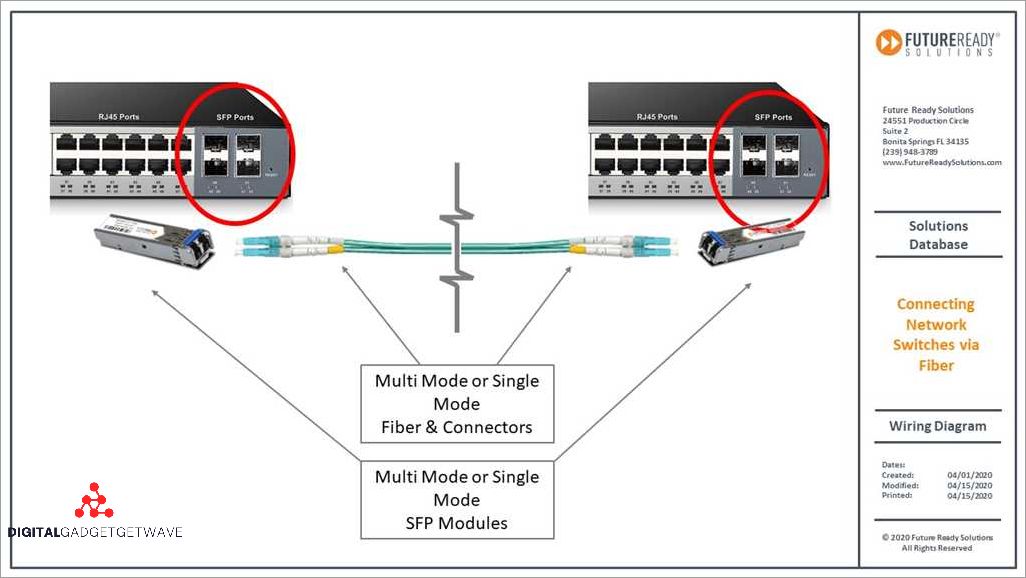
In today’s world, datacenters are essential for communication and network connectivity. They serve as the backbone for storing and processing data, and are crucial for the smooth functioning of various industries. Within these datacenters, servers are connected through a network infrastructure using various technologies, one of which is optical fiber switches.
Optical fiber switches are devices that enable data transfer between servers by connecting them through fiber optic cables. These switches play a vital role in managing and directing data traffic within a network. Unlike traditional copper-based switches, optical fiber switches offer higher bandwidth and faster transmission speeds, making them ideal for high-demand applications.
With the increasing need for faster and more reliable data transfer, optical fiber switches have become an integral part of network infrastructure. They provide multiple ports to enable connectivity between routers, servers, and other network devices. By efficiently routing data traffic, these switches ensure that data reaches its destination without any loss or delay, resulting in a seamless and uninterrupted internet experience for users.
Optical fiber switches utilize optical technology to transmit data, taking advantage of the superior speed and bandwidth offered by fiber optic cables. This technology allows for the transmission of large amounts of data across long distances, making it ideal for interconnecting multiple servers within a datacenter. Furthermore, optical fiber switches are not affected by electromagnetic interference, ensuring reliable and stable data transfer.
In conclusion, optical fiber switches are a key component in the network infrastructure of datacenters. Their ability to handle high bandwidth and fast data transfer speeds make them essential for efficient communication and data management. As technology continues to advance, the demand for optical fiber switches will only grow, further enhancing the performance and reliability of datacenter networks.
Contents
- 1 What are optical fiber switches?
- 2 Why are optical fiber switches important?
- 3 How do optical fiber switches work?
- 4 Main Features of Optical Fiber Switches
- 5 Switching Speed
- 6 Port Density
- 7 Scalability
- 8 Types of Optical Fiber Switches
- 9 Mechanical Optical Fiber Switches
- 10 Micro-mechanical Optical Fiber Switches
- 11 Optical Cross Connect Switches
- 12 Applications of Optical Fiber Switches
- 13 Telecommunications
- 14 Data Centers
- 15 Optical Test and Measurement
- 16 FAQ about topic “Understanding the Basics of Optical Fiber Switches: A Comprehensive Guide”
- 17 What is an optical fiber switch?
- 18 How does an optical fiber switch work?
- 19 What are the benefits of using optical fiber switches?
- 20 Are optical fiber switches compatible with different types of optical fibers?
- 21 What are some common applications of optical fiber switches?
What are optical fiber switches?
An optical fiber switch is a device that allows the routing of optical signals in a network infrastructure. It acts as a communication technology that enables high-speed and efficient data transfer over fiber optic cables.
Optical fiber switches play a crucial role in the transmission of data between different devices, such as routers, servers, and datacenters. They provide the necessary connectivity and flexibility to manage the flow of data within a network.
These switches have multiple ports that can connect to various devices and networks, allowing for the efficient routing and management of data. They enable the seamless transfer of information between different parts of a network, ensuring fast and reliable communication.
One of the main advantages of optical fiber switches is their ability to handle large amounts of data at high speeds. They are designed to support the bandwidth requirements of modern network infrastructures, making them indispensable in today’s digital age.
With the increasing demand for faster and more reliable internet connectivity, optical fiber switches have become an essential component in network infrastructures. They play a crucial role in ensuring efficient data transfer and maintaining the overall performance of a network.
In summary, optical fiber switches are key components in network infrastructures that enable the efficient routing and management of data. They provide high-speed connectivity and support the transmission of large amounts of data between devices and networks. Without these switches, the seamless communication and data transfer we rely on in today’s digital world would not be possible.
Why are optical fiber switches important?
Optical fiber switches play a crucial role in ensuring the smooth functioning of a network infrastructure. They are responsible for directing data traffic in a network, allowing for efficient data transfer and connectivity.
Traditionally, routers were used to handle the routing of data between different networks. However, with the increasing demand for higher bandwidth and faster transmission speeds, optical fiber switches have become an integral part of modern networks.
In a datacenter or internet service provider’s infrastructure, optical fiber switches enable fast and reliable communication between various devices. They provide multiple ports for connecting different fiber optic cables, allowing for simultaneous data transmission.
One of the key advantages of optical fiber switches is their ability to handle high volumes of data traffic. They can efficiently manage the flow of data, ensuring that it reaches its intended destination quickly and without any loss of quality.
Furthermore, optical fiber switches offer enhanced security features, helping to protect sensitive information during transmission. They can encrypt data and authenticate devices, adding an extra layer of security to the network.
In conclusion, optical fiber switches are essential components in modern network infrastructure. Their ability to handle large volumes of data, ensure fast and reliable connectivity, and provide advanced security features make them indispensable for any organization or data-driven operation.
How do optical fiber switches work?
An optical fiber switch is a crucial component in the network infrastructure that facilitates high-speed data transmission through fiber optic cables. It plays a vital role in directing, managing, and controlling the flow of data within a network.
Optical fiber switches function by receiving optical signals from different sources and routing them to their intended destination. These switches are capable of handling large amounts of bandwidth and can support high-speed data transfer rates. They work by converting incoming optical signals into electronic signals, processing them, and then converting them back into optical signals for transmission.
The switch uses advanced optical switching technology to establish connectivity between various network devices, such as routers, servers, and data centers. It enables seamless communication between different parts of the network, ensuring efficient data transfer and reliable connectivity.
When a data packet arrives at the switch, it examines the packet header to determine the destination address. The switch then uses its internal routing table to decide the best path for forwarding the data. It connects the incoming and outgoing fibers to establish a direct link between the sender and receiver, allowing the data to be transmitted without interference.
Optical fiber switches are particularly useful in data centers and enterprises where large amounts of data need to be transmitted quickly and reliably. They provide a centralized and efficient solution for managing network traffic, improving overall network performance, and enhancing the scalability of the network infrastructure.
Main Features of Optical Fiber Switches

An optical fiber switch is a crucial component in a network infrastructure that allows the seamless transfer of data between various devices. It serves as a connection point for cables, enabling efficient communication and data transmission.
One of the key features of optical fiber switches is the number of ports it has. These ports are used to connect to other devices such as switches, routers, servers, or data centers. With multiple ports, optical fiber switches can handle a larger volume of data and provide better connectivity.
Another important feature of optical fiber switches is their speed. The advanced technology employed in these switches allows for high-speed data transfer, making them ideal for applications that require fast and reliable communication, such as internet connections or datacenter operations.
Optical fiber switches also offer exceptional bandwidth capabilities. They can handle large amounts of data simultaneously, allowing for smooth and efficient data transfer. This is particularly beneficial for organizations that rely heavily on data-intensive tasks or require continuous and uninterrupted connectivity.
One of the main advantages of optical fiber switches is their compatibility with optical fiber cables. Unlike traditional copper cables, fiber optic cables provide faster and more reliable data transmission. Optical fiber switches are designed to work seamlessly with these cables, ensuring optimal performance and data security.
Overall, optical fiber switches play a crucial role in establishing and maintaining an efficient and reliable network infrastructure. Their ability to connect multiple devices, provide high-speed communication, and handle large volumes of data makes them an essential component for organizations seeking robust and fast connectivity.
Switching Speed

The switching speed of optical fiber switches refers to the rate at which data can be transmitted and received in a network. It is a crucial factor in determining the efficiency and performance of internet connections, particularly in data-intensive applications such as servers and datacenters.
Optical fiber switches are designed to handle high-speed data transfer, allowing for faster and more efficient communication between devices. They use fiber optic cables, which have the capability to transmit data at incredibly high speeds over long distances without signal degradation or loss.
With the increasing demand for bandwidth-intensive applications and the growth of network infrastructure, the need for faster switching speeds has become more important than ever. Optical fiber switches enable the seamless transfer of large amounts of data, ensuring smooth and uninterrupted communication between servers, routers, and other network devices.
High switching speeds also allow for efficient load balancing and traffic management within a network. By quickly routing data packets, optical fiber switches can optimize the flow of information and prevent congestion, improving overall network performance.
In summary, switching speed plays a vital role in the performance of optical fiber switches and the efficiency of data transfer in communication networks. With the advancements in fiber optic technology, these switches have become essential components in modern internet infrastructure, facilitating fast and reliable data transmission for various applications.
Port Density
Port density is an important consideration when it comes to optical fiber switches. It refers to the number of ports that a switch can accommodate in a given space. A higher port density means that more cables can be connected to the switch, allowing for greater speed and connectivity in a network.
Port density is crucial for organizations that require fast and reliable internet communication, such as data centers and large enterprises. With a higher port density, more data can be transmitted simultaneously, increasing the overall bandwidth and improving network performance.
Optical fiber switches with high port density are especially beneficial in situations where a large number of devices need to be connected to the network infrastructure. This could include routers, servers, and other components of a data center or communication network.
By using a switch with high port density, organizations can optimize their network performance and ensure seamless data transmission. It allows for efficient connectivity between different devices, eliminating bottlenecks and enabling smooth data flow.
The advancements in optical fiber technology have made it possible to achieve higher port densities without sacrificing performance. Optical fiber switches can now support hundreds or even thousands of ports, providing organizations with the flexibility and scalability they need to meet their evolving network requirements.
In summary, port density is a crucial factor to consider when selecting an optical fiber switch. It determines the number of ports that can be connected to the switch, enabling faster and more reliable data transmission. With high port density, organizations can optimize their network infrastructure and ensure efficient connectivity for their datacenter, routers, and other devices.
Scalability
Optical fiber switches are essential components for the scalability of communication networks. With the increasing demand for high-speed data transmission, optical fiber technology has become the backbone of the internet and data transfer. Scalability refers to the ability of a network infrastructure to handle the growing amount of data and provide seamless connectivity.
Scalability is crucial in various applications, such as data centers, where large amounts of data need to be processed and transferred simultaneously. Optical fiber switches offer the necessary speed and bandwidth to accommodate the increasing demands of data-intensive tasks. They enable efficient data transfer among servers, routers, and other network devices within the data center, ensuring smooth operations and seamless communication.
The scalability of optical fiber switches lies in their ability to support a larger number of ports. These switches can easily connect multiple devices, allowing for flexible expansion and connectivity options. Whether it’s expanding the number of servers or adding more routers to the network infrastructure, optical fiber switches can handle the increasing data flow without compromising on speed or performance.
Moreover, the scalability of optical fiber switches also enhances the overall network performance and reliability. With the ability to handle large data volumes, these switches minimize data congestion and ensure efficient data routing. This scalability ensures that the network can handle the growing demands of data-intensive applications and meet the requirements of evolving technologies.
In summary, the scalability of optical fiber switches is crucial for the efficient and seamless operation of communication networks. Whether it’s in data centers or other network infrastructure, these switches provide the necessary connectivity and bandwidth to handle the increasing demands of high-speed data transmission. With their ability to support a larger number of ports and handle large data volumes, optical fiber switches play a vital role in the scalable and reliable functioning of modern communication systems.
Types of Optical Fiber Switches
Optical fiber switches are devices used in fiber-optic networks to control the flow of data between different cables or network devices. There are several types of optical fiber switches available, each serving different purposes and offering unique capabilities.
1. Mechanical Optical Fiber Switch: This type of switch uses mechanical components to physically move the fiber cables and establish or break the connection. Mechanical switches are simple and reliable, making them suitable for small-scale applications.
2. Electro-Optical Fiber Switch: Electro-optical switches utilize electrical signals to control the switching action. They use electrically controlled waveplates or liquid crystal devices to redirect the optical signal. These switches are faster and more precise than mechanical switches, making them ideal for high-speed data transfer and transmission.
3. MEMS Optical Fiber Switch: MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) switches use tiny movable mirrors to redirect the fiber cables. These mirrors are controlled by applying an electrical voltage, which causes them to move and direct the light signal. MEMS switches have higher bandwidth and lower insertion loss compared to mechanical switches, making them suitable for complex network infrastructures.
4. Optical Cross-Connect Switch: Optical cross-connect switches are used in large-scale network environments such as datacenters or server rooms. These switches provide a high level of connectivity and flexibility by allowing multiple fibers to be connected to each other in a controlled manner. They can handle high bandwidth and can be remotely controlled.
5. Wavelength-selective Optical Switch: Wavelength-selective switches work by filtering and redirecting specific wavelengths of light. They are used in wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) systems to manage the transmission of different optical signals. These switches enable efficient use of bandwidth and improve network performance.
Overall, optical fiber switches play a crucial role in modern network infrastructure, ensuring efficient connectivity, high-speed data transfer, and reliable transmission of optical signals. The choice of switch type depends on the specific requirements of the network and the technology being used, such as routers, internet connectivity, or datacenter operations.
Mechanical Optical Fiber Switches
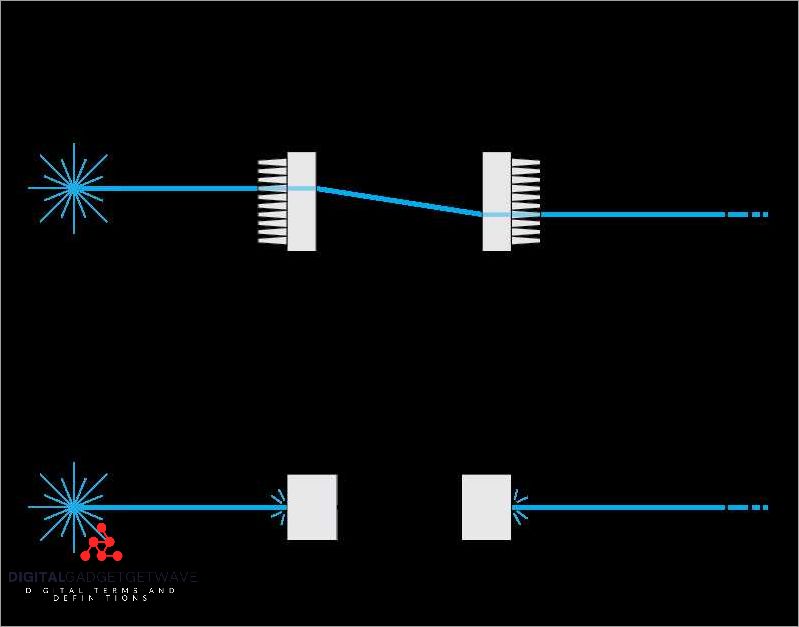
Mechanical optical fiber switches are devices used in network infrastructure to enable the switching of light signals between different ports. These switches are crucial for ensuring efficient data transfer in datacenters, communication networks, and server rooms. With the ever-increasing demand for high-speed data transmission, the use of optical fiber technology has become common due to its ability to support large bandwidth and faster transmission speeds compared to traditional copper cables.
Mechanical optical fiber switches are designed to provide connectivity between different optical fibers, allowing for the efficient routing of data between network devices. They can be used in various applications, such as connecting different routers or switches in a network, or connecting servers to the internet. These switches play a crucial role in managing and directing data traffic in a network, ensuring that data is efficiently transferred between different devices.
One of the main advantages of mechanical optical fiber switches is their ability to handle large volumes of data at high speeds. With the increasing demand for faster internet connectivity and the growing number of devices connected to a network, it has become essential to have switches that can support high-speed data transfer. Mechanical optical fiber switches are capable of handling data rates of up to several terabits per second, making them ideal for use in high-speed datacenter environments.
These switches also offer flexibility and scalability, allowing for easy expansion and modification of network infrastructure. With mechanical optical fiber switches, it is possible to add or remove connections without disrupting the overall network connectivity. This makes them highly reliable and efficient in managing network resources while minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
In conclusion, mechanical optical fiber switches are integral components of modern network infrastructure. They enable the efficient routing of data between different devices and provide high-speed connectivity for applications such as datacenters, servers, and routers. With their ability to handle large volumes of data at high speeds, these switches play a crucial role in ensuring smooth and efficient communication in today’s digital world.
Advantages
Fiber optic switches have numerous advantages that make them an essential component in modern network infrastructure. Here are some key advantages:
- High-speed connectivity: Fiber optic switches are capable of handling extremely high data transfer rates, making them ideal for applications that require fast and reliable communication.
- Enhanced network performance: Optical switches improve network performance by minimizing latency and increasing the speed of data transmission. This allows for faster and more efficient communication between devices.
- Increased network capacity: Fiber optic switches have the ability to support a large number of ports, allowing for the expansion of network infrastructure and accommodating growing data requirements.
- Improved reliability: Optical switches provide greater reliability compared to traditional copper cables, as they are less susceptible to electromagnetic interference and signal loss. This ensures consistent and uninterrupted data transmission.
- Flexibility and scalability: Fiber optic switches can be easily integrated into existing network setups, making them a flexible solution for upgrading or expanding network infrastructure. They can also be scaled up or down to meet changing network demands.
- Support for long-distance communication: Optical switches enable long-distance transmission of data, making them suitable for connecting different locations, such as data centers or remote offices, over vast distances.
- Compatibility with existing technology: Fiber optic switches can work seamlessly with existing routers, servers, and other network devices, making them a convenient choice for integrating into an existing network setup without requiring a complete overhaul.
In summary, fiber optic switches offer advantages such as high-speed connectivity, enhanced network performance, increased network capacity, improved reliability, flexibility, support for long-distance communication, and compatibility with existing technology. These advantages make optical switches a crucial component for efficient and reliable data transfer in modern network infrastructures.
Disadvantages
Although optical fiber switches offer many advantages, they also come with some disadvantages. One of the major disadvantages is the high cost of implementing the technology. The network infrastructure required for optical fiber switches is expensive to install and maintain. This includes the cost of fiber cables, routers, and other equipment necessary for data transfer.
Another disadvantage is the complexity of the technology. Optical fiber switches require specialized knowledge and skills to set up and configure. This can be a challenge for organizations that do not have the necessary expertise. Additionally, troubleshooting and maintenance can be more difficult compared to traditional copper-based network systems.
The speed of optical fiber transmission is another disadvantage. While optical fiber offers high-speed data transfer, it is not as fast as some other technologies, such as certain copper-based systems. This can be a limitation in certain applications where extremely high-speed connectivity is required.
Furthermore, optical fiber switches have limited port availability. Most switches come with a limited number of ports, which can be a limitation for large network environments. This can require additional investment in switches or other network equipment to accommodate the required number of connections.
Another disadvantage is the dependence on external power sources. Optical fiber switches require power to operate, and any disruption in the power supply can result in a loss of connectivity. This can be a concern for datacenters or organizations that require uninterrupted communication and data transfer.
Lastly, the bandwidth of optical fiber switches can be a limitation. While optical fiber offers high bandwidth, there can still be limitations based on the specific switch model and network configuration. This can impact the overall performance and scalability of the network.
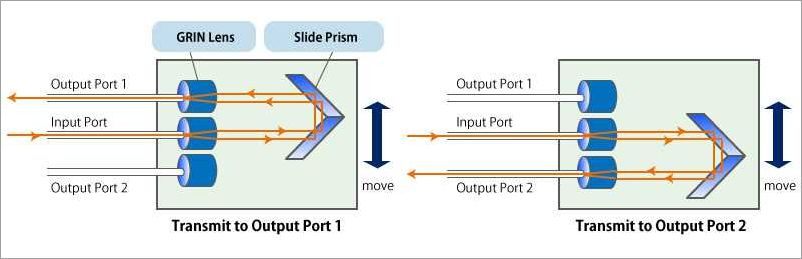
Micro-mechanical Optical Fiber Switches
Micro-mechanical optical fiber switches are a crucial component in the optical network infrastructure. They play a vital role in managing the bandwidth and ensuring efficient communication within the network. These switches are responsible for routing optical signals between different fiber cables, connecting various devices such as routers, switches, and servers, and enabling high-speed data transmission.
Unlike traditional electrical switches, micro-mechanical optical fiber switches are designed specifically for optical signals. They utilize advanced technology to switch the optical signals from one fiber cable to another without converting them into electrical signals. This ensures minimal loss of data and allows for faster and more reliable connectivity.
The main advantage of micro-mechanical optical fiber switches is their ability to handle large amounts of data transfer. With the increasing demand for higher bandwidth and faster data transmission, these switches are a critical component in datacenters and internet infrastructure. They enable seamless connectivity between different devices and facilitate the efficient transmission of data without any bottlenecks.
Micro-mechanical optical fiber switches are typically equipped with multiple ports, allowing for easy integration into existing network setups. They can be used to connect multiple devices, such as routers, servers, and other networking equipment, and enable efficient data transfer between them. These switches are also often used in datacenters, where they provide the necessary connectivity for high-speed data transmission between servers and other devices.
In summary, micro-mechanical optical fiber switches are a key technology in the field of optical communication. They enable high-speed data transfer, ensure efficient connectivity between devices, and play a vital role in the overall functioning of network infrastructure. With the increasing reliance on fiber optic technology, these switches are becoming more important than ever in ensuring reliable and fast data transmission.
Advantages
The use of optical fiber switches offers several advantages in network connectivity and data transmission:
- High speed: Optical fiber switches have the ability to transmit data at extremely high speeds, allowing for faster and more efficient communication between devices in a network.
- Increased bandwidth: The use of optical fibers enables a higher bandwidth, which means more data can be transmitted simultaneously, leading to an improved network performance.
- Low latency: Optical fiber switches have lower latency compared to traditional copper cables, resulting in reduced delay in data transmission and improved responsiveness in network applications.
- Longer transmission distance: Optical fibers can transmit data over long distances without significant loss in signal quality, making them suitable for connecting devices in different locations.
- Secure data transmission: The use of optical fibers provides a higher level of security for data transmission as they are more difficult to tap or intercept compared to copper cables.
- Scalability: Optical fiber switches can easily accommodate the increasing demands of network infrastructure, allowing for future expansion and upgrading without the need for major reconfigurations.
- Reliability: Optical fibers are less prone to electromagnetic interference and signal degradation, resulting in a more reliable and stable network connection.
- Multiple ports: Optical fiber switches often come with multiple ports, allowing for easy connection to multiple devices such as servers, routers, and datacenter equipment.
In summary, optical fiber switches provide significant advantages in terms of speed, bandwidth, security, and reliability for network communication and data transmission. They play a crucial role in maintaining efficient and high-performance network infrastructures.
Disadvantages
1. Limited speed: While optical fiber switches offer high-speed data transmission, they are still limited by the speed of the technology used. In comparison to other networking technologies, such as Ethernet, the speed of optical fiber switches may be relatively slower.
2. Limited bandwidth: Optical fiber switches may have limited bandwidth, which can affect the amount of data that can be transferred at any given time. This limitation can become a bottleneck in data transfer within a network or datacenter.
3. Limited number of ports: Optical fiber switches may have a limited number of ports available for connectivity. This can pose a challenge when trying to connect multiple devices or expand the network infrastructure.
4. Expensive setup: Setting up an optical fiber switch can be expensive, especially when considering the cost of optical cables, routers, and other network infrastructure. This can make it less viable for small-scale or budget-conscious setups.
5. Complex maintenance: Maintaining an optical fiber switch can be complex and requires specialized knowledge and tools. This can increase the cost of maintenance and make it more challenging to troubleshoot and fix issues that may arise.
6. Limited availability: Optical fiber switches may not be widely available in all regions, making it difficult to procure and deploy them in certain areas. This can limit the options for organizations looking to upgrade their network connectivity.
7. Dependency on optical fiber cables: Optical fiber switches rely on the use of optical fiber cables for data transmission. If these cables get damaged or experience issues, it can disrupt communication and require troubleshooting or replacement.
Overall, while optical fiber switches offer many advantages for high-speed data transfer and connectivity, they also come with a range of disadvantages that need to be considered when choosing networking technology for a datacenter, network, or server infrastructure.
Optical Cross Connect Switches
Optical cross connect switches are essential components in optical network infrastructure that help facilitate efficient data transfer and communication. These switches are designed specifically for handling the increasing demand for high-speed internet and data transmission.
Using optical cables and the latest fiber optic technology, these switches enable the seamless connectivity and transmission of data between different network devices, such as routers and data centers. They provide a reliable and fast means of switching data traffic between various ports, allowing for efficient network management and optimization.
One of the main advantages of optical cross connect switches is their ability to handle large amounts of data and bandwidth. These switches can support multiple ports and allow for simultaneous data transfer, making them ideal for high-traffic network environments.
With their advanced switching capabilities, optical cross connect switches offer flexibility and scalability in network design. They can be easily integrated into existing network infrastructure, allowing for future expansion and upgrades without significant disruptions to the network.
Overall, optical cross connect switches play a crucial role in ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of internet and data networks. They provide the necessary connectivity and technology to handle the increasing demands for data transfer and communication in today’s digital age.
Advantages
Optical fiber switches offer several key advantages in datacenter and network infrastructure.
- High bandwidth: Optical fiber switches provide high-speed transmission of data, allowing for fast and efficient data transfer. This is especially important in today’s data-intensive world where large amounts of data need to be transmitted quickly.
- Improved data connectivity: With optical fiber switches, multiple fiber cables can be connected to a single switch, providing increased connectivity options for servers, routers, and other network devices. This allows for more efficient communication and data exchange within the network.
- Greater flexibility: Optical fiber switches can support a large number of ports, making them suitable for use in large-scale datacenter and network environments. This flexibility allows for easy expansion and scalability as the network grows.
- Reduced latency: Optical fiber switches have lower latency compared to traditional copper-based switches. This means that data can be transmitted faster and with less delay, resulting in improved performance and responsiveness in network communication.
- Enhanced security: Fiber optic technology used in optical fiber switches offers a higher level of security compared to copper-based cables. This makes it more difficult for hackers to tap into the network and intercept sensitive data.
Disadvantages
While optical fiber switches offer many advantages for datacenters and network infrastructure, there are also some disadvantages to consider.
Firstly, optical fiber switches can be quite expensive to install and maintain. The cost of the fiber cables, routers, and switches themselves can be high, especially for larger networks or datacenters. Additionally, specialized technicians may be needed to install and configure the equipment, adding to the overall cost.
Another disadvantage is that optical fiber switches can be more fragile than traditional copper cables. They are sensitive to bending and can break easily if mishandled during installation or maintenance. This can lead to interruptions in data transmission and require costly repairs.
Furthermore, optical fiber switches may require more power than traditional switches. This can be a concern in datacenters or locations where power efficiency is essential. The higher power consumption may also result in increased heat generation, requiring additional cooling measures.
Lastly, while optical fiber provides high-speed transmission and bandwidth, it may not be compatible with all devices. Some older servers, routers, or communication equipment may not have the necessary ports or connectivity options for optical fiber. This can limit the usability and effectiveness of optical fiber switches in certain network environments.
Applications of Optical Fiber Switches
Optical fiber switches have numerous applications in various industries, ranging from datacenters to network infrastructure. These switches play a critical role in ensuring high-speed connectivity and efficient data transfer.
In datacenters, optical fiber switches are used to connect multiple servers, routers, and other network devices. These switches provide the necessary bandwidth and enable the seamless transmission of data between different devices in the datacenter. They allow for quick and reliable communication within the network, ensuring smooth operations and minimal downtime.
Router manufacturers also utilize optical fiber switches to enhance the performance of their devices. These switches allow for faster data transfer between routers and improve the overall efficiency of the network. With the increasing demand for high-speed internet connectivity, optical fiber switches help meet the requirements for faster and reliable internet access.
Furthermore, optical fiber switches find applications in network infrastructure setups. They are commonly used to connect various network components, such as switches, routers, and servers, to ensure a reliable and efficient communication network. With multiple ports available on optical fiber switches, they can accommodate the growing number of devices in a network, providing flexibility and scalability.
The use of optical fiber switches is particularly important in industries that rely heavily on fast and secure data transfer, such as finance, healthcare, and telecommunications. These switches enable seamless communication between different nodes and devices, facilitating the transfer of critical data without any data loss or latency issues.
In summary, optical fiber switches are crucial for enabling high-speed data transmission and ensuring efficient communication in various applications, including datacenters, routers, and network infrastructure. With their ability to handle large bandwidth requirements and provide reliable connectivity, these switches are essential components for modern-day network setups.
Telecommunications
In the field of telecommunications, bandwidth is a crucial concept. It refers to the capacity for transmitting data over a network, indicating how much information can be sent and received at a given time. High bandwidth is essential for ensuring fast and efficient transmission of data in various applications, such as datacenters, servers, and internet connectivity.
Communication networks rely on switches and routers to facilitate data transfer. Optical fiber switches are an important component of network infrastructure, enabling the efficient routing of data through fiber cables. These switches provide high-speed connectivity between various devices, such as servers and routers, allowing for seamless communication and data transfer.
Optical fiber switches are designed to handle the high bandwidth requirements of modern networks. With multiple ports, these switches can accommodate numerous connections simultaneously, enabling efficient data routing and ensuring reliable connectivity. Their ability to handle large volumes of data makes them ideal for supporting high-speed internet connections and data-intensive applications.
Furthermore, the use of optical fiber switches in telecommunications helps optimize network performance. By directing data traffic efficiently, these switches minimize latency and improve overall network speed. The optical technology used in these switches allows for faster transmission of data over long distances, making them suitable for long-haul communication applications.
In summary, in the realm of telecommunications, optical fiber switches play a crucial role in ensuring efficient data transmission and network connectivity. With their high bandwidth capabilities and ability to handle large volumes of data, these switches are essential components of network infrastructure in datacenters, server environments, and other communication networks.
Data Centers
Data centers are centralized facilities that store, manage, and distribute large amounts of data. They are critical components of modern communication networks, supporting the transmission and processing of data across various devices and platforms. In a data center, different types of equipment are used to ensure efficient data transfer and connectivity, such as routers, switches, and optical fiber cables.
Routers play a vital role in data centers as they direct network traffic between different devices and networks. They determine the best path for data transmission, ensuring efficient data transfer and minimizing latency. Switches, on the other hand, are used to connect multiple devices within a network. They provide communication between devices using Ethernet ports and help create a network infrastructure that allows data to flow between devices.
The use of optical fiber technology in data centers has revolutionized data transmission. Fiber optic cables transmit data through pulses of light, allowing for faster and more reliable data transfer compared to traditional copper cables. This technology has greatly increased the bandwidth capabilities of data centers, enabling them to handle larger amounts of data and support high-speed internet connectivity.
Data centers are essential for businesses and organizations that rely on the storage and processing of large amounts of data. They house powerful servers and networking equipment that ensure the availability and security of data. They also provide the necessary infrastructure for cloud computing, allowing businesses to access and store data remotely.
In conclusion, data centers are the backbone of modern data communication and storage. They utilize advanced technologies such as optical fiber, routers, switches, and servers to enable fast and reliable data transfer. With the increasing demand for data-driven applications and services, data centers continue to play a crucial role in supporting our digital world.
Optical Test and Measurement
Optical test and measurement play a crucial role in ensuring the efficient operation of network infrastructures in the internet age. With the exponential growth in data traffic and the increasing demand for high-speed data transfer, accurate testing and measurement of optical networks have become paramount.
In a datacenter or a communication network, servers and switches are connected through optical fibers to ensure high-speed data transmission and sufficient bandwidth. Optical test and measurement tools enable network administrators to assess the connectivity and performance of these optical fibers, ensuring that data transfer is smooth and uninterrupted.
Optical switches and routers are key components in any optical network, responsible for routing data packets to their intended destinations. Through optical test and measurement, network administrators can evaluate the performance of these switches and routers, ensuring optimal functionality and minimizing data loss.
Optical test and measurement technologies employ various techniques to assess the performance of optical networks. These techniques include optical power measurement, optical spectrum analysis, optical time-domain reflectometry (OTDR), and polarization mode dispersion (PMD) measurement. These tests help identify any network issues, such as signal loss, fiber degradation, or connection failures, enabling timely troubleshooting and ensuring uninterrupted data transmission.
With the ever-increasing demand for faster and more reliable network connectivity, optical test and measurement technologies continue to evolve. New advancements in optical power meters, optical spectrum analyzers, and optical time-domain reflectometers enable network administrators to accurately assess the performance of optical networks, identify potential bottlenecks, and optimize network efficiency.
In conclusion, optical test and measurement are critical components of network maintenance and optimization in the modern era. These technologies ensure the smooth functioning of optical networks, support high-speed data transfer, and facilitate seamless communication in an increasingly connected world.
FAQ about topic “Understanding the Basics of Optical Fiber Switches: A Comprehensive Guide”
What is an optical fiber switch?
An optical fiber switch is a device that is used to control the flow of data through optical fibers. It allows for the switching of signals between different fiber optic cables or channels.
How does an optical fiber switch work?
An optical fiber switch works by using tiny mirrors, lasers, and other components to redirect light signals from one fiber optic cable to another. When a signal is received, the switch determines the intended destination and redirects the signal accordingly.
What are the benefits of using optical fiber switches?
There are several benefits of using optical fiber switches. Firstly, they provide high-speed data transmission with low latency. Secondly, they offer increased bandwidth capacity, allowing for the transfer of large amounts of data. Additionally, they are reliable and resistant to electromagnetic interference.
Are optical fiber switches compatible with different types of optical fibers?
Yes, optical fiber switches are generally compatible with different types of optical fibers. They can work with single-mode fibers, which are used for long-distance communications, as well as multi-mode fibers, which are used for shorter distances. However, it is always recommended to check the specifications of the specific switch to ensure compatibility.
What are some common applications of optical fiber switches?
Optical fiber switches are commonly used in telecommunications networks, data centers, and other high-speed data transmission systems. They are also used in fiber optic sensing applications, such as monitoring structures for deformation or detecting leaks in pipelines.


