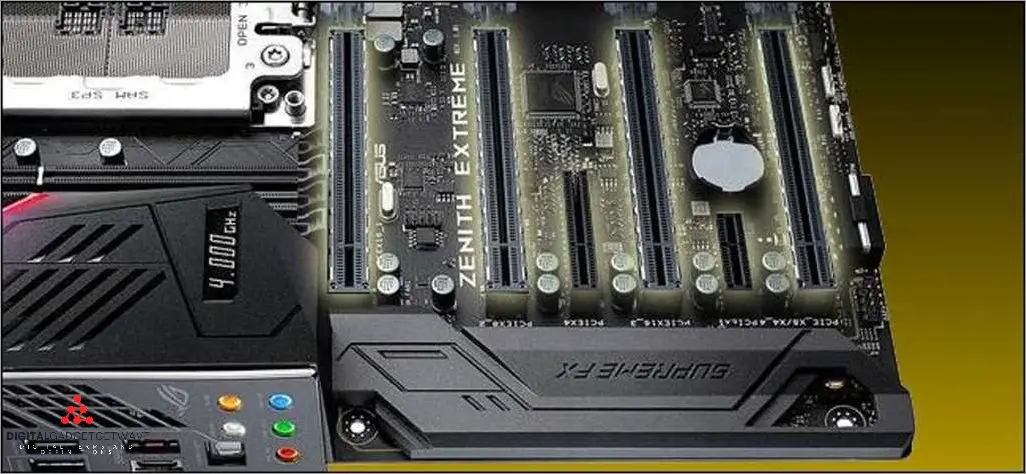
The expansion slots on a motherboard allow you to connect additional devices to your computer, such as graphics cards, network cards, and storage devices. One of the most popular and widely used types of expansion slots is the PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) slots. PCIe slots come in various types and configurations to support different devices and offer different speeds and bandwidths.
There are four main types of PCIe slots: x1, x4, x8, and x16. The x1 slots are the smallest and offer the least amount of bandwidth, while the x16 slots are the largest and offer the highest bandwidth. These slots are identified by their physical size and the number of connectors they have. The x1 slots have a single connector, the x4 slots have four connectors, the x8 slots have eight connectors, and the x16 slots have sixteen connectors.
The PCIe interface architecture allows for high-speed communication between the motherboard and the expansion cards. The latest generation of PCIe slots, known as PCIe 4.0 and PCIe 5.0, offer even faster speeds and increased bandwidth compared to previous generations. These advancements in PCIe technology enable faster data transfer rates and better performance for devices connected to these slots.
PCIe slots are commonly used for connecting graphics cards in gaming computers and workstations. The x16 slots are typically used for high-end graphics cards that require a significant amount of bandwidth for optimal performance. Other devices, such as network cards and storage devices, can also be connected to PCIe slots, depending on their requirements and the available slots on the motherboard.
It is important to consider the type and number of PCIe slots available on a motherboard when building or upgrading a computer. Different devices may require different types of slots or multiple slots for optimal performance. Understanding the different types of PCIe slots and their capabilities can help ensure that you choose the right motherboard and expansion cards for your specific needs.
Contents
- 1 What is PCIe?
- 2 Advantages of PCIe over other Slot Types
- 3 Importance of Understanding Different Types of PCIe Slots
- 4 Types of PCIe Slots
- 5 Factors to Consider When Choosing a PCIe Slot
- 6 Common Uses and Applications of Different PCIe Slots
- 7 FAQ about topic “A Comprehensive Guide to Different Types of PCIe Slots”
- 8 What are the different types of PCIe slots available?
- 9 How do PCIe slots differ from each other in terms of bandwidth?
- 10 Can I use a PCIe x16 card in a PCIe x1 slot?
- 11 What are the primary uses of PCIe slots?
- 12 What is the difference between a PCIe slot and a conventional PCI slot?
What is PCIe?
PCIe, which stands for Peripheral Component Interconnect Express, is a high-speed interface commonly used in computers and other electronic devices for connecting various types of expansion cards and devices. It is a newer and faster replacement for older interfaces such as PCI and AGP.
PCIe comes in different types, also known as generations, which include PCIe 1.0, PCIe 2.0, PCIe 3.0, PCIe 4.0, and the latest PCIe 5.0. Each generation offers increased bandwidth and faster speeds compared to the previous one.
The PCIe architecture consists of multiple lanes, with each lane capable of transmitting data in both directions simultaneously. The most common types of PCIe connectors used are x1, x4, and x8. The “x” represents the number of lanes available for data transmission.
A PCIe slot on a motherboard is designed to accommodate different types of PCIe cards and expansion devices. These slots are backward compatible, meaning that a PCIe 3.0 card can be plugged into a PCIe 4.0 slot, but it will operate at the speed of the slower generation.
Bandwidth is a crucial aspect of PCIe. Each lane in a PCIe connection provides a specific amount of bandwidth, and the total bandwidth of a slot is determined by the number of lanes it has. For example, a PCIe x1 slot provides a bandwidth of around 500 MB/s, while a PCIe x16 slot can offer up to 16 GB/s.
PCIe is widely used for connecting various devices and expansion cards, such as graphics cards, network cards, sound cards, storage controllers, and more. Its high-speed and reliable data transfer capabilities make it essential for modern computing needs.
Advantages of PCIe over other Slot Types
PCIe, or Peripheral Component Interconnect Express, is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard. It has several advantages over other slot types:
- Higher Bandwidth: PCIe offers much higher bandwidth compared to other slot types. With each generation, the bandwidth doubles. For example, PCIe 3.0 x16 slot provides a maximum bandwidth of 32GB/s, whereas PCIe 4.0 x16 slot offers a maximum bandwidth of 64GB/s. This high bandwidth allows for faster data transfer speeds and improved performance.
- Multiple Lane Configurations: PCIe slots can be configured to support different lane sizes, such as x1, x4, x8, and x16. This flexibility allows for various combinations of devices and expansion cards to be connected to the motherboard. For example, a motherboard may have multiple PCIe x1 slots for connecting sound cards or network adapters, while also having PCIe x16 slots for high-performance graphics cards.
- Hot-Swap Capability: PCIe slots support hot-plugging, which means that devices can be connected or disconnected while the computer is running. This feature is particularly useful in enterprise environments where it is necessary to add or remove devices without shutting down the entire system.
- Improved Power Efficiency: PCIe architecture allows for better power management compared to other slot types. Devices connected to PCIe slots can negotiate power requirements with the motherboard, allowing for energy-efficient operation.
- Backward Compatibility: PCIe versions are backward compatible, meaning that newer generation cards can be used in older generation slots. For example, a PCIe 4.0 graphics card can be used in a PCIe 3.0 slot, albeit at reduced speeds. This compatibility ensures that older devices can still be used with newer computers.
- Strong Interconnect: PCIe uses point-to-point connections, which means that each device is directly connected to the motherboard. This eliminates the need for shared bus architectures, improving data transfer efficiency and reducing latency.
In summary, PCIe offers higher bandwidth, multiple lane configurations, hot-swap capability, improved power efficiency, backward compatibility, and a strong interconnect. These advantages make PCIe the preferred choice for connecting expansion cards and devices in modern computers.
Importance of Understanding Different Types of PCIe Slots
Understanding the different types of PCIe slots is crucial for computer enthusiasts and professionals alike. PCIe, or Peripheral Component Interconnect Express, is an advanced expansion interface architecture that allows devices to connect to a computer’s motherboard. It provides high-speed bandwidth for data transfer and supports various types of cards and connectors.
PCIe slots come in different sizes, including x1, x4, x8, and x16, with each offering different levels of bandwidth and speeds. It’s important to know the specific PCIe specification and generation your motherboard supports to ensure compatibility with expansion cards and devices you plan to use.
One of the key reasons for understanding PCIe slots is to determine the maximum bandwidth available for different types of devices. A higher PCIe generation and larger slot size like x16 can offer more bandwidth, allowing for faster data transfer speeds and improved performance for graphics cards, storage devices, network adapters, and other high-bandwidth peripherals.
Compatibility between PCIe slots and expansion cards is also crucial. For instance, a PCIe x4 card can fit into an x8 or x16 slot, but the bandwidth will be limited to that of the x4 slot. Conversely, a larger card like x8 or x16 won’t fit into an x1 slot.
Understanding the different types of PCIe slots is particularly important when building a computer or upgrading its components. Knowing which types of PCIe slots are available on your motherboard can help ensure compatibility with existing and future expansion cards. It can also guide you in making informed decisions when purchasing new components, such as graphics cards or high-speed storage devices, to optimize your computer’s performance.
In summary, comprehending the different types of PCIe slots is essential for understanding the capabilities and limitations of your computer’s expansion capabilities. It enables you to select the appropriate PCIe cards, connectors, and slots based on your specific requirements and ensures optimal compatibility and performance for your devices.
Types of PCIe Slots
PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) slots are an important component of a motherboard’s architecture, allowing for the expansion of a computer’s capabilities. These slots come in various types, each with its own specification and capabilities.
One of the most common types of PCIe slots is the x1 slot, which provides a single lane for data transfer. These slots are typically used for low-bandwidth devices such as sound cards or network adapters.
Another type is the x4 slot, which provides four lanes for data transfer. This allows for faster speeds and higher bandwidth compared to the x1 slot. The x4 slot is often used for higher-end devices such as RAID controllers or high-performance graphics cards.
The x8 slot is similar to the x4 slot in terms of its architecture, but provides eight lanes for data transfer. This allows for even faster speeds and higher bandwidth compared to the x4 slot. The x8 slot is commonly used for high-performance graphics cards or other bandwidth-intensive devices.
Finally, the x16 slot is the largest and most powerful PCIe slot available. It provides sixteen lanes for data transfer, allowing for the highest speeds and bandwidth. The x16 slot is typically used for top-of-the-line graphics cards and other high-performance devices.
Overall, PCIe slots come in various types and generations, each offering different speeds, bandwidth, and capabilities. These slots are essential for expanding a motherboard’s functionality and connecting various devices and cards.
PCIe x1
The PCIe x1 interface is one of the expansion slot types found on motherboards. It is part of the PCIe specification, which defines the different types of slots and their capabilities.
The x1 in PCIe x1 refers to the number of lanes or connections available for data transfer. In this case, there is only one lane available, which limits the amount of bandwidth that can be used for communication between the motherboard and the device connected to the slot.
Compared to other PCIe slot types, such as PCIe x4, x8, or x16, the PCIe x1 slot has lower bandwidth and slower speeds. However, it is still suitable for many devices that do not require high-speed data transfer, such as sound cards, network adapters, and small expansion cards.
The PCIe x1 slot uses a different physical connector compared to other PCIe slot types. It has a smaller size and a shorter length, allowing it to fit into smaller spaces on the motherboard. This makes it convenient for adding additional functionality or upgrading existing systems without taking up too much space.
It’s worth noting that PCIe is an architecture that has gone through different generations over time, with each generation offering increased performance. The PCIe x1 slot can be found in motherboards that support various generations of PCIe, such as PCIe 2.0, 3.0, or 4.0. The generation number indicates the speed and capabilities of the PCIe interface.
In summary, the PCIe x1 slot is a type of expansion slot found on motherboards, providing a single lane of data transfer. It is suitable for devices that do not require high-speed communication and offers a smaller size and form factor compared to other PCIe slot types.
PCIe x4
PCIe x4 is one of several types of PCIe slots found on motherboards and expansion cards. It is part of the PCIe Gen (generation) 3.0 architecture, which is the most common version currently in use. The “x4” designation refers to the number of electrical lanes in the slot, with x1 being the smallest and x16 being the largest.
PCIe x4 slots provide significantly more bandwidth than PCIe x1 slots, allowing for faster data transfer between the motherboard and expansion cards. The x4 slot has a maximum bandwidth of 2 gigabytes per second (GB/s) in each direction, for a total of 8 gigabits per second (Gbps) in full duplex mode.
This type of slot is commonly used for connecting high-speed devices such as solid-state drives (SSDs), graphics cards, network interface cards (NICs), and RAID controllers. This is because these devices require more bandwidth than what is available in a PCIe x1 slot, but do not necessarily need the full bandwidth provided by an x8 or x16 slot.
PCIe x4 slots use a different physical connector than the other types of PCIe slots. The x4 slot has a shorter length than the x8 and x16 slots, and uses a smaller number of pins. This allows for easier identification and differentiation between the different types of slots on a motherboard.
In summary, PCIe x4 slots provide a balance of bandwidth and size for connecting high-speed devices to a computer motherboard. They offer faster data transfer speeds than x1 slots, but are not as large or powerful as x8 or x16 slots.
PCIe x8

PCIe x8 is one of the different types of PCIe slots available on motherboards for expansion cards and devices. It is a shorter version of the PCIe x16 slot, providing fewer electrical connections and fewer available lanes for data transfer.
The PCIe interface is used in modern computers to connect various expansion cards and devices to the motherboard. It provides faster speeds and higher bandwidth compared to older interfaces, such as the PCI or AGP.
PCIe x8 slots are designed to accommodate expansion cards that require eight lanes of data transfer. These slots have eight physical connectors, allowing for a maximum transfer speed of 8 gigatransfers per second (GT/s) per lane, resulting in a total bandwidth of 32 gigatransfers per second.
PCIe x8 slots can also support smaller cards, such as PCIe x4 or PCIe x1 cards. However, the bandwidth available to these cards will be limited by the number of lanes provided by the slot. For example, a PCIe x4 card in an x8 slot will only have access to four lanes, reducing its maximum potential bandwidth.
When selecting a motherboard or expansion card, it is important to consider the PCIe slot type and speed you will need for your specific requirements. PCIe x8 slots are commonly found on motherboards that support multiple PCIe slots, allowing for a variety of expansion card configurations.
PCIe x16
PCIe x16 is one of the most common types of PCIe slots found on motherboards for desktop computers. It belongs to the PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) generation of connectors and is used for high-speed communication between the motherboard and various expansion cards or devices.
The “x16” in PCIe x16 refers to the number of lanes that the slot contains. A lane is a data pathway that provides bi-directional communication between the motherboard and the connected device. PCIe x16 slots are capable of providing a higher bandwidth compared to other types, such as PCIe x1, x4, or x8.
The architecture of PCIe x16 allows for faster data transfer speeds, making it suitable for high-performance devices like graphics cards or RAID controllers. With its higher bandwidth, PCIe x16 slots can accommodate the needs of demanding applications and tasks, such as video editing, gaming, or professional 3D modeling.
PCIe x16 slots are usually longer and have a higher number of pins compared to other PCIe slots. This physical design allows for more data lanes and increased bandwidth, enabling faster communication between the motherboard and the connected device. It is essential to note that PCIe x16 slots are backward compatible, meaning they can support PCIe x1, x4, and x8 cards.
In summary, PCIe x16 is a type of PCIe slot that offers high-speed communication and bandwidth for various expansion cards and devices. Its architecture and design provide faster data transfer speeds, making it an ideal choice for demanding applications and devices that require high-performance capabilities.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a PCIe Slot
When choosing a PCIe slot for your computer, there are several factors to consider:
- Speeds: PCIe slots come in different speeds, such as x1, x4, x8, and x16. The speed determines the amount of bandwidth available for data transfer between the devices and the expansion cards inserted into the slot. Higher speeds offer faster data transfer rates.
- Types: There are several types of PCIe slots, including PCIe 1.0, PCIe 2.0, PCIe 3.0, and PCIe 4.0. Each generation offers improved performance and bandwidth compared to the previous one. It is important to choose a slot that is compatible with the devices and expansion cards you plan to use.
- Connectors: PCIe slots come with different connectors, such as PCIe x16, PCIe x8, and PCIe x4. The connector type determines the physical size and shape of the slot. Make sure to choose a slot that matches the connector on your expansion card.
- Bandwidth: Each PCIe slot provides a specific amount of bandwidth based on its speed and generation. The bandwidth determines how much data can be transferred between the devices and the expansion cards. Consider the bandwidth requirements of the devices you plan to use and choose a slot that can support them.
- Interface: PCIe slots use a serial interface for data transfer, which allows for faster speeds and better performance compared to older parallel interfaces. Make sure your computer’s motherboard supports PCIe slots and check for compatibility with the devices and expansion cards you plan to use.
Considering these factors will help you choose the right PCIe slot for your computer and ensure optimal performance for your devices and expansion cards.
Speed and Bandwidth Requirements
The speed and bandwidth requirements of PCIe slots vary depending on the generation and architecture of the motherboard. PCIe, or Peripheral Component Interconnect Express, is a high-speed interface specification used for connecting expansion cards and devices to computers. There are different types of PCIe slots, including x1, x4, x8, and x16 slots, each offering different amounts of bandwidth.
The bandwidth of a PCIe slot is determined by the number of lanes it has. Each lane provides a certain amount of bandwidth, and multiple lanes can be combined to increase the total bandwidth of the slot. For example, an x1 slot provides one lane and has a bandwidth of up to 250 megabytes per second (MB/s), while an x16 slot provides 16 lanes and has a bandwidth of up to 4 gigabytes per second (GB/s).
The PCIe specification defines the maximum bandwidth that each slot can provide. For example, PCIe 3.0, which is the most common version in use today, provides a maximum bandwidth of 1 GB/s per lane. This means that an x1 slot can provide up to 1 GB/s, an x4 slot can provide up to 4 GB/s, an x8 slot can provide up to 8 GB/s, and an x16 slot can provide up to 16 GB/s.
When selecting a PCIe slot for a specific expansion card or device, it is important to consider the speed and bandwidth requirements of the device. For example, a high-performance graphics card may require an x16 slot to deliver the necessary bandwidth for optimal performance. On the other hand, a network card or sound card may only require an x1 or x4 slot.
In addition to the bandwidth provided by the PCIe slot, the type of connectors used also affect the overall speed. PCIe slots can have different generations, such as PCIe 2.0, PCIe 3.0, and PCIe 4.0. Each generation provides faster speeds and increased bandwidth compared to the previous generation.
Compatibility with Motherboard and Other Components
When considering the compatibility of PCIe slots with a motherboard and other components, it is important to understand the different types of connectors and their capabilities. PCIe slots come in various sizes, including x1, x4, x8, and x16, each of which refers to the number of lanes or data channels available for data transfer.
The PCIe specification for each generation determines the bandwidth available for these slots. For example, a PCIe 3.0 x1 slot has a maximum bandwidth of 1 GB/s, while a PCIe 3.0 x16 slot can provide up to 16 GB/s. The generation and number of lanes in a slot determine the maximum bandwidth available for expansion cards and other devices.
When selecting a PCIe slot for your motherboard, it is important to ensure compatibility not only with the slot size but also with the slot version. For example, a PCIe 4.0 x16 card will not work in a PCIe 3.0 x16 slot. However, a PCIe 3.0 x16 card can still work in a PCIe 4.0 x16 slot, albeit at a lower maximum bandwidth.
Additionally, it is crucial to consider the overall architecture and capabilities of your motherboard. Some motherboards may have a limited number of PCIe slots or may prioritize certain slots over others for specific devices or functionalities. It is recommended to consult the motherboard manual or manufacturer’s specifications to determine the compatibility and limitations of PCIe slots in your specific setup.
Furthermore, compatibility with other components, such as graphics cards or other expansion cards, must also be considered. Graphics cards, for example, typically require higher bandwidth and therefore benefit from being installed in x16 slots. Other expansion cards, such as network adapters or sound cards, may be compatible with x1 or x4 slots, depending on their bandwidth requirements.
In conclusion, when considering compatibility with a motherboard and other components, it is essential to take into account the size, version, and bandwidth capabilities of PCIe slots. Additionally, understanding the needs of specific devices or expansion cards can help determine the optimal slot selection for your computer setup.
Future Expansion and Upgradability
One of the key advantages of PCIe slots is their ability to provide future expansion and upgradability for computers. With the increasing speeds and performance requirements of modern devices, having the right connectors and slots on the motherboard is essential to keep up with the latest technology.
The PCIe specification is constantly evolving, with new generations and architectures being introduced to meet the growing demands of high-bandwidth devices. The most common PCIe slot types are x1, x4, and x16, each offering different levels of bandwidth and compatibility.
By having multiple PCIe slots on a motherboard, users have the flexibility to add expansion cards or devices as needed. For example, a user may start with a single graphics card using an x16 slot, but later on, they can add additional cards for multi-GPU setups or even use the x4 or x1 slots for other devices such as network cards or solid-state drives.
Furthermore, PCIe slots also support backward compatibility, meaning that newer generation cards can be used in older generation slots. For example, a PCIe 4.0 card can be inserted into a PCIe 3.0 slot, albeit with reduced performance. This allows users to upgrade their system components without having to replace the entire motherboard.
Overall, the future expansion and upgradability provided by PCIe slots make them an essential component of modern computers. They offer the flexibility to support a wide range of devices and ensure compatibility with the latest technologies through their evolving specifications and architectures.
Common Uses and Applications of Different PCIe Slots
The PCIe architecture provides different types of slots or connectors on a motherboard, which can be used to connect various expansion cards and devices. These slots differ in terms of their bandwidth, speeds, and the number of lanes they support.
The PCIe x1 slot is commonly used for connecting low-bandwidth devices such as sound cards, network cards, and USB expansion cards. These devices do not require high speeds or extensive data transfer capabilities, making the x1 slot suitable for their usage.
The PCIe x4 slot offers four lanes of data transfer, making it ideal for connecting devices that require higher bandwidth, such as RAID controllers and solid-state drives. These devices can benefit from the increased bandwidth provided by the x4 slot to deliver improved performance and faster data transfer rates.
The PCIe x8 slot provides eight lanes of data transfer, making it suitable for connecting high-performance networking cards and graphics cards. These devices often require a higher amount of bandwidth to ensure smooth and uninterrupted data flow, and the x8 slot can fulfill these requirements.
The PCIe x16 slot is the highest-speed slot available and is commonly used for connecting high-powered graphics cards, which require the maximum amount of bandwidth to deliver optimal performance for gaming, video editing, and other intensive tasks. This slot offers 16 lanes of data transfer, allowing for the highest speeds and the most efficient communication between the graphics card and the rest of the system.
It is important to note that while PCIe slots may have different numbers of lanes (x1, x4, x8, x16), they are all compatible with each other. This means that a device designed for an x1 slot can be used in an x16 slot, although it will only utilize the available number of lanes. This flexibility allows for greater compatibility and expandability in computers and ensures that different types of devices can be connected using the appropriate PCIe slot.
PCIe x1 Applications
The PCIe x1 slot is a type of expansion slot commonly found on motherboards. It is one of the smaller PCIe slot types, with the x1 designation indicating that it has a single lane for data transfer. Despite its smaller size, the PCIe x1 slot can be used for a variety of applications.
One common application of the PCIe x1 slot is for adding additional connectivity options to a computer. Many expansion cards, such as network interface cards and sound cards, can be connected to a computer through a PCIe x1 slot. These cards provide additional functionality and can enhance the performance of a computer by adding new features or improving existing ones.
The PCIe x1 slot is also used for adding additional storage options to a computer. Storage expansion cards, such as RAID controllers or solid-state drive (SSD) adapters, can be connected to a computer through a PCIe x1 slot. These cards allow for faster data transfer speeds and can increase the storage capacity of a computer.
Another application of the PCIe x1 slot is for adding additional USB ports to a computer. USB expansion cards, which typically have multiple USB connectors, can be connected to a computer through a PCIe x1 slot. These cards provide additional USB ports for connecting peripherals and devices, allowing for greater flexibility in terms of connectivity.
In addition to the above applications, the PCIe x1 slot can also be used for connecting other types of expansion cards and devices. The PCIe x1 slot is compatible with other PCIe slot types, such as x4, x8, and x16, allowing for greater flexibility in terms of compatibility. It also supports different speeds depending on the generation of the PCIe interface, with newer generations offering faster data transfer rates.
PCIe x4 Applications
The PCIe x4 interface, with a theoretical bandwidth of 2 GB/s in each direction, offers a mid-range solution for applications that require more bandwidth than the PCIe x1 interface but less than the PCIe x8 or x16 interfaces. This makes it a popular choice for a variety of devices and expansion cards.
One common use for PCIe x4 slots is for adding additional storage options to a computer. PCIe x4 SSDs can provide faster data transfer speeds compared to traditional SATA drives, making them ideal for applications that require high-speed data storage, such as video editing or gaming.
Another common use for PCIe x4 slots is for adding network cards or adapters. PCIe x4 network cards can offer faster networking speeds and reduced latency, making them suitable for applications that require fast and reliable network connections, such as online gaming or high-performance computing.
PCIe x4 slots can also be used for adding expansion cards that provide additional connectivity options. For example, a PCIe x4 slot can be used to add a USB 3.1 card, which allows for faster data transfer speeds and compatibility with newer USB peripherals.
The PCIe x4 interface is also compatible with PCIe x1 and x16 devices, allowing for greater flexibility in system design. This means that a PCIe x4 slot can be used to connect PCIe x1 or x16 devices, making it a versatile option for motherboard manufacturers.
In conclusion, the PCIe x4 interface offers a balance of bandwidth and compatibility, making it suitable for a variety of applications. Whether it’s adding storage options, network connectivity, or expansion cards, the PCIe x4 slot provides the necessary interface and bandwidth to support these devices in modern computers.
PCIe x8 Applications
PCIe x8 slots are a type of expansion slots commonly found on motherboards of computers. These slots provide a high-speed interface for connecting various PCIe x8 cards to the motherboard. The x8 in PCIe x8 refers to the number of lanes available for data transmission.
The PCIe x8 architecture is part of the PCIe specification, which defines the types of connectors, slots, and bandwidth available for expansion cards. PCIe x8 slots are designed to provide faster speeds and higher bandwidth compared to older generations of PCIe slots, such as PCIe x1.
Some common applications of PCIe x8 slots include adding high-performance graphics cards to a system, connecting storage devices like SSDs or RAID controllers, and expanding the networking capabilities of a computer through the use of network interface cards (NICs).
PCIe x8 slots can also be used to connect other types of expansion cards, such as audio or video capture cards, to enhance the multimedia capabilities of a system. Additionally, they can be used to add specialized hardware accelerators for tasks like encryption or video processing.
Overall, the PCIe x8 interface provides a versatile and high-performance solution for expanding the functionality of computers and devices. With its increased bandwidth and faster speeds, PCIe x8 slots offer a wide range of possibilities for enhancing system performance and adding new features.
PCIe x16 Applications

PCIe x16 slots are one of the most common types of PCIe slots found on motherboards. These slots are designed to support high-speed expansion cards that require a large amount of bandwidth. The x16 designation refers to the number of lanes available for data transmission. PCIe x16 slots provide the highest bandwidth and are primarily used for graphics cards and other high-performance peripherals.
The x16 specification allows for up to 16 lanes, providing a total bandwidth of up to 16GB/s. This high bandwidth makes PCIe x16 slots ideal for gaming computers and workstations that require fast and smooth graphics performance.
PCIe x16 slots are typically used for connecting graphics cards, as they provide the necessary bandwidth for rendering complex 3D graphics and supporting multiple displays. These slots are also used for other high-performance expansion cards, such as RAID controllers, network adapters, and solid-state drives.
It’s important to note that PCIe x16 slots can also support lower lane configurations, such as x8, x4, and x1. This means that x8, x4, and x1 cards can be inserted into a PCIe x16 slot without any issues. However, the bandwidth will be limited to the number of available lanes.
In addition to graphics cards and high-performance peripherals, PCIe x16 slots can also be used for connecting specialized devices such as FPGA (Field-Programmable Gate Array) cards, which are used for tasks like digital signal processing and data encryption. This versatility makes PCIe x16 slots a key component in modern computers.
Overall, PCIe x16 slots play a crucial role in providing high-speed data transfer for a wide range of devices and applications. Whether it’s for gaming, graphics design, or data-intensive tasks, the PCIe x16 interface offers the necessary bandwidth and speed required to ensure optimal performance.
FAQ about topic “A Comprehensive Guide to Different Types of PCIe Slots”
What are the different types of PCIe slots available?
The different types of PCIe slots available include PCIe x1, PCIe x4, PCIe x8, and PCIe x16.
How do PCIe slots differ from each other in terms of bandwidth?
PCIe slots differ from each other in terms of bandwidth based on the number of lanes they have. PCIe x1 has 1 lane and offers the least bandwidth, while PCIe x16 has 16 lanes and offers the most bandwidth.
Can I use a PCIe x16 card in a PCIe x1 slot?
No, you cannot use a PCIe x16 card in a PCIe x1 slot. PCIe slots are not backwards compatible, meaning a larger card cannot be inserted into a smaller slot.
What are the primary uses of PCIe slots?
PCIe slots are primarily used for connecting expansion cards to the motherboard. These expansion cards can include graphics cards, network cards, sound cards, and storage controllers.
What is the difference between a PCIe slot and a conventional PCI slot?
A PCIe slot provides higher bandwidth and faster data transfer rates compared to a conventional PCI slot. Additionally, PCIe slots are not physically compatible with conventional PCI cards.


