Oracle Solaris, also known as simply Solaris, is a widely used operating system developed by Oracle Corporation. It is designed to run on various hardware platforms and provides a reliable and secure environment for a wide range of applications. Solaris is known for its robustness and scalability, making it an ideal choice for large-scale enterprise systems.
Solaris offers advanced features such as virtualization, allowing the creation of multiple virtual machines on a single physical computer. This enables efficient utilization of resources and simplifies the management of complex computing environments. With Solaris, developers can easily deploy, configure, and seamlessly integrate software applications.
The Solaris operating system includes a powerful command line interface, providing administrators with a comprehensive set of tools for system administration and configuration. It offers a rich set of networking capabilities, enabling seamless integration with various network services and protocols. Solaris also provides extensive file system functionality, including support for advanced file management and security features.
Underneath the hood, Solaris utilizes a highly optimized kernel that ensures high performance and stability. It incorporates various performance-enhancing technologies, such as dynamic tracing and resource management, to deliver optimal performance even under heavy workloads. Solaris also supports a wide array of hardware platforms, making it a versatile choice for diverse computing environments.
Originally developed by Sun Microsystems, Solaris has a rich heritage in the Unix operating system lineage. It has evolved over the years through continuous development and enhancements, incorporating the latest technologies and addressing the changing needs of the industry. Today, Solaris remains a popular choice for businesses and organizations that value reliability, security, and performance in their operating system.
Contents
- 1 What is Solaris?
- 2 Overview of Solaris
- 3 History of Solaris
- 4 Features of Solaris
- 5 An In-depth Definition of Solaris Operating System
- 6 Architecture of Solaris
- 7 Networking in Solaris
- 8 Virtualization in Solaris
- 9 Benefits and Applications of Solaris
- 10 FAQ about topic “What is Solaris? An In-depth Definition of Solaris Operating System”
- 11 What is the history of Solaris?
- 12 What are the key features of Solaris?
- 13 Is Solaris still actively maintained?
- 14 Can Solaris run on x86-based systems?
- 15 What advantages does Solaris offer over other operating systems?
What is Solaris?
Solaris is a powerful operating system developed by Sun Microsystems (now Oracle) that is designed to run on various platforms, including SPARC and x86 systems. It is based on the UNIX operating system, with its own unique kernel and file systems.
Solaris is known for its high performance and scalability, making it a popular choice for mission-critical environments and enterprise applications. It offers advanced features such as dynamic tracing, virtualization support, and extensive networking capabilities.
One of the key features of Solaris is its command line interface, which allows for efficient system administration and software development. It provides a wide range of tools and utilities for managing the operating system, including package management, user and group administration, and file system maintenance.
Solaris also supports virtualization technologies, such as the Oracle VM Server for SPARC and the Oracle VM Server for x86, which allow multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical server. This enables organizations to consolidate their hardware resources and improve overall system efficiency.
In addition to its robustness and performance, Solaris is also known for its security features. It includes advanced security mechanisms, such as role-based access control and secure networking protocols, to protect against unauthorized access and ensure the integrity of data.
Overall, Solaris is a versatile and feature-rich operating system that provides a stable and reliable platform for a wide range of applications and workloads. It continues to be actively developed and supported by Oracle, ensuring that it remains a viable choice for organizations seeking a robust and secure operating system.
Overview of Solaris
Solaris is an operating system developed by Sun Microsystems. It is a Unix-based operating system that is designed to run on a variety of different computers. Solaris is known for its high-performance capabilities and its robustness. It provides a command line interface for system administration and is widely used in enterprise environments.
Solaris is built on a powerful and flexible platform, with its own kernel and file system. It supports virtualization technologies, allowing multiple operating systems to run on a single physical machine. This makes it a popular choice for server consolidation and resource optimization.
One of the key features of Solaris is its networking capabilities. It supports a wide range of networking protocols and provides advanced networking features such as load balancing and network virtualization. This makes it a reliable choice for businesses that rely heavily on networking.
In addition to its robustness and networking capabilities, Solaris also provides a range of developer tools and programming interfaces. It supports a variety of development languages and frameworks, making it an attractive choice for software development projects.
Solaris is now owned and developed by Oracle Corporation. Oracle continues to enhance and improve the Solaris operating system, ensuring that it remains a reliable and high-performing platform for enterprise computing.
History of Solaris
The Solaris operating system, developed by Sun Microsystems, has a long and impressive history. It was first released in 1992 as SunOS 5.0, following the company’s acquisition of AT&T’s Unix System V Release 4. After its initial release, Solaris quickly gained popularity for its superior performance and scalability, solidifying its place as one of the leading operating systems in the industry.
Throughout its development, Solaris has introduced numerous groundbreaking features and technologies. One of its key strengths is its networking capabilities, enabling seamless communication between systems. Solaris also excels in areas such as virtualization, providing robust support for running multiple operating systems on a single physical machine. This makes it an ideal platform for businesses that require efficient resource management.
At the heart of the Solaris operating system is its kernel, which is the core component responsible for managing system resources and executing system calls. The Solaris kernel has undergone continuous refinement over the years, resulting in increased stability and reliability. It is highly optimized to deliver top-notch performance, making Solaris an attractive choice for high-demand computing environments.
The administration of Solaris systems is made easier through a comprehensive suite of management tools. These tools provide administrators with the necessary functionality to configure, monitor, and maintain Solaris servers. From managing user accounts to configuring networking settings, Solaris administration can be done efficiently and effectively.
Solaris also offers a rich set of software packages that cover a wide range of needs. It includes a vast collection of Unix commands and utilities, allowing users to perform various tasks from the command line. Additionally, Solaris supports a large number of third-party applications, enabling users to leverage a diverse software ecosystem to meet their specific requirements.
In 2010, Sun Microsystems was acquired by Oracle Corporation, and Solaris became part of the Oracle product portfolio. Under Oracle’s leadership, Solaris has continued to evolve, with new features and enhancements being added regularly. The commitment to innovation and the strong focus on maintaining compatibility with existing Solaris applications have ensured the longevity and relevance of the Solaris operating system in today’s rapidly changing technological landscape.
Features of Solaris
1. Unix-based Operating System: Solaris is an operating system that is based on the Unix platform. It is designed to run on a wide range of computers and is known for its stability, reliability, and security.
2. Software Virtualization: Solaris provides advanced virtualization capabilities, allowing multiple operating systems to run on a single physical server. This helps in maximizing server utilization and reducing hardware costs.
3. High Performance: Solaris is renowned for its high-performance capabilities. It is optimized for performance and scalability, making it ideal for mission-critical applications and high-demand environments.
4. Integrated File and Networking Services: Solaris includes integrated file and networking services, making it easy to access and manage files and network resources. It supports a variety of file systems and provides extensive networking capabilities.
5. Command-Line Administration: Solaris offers a powerful command-line interface for system administration. This allows administrators to efficiently manage and configure the system, perform troubleshooting tasks, and automate administrative tasks.
6. Advanced Kernel: Solaris has an advanced kernel that provides robust and secure operating system services. It includes features such as support for multi-threading, high-performance networking, and advanced memory management.
7. Enterprise-Grade Security: Solaris is known for its enterprise-grade security features. It provides extensive security mechanisms, such as built-in encryption and access control, to protect against unauthorized access and ensure data privacy.
8. Oracle Support: Solaris is developed and supported by Oracle, a leading provider of enterprise software. This ensures ongoing development, regular updates, and dedicated support for Solaris users.
9. Cross-Platform Compatibility: Solaris is compatible with a wide range of hardware platforms, making it versatile and flexible. It can be used on both x86 and SPARC-based systems, allowing organizations to choose the hardware that best suits their needs.
10. Built-in System Monitoring: Solaris includes built-in system monitoring tools that help administrators monitor system performance, identify bottlenecks, and troubleshoot issues. This allows for proactive management and optimization of the system.
11. Scalability and Reliability: Solaris is designed to scale efficiently across different hardware configurations and workloads. It provides a reliable and robust platform for demanding applications and critical business services.
12. Extensive Documentation and Resources: Solaris is well-documented, with comprehensive guides, tutorials, and resources available online. This makes it easier for administrators and developers to learn and leverage the capabilities of the operating system.
An In-depth Definition of Solaris Operating System
The Solaris Operating System, developed by Sun Microsystems (now Oracle) is a Unix-based computer operating system. It is known for its robustness, stability, and scalability, making it a popular choice for mission-critical environments such as enterprise-level servers and high-performance computing systems.
The Solaris kernel is the core of the operating system, responsible for managing system resources, file systems, and process scheduling. It provides a secure and reliable platform for running critical applications.
Solaris offers a wide range of features and capabilities that make it a powerful operating system. It supports various software development tools and programming languages, making it suitable for application development. It also includes advanced networking capabilities, allowing for efficient communication and data transfer between systems.
One of the key strengths of Solaris is its administration and performance monitoring capabilities. It provides a comprehensive suite of tools for system administration, allowing administrators to manage and configure the system efficiently. It also includes performance monitoring tools that help identify and resolve performance issues.
Solaris allows for software virtualization, enabling multiple operating systems to run concurrently on a single physical machine. This feature, known as Solaris Zones, provides flexibility and resource utilization, making it an ideal choice for virtualized environments.
With its long history and continuous development, Solaris has established itself as a reliable and secure operating system. It is widely used in various industries and sectors, including finance, telecommunications, and government.
Architecture of Solaris
Solaris is a highly advanced and versatile operating system developed by Sun Microsystems, now owned by Oracle. It is based on the UNIX platform and is known for its exceptional performance and scalability, making it suitable for a wide range of computing tasks.
The architecture of Solaris is designed to provide efficient and reliable performance for both single and multi-processor systems. At the core of Solaris is the kernel, which handles low-level functions such as memory management, process scheduling, and device drivers. The kernel is responsible for the overall management and coordination of the system resources.
Solaris provides a comprehensive set of tools and utilities for system administration, development, and networking. It supports a wide range of hardware platforms, from desktop computers to high-end servers, allowing organizations to utilize Solaris across their entire infrastructure.
One of the key features of Solaris is its virtualization capabilities. It allows multiple instances of the operating system to run on a single physical server, enabling organizations to consolidate their computing resources and increase efficiency. Solaris also supports the creation of virtual networks, enabling easier management and deployment of networking resources.
The file system in Solaris is based on the ZFS (Zettabyte File System) technology, which provides advanced features such as data integrity, data compression, and scalability. ZFS ensures the reliability and efficiency of data storage, making it ideal for both small-scale and enterprise-level deployments.
Solaris provides a command-line interface for interacting with the system, allowing administrators and developers to perform various tasks and configurations. It also supports a wide range of software development tools and languages, making it a preferred platform for software development and testing.
Solaris Kernel
The Solaris Kernel is the heart of the Solaris operating system developed by Oracle. It provides the essential functions for the administration, virtualization, and performance of the Solaris platform.
The Solaris Kernel is responsible for managing the system’s resources, such as memory, processors, and networking. It provides a reliable and secure foundation for running software applications and services on Solaris systems.
One of the key features of the Solaris Kernel is its support for file systems. It includes built-in support for the ZFS file system, which offers advanced features such as data integrity, data compression, and snapshots.
The Solaris Kernel also includes a wide range of command-line tools for system administration, performance monitoring, and software development. These tools allow system administrators and developers to efficiently manage and troubleshoot Solaris systems.
In addition to its core functionality, the Solaris Kernel also provides support for virtualization. It includes the Oracle VM Server for SPARC, which allows multiple operating systems to run concurrently on a single physical server, maximizing resource utilization and simplifying system administration.
The Solaris Kernel has a long history dating back to the original UNIX operating system developed by AT&T Bell Laboratories. It inherits many of the robust and scalable features of UNIX, making Solaris a trusted platform for both large-scale enterprise systems and individual computers.
Overall, the Solaris Kernel is a critical component of the Solaris operating system, providing the underlying software infrastructure for networking, file management, performance optimization, and system administration on Oracle’s UNIX-based platform.
File System Architecture
The file system architecture in Solaris, an operating system developed by Oracle, is an essential component of the overall system design. It provides the necessary structure and organization for storing and accessing files, ensuring efficient administration and utilization of storage resources.
Solaris employs a hierarchical file system structure, which is similar to the file system architecture used in other Unix-based operating systems. The file system hierarchy starts with the root directory (“/”) and branches out into various directories and subdirectories.
The Solaris file system architecture enables efficient file management through the use of advanced features and technologies. For example, Solaris supports the ZFS (Zettabyte File System), which is a next-generation file system that provides built-in data protection, virtualization capabilities, and impressive scalability.
Within the file system architecture, Solaris provides several command-line tools and utilities that allow users to interact with the file systems. These tools enable various operations, including file creation, deletion, modification, and permissions management. The command-line interface provides flexibility and control for administrators and developers.
Additionally, Solaris offers extensive networking capabilities within its file system architecture. It supports network file systems (NFS) and distributed file systems (DFS), enabling seamless file sharing and access across multiple computers and platforms.
The file system architecture in Solaris is tightly integrated with the operating system’s kernel, which facilitates efficient file I/O operations and overall system performance. The kernel interacts with the file system to handle file-related requests and ensure data integrity and security.
In summary, the file system architecture in Solaris is a critical component of the overall operating system. It provides a robust and flexible foundation for file management, networking, and system administration. With its advanced features and technologies, Solaris offers a reliable and efficient platform for software development and deployment.
Process Management
Solaris is an operating system developed by Sun Microsystems (now Oracle) for computers running on the SPARC architecture. It is a UNIX-based platform that provides robust process management capabilities.
In Solaris, process management involves the creation, execution, and termination of software programs. The kernel, the core component of the operating system, oversees the management of processes. It allocates system resources, such as CPU time and memory, to each process to ensure efficient operation.
The Solaris operating system offers various tools and utilities for process management. The ps command, for example, displays information about currently running processes, including their process ID, status, and resource usage.
Solaris also supports multi-threading, allowing multiple threads of execution within a single process. This enables efficient parallelism and better utilization of system resources.
In addition to managing individual processes, Solaris provides features for managing process groups and controlling process execution. The prctl command, for instance, allows administrators to modify attributes and control the behavior of specific processes.
Process management in Solaris is crucial for effective system administration, software development, and performance optimization. By efficiently managing processes, Solaris ensures the stability, reliability, and performance of the operating system and the applications running on it.
Networking in Solaris
Solaris, the operating system developed by Sun Microsystems, is known for its robust networking capabilities. The networking features in Solaris are designed to provide high performance and reliability for various software applications.
Networking in Solaris includes a wide range of functionalities, such as virtualization, network administration, and command-line tools for network configuration. Solaris supports both IPv4 and IPv6 protocols, allowing for seamless integration with different network environments.
One of the key components of networking in Solaris is the network stack, which is implemented in the kernel. The network stack handles the low-level aspects of networking, such as packet processing, routing, and socket management. This helps in achieving optimal performance and efficiency in network communication.
Solaris also provides comprehensive networking tools for network administrators. These tools enable administrators to configure and monitor network interfaces, set up network services, and troubleshoot network issues. The command-line utilities, such as ifconfig and netstat, provide a powerful interface for network administration tasks.
In addition to networking administration, Solaris enables developers to build network-enabled applications easily. The Solaris networking APIs and libraries provide a rich set of functions for socket programming, network protocols, and file I/O. This allows developers to take full advantage of the networking capabilities of Solaris in their application development process.
Furthermore, Solaris supports a wide range of networking protocols and services, including TCP/IP, UDP, IPsec, DNS, DHCP, and NFS. It also supports advanced networking features like IPMP (Internet Protocol Multipathing) and DTrace, which provide enhanced performance and debugging capabilities for networking applications.
Overall, networking in Solaris plays a crucial role in the overall functionality and performance of the operating system. It offers a robust and scalable platform for building and managing networked systems, making Solaris a preferred choice for mission-critical applications and large-scale computer environments.
Network Protocols
In the context of Solaris operating system, network protocols play a crucial role in facilitating communication between computers and devices. Solaris, developed by Sun Microsystems (now Oracle), is a powerful operating system known for its robust networking capabilities.
Solaris supports a wide range of network protocols, allowing for seamless integration and administration of network resources. These protocols enable the transfer and exchange of data between systems, ensuring efficient and reliable communication.
Some of the commonly used network protocols in Solaris include TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol), UDP (User Datagram Protocol), FTP (File Transfer Protocol), SSH (Secure Shell), and DNS (Domain Name System).
The kernel of the Solaris operating system implements these network protocols, providing a solid foundation for networking functionality. It manages the low-level operations, such as packet routing, connection establishment, and data transmission, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Solaris also provides various network administration tools and utilities, accessible through the command line interface. These tools enable system administrators to configure, manage, and monitor network settings and resources.
In addition to networking capabilities, Solaris includes advanced features like virtualization and extensive support for development and deployment of enterprise-level applications. The robust network protocols in Solaris contribute to its reputation as a reliable and secure platform for both small-scale and large-scale systems.
Network Virtualization
Network virtualization is a software-defined networking technology that enables the creation of virtual networks on one or more physical computers or servers. It abstracts the underlying network infrastructure and allows multiple virtual networks to coexist and operate independently.
In the context of Solaris, network virtualization refers to the ability of the Solaris operating system to create and manage virtual networks. Solaris, developed by Sun Microsystems (now owned by Oracle Corporation), is a Unix-based operating system known for its robustness and security.
The network virtualization capabilities in Solaris are enabled through the use of networking features such as the IP network multipathing, link aggregation, and virtual LAN (VLAN) support. These features allow administrators to create virtual network interfaces, manage network traffic, and improve network performance.
Solaris provides a command-line interface for network virtualization administration, giving administrators full control over the virtual network configurations. Through the command-line interface, administrators can configure IP addresses, routes, subnets, and other network settings for the virtual networks.
Network virtualization in Solaris is often used in cloud computing environments, where virtual machines or containers are hosted on a single physical server. By using network virtualization, multiple virtual machines or containers can have their own separate network environments, isolated from each other, while sharing the same physical network infrastructure.
In conclusion, network virtualization in Solaris is a powerful feature that allows for the creation and management of virtual networks on the Solaris operating system. It provides administrators with control over network configurations and improves network performance, making Solaris an ideal platform for networking virtualization.
Firewall and Security Features
The Solaris operating system, developed by Sun and now owned by Oracle, offers a range of firewall and security features to protect networking and system resources.
One of the key security features of Solaris is the Trusted Extensions, which provides mandatory access control to protect sensitive data and resources. It allows administrators to define and enforce security policies based on the classification of information.
Solaris also includes IPFilter, a powerful stateful packet filtering firewall. IPFilter allows administrators to control the traffic on a network level, filtering packets based on various criteria such as source and destination IP addresses, ports, and protocols. It provides an additional layer of security to prevent unauthorized access to the system.
Another important security feature in Solaris is the Secure Shell (SSH), which provides secure remote administration and file transfer capabilities. SSH encrypts all communication between the client and server, protecting sensitive information from eavesdropping and unauthorized access. It also supports public key authentication, enhancing the security of remote access.
Solaris also includes the Solaris Auditing system, which allows administrators to monitor and track system activities. This feature generates logs and records events such as login attempts, file access, and system configuration changes. It helps in identifying and investigating security breaches and unauthorized activities.
In addition, Solaris provides various security-focused tools such as the Solaris Management Console, which allows administrators to configure and manage security settings and policies. The Secure by Default feature ensures that the system is deployed with secure configurations, reducing the risk of security vulnerabilities.
Overall, the firewall and security features in Solaris provide robust security measures to protect networking and system resources, making it a reliable operating system for critical environments and sensitive data.
Virtualization in Solaris
Solaris is a software line of operating systems developed by Sun Microsystems. It is a platform that enables virtualization, which allows multiple operating systems to run on a single physical server. Solaris has a unique feature called “Containers”, which provides an efficient and secure way to virtualize applications and services. Containers are lightweight and isolated environments that share the Solaris operating system kernel.
Virtualization in Solaris allows for the creation of multiple virtual machines (VMs) within a single physical server. These VMs can run different operating systems, such as Windows and Linux, simultaneously. This enables organizations to consolidate their computing resources and improve hardware utilization. With virtualization, administrators can easily manage and provision resources for different applications and workloads.
In addition to virtualization, Solaris provides various features for efficient administration and performance optimization. The ZFS file system, a key component of Solaris, offers advanced storage capabilities such as data integrity, dynamic scaling, and simplified management. Solaris also includes command-line tools and graphical interfaces for system administration, networking, and performance analysis.
The virtualization capabilities of Solaris, combined with its robust operating system features, make it a preferred choice for many organizations. Whether it is for development, testing, or production environments, Solaris provides a reliable and scalable platform for running critical applications and services. With Oracle’s acquisition of Sun Microsystems in 2010, Solaris continues to be actively developed and supported.
Zone Virtualization
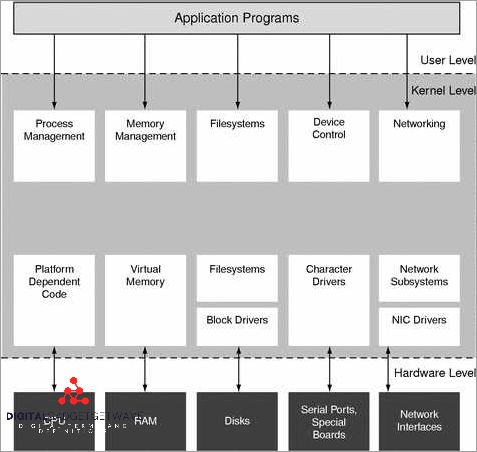
Zone Virtualization is a feature of the Solaris operating system developed by Oracle. It allows for the creation of virtual environments within a single Solaris instance, enabling multiple isolated operating system instances to run on a single physical server. Each zone functions as a separate platform, allowing for the efficient utilization of resources and improved system performance.
With zone virtualization, administrators can create and manage multiple zones, each with its own networking, file system, and user environment. This enables the isolation and separation of applications and services, reducing the risk of conflicts and providing improved security. Each zone runs its own instance of the Solaris kernel, providing complete isolation between zones. This allows for better resource management and improved stability of the overall system.
Zone virtualization provides a flexible environment for software development, testing, and production environments. Developers can create multiple zones for different stages of development and easily test and deploy applications within each zone. It also allows for easy scaling and consolidation of resources, as additional zones can be created and managed as needed.
Administrators can manage zones through a command-line interface, using various commands and utilities to create, modify, and delete zones. They can also monitor and control resources allocated to each zone, ensuring optimal performance and resource utilization. Zones can be easily migrated between physical servers, allowing for efficient system administration and maintenance.
In summary, zone virtualization is a powerful feature of the Solaris operating system that allows for the efficient allocation and management of resources. It provides isolation and separation of applications and services, improving security and stability. With zone virtualization, Solaris offers a robust and flexible platform for development, testing, and production environments.
Logical Domains (LDoms)
Logical Domains (LDoms) is a technology developed by Sun Microsystems, which is now owned by Oracle, for partitioning a single physical server into multiple logical servers, each running its own operating system instance. LDoms provide a way to isolate different applications and workloads on the same server, allowing for better utilization and resource allocation.
The LDoms software is built into the Solaris operating system, making it a native feature of the platform. It enables virtualization at the hardware level, allowing multiple operating systems to run concurrently on a single machine. This virtualization technology is based on a combination of hardware and software components that work together to provide a flexible and scalable virtual environment.
With LDoms, administrators can create and manage multiple virtual servers, known as logical domains, from a single physical server. Each logical domain functions as an independent and isolated system, with its own CPU, memory, networking, and storage resources. This allows for efficient resource utilization and isolation of workloads, enhancing the performance and security of the system.
The LDoms technology provides advanced features and capabilities for managing and administering the logical domains. Administrators can dynamically allocate and reallocate system resources, such as CPU and memory, to meet the changing needs of the applications. They can also manage network connections, storage devices, and file systems within each logical domain, enabling fine-grained control over the networking and storage configurations.
In addition to administration, LDoms also provide a platform for software development and testing. Developers can create virtual environments to test their applications on different operating systems and configurations, without the need for multiple physical computers. This simplifies the development and testing process and reduces the cost and complexity of managing multiple systems.
In summary, Logical Domains (LDoms) is a virtualization technology within the Solaris operating system that allows for the partitioning of a single physical server into multiple logical servers. LDoms provide a scalable and efficient platform for operating system virtualization, administration, and development. With LDoms, administrators can better utilize server resources, enhance system performance, and create isolated environments for different applications.
Oracle VM Server for SPARC
Oracle VM Server for SPARC, formerly known as Sun Logical Domains (LDoms), is an operating system virtualization technology provided by Oracle. It allows the creation and management of multiple virtualized operating systems, called domains, on a single physical SPARC-based server.
This virtualization platform enables developers to consolidate multiple applications and operating systems onto a single server, optimizing hardware resources and reducing data center costs. It provides a flexible and efficient solution for workload deployment and management in complex enterprise environments.
Oracle VM Server for SPARC leverages the underlying Solaris operating system to provide robust performance, security, and reliability. It supports a wide range of networking and storage options, allowing administrators to configure and manage virtualized environments to meet specific business needs.
The technology utilizes a hypervisor layer, known as the Logical Domains Manager, to create and manage domains. Each domain contains its own instance of the Solaris kernel, providing a fully isolated and independent operating environment.
With Oracle VM Server for SPARC, administrators have full control over virtual machine allocation, resource management, and performance monitoring. They can easily adjust the allocation of CPU, memory, and I/O resources to meet changing workload demands.
Administration of Oracle VM Server for SPARC can be done through a command-line interface or through the Oracle VM Manager, a graphical user interface that provides centralized management and monitoring capabilities. The command-line interface allows for automation and scripting of administrative tasks, streamlining the management of virtualized environments.
In conclusion, Oracle VM Server for SPARC is a powerful virtualization solution that leverages the Solaris operating system to provide a flexible and efficient platform for the development and administration of multiple virtualized operating systems on SPARC-based servers.
Benefits and Applications of Solaris
Solaris, an operating system developed by Sun Microsystems, provides numerous benefits and applications for computers and systems. Here are some key advantages:
- Virtualization: Solaris offers advanced virtualization capabilities, allowing for efficient utilization of hardware resources and improved system performance.
- Scalability: Solaris is highly scalable, capable of supporting large-scale systems and workloads. It can handle high numbers of concurrent users and processes without compromising performance.
- Reliability: Solaris is known for its robustness and stability.
It has a reliable file system and kernel that ensures data integrity, minimizing the risk of system failures or data corruption. - Security: Solaris incorporates various security features to protect sensitive data and secure system resources. It provides built-in encryption, access controls, and security frameworks.
- Compatibility: Solaris is compatible with a wide range of software and hardware platforms, providing flexibility and ease of integration in diverse computing environments.
- Networking: Solaris offers extensive networking capabilities, supporting protocols such as TCP/IP and providing advanced networking features like virtual LANs and network resource controls.
- Development Environment: Solaris provides a rich development environment for software developers. It includes tools and libraries for application development, debugging, and profiling, facilitating the creation of high-performance and scalable software.
The applications of Solaris span various industries and sectors, including finance, telecommunications, research, and education. Solaris is commonly used for high-performance computing, database management, web hosting, and enterprise-level applications. Leading companies and organizations utilize Solaris for its stability, scalability, and security.
Enterprise-scale Applications
Solaris, the operating system developed by Oracle, is widely used in enterprise-scale applications. Its robust architecture and high performance make it an ideal choice for running mission-critical software on large-scale systems.
With Solaris, developers can create and deploy enterprise applications with ease. The system provides a powerful development environment, including a rich set of tools and libraries for building complex software solutions.
The Solaris kernel, the core of the operating system, is designed to handle the demands of enterprise-scale applications. It provides advanced features such as process management, file system support, and networking capabilities, all optimized for high performance and reliability.
In addition to serving as a platform for application development, Solaris also offers robust system administration tools. Administrators can easily manage and configure the operating system using command line interfaces, graphical user interfaces, and web-based administration tools.
Solaris supports virtualization, allowing enterprises to consolidate multiple applications and services onto a smaller number of physical computers. This reduces hardware costs and simplifies system management, while still maintaining high levels of performance and security.
Furthermore, Solaris is highly interoperable with other systems, making it an excellent choice for enterprise environments where different platforms and technologies need to coexist. It supports a wide range of industry standards, ensuring seamless integration with existing software and hardware systems.
In conclusion, Solaris is the operating system of choice for enterprise-scale applications. Its robust architecture, high performance, and extensive feature set make it an ideal platform for developing, deploying, and managing large-scale software solutions in mission-critical environments.
High Availability and Scalability
The Solaris Operating System, developed by Sun Microsystems and currently owned by Oracle, is known for its high availability and scalability. These features make it an ideal choice for businesses and organizations that require a reliable and efficient platform for their critical applications and services.
One of the key factors contributing to Solaris’ high availability is its advanced virtualization capabilities. Solaris allows multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical server, enabling efficient utilization of computing resources and minimizing downtime. This virtualization technology also provides the flexibility to dynamically add or remove virtual machines based on workload demands, ensuring optimal performance and scalability.
Solaris’ high availability is further enhanced by its robust file system and networking capabilities. The ZFS file system offers built-in data integrity and protection features, such as snapshots and automatic error detection and correction. Solaris also supports advanced networking protocols and technologies, allowing for seamless integration with existing network infrastructure and high-speed data transfer between systems.
The Solaris kernel, which serves as the core of the operating system, is designed to handle high-demand workloads efficiently. It is optimized for performance and can scale to support hundreds or even thousands of concurrent processes. This scalability is crucial for businesses that need to handle large volumes of data and ensure quick response times for their users.
In addition to its high availability, Solaris also provides comprehensive administration and management tools. The operating system includes a powerful command-line interface, as well as graphical user interfaces for system configuration and monitoring. These tools simplify system administration tasks and allow administrators to efficiently manage the platform.
Overall, Solaris offers a reliable and scalable platform for enterprise-level applications and services. Its high availability and scalability features, combined with its advanced file system, networking capabilities, and administration tools, make it an ideal choice for businesses that prioritize performance and reliability.
Cloud Computing and Virtualization Support
Solaris is a powerful and versatile operating system that provides comprehensive support for cloud computing and virtualization. It is designed to efficiently run large-scale enterprise applications and offer high performance and reliability.
A key feature of Solaris is its advanced kernel, which supports virtualization technologies such as Oracle VM Server for SPARC and Oracle Solaris Zones. These technologies allow for the efficient and secure sharing of system resources among multiple virtual machines or containers, enabling organizations to consolidate their computing infrastructure and reduce costs.
Solaris also provides robust networking capabilities, allowing for seamless integration with cloud platforms and enabling efficient data transfer and communication between systems. The operating system supports various networking protocols and offers advanced features for network administration and security.
In addition to its cloud computing support, Solaris is widely used for its excellent performance and scalability. The system is optimized to take advantage of modern hardware technologies, such as multi-core processors and solid-state drives, to deliver exceptional computing power and storage performance.
Solaris also provides a comprehensive set of tools and utilities for system administration and software development. Its command-line interface and scripting capabilities allow for efficient management of the operating system and the deployment of applications. The system also includes a robust file system that provides advanced features such as snapshots, encryption, and compression.
Overall, Solaris is a reliable and feature-rich operating system that offers robust cloud computing and virtualization support. It is widely used in enterprise environments for its performance, reliability, and security features, and it continues to be actively developed and supported by Oracle.
FAQ about topic “What is Solaris? An In-depth Definition of Solaris Operating System”
What is the history of Solaris?
Solaris is a Unix operating system originally developed by Sun Microsystems in the 1990s. It was based on the AT&T System V Release 4 (SVR4) Unix specification and was designed to run on Sun’s SPARC architecture.
What are the key features of Solaris?
Solaris offers several key features including advanced file systems, dynamic tracing, network virtualization, and built-in security mechanisms. It also has support for modern hardware platforms and technologies, such as multiprocessing and large memory systems.
Is Solaris still actively maintained?
Yes, Solaris is still actively maintained. Oracle acquired Sun Microsystems in 2010 and continues to develop and release new versions of Solaris. The latest version of Solaris, as of 2021, is Solaris 11.4.
Can Solaris run on x86-based systems?
Yes, Solaris can run on x86-based systems in addition to the SPARC architecture. This allows Solaris to be used on a wide range of hardware platforms, giving users more flexibility in their choice of hardware.
What advantages does Solaris offer over other operating systems?
Solaris has several advantages over other operating systems. It has a reputation for being highly stable and reliable, making it a popular choice for enterprise environments. It also offers advanced performance and scalability features, as well as strong security capabilities. Additionally, Solaris has a rich set of integrated tools and utilities that can help administrators manage and troubleshoot their systems more effectively.


