
The internet has become an integral part of our lives, and understanding how it works is essential for a seamless online experience. One of the key factors that determines your internet speed is the rate at which data is transferred, often measured in kilobits per second (Kb/s) or megabits per second (Mb/s).
When you download or stream content, such as movies or music, the speed at which this data is transferred from the server to your device is crucial. Kb/s indicates the transfer rate for downloading data, while Mb/s indicates a higher transfer rate, which is typically used for measuring the speed of your internet connection.
Your internet speed can impact various online activities. For example, if you have a slow internet speed, it may take longer to load webpages, download files, or stream videos without buffering. To determine your actual internet speed, you can use online speedtest tools that calculate your download and upload speeds and provide valuable insights into the overall performance of your internet connection.
Several factors can affect your internet speed, including the type of connection you have, the quality of your modem and router, and the bandwidth provided by your internet service provider. Broadband connections, such as cable or fiber-optic, typically offer higher speeds compared to dial-up or DSL connections.
Understanding Kb/s, Mb/s, and their impact on your internet speed is essential for troubleshooting slow connections, optimizing your network setup, and ensuring a smooth online experience for all your data-intensive activities.
Contents
- 1 What is Kb/s?
- 2 Factors affecting Kb/s
- 3 Importance of Kb/s for internet speed
- 4 Improving Kb/s and internet speed
- 5 FAQ about topic “Understanding Kb/s: Exploring the Impact of Internet Speed and Bandwidth”
- 6 What is Kb/s and how does it affect my internet speed?
- 7 How do I calculate the actual download speed based on the Kb/s?
- 8 Is Kb/s the only factor that affects my internet speed?
- 9 What is the difference between Kb/s and Mbps?
- 10 How can I increase my Kb/s and improve my internet speed?
What is Kb/s?
Kb/s stands for kilobits per second. It is a unit of measurement that is used to describe the download, transfer, or uploading rate of data over a network or internet connection. It is a measure of the amount of data that can be transmitted in one second.
When you stream videos or download files from the internet, your internet speed is measured in Kb/s. It determines how quickly you can access and transfer data from the internet to your device. The higher the Kb/s rate, the faster your internet speed will be, allowing you to stream videos, download files or browse the web more efficiently.
Your Kb/s rate depends on various factors, including the bandwidth of your network connection, the type of router or modem you are using, and the quality of your internet service provider. An internet speed test can be done to measure the Kb/s rate and determine the efficiency of your internet connection.
It’s important to note that Kb/s is different from kilobytes per second (KB/s). While Kb/s measures the speed in bits, KB/s measures it in bytes. 1 byte is equal to 8 bits. So if you have a Kb/s rate of 1000, your download speed in KB/s would be approximately 125 (1000 divided by 8).
In summary, Kb/s is a measure of the transfer rate of data over a network or internet connection. It determines the speed at which you can download, stream, or upload data. Understanding your Kb/s rate is essential for assessing your internet speed and ensuring that it meets your requirements for online activities such as streaming videos or downloading files.
Definition of Kb/s
In the world of networking and internet speeds, Kb/s stands for kilobits per second. It is a measurement used to quantify the rate at which data is transferred or uploaded over a network. A kilobit is equivalent to 1,000 bits.
When you connect your router or modem to the internet, you can experience different levels of bandwidth, which determines the maximum speed at which you can send and receive data. Kb/s is a commonly used unit to measure the speed of your internet connection, especially for broadband connections.
Kb/s is crucial for various online activities such as web browsing, streaming, online gaming, and file downloading. For example, when you perform a speedtest, the result is presented in Kb/s to give you an idea of the speed at which data is being transferred.
It’s important to note that Kb/s is different from kilobytes per second (KB/s), where one kilobyte is equivalent to 8 kilobits. While Kb/s refers to the speed of your internet connection, KB/s is commonly used to measure the size of files or the rate of uploading and downloading.
Having a higher Kb/s indicates a faster internet connection, which means websites will load quickly, videos will stream smoothly, and downloads will complete faster. On the other hand, if you experience a lower Kb/s, you may face buffering issues while streaming or slower downloads and uploads.
How Kb/s is measured
When it comes to measuring internet speed, Kb/s stands for kilobits per second. It is a unit used to quantify the rate at which data is transferred over a network connection. This measurement is commonly used for both downloading and uploading data.
The speed of your internet connection, measured in Kb/s, is determined by several factors. One of the main factors is the type of internet connection you have. For example, if you have a broadband connection, your internet speed can range from a few Kb/s to hundreds of megabits per second.
In order to measure your Kb/s speed, you can use various speedtest tools available online. These tools help you determine the speed of your internet connection by measuring the time it takes to download and upload a sample file. The result is usually expressed in Kb/s.
Networking equipment, such as a modem or router, also plays a role in determining your Kb/s speed. The quality and capability of these devices can affect the overall speed and performance of your internet connection. It is important to ensure that your equipment is up to date and compatible with the broadband service you subscribe to.
Bandwidth is another important factor when it comes to measuring Kb/s. Bandwidth refers to the maximum amount of data that can be transferred over a network connection in a given period of time. The more bandwidth you have, the higher your Kb/s speed can be.
In conclusion, Kb/s is a unit of measurement used to quantify the rate at which data is transferred over an internet connection. It is essential to have a reliable and fast internet connection, especially when it comes to activities such as streaming, downloading, and uploading large files. By understanding how Kb/s is measured and the factors that can affect it, you can make informed decisions to optimize your internet speed and enjoy a seamless online experience.
Relationship between Kb/s and internet speed
When it comes to internet speed, the measurement unit frequently used is Kilobits per second (Kb/s). It refers to the rate at which data is transferred over a network or an internet connection. The higher the Kb/s value, the faster the data is being transmitted.
Bandwidth plays a crucial role in determining the internet speed. It represents the capacity of a network or an internet connection to transmit data. The greater the bandwidth, the more data can be uploaded or downloaded within a given time period.
The upload and download speeds are also important factors to consider when talking about internet speed. The upload speed refers to the rate at which data can be sent from a device to the internet, while the download speed is the rate at which data can be received from the internet to a device.
When conducting a speedtest, it measures the transfer rate of data and provides results in Kb/s or Megabits per second (Mbps). A download speed of 50 Mbps, for example, indicates that data can be downloaded at a rate of 50 million bits per second.
Internet speed is crucial for various online activities such as streaming, online gaming, video conferencing, and downloading large files. Streaming services like Netflix or YouTube require a minimum internet speed to ensure smooth playback. The higher the internet speed, the better the streaming quality.
A reliable internet connection depends on various factors such as the type of modem or router, the quality of networking equipment, and the type of broadband connection. Fiber-optic connections typically offer higher download and upload speeds compared to DSL or cable connections.
In conclusion, Kb/s is a crucial unit for measuring internet speed. It represents the rate at which data can be transferred over a network or internet connection. Factors such as bandwidth, upload and download speeds, and the type of internet connection all contribute to the overall internet speed experienced by users.
Factors affecting Kb/s
There are several factors that can affect the Kb/s (kilobits per second) rate of your internet connection. These factors include:
- Modem and router: The quality and capabilities of your modem and router can have a significant impact on your internet speed. Older or lower-quality devices may not be able to handle higher speeds, resulting in slower Kb/s rates.
- Broadband connection: The type of broadband connection you have can also affect your Kb/s rate. Different broadband technologies, such as DSL, cable, fiber-optic, and satellite, offer varying speeds and bandwidth capabilities.
- Internet service provider (ISP): The ISP you subscribe to plays a crucial role in determining your Kb/s rate. Different ISPs may have different network infrastructures and capacity, leading to variations in internet speeds.
- Network congestion: The amount of traffic on your network can impact your Kb/s rate. During peak usage times or in congested areas, the network may become overloaded, resulting in slower speeds for all users.
- Upload and download activities: The amount of data you are uploading or downloading can affect your Kb/s rate. If you are performing large file transfers or streaming high-definition videos, it can consume significant bandwidth and reduce your Kb/s rate.
- Streaming and online gaming: Streaming services and online gaming require a stable and fast internet connection. If you frequently stream videos or play online games, your Kb/s rate may be affected by the demand placed on your network.
- Speedtest results: Regularly conducting speedtests can provide insights into your internet speed and help identify any issues that may be affecting your Kb/s rate. These tests measure your upload and download speeds and can help troubleshoot any problems.
- Networking equipment: The quality and configuration of your networking equipment, such as switches and cables, can impact your Kb/s rate. Using outdated or faulty equipment can result in slower speeds.
It is important to consider these factors and optimize your internet setup to ensure a smooth and fast browsing experience. Consult with your ISP or IT professionals for assistance with improving your Kb/s rate.
Bandwidth limitations
Bandwidth refers to the amount of data that can be transferred over a network connection within a given time frame. It is a measure of the capacity of a network and affects the speed at which data can be downloaded, uploaded, or streamed online.
Bandwidth limitations can have an impact on various online activities. For example, when downloading a large file, the bandwidth of your internet connection determines how quickly the file will be transferred to your device. Similarly, when uploading files or streaming content, the available bandwidth affects the speed and quality of the transfer or stream.
Your internet connection’s bandwidth is influenced by several factors, including the type of connection you have. Broadband connections, such as cable or fiber, typically provide higher bandwidths compared to dial-up or satellite connections.
In addition to the connection type, the bandwidth can also be affected by the capabilities of your router and modem. Upgrading to a more advanced router or modem can potentially improve your internet speed by increasing the available bandwidth.
To determine the actual bandwidth you have, you can use a speed test tool. This online tool measures the speed of your internet connection in terms of megabits per second (Mbps). The higher the Mbps, the faster your internet speed and the more data you can transfer in a given time.
Understanding the bandwidth limitations of your internet connection is crucial for optimizing your online experience. Whether you are downloading large files, uploading content, or streaming videos, a higher bandwidth allows for faster transfers and smoother streaming without buffering.
Network congestion
Network congestion refers to the condition when there is an excessive amount of data being transferred through a network, resulting in a decrease in the speed and efficiency of data transmission. This can be observed during peak usage hours or in areas where there is a high number of users connected to the network simultaneously.
When network congestion occurs, it can cause delays in data transfer, affecting the download and upload speeds experienced by users. This means that tasks such as streaming videos or downloading large files may take longer to complete, as the congestion slows down the rate of data transfer.
One of the main causes of network congestion is the limited bandwidth available in the network. Bandwidth refers to the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted in a given time period. If the available bandwidth is not sufficient to handle the volume of data being transmitted, congestion can occur.
Network congestion can also be caused by inefficient routing, where the data packets are not being directed in the most optimal manner. In addition, issues with the network infrastructure, such as outdated routers or modems, can contribute to congestion.
To check for network congestion and determine if it is affecting your internet speed, you can perform a speedtest. This test measures the upload and download speeds of your internet connection and provides an indication of the overall network performance. If the speedtest results show significantly lower speeds than what you are paying for, network congestion may be a contributing factor.
To mitigate the effects of network congestion, internet service providers may implement techniques such as Quality of Service (QoS) or traffic shaping. These methods prioritize certain types of data, such as streaming or VoIP, over others to ensure a smoother user experience. However, it’s important to note that during periods of high congestion, these measures may not completely eliminate the impact on internet speeds.
In conclusion, network congestion is a common issue that can affect internet speeds. Understanding its causes and effects can help users better manage their internet connection and seek solutions to improve their browsing, streaming, and downloading experiences.
Importance of Kb/s for internet speed
In the world of technology and connectivity, internet speed plays a crucial role in the overall browsing experience. One of the key factors that determine the internet speed is the upload and download speed, measured in kilobits per second (Kb/s). Upload speed refers to the rate at which data is transferred from your device to the internet, while download speed refers to the rate at which data is transferred from the internet to your device.
Bandwidth, also known as network speed, is the maximum rate at which data can be transferred over a network. It determines the capacity of your internet connection and is often an important factor in determining the Kb/s rate. A higher bandwidth allows for faster Kb/s rate, resulting in quicker upload and download speeds.
Modem and router are two crucial devices that affect the Kb/s rate. A modem is used to connect your home network to the internet, while a router helps in creating a local network for multiple devices. The quality and capabilities of these devices have a direct impact on the speed and stability of your internet connection. Upgrading your modem or router can significantly improve the Kb/s rate and overall internet speed.
Streaming services, such as Netflix or YouTube, rely heavily on Kb/s rate for smooth playback. The Kb/s rate determines the speed at which the data is transferred to your device for streaming. A higher Kb/s rate ensures uninterrupted streaming without buffering or lagging issues.
Furthermore, uploading large files or data to the internet requires a good Kb/s rate. Whether you are sharing files online or using cloud storage services, a faster upload speed ensures quicker and smoother data transfer.
It is important to regularly check your internet speed using speedtest tools to ensure you are getting the desired Kb/s rate. A slower Kb/s rate can lead to slow loading times, buffering issues, and overall poor internet experience. By monitoring and optimizing your Kb/s rate, you can enhance your online activities, such as browsing, streaming, gaming, and file transfer.
- Key points:
- – Kb/s rate determines the upload and download speed of your internet connection
- – Bandwidth plays a crucial role in determining the Kb/s rate
- – Modem and router quality affects the Kb/s rate
- – Streaming services and uploading large files require a good Kb/s rate
- – Regularly checking and optimizing your Kb/s rate is essential for a better internet experience
Downloading and streaming content
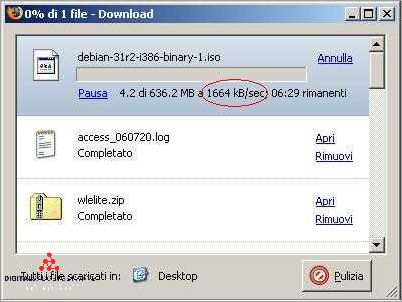
When it comes to accessing content on the internet, there are two common methods: downloading and streaming. Both methods involve transferring data from a source to your device, but they differ in terms of how the data is processed and accessed.
Downloading refers to the process of copying files from a remote server and saving them on your device’s storage. This can include files such as documents, images, videos, or software. When you download content, the data is transferred from the server to your device through your internet connection.
Streaming, on the other hand, involves playing media content in real-time directly from a server without having to download the files. This is commonly used for online video and music platforms where users can watch or listen to content without the need to wait for the entire file to be downloaded.
Your internet speed and network connection play significant roles in both downloading and streaming. The download and upload speeds, measured in kilobits per second (Kb/s) or megabits per second (Mb/s), determine the rate at which data can be transferred between your device and the internet.
With a faster internet speed and a stable connection, you can download and stream content more quickly and smoothly. Slow internet speeds can result in buffering or delays when streaming, causing interruptions in the content playback. To check your internet speed, you can use online speed test tools that measure your download and upload speeds.
It’s important to note that while downloading requires a one-time transfer of the entire file, streaming involves a continuous transfer of data. This means that streaming typically requires a faster internet speed than downloading, as your device needs to receive enough data in real-time to play the media content without interruptions.
Additionally, streaming consumes more bandwidth compared to downloading. Bandwidth refers to the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted over your internet connection at a given time. The higher the bandwidth, the more data can be transferred, allowing for smoother and higher-quality streaming experiences.
Having a stable and reliable internet connection is crucial for both downloading and streaming. This requires a well-functioning router, modem, and networking equipment to ensure a consistent flow of data between your device and the internet. It’s also essential to monitor your data usage, as streaming content, especially in high definition, can consume a significant amount of data.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between downloading and streaming, as well as the factors that affect your internet speed, can help you make informed decisions when it comes to accessing and enjoying online content.
Online gaming and video conferencing
Online gaming and video conferencing require a stable and high-speed internet connection to ensure a smooth and uninterrupted experience. The data transfer speed, measured in kilobits per second (Kb/s) or megabits per second (Mb/s), plays a crucial role in determining the quality of these activities.
Broadband internet, provided by your internet service provider (ISP), is essential for online gaming and video conferencing. The broadband connection, usually established through a modem and a router, allows for faster data transmission compared to dial-up connections.
When it comes to online gaming, a high speed and low latency, or network delay, are crucial for a seamless experience. Gamers need to have a fast and stable connection to interact with other players and respond to the game’s actions in real-time. Slow speeds can result in lag, which can be frustrating and affect gameplay.
For video conferencing, a fast upload and download speed are important for smooth streaming and clear communication. Uploading and downloading large chunks of data in real-time ensures that video and audio streams are sent and received without delays or interruptions. Bandwidth, which refers to the maximum amount of data that can be transferred over an internet connection within a given time frame, also plays a role in determining the quality of video conferencing.
To ensure your network is capable of supporting online gaming and video conferencing, you can use online speed testing tools to measure your connection’s speeds. A speed test measures the download and upload speeds, as well as ping, which indicates the latency or delay in milliseconds. These tests can help identify any network issues and allow you to take necessary steps to improve your internet connection.
Overall, a fast and reliable internet connection is essential for online gaming and video conferencing. Understanding your network’s speed and taking measures to optimize it can greatly enhance your gaming experience and ensure clear and uninterrupted video conferences.
Improving Kb/s and internet speed
There are several steps you can take to improve your Kb/s and internet speed. First, check the speed of your internet connection by running a speedtest. This will give you an idea of the current upload and download speeds.
If you are experiencing slow speeds, it may be due to your modem or router. Consider upgrading to a faster modem or router that supports higher bandwidth. This can provide a more stable and faster connection, improving your overall internet speed.
Another factor that can affect your internet speed is the number of devices connected to your network. If you have multiple devices connected to the same network, it can cause congestion and slow down your internet speed. Consider disconnecting unused devices or upgrading your network to handle more devices.
Optimizing your network settings can also help improve your Kb/s and internet speed. Make sure your network is properly configured and that you are using the latest firmware for your modem and router. This can help optimize your network and improve its performance.
In addition, consider using a wired connection instead of Wi-Fi if possible. A wired connection can provide a more stable and faster connection compared to Wi-Fi, especially for activities such as streaming or online gaming.
If you frequently download or upload large amounts of data, consider upgrading to a broadband plan with higher speeds. This can provide faster transfer rates, allowing you to download or upload files more quickly.
Finally, be mindful of your internet activities that may affect your speed. Streaming videos or music, playing online games, and downloading large files can all consume a significant amount of bandwidth and slow down your internet speed. Limiting these activities or scheduling them during off-peak hours can help improve your Kb/s and overall internet speed.
Upgrading internet connection
If you find that your internet speed is not meeting your needs, it may be time to consider upgrading your internet connection. There are several factors to consider when upgrading, including your internet speed, router, and modem.
First, you need to determine your current internet speed. This can be done by running a speedtest, which measures the rate at which data is transferred over your network. The results will be displayed in kilobits per second (Kb/s) or megabits per second (Mb/s), indicating the speed at which you can download or upload data.
If your speedtest results show a slow internet speed, it may be due to outdated equipment. Upgrading your router and modem can significantly improve your internet speed. A router is responsible for transmitting data between your devices and the internet, while a modem connects your network to your internet service provider (ISP).
In addition to upgrading your equipment, consider increasing your bandwidth. Bandwidth is the amount of data that can be transmitted over a network at a given time. By increasing your bandwidth, you can support activities such as streaming, gaming, and downloading large files without experiencing buffering or lagging.
When upgrading your internet connection, consider your specific needs. If you frequently stream videos or participate in online gaming, you may require a higher download speed. On the other hand, if you regularly upload large files, a higher upload speed may be necessary. Check with your ISP to see what options are available for your specific needs.
Finally, it’s important to understand the difference between broadband and networking. Broadband refers to high-speed internet access that is always on and faster than traditional dial-up connections. Networking, on the other hand, involves connecting multiple devices to share resources and access the internet. Understanding these concepts can help you make informed decisions when upgrading your internet connection.
Optimizing network settings
If you want to maximize your internet speed and ensure a smooth online experience, optimizing your network settings is key. Here are some tips to help you get the most out of your internet connection.
1. Run a speedtest: Before making any adjustments to your network settings, it’s important to know your current internet speed. Use an online speedtest tool to measure your download and upload speeds in megabits per second (Mbps).
2. Upgrade your modem/router: If you’re experiencing sluggish internet speeds, it may be time to upgrade your modem or router. Older devices may not be capable of handling higher broadband speeds, causing slower data transfer rates.
3. Check your network bandwidth: Make sure your internet service provider (ISP) is delivering the bandwidth speed you’re paying for. If you’re not getting the promised speed, contact your ISP for support.
4. Optimize your network settings: Adjust your router’s settings to prioritize certain types of network traffic. For example, you can set it to give priority to streaming services, which will ensure smoother playback and fewer buffering issues.
5. Limit background downloads: Some devices or applications may be using up your internet bandwidth without you realizing it. Check for any active downloads or updates and pause or limit them to improve your internet speed.
6. Secure your network: Protect your network from unauthorized access by setting a strong password for your Wi-Fi network. This will prevent others from piggybacking on your connection and potentially slowing it down.
7. Consider a wired connection: If you’re experiencing slow internet speeds while using Wi-Fi, try connecting your device directly to the router using an Ethernet cable. Wired connections tend to offer more stable and faster speeds.
8. Clear cache and temporary files: Regularly clear your browser cache and temporary files to optimize your internet browsing speed. These files can accumulate over time and slow down your online experience.
By following these optimization tips, you can ensure a faster and more reliable internet connection, whether you’re streaming your favorite shows, browsing the web, or gaming online.
Using wired connections instead of wireless
One way to improve your internet speed is by using wired connections instead of relying on wireless connections. While wireless connections are convenient and allow for mobility, they often have limitations that can affect your internet speed and overall experience.
With a wired connection, you can take advantage of a dedicated physical connection to your modem or router, which can provide a more stable and consistent internet connection. This can result in faster upload and download speeds, as well as reduce buffering and lag when streaming or gaming online. Wired connections also typically offer higher bandwidth and lower latency compared to wireless connections.
To set up a wired connection, you will need an Ethernet cable to connect your computer or device directly to your modem or router. This allows for a direct transfer of data between your device and the internet, bypassing any potential interference or limitations that may occur with wireless connections.
When using a wired connection, it is important to ensure that you have a compatible network adapter on your device, such as an Ethernet port or a USB-to-Ethernet adapter. You may also need to configure your network settings to prioritize the wired connection over any available wireless connections.
Overall, using a wired connection can greatly improve your internet speed and provide a more reliable and consistent online experience. If you regularly perform tasks that require high-speed internet, such as streaming or uploading large files, a wired connection is recommended to optimize your broadband connection.
FAQ about topic “Understanding Kb/s: Exploring the Impact of Internet Speed and Bandwidth”
What is Kb/s and how does it affect my internet speed?
Kb/s stands for kilobits per second. It is a unit of measurement used to quantify the data transfer rate of your internet connection. The higher the Kb/s, the faster your internet speed, as it indicates how quickly data can be downloaded or uploaded.
How do I calculate the actual download speed based on the Kb/s?
To calculate the actual download speed, you need to convert Kb/s to kilobytes per second (KB/s). Since there are 8 kilobits in a kilobyte, you can divide the Kb/s value by 8 to get the download speed in KB/s. For example, if your internet speed is 512 Kb/s, the actual download speed would be 64 KB/s.
Is Kb/s the only factor that affects my internet speed?
No, Kb/s is not the only factor that affects your internet speed. Other factors include your internet service provider’s (ISP) infrastructure, the type of internet connection you have (such as DSL or fiber optic), network congestion, and the distance between your device and the ISP’s servers. These factors can influence your internet speed and performance.
What is the difference between Kb/s and Mbps?
Kb/s and Mbps are both units of measurement for data transfer rates, but they represent different scales. Kb/s stands for kilobits per second, while Mbps stands for megabits per second. 1 Mbps is equivalent to 1000 Kb/s. Mbps is typically used to describe higher internet speeds, while Kb/s is used for slower internet connections.
How can I increase my Kb/s and improve my internet speed?
There are several ways to increase your Kb/s and improve your internet speed. First, you can contact your ISP and inquire about upgrading your internet plan to a higher speed tier. Additionally, you can optimize your Wi-Fi network by placing your router in a central location, minimizing interference from other devices, and using a wired connection if possible. Cleaning up your computer system by removing unnecessary programs and malware can also help improve internet speed.


