing these preventive measures, the bastion host acts as a strong defense against unauthorized access attempts, safeguarding the overall network security.
Benefits of Using a Bastion Host
A bastion host provides several benefits when it comes to access control and security in your network infrastructure:
- Enhanced Authentication: A bastion host acts as a gateway that authenticates users before granting them access to other servers and resources in the network.
- Improved Server Protection: With a bastion host, you can add an extra layer of defense for your servers by ensuring that all incoming traffic passes through it. This helps to filter and monitor the traffic, ensuring that only authorized connections are allowed.
- Better Management and Control: By using a bastion host, you can gain better control over user access and privileges. It allows you to define and enforce strict access policies to regulate who can access specific servers and resources.
- Endpoint Security: A bastion host can help protect the endpoint devices within your network by acting as a secure entry point. It can monitor and analyze network traffic, detecting any potential threats or vulnerabilities.
- Centralized Monitoring: With a bastion host, you can centralize the monitoring and logging of all incoming traffic. This allows for easier analysis of security events and quicker response to any suspicious activities.
In summary, a bastion host provides a secure and controlled access point for users, enhances the protection of your servers, improves management and control over user privileges, helps to secure endpoint devices, and allows for centralized monitoring of network traffic. By implementing a bastion host, organizations can strengthen their overall network security and reduce the risk of unauthorized access or attacks.
Enhanced Security
In order to ensure enhanced security, a bastion host plays a crucial role in protecting a server or network from potential threats. It acts as a gateway that controls and monitors traffic between the internal and external networks. By using a bastion host, organizations can establish a secure connection and authenticate users before granting them access to the network.
One of the key benefits of a bastion host is its ability to enforce strict access controls. It acts as a defensive barrier, allowing only authorized users to enter the network. It implements strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication, to verify the identity of users before granting them access.
The bastion host also ensures secure management of privileged access. It centralizes the control of administrative functions, limiting the number of users who have direct access to critical systems. This reduces the risk of unauthorized access and potential misuse of privileged accounts.
In addition to controlling access, a bastion host provides continuous monitoring of network traffic. It examines incoming and outgoing data packets, searching for any signs of malicious activity or intrusion attempts. If any suspicious activity is detected, the bastion host can take immediate action to block the connection or alert the network administrators.
Another important aspect of enhanced security provided by a bastion host is endpoint defence. It acts as a secure endpoint for remote connections, protecting the internal network from potential threats originating from external sources. By channeling all external traffic through the bastion host, it becomes an additional layer of defence against cyber attacks.
Overall, the use of a bastion host significantly enhances the security of a server or network. It acts as a secure gateway, controlling access, monitoring traffic, enforcing strict authentication, and providing an additional layer of defence against potential threats.
Protecting sensitive data
When it comes to protecting sensitive data, a bastion host plays a crucial role in ensuring the security of the network. By acting as a gateway between the internal network and the external world, the bastion host controls and monitors all incoming and outgoing traffic. This allows for the efficient management and defense of the server and the network as a whole.
One of the key functions of a bastion host is to provide a secure and authorized access point for privileged users. By implementing strict access control measures, the bastion host ensures that only authorized users can connect to the network. This prevents unauthorized access and potential data breaches.
Additionally, the bastion host acts as a monitoring endpoint, allowing network administrators to monitor and analyze the traffic passing through the network. By using specialized tools and techniques, administrators can detect and mitigate any potential security threats or vulnerabilities. This proactive approach helps to ensure the ongoing protection of sensitive data.
Another important aspect of data protection is the implementation of firewalls on the bastion host. Firewalls are essential in filtering and controlling network traffic, allowing only authorized connections and blocking any potential threats. By configuring the firewalls properly, the bastion host enhances the security of the network by preventing unauthorized access and protecting sensitive data from external threats.
Overall, a bastion host is a critical component in the defense and protection of sensitive data. By providing secure and authorized access, controlling and monitoring traffic, implementing firewalls, and acting as a central management point, the bastion host contributes to a secure and robust network environment.
Reducing attack surface
One of the main benefits of using a bastion host is the ability to reduce the attack surface of an organization’s network. A bastion host acts as a secure gateway for all incoming and outgoing traffic, providing an additional layer of protection for the endpoint devices within the network.
By implementing a bastion host, organizations can ensure that only authorized connections are allowed to access the internal network. This is achieved through strong authentication and access control mechanisms, which require privileged users to authenticate themselves before accessing the network.
Firewalls are commonly used to secure the perimeter of a network, but they can only provide limited protection to the internal servers and endpoints. A bastion host, on the other hand, acts as a dedicated security host, providing a higher level of protection and control.
With a bastion host in place, organizations can effectively manage and control access to their network resources. This includes managing user privileges and controlling the types of connections that are allowed to access the network.
Furthermore, a bastion host can serve as a central point for monitoring and auditing network activity. It can log all incoming and outgoing traffic, providing valuable insight into potential security threats and ensuring compliance with security policies.
In summary, a bastion host plays a crucial role in reducing the attack surface of an organization’s network. By acting as a secure gateway, it helps to protect endpoints and internal servers from unauthorized access, while allowing organizations to effectively control and manage network connections.
Improved Compliance and Auditability
One of the key benefits of utilizing a bastion host is improved compliance and auditability. By incorporating a bastion host into your network infrastructure, you can strengthen the security measures in place to authenticate and authorize access to sensitive systems and resources.
A bastion host serves as a single point of control for all inbound and outbound connections, acting as a secure gateway between the internet and the internal network. This centralized approach allows for better monitoring and management of network traffic, providing an added layer of protection against unauthorized access.
Bastion hosts also enable organizations to enforce strict access policies, granting privileged access only to authorized users and endpoints. This level of control not only helps prevent unauthorized access but also ensures that compliance with industry regulations and security best practices is maintained.
Moreover, the use of a bastion host enhances the overall security posture of an organization by limiting the attack surface and reducing the risk of potential breaches. Firewall rules can be configured on the bastion host to restrict incoming and outgoing connections, effectively isolating the internal network from potential threats.
Furthermore, bastion hosts facilitate effective security auditing and monitoring. By logging and analyzing all incoming and outgoing traffic, organizations can track and review user activities, detect and investigate any suspicious behavior, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
In summary, incorporating a bastion host into your network architecture provides improved compliance and auditability by centralizing and controlling access to sensitive systems, enhancing security measures, and enabling effective monitoring and auditing of network activities. It serves as a crucial defense mechanism in protecting organizations against unauthorized access and maintaining a secure and compliant network environment.
Meeting regulatory requirements

In order to comply with regulatory requirements, organizations need to ensure their systems meet certain standards of security and privacy. Bastion hosts play a crucial role in meeting these requirements by providing an additional layer of defence and secure access control.
Firewalls are commonly used to protect networks and servers from unauthorized access, but a bastion host goes a step further by providing an extra level of protection. This can be achieved through various security measures such as user authentication, traffic monitoring, and privileged management.
Bastion hosts act as gateways between the internal network and the outside world. They serve as a centralized point of control for incoming and outgoing connections, allowing only authorized traffic to pass through. This ensures that only authenticated and authorized users are able to access the internal network resources.
With the use of bastion hosts, organizations can effectively monitor and control network traffic. They can track and analyze the flow of data, identify any suspicious activities, and take immediate actions to mitigate security risks. This level of security and monitoring is especially important for organizations handling sensitive data, such as financial information or personally identifiable information (PII).
Bastion hosts also contribute to regulatory compliance by providing secure endpoint management. By restricting access to critical systems and resources, organizations can minimize the risk of unauthorized access and potential data breaches. Additionally, bastion hosts can enforce strict privilege management, ensuring that only trusted individuals have the necessary permissions to make changes or access sensitive data.
In summary, bastion hosts are essential for meeting regulatory requirements as they provide an extra layer of security and control for network and server access. By implementing bastion hosts, organizations can better protect their systems, authenticate users, control traffic, and meet the necessary standards for regulatory compliance.
Auditing and monitoring access
When it comes to bastion hosts, auditing and monitoring access are key components in ensuring the security of your network. Auditing refers to the process of recording and analyzing the activity on the bastion host, while monitoring involves actively observing and analyzing the traffic that passes through the host.
One of the main functions of a bastion host is to act as a gateway for incoming connections, providing protection for the internal network by controlling access to resources. Auditing and monitoring help in managing this access by providing visibility into which users are connecting to the bastion host and what actions they are taking.
Firewalls and other security measures are typically used in conjunction with bastion hosts to provide an extra layer of defence. Auditing and monitoring can help in detecting any unauthorized access attempts or suspicious activity, allowing for prompt action to be taken.
By monitoring the network traffic that passes through the bastion host, administrators can keep track of what resources are being accessed and ensure that only authorized users are connecting to the server. This helps in maintaining the overall security of the network.
Auditing and monitoring also play a crucial role in ensuring the security of privileged accounts. These accounts have elevated privileges and can access sensitive information or perform critical tasks. By properly auditing and monitoring access to these accounts, administrators can detect any unauthorized use and take immediate action to prevent any potential security breaches.
In summary, auditing and monitoring access to the bastion host are important for maintaining the security of your network. These processes enable administrators to detect and respond to any suspicious activity, authenticate users, and control access to sensitive resources, ultimately ensuring a secure environment for your organization.
Best Practices for Implementing a Bastion Host
A bastion host is a critical component in ensuring the security of a network. It acts as a gateway for users to access the internal network, while also providing a layer of defence and protection against unauthorized access. Implementing a bastion host requires careful planning and adherence to best practices to ensure its effectiveness.
1. Limit access: Only grant access to users who require it for their job responsibilities. This ensures that only authorized individuals can connect to the bastion host and reduces the risk of potential breaches.
2. Centralized management: Implement a centralized management system to monitor and control access to the bastion host. This allows for easy tracking and auditing of user connections and ensures that proper security measures are in place.
3. Two-factor authentication: Enforce the use of two-factor authentication for users connecting to the bastion host. This adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide additional information, such as a physical token or a biometric verification, in addition to a password.
4. Secure communication: Use secure protocols, such as SSH or HTTPS, for connections between the users and the bastion host. This ensures that the traffic is encrypted and protected from interception or tampering.
5. Privileged access control: Implement strict controls and policies for granting privileged access to the internal network from the bastion host. Only allow access to authorized individuals who require elevated privileges for their specific roles.
6. Continuous monitoring: Regularly monitor the bastion host for any suspicious activity or potential security breaches. Implement logging and monitoring systems to analyze traffic and detect any unauthorized access attempts.
7. Implement firewalls: Configure firewalls on the bastion host to restrict access to specific IP addresses or networks. This helps to prevent unauthorized access and protects the host from potential attacks.
8. Endpoint security: Ensure that the devices connecting to the bastion host are secure and up-to-date with the latest security patches. Implement endpoint security measures, such as antivirus software and intrusion detection systems, to protect against malware and other threats.
9. Regularly authenticate and update the host: Regularly authenticate and update the bastion host to ensure that it remains secure and up-to-date with the latest security patches. This helps to patch any vulnerabilities and mitigate potential risks.
10. Regular security assessments: Conduct regular security assessments of the bastion host to identify any potential weaknesses or vulnerabilities. This allows for proactive measures to be taken, ensuring the ongoing security and effectiveness of the bastion host.
Hardening the Host
To ensure the security of a bastion host, it is crucial to implement various measures to harden the host and protect it from potential attacks and unauthorized access. Here are several key steps to strengthen the security of a bastion host:
- Endpoint Protection: Install and regularly update endpoint protection software on the host to detect and prevent malware and other malicious activities.
- Secure Connections: Enforce the use of secure protocols, such as SSH, to establish connections with the bastion host. This ensures that all communication is encrypted and protects against eavesdropping and unauthorized interception.
- Privileged Access: Limit the number of privileged accounts on the host and carefully manage their access rights. Regularly audit and review privilege levels to maintain a least privilege principle.
- Network Segmentation: Implement network segmentation to isolate the bastion host from other systems and networks. This reduces the attack surface and prevents lateral movement by potential attackers.
- Authentication: Implement multi-factor authentication to increase the security of user accounts accessing the bastion host. This adds an extra layer of verification, making it more difficult for unauthorized users to gain access.
- Gateway Functionality: Utilize the bastion host as a gateway to control and monitor incoming and outgoing traffic. This allows for granular control over network connections and provides an additional layer of security.
- Continuous Monitoring: Implement monitoring and logging mechanisms to track and detect any suspicious activities on the bastion host. Regularly review and analyze the logs to identify potential security incidents.
- Firewalls and Access Control: Configure firewalls and access control lists to restrict access to the bastion host. Only allow connections from authorized IP addresses and limit the range of port numbers that can be accessed.
- User Management: Implement strong user account management practices, such as regularly reviewing and disabling inactive accounts, enforcing password complexity, and implementing account lockout policies.
By following these measures, the bastion host can be hardened and provide a secure environment for remote access and management, offering effective protection and defense against potential attacks.
Securing operating system and applications
To ensure the security of an operating system and its applications, a bastion host can be used as a secure gateway for privileged access. This host acts as the point of entry for users who want to authenticate and connect to the server. By implementing strict access controls and user authentication, the bastion host provides an additional layer of protection against unauthorized access.
One of the key functions of a bastion host is to monitor and control the traffic between the endpoint users and the server. This includes inspecting incoming and outgoing connections, as well as filtering and regulating access based on predefined security policies. By acting as a dedicated security defence, the bastion host can mitigate potential vulnerabilities and prevent malicious activities.
By implementing firewalls and access control mechanisms, the bastion host ensures that only authorized users can gain access to the server. It provides a secure environment for managing user access, enforcing secure configurations, and monitoring user activities. Through proper user management and authentication protocols, the bastion host reduces the risk of unauthorized access and strengthens the overall security posture.
In addition to its role as a secure gateway, the bastion host also plays a crucial role in managing the security of operating system and applications. It can be configured to regularly scan for vulnerabilities, apply patches and updates, and enforce secure configurations. By continuously monitoring the system and its applications, the bastion host helps to identify and remediate security risks promptly.
Regular patching and updates
Patching and updating a bastion host is a critical aspect of its security management. This is because vulnerabilities in the host’s software can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access to the host and potentially the rest of the network. Regular patching ensures that any known security vulnerabilities in the host’s operating system, applications, firewalls, and other components are fixed, reducing the risk of exploitation.
The patching process involves regularly checking for and applying updates provided by the host’s software vendors. This can be done manually or through automated tools that scan for vulnerabilities and apply patches as needed. It is important to prioritize the most critical patches and updates, especially those related to security and stability.
In addition to patching, regular monitoring of the host’s security is essential. This includes monitoring the host’s activity logs, network traffic, and user authentication attempts. Any suspicious activity should be investigated immediately to detect and mitigate potential security breaches.
Furthermore, it is important to control and restrict access to the bastion host. Only authorized users should have access to the host, and their activities should be carefully monitored and logged. Strong authentication mechanisms, such as two-factor authentication, should be implemented to ensure that only authorized users can connect to the host.
A bastion host should also be equipped with strong endpoint protection to defend against malware and other malicious software. This includes using up-to-date antivirus software, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and other security measures.
In summary, regular patching and updates are crucial for maintaining the security of a bastion host. By keeping the host’s software and components up to date, monitoring its activity, controlling access, and implementing strong security measures, organizations can ensure that their bastion host remains a secure gateway and defence against unauthorized access to their network.
Limiting Access and Privileges
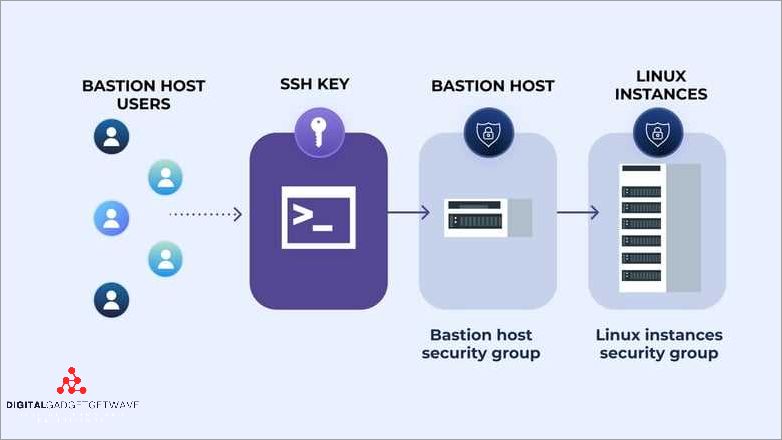
A bastion host is a privileged server that acts as a secure gateway for managing connections and traffic between authorized users and the internal network. One of the key functions of a bastion host is to control and monitor access to the network by enforcing strict security measures.
To ensure the defence of the network, bastion hosts are equipped with firewalls that filter incoming and outgoing traffic. This allows only authorized users to authenticate and gain access to the network, while keeping the unauthorized users at bay. By restricting access, bastion hosts provide an additional layer of security to the network infrastructure.
Additionally, a bastion host can be configured to enforce strict user privileges. This means that users are only granted access to specific resources and functions based on their role and responsibilities. By limiting privileges, the risk of unauthorized access or misuse of network resources is mitigated, providing a more secure environment for sensitive data and operations.
Furthermore, bastion hosts can also act as an endpoint for monitoring and logging network activities. This allows administrators to track and analyze network traffic, identify potential security threats, and respond promptly to any suspicious activities. By actively monitoring the network, administrators can ensure the overall security and protection of the network infrastructure.
In conclusion, a bastion host plays a crucial role in limiting access and privileges within a network. By acting as a secure gateway, enforcing strict access controls, and monitoring network activities, bastion hosts significantly enhance the security and protection of the network infrastructure.
Implementing strict access controls

In order to ensure the security of a bastion host, it is crucial to implement strict access controls. This involves carefully managing connections to the host and controlling the traffic that passes through it.
One way to implement access controls is by using firewalls. By configuring the host’s firewall, you can specify which IP addresses are allowed to connect to the host and what types of traffic are permitted. This helps to prevent unauthorized access and ensures that only authorized users can access the host.
Another important aspect of access control is gateway authentication. This involves requiring users to authenticate themselves before they are granted access to the host. By implementing this authentication process, you can ensure that only privileged users can connect to the bastion host.
Monitoring is also an essential part of access control. By closely monitoring the traffic that passes through the host, you can identify any suspicious or unauthorized activity. This allows you to take immediate action and strengthen the security measures in place.
In addition, it is important to implement security measures on the server and endpoint level. This includes using secure protocols and encryption to protect data in transit. By securing the server and endpoint, you can further enhance the security of the bastion host.
Furthermore, access control should also extend to the management of the bastion host itself. This involves limiting the number of authorized admins and regularly reviewing their access privileges. By regularly reviewing and updating access privileges, you can ensure that only trusted individuals have administrative control over the host.
In summary, implementing strict access controls is crucial for ensuring the security of a bastion host. By carefully managing connections, controlling traffic, and enforcing authentication and monitoring measures, you can significantly enhance the overall security and defense of your network.
Following the principle of least privilege
In the context of network security, the principle of least privilege is an important concept to consider when designing and implementing a bastion host. The idea behind this principle is to limit the access and privileges that users have by default, allowing them only the minimum necessary access to perform their tasks.
By implementing this principle, a bastion host acts as a gateway that provides protection for the other hosts in the network. It serves as a control point for managing inbound and outbound traffic, ensuring that only authorized and authenticated users can access the network resources.
One of the key benefits of implementing a bastion host is that it helps to strengthen the security of the network infrastructure. By having a dedicated server that is specifically designed to handle and authenticate user connections, the risk of unauthorized access is greatly reduced.
In addition, a bastion host enables administrators to have better control over the privileged accounts and access privileges. All user activities and connections can be logged and monitored, allowing for real-time threat detection and response. This way, any suspicious or malicious activity can be flagged and mitigated before it can cause any harm to the network.
Furthermore, a bastion host can be configured with additional security measures, such as firewalls, to provide an added layer of defence. These firewalls can be used to filter and monitor inbound and outbound traffic, ensuring that only necessary and authorized traffic is allowed through.
In summary, following the principle of least privilege, a bastion host acts as a secure access point that controls and monitors user connections to the network. By implementing this concept, the network can be better protected and potential security risks can be minimized.
FAQ about topic “What is a bastion host: everything you need to know”
What is a bastion host?
A bastion host is a highly secured computer system that is intentionally exposed to the public network. It acts as a bridge between the public internet and a private network, providing controlled access to specific services or resources within the private network.
Why is a bastion host important for network security?
A bastion host is important for network security because it acts as a single point of entry that can be monitored and controlled. By keeping all traffic going through the bastion host, organizations can enforce strict security measures and prevent unauthorized access to their private network.
What are the typical features of a bastion host?
A typical bastion host has a minimalistic configuration, running only the necessary services and applications. It is usually hardened to resist attacks, has secure access controls, logs all access attempts, and is constantly monitored for any suspicious activity.
How can a bastion host protect against cyber attacks?
A bastion host can protect against cyber attacks by implementing various security measures. It can use strong authentication mechanisms, such as two-factor authentication, to ensure only authorized users can access the private network. It can also employ intrusion detection systems and firewalls to monitor and filter incoming traffic, blocking any potential threats.
Can a bastion host be compromised?
While a bastion host is designed to be highly secure, it is not immune to being compromised. Like any other computer system, vulnerabilities can be exploited, and attackers may find ways to bypass its defenses. Organizations must regularly update and patch their bastion host to mitigate any potential risks.

