The International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) is a unique identification number used in the GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) mobile telephony protocol. It is an essential component of the SIM (Subscriber Identity Module) card, which is provided by the mobile operator to identify and authenticate subscribers in a telecommunication network.
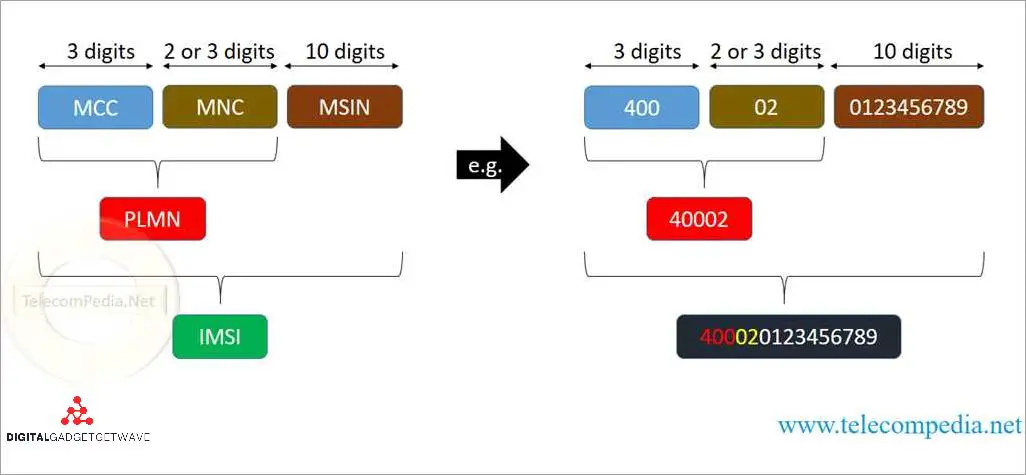
The IMSI is a 15-digit number that consists of three parts: a Mobile Country Code (MCC), a Mobile Network Code (MNC), and a Mobile Subscriber Identification Number (MSIN). The MCC is a three-digit code that identifies the country where the mobile operator is registered. The MNC is a two-digit or three-digit code that identifies the mobile network within the country. The MSIN is a 10-digit number that identifies the individual subscriber within the network.
The IMSI plays a crucial role in various aspects of mobile telephony. It is used for authentication purposes during the registration process when a subscriber connects to the network. The IMSI is exchanged between the mobile device and the network during the authentication process to verify the subscriber’s identity and ensure secure communication. It is also used for roaming services, allowing subscribers to use their mobile devices in different countries by connecting to partner networks.
The IMSI is an important element in the air interface of the GSM protocol, which defines the communication between the mobile device and the network. It enables the network to provide various services to the subscriber, such as voice calls, text messaging, internet access, and other value-added services. The IMSI is used within the network to route calls and messages to the correct subscriber, ensuring efficient and reliable communication within the cellular telephony infrastructure.
In addition to its role in GSM, the IMSI is also used in other telecommunication protocols, such as ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network), to identify and authenticate subscribers. As mobile telephony continues to evolve and new technologies such as 5G emerge, the IMSI remains a crucial element in ensuring secure and efficient communication within the telecom industry.
Contents
- 1 How does IMSI work?
- 2 Benefits and importance of IMSI
- 3 Issues and concerns with IMSI
- 4 FAQ about topic “What is IMSI: Understanding the International Mobile Subscriber Identity”
- 5 What is IMSI?
- 6 How is IMSI different from IMEI?
- 7 Why is IMSI important?
- 8 Can IMSI be changed?
- 9 What information can be derived from IMSI?
How does IMSI work?
The International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) is a unique identifier assigned to every mobile subscriber in a cellular network. It is an integral part of the GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) and ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) protocol used in telecommunication services.
IMSI is stored on the SIM (Subscriber Identity Module) card and is used by the mobile operator to identify and authenticate the subscriber. When a mobile user accesses the network, the operator requests the IMSI from the SIM card to establish the subscriber’s identity.
IMSI plays a crucial role in the roaming process. When a subscriber travels to a different country and connects to a foreign mobile network, the IMSI is used to identify the home network and retrieve the subscriber’s profile. This allows the subscriber to access their subscribed services and ensures a seamless mobile experience while roaming.
In addition to identifying the subscriber, the IMSI also helps in managing the network resources. By associating the IMSI with the subscriber’s mobile device, the operator can track the usage, allocate appropriate network resources, and bill the subscriber accordingly.
IMSI is transmitted over the air interface during telephony signaling and is exchanged between the mobile device and the base station. It contains a three-digit Mobile Country Code (MCC), a two or three-digit Mobile Network Code (MNC), and a variable-length Mobile Subscriber Identification Number (MSIN). Together, these components uniquely identify the subscriber’s international mobile identity within the network.
In summary, IMSI acts as a unique identifier for mobile subscribers in a telecom network. It enables the operator to authenticate the subscriber, manage network resources, and provide seamless roaming services.
Understanding the basics
IMSI stands for International Mobile Subscriber Identity and is a unique identifier used in the cellular telephony network. It is assigned to each subscriber in a GSM or UMTS network and is stored on a SIM card. The IMSI is a fundamental part of the authentication process and enables access to various services provided by the telecom network.
As the primary identifier for a mobile subscriber, the IMSI plays a crucial role in establishing a secure connection between the subscriber’s device and the network. It is transmitted over the air during the initial registration and authentication process, allowing the network to verify the subscriber’s identity and grant access to services.
With the IMSI, a mobile subscriber can access voice and data services, send and receive text messages, make phone calls, and engage in other mobile telecommunication activities. The IMSI also facilitates roaming, enabling subscribers to use their mobile devices in different countries and access services from foreign telecom operators.
The IMSI is a structured code that consists of three main parts: the Mobile Country Code (MCC), Mobile Network Code (MNC), and Mobile Subscriber Identification Number (MSIN). The MCC identifies the country, the MNC identifies the telecom network within that country, and the MSIN identifies the specific subscriber within the network. Together, these components provide a unique identifier for each mobile subscriber.
In addition to being used in GSM and UMTS networks, the IMSI can also be found in other telecommunication protocols, such as ISDN. It is an essential component of the telecommunication infrastructure, ensuring the accurate identification and authentication of mobile subscribers in both national and international contexts.
The role of IMSI in mobile networks
The International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) plays a vital role in mobile networks. It is a unique identifier assigned to each subscriber in a mobile network. The IMSI is an internationally recognized identifier that allows for seamless communication and roaming between different networks.
IMSI is used by mobile network operators to identify and authenticate subscribers on their networks. When a subscriber enters a new network, the IMSI is used to verify their identity and to grant access to network services. It ensures that only authorized users can connect to the network and use its services.
IMSI is an essential part of the Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) protocol, which is the standard for cellular telephony and data transfer. It enables the secure exchange of information between the subscriber’s mobile device and the network.
IMSI is stored on a Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) card, a small chip that is inserted into the mobile device. The SIM card contains essential subscriber information, including the IMSI, which is used for network registration and authentication. The IMSI is also used for billing purposes, as it helps mobile operators track and manage the usage of their subscribers.
In addition to its role in the GSM network, IMSI also plays a crucial role in other telecommunication technologies, such as ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) and telecommunication signaling protocols. It ensures seamless connectivity and interoperability between different network operators and technologies.
In summary, IMSI is an international identifier that plays a vital role in mobile networks. It is used to identify and authenticate subscribers, enable secure communication, and ensure seamless connectivity and roaming between different networks. IMSI is an essential component of the mobile telephony infrastructure and is crucial for the proper functioning of mobile services.
Benefits and importance of IMSI
The International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) is a unique identifier that is associated with a mobile subscriber on a cellular network. It plays a crucial role in facilitating various mobile services and operations. Here are some of the benefits and importance of IMSI:
- Subscriber Identification: IMSI serves as a fundamental element for identifying a mobile subscriber within the cellular network. It enables the network to differentiate between different subscribers and assign relevant services and resources.
- International Roaming: IMSI is essential for international roaming, as it allows a subscriber to connect to different cellular networks around the world. When roaming, the IMSI enables the visited network to authenticate the subscriber and provide the necessary services.
- Authentication and Security: IMSI plays a crucial role in subscriber authentication and security. It is used as part of the authentication process to verify the legitimacy of a subscriber’s mobile device and ensure secure access to the network.
- Subscriber Data Management: IMSI helps in managing subscriber data, such as the associated phone number, billing information, and service subscriptions. It allows the telecom operator to store and access the subscriber’s profile and provide personalized services.
- Efficient Network Operations: By using IMSI, the cellular network can efficiently manage and allocate network resources to subscribers. It helps in optimizing network performance, ensuring better quality of service, and supporting various value-added services.
In summary, IMSI is a vital element in the international telecommunication industry. It enables mobile operators to identify subscribers, support international roaming, ensure secure authentication, manage subscriber data efficiently, and optimize network operations. With the growth of mobile services, IMSI continues to play a critical role in providing seamless and secure connectivity for mobile subscribers worldwide.
Enhanced security
In the cellular telephony industry, security is of utmost importance. With the use of IMSI, Enhanced security measures can be implemented to protect the subscriber’s identity and ensure the confidentiality of their communications.
The SIM card contains the International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI), which serves as a unique identifier for each subscriber. This identifier is securely stored in the SIM card and is used during authentication and authorization procedures.
When a subscriber initiates a connection to a network, the IMSI is sent over the air interface to the network operator. The network operator then uses the IMSI to verify the subscriber’s identity and grant access to network services.
One of the key security features of IMSI is its use in the authentication process. The IMSI, along with other authentication parameters, is used to generate authentication tokens that are exchanged between the subscriber’s device and the network operator. This ensures that only authorized devices can access the network.
Furthermore, the use of IMSI helps in preventing unauthorized access to network resources. The network operator can validate the IMSI against a list of authorized subscribers and reject any attempts from unauthorized devices or subscribers to connect to the network.
In addition to authentication and access control, the use of IMSI also enables encryption of the communication channels, ensuring the confidentiality of the subscriber’s data. With encrypted communication, eavesdroppers cannot intercept and decipher the subscriber’s communications.
In summary, the use of IMSI in the cellular telephony protocol enhances security measures by providing a unique identifier for subscribers, enabling authentication, access control, and encryption of communications. This ensures the subscriber’s identity and data are protected from unauthorized access and interception.
Global roaming capabilities

Global roaming is a key feature enabled by the International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) in the cellular telecommunication network. The IMSI is a unique identifier assigned to each subscriber’s SIM card, allowing them to access mobile services not only within their home network but also when traveling to other countries.
When a subscriber roams in a foreign country, their IMSI is used for authentication purposes. The subscriber’s SIM card is registered on the visited network, and the IMSI is communicated to the network for verification. This ensures that the subscriber can access telephony and data services while roaming in the foreign network.
Global roaming capabilities are not limited to a specific telecommunication protocol or technology. Whether the subscriber is using GSM, ISDN, or other cellular networks, the IMSI remains the common identifier that enables roaming. This allows subscribers to seamlessly switch between different network providers and technologies while traveling internationally.
Global roaming is facilitated by agreements between network operators, ensuring that subscribers can access services on partner networks. These agreements typically involve the exchange of IMSI information and billing arrangements between the home and visited networks. The IMSI acts as the bridge that links the subscriber to their home network, even when they are physically located in another country.
Thanks to the IMSI and global roaming capabilities, subscribers can enjoy uninterrupted connectivity and access to their mobile services, regardless of their location. This feature has greatly enhanced the convenience and flexibility of mobile telecommunication, enabling users to stay connected and utilize their preferred services while traveling internationally.
Improved network management
The International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) plays a crucial role in the improved network management of cellular telephony systems. As a unique identifier for subscribers, the IMSI allows operators to authenticate their customers and secure their access to various telecommunication services.
With the IMSI, operators can accurately identify and track subscribers as they move across different networks and countries. This is particularly important for roaming services, where a subscriber can seamlessly connect to foreign networks using their GSM SIM card.
By knowing the IMSI of a subscriber, operators can efficiently manage network resources and ensure quality of service. They can prioritize network traffic, allocate bandwidth, and optimize network coverage based on the demands of individual subscribers. This enhanced management capability leads to improved network performance and overall user experience.
The IMSI is exchanged over the air interface between the subscriber’s mobile device and the network using the GSM protocol. It is transmitted securely to prevent unauthorized access to the subscriber’s identity and to protect their privacy. This crucial mechanism enables seamless connectivity and ensures the smooth operation of international mobile telecommunication services.
Issues and concerns with IMSI
The International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) raises several issues and concerns within the international mobile network. The IMSI serves as a unique identifier for every subscriber in a GSM network, allowing for authentication and access to various telecom services.
One significant concern is the potential privacy and security risks associated with the exposure of IMSI. Since IMSI is transmitted over the air, it can be intercepted by malicious actors who can exploit it for illegal activities. Therefore, telecom operators need to implement robust security measures to protect IMSI from unauthorized access.
Another challenge is that IMSI is not compatible with all telephony systems, particularly those based on Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) protocols. This compatibility issue can hinder the interoperability of cellular networks, especially when it comes to roaming services.
Furthermore, the increasing reliance on IMSI for authentication purposes can result in a single point of failure. In the event of an IMSI-related issue, such as SIM card damage or loss, the subscriber may be unable to access essential telecom services until the problem is resolved.
Additionally, as international mobile networks continue to expand and evolve, managing the large number of IMSI becomes a complex task for telecom operators. The provisioning and administration of IMSI can be time-consuming, requiring efficient processes and systems to handle the growing subscriber base.
In conclusion, while IMSI plays a vital role in the authentication and identification of mobile subscribers, it presents challenges in terms of privacy, compatibility, reliability, and management. Addressing these issues is crucial to ensure the smooth functioning and security of the international mobile network.
Privacy and data protection
Privacy and data protection are important considerations when it comes to the International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) and the services provided by the telecommunications network. The IMSI serves as a unique identifier for mobile subscribers, allowing for authentication and roaming across different networks.
With the advancement of mobile telephony, the protection of personal data and privacy has become a crucial aspect in the telecommunications industry. The IMSI allows for secure communication between the mobile subscriber’s SIM card and the network, ensuring that only authorized devices can access the subscriber’s information and services.
Telecommunication operators must adhere to strict privacy regulations to ensure that the IMSI and other personal data are kept confidential. This includes implementing encryption techniques to safeguard the transmission of data over the air and safeguarding the integrity of the subscriber’s identity.
The IMSI is part of the Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM), which is widely used for cellular telephony and mobile data services. The GSM standard ensures that mobile subscribers’ data is protected and that their identities are not compromised.
In addition to GSM, the IMSI is also used in other telecommunication standards such as Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) and the Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), further emphasizing the importance of privacy and data protection in the industry.
To further enhance privacy and data protection, mobile telecommunication operators often implement additional security measures such as two-factor authentication and secure communication protocols. These measures help prevent unauthorized access to subscribers’ personal data and ensure the safety of their information within the network.
Identity theft and fraud
Identity theft and fraud are serious concerns in the cellular telecom network, particularly with the use of International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) in services such as Global System for Mobile communication (GSM) and International Mobile Telecommunications-2000 (IMT-2000) protocols. The SIM card, which holds the IMSI, is a crucial authentication tool, as it enables the network operator to securely identify and authenticate the mobile subscriber.
However, in the case of identity theft, an unauthorized individual may gain access to a subscriber’s IMSI and use it to impersonate the subscriber, potentially resulting in fraudulent activities and unauthorized use of services. This can lead to financial losses for both the subscriber and the network operator.
To mitigate the risk of identity theft and fraud, network operators implement security measures such as strong authentication protocols and encryption algorithms. They also closely monitor network activities to identify any suspicious behavior or unauthorized use of IMSI. In addition, subscribers are encouraged to protect their SIM cards and personal information, keeping them safe and secure.
In the context of roaming services, where a subscriber uses their mobile device in a foreign network, there is an added risk of identity theft and fraud. The subscriber’s IMSI is transmitted over the air to the foreign network, which may have different security measures in place. This creates an opportunity for hackers or criminals to intercept the IMSI and exploit it for fraudulent purposes.
To combat identity theft and fraud when using roaming services, network operators and telecommunication authorities collaborate to establish secure roaming agreements and enforce strict security protocols. They continuously evaluate and upgrade their security systems to ensure the protection of subscribers’ identities and prevent fraudulent activities.
Regulatory challenges
As the telecom industry continues to evolve and advance, regulatory challenges arise in the realm of international mobile subscriber identity (IMSI) management. The cellular telephony protocol used in mobile networks, such as GSM, relies on the IMSI as a unique identifier for each subscriber. This identifier is essential for various telecommunication functions like authentication, roaming, and billing.
The international nature of mobile telephony presents challenges for regulatory bodies, as different countries may have varying regulations and policies regarding IMSI management. These regulations can impact the operations of mobile network operators and the interoperability of their networks.
Regulatory challenges also extend to issues related to subscriber privacy and security. The IMSI, being a unique identifier, can be vulnerable to misuse or unauthorized access. Regulatory bodies need to ensure that appropriate measures are in place to protect the confidentiality and integrity of the IMSI data.
Furthermore, the advent of new telecommunication technologies and services, such as ISDN and mobile roaming, adds complexity to the regulatory landscape. As these technologies continue to evolve, regulatory bodies must adapt their policies and guidelines to address the emerging challenges.
In conclusion, regulatory challenges in IMSI management are a crucial aspect of the telecommunication industry. Addressing these challenges requires a collaborative effort between regulatory bodies, mobile network operators, and other stakeholders to ensure the efficient and secure functioning of mobile telephony networks worldwide.
FAQ about topic “What is IMSI: Understanding the International Mobile Subscriber Identity”
What is IMSI?
IMSI stands for International Mobile Subscriber Identity. It is a unique identification number that is stored on a SIM card and is used to identify individual mobile subscribers within a mobile network.
How is IMSI different from IMEI?
IMSI and IMEI are two different identification numbers used in mobile devices. While IMSI is used to identify individual mobile subscribers, IMEI (International Mobile Equipment Identity) is used to identify the device itself.
Why is IMSI important?
IMSI is important because it plays a crucial role in identifying and authenticating mobile subscribers on a network. It is used by mobile networks to ensure that only authorized users have access to their services and to track the usage of individual subscribers.
Can IMSI be changed?
IMSI is stored on the SIM card and is not easily changeable. However, in some cases, mobile operators may change a subscriber’s IMSI due to certain reasons, such as network migration or equipment upgrade. This process is usually done by the operator and requires updating the SIM card with the new IMSI.
What information can be derived from IMSI?
IMSI contains various information about the subscriber, including the country code, mobile network code, and mobile subscriber identification number. It can also provide information about the type of subscription (e.g., prepaid or postpaid) and the services enabled for the subscriber.


