
When it comes to acronyms and abbreviations, it can sometimes be difficult to understand their true meaning. They often carry a sense of significance and symbolize something specific. One such acronym is SFM, which has an interpretation that might not be immediately clear to everyone.
The term SFM stands for “Synchronous Form Method”, and it conveys a particular implication in the field of computer graphics. It is commonly used to represent a specific technique or approach used in 3D animation and modeling. SFM is a popular tool among artists and designers, as it helps to streamline the process of creating realistic and visually stunning animations.
The abbreviation SFM denotes a specific set of techniques and practices that allow artists to create lifelike and dynamic animations. It refers to the use of mathematical algorithms and computational models to generate realistic movement and motion. SFM is often used in the creation of video games, movies, and other forms of digital media.
It is important to note that SFM has a specific connotation within the field of computer graphics and animation. While it may have other meanings in different contexts, in the realm of CGI, SFM is primarily associated with the techniques and tools used to create realistic and visually stunning animations.
In conclusion, SFM is an acronym that stands for “Synchronous Form Method” and refers to a specific set of techniques used in computer graphics and animation. The term carries a specific connotation and is commonly used in the creation of lifelike and dynamic visuals in various forms of digital media. Understanding the meaning and implications of SFM is crucial for anyone involved in the field of 3D animation and modeling.
Contents
- 1 Section 1: Understanding the Meaning of SFM
- 2 Section 2: Importance of SFM
- 3 Section 3: Implementing SFM Practices
- 4 Section 4: Examples of SFM in Action
- 5 FAQ about topic “Understanding SFM: Decoding the Meaning behind the Acronym”
- 6 What is SFM?
- 7 Is SFM free to use?
- 8
- 9 Can I import my own models and assets into SFM?
- 10
Section 1: Understanding the Meaning of SFM
In the world of abbreviations, SFM is one that might not be immediately recognizable to everyone. However, it is important to familiarize oneself with this acronym as it has a specific meaning and significance in various contexts.
SFM, short for “Simplified Feature Model,” is an abbreviation commonly used in the field of computer science. In this sense, SFM is a term used to denote a simplified representation of a feature model, which is a conceptual model used in software engineering to represent the features and configurations of a software product.
Furthermore, SFM can also stand for “Science Fiction and Fantasy Movies,” which refers to a genre of movies that combine elements of science fiction and fantasy. In this context, SFM represents a specific genre that is often characterized by futuristic settings, advanced technology, and imaginative storytelling.
It is essential to note that the interpretation of SFM can vary depending on the context in which it is used. Therefore, it is crucial to seek clarification to ensure a proper understanding of the acronym’s intended meaning. Whether it is used in the field of computer science or to refer to a specific genre of movies, SFM is an acronym that conveys a particular sense and implication.
In summary, SFM can mean different things depending on the context. It can be an abbreviation for “Simplified Feature Model” in the field of computer science or “Science Fiction and Fantasy Movies” in the context of film genres. Each interpretation has its own significance and requires an explanation or clarification to fully understand the meaning that SFM is intended to convey.
Subsection 1.2: Origins of SFM
The term SFM is an abbreviation for “Spare the Female Mosquito,” which is a phrase that originated in the field of entomology. It was first used to convey the importance of preserving female mosquitoes for scientific research and control measures.
The interpretation of SFM can also symbolize the high significance of female mosquitoes in various ecological and public health contexts. The implication of SFM is that female mosquitoes play a crucial role in disease transmission, as they are typically the ones responsible for biting and infecting humans with pathogens.
Furthermore, SFM can be seen as a clarification of the connotation associated with female mosquitoes, as it highlights their importance rather than solely focusing on their nuisance value. The term SFM serves as a means to denote the representation of female mosquitoes beyond their reputation as blood-sucking pests.
Therefore, SFM serves as a sense of explanation and definition for the term “Spare the Female Mosquito,” emphasizing the need to understand the role of female mosquitoes in order to develop effective control strategies. It stands for the idea that female mosquitoes should not be eradicated but rather managed to reduce disease transmission.
Subsection 1.3: Definition and Scope of SFM
The term SFM represents the acronym for “Shared Family Media”, an abbreviation commonly used to denote the concept of sharing media content within a family unit. In this sense, the term SFM is used as a representation of the practice of families sharing various types of media, such as photos, videos, and music, amongst themselves.
Having a clear definition and scope for SFM is important for proper interpretation and understanding of its implication. SFM, in its broadest sense, refers to the act of sharing media content within a family, encompassing the various ways in which families choose to share and consume media as a unit.
It is essential to clarify that SFM does not solely imply sharing media content through traditional means, such as physical copies or storage devices. In the digital age, SFM also encompasses the sharing of media through online platforms, social media, and cloud-based services.
The significance of SFM lies in the way it symbolizes the changing dynamics of media consumption and the evolving role of technology within families. Understanding SFM helps convey the idea that media is not limited to individual experiences but is also meant to be shared and enjoyed collectively within a family unit.
In conclusion, SFM, as an abbreviation, serves as a shorthand representation of the practice and concept of sharing media within a family. Its definition and scope have expanded to include both traditional and digital means of sharing, symbolizing the changing dynamics of media consumption in modern households.
Section 2: Importance of SFM
The term “SFM” stands for “Sustainable Forest Management.” It is an important concept in the field of forestry that refers to the responsible and sustainable management of forests. SFM is a representation of the efforts taken to ensure the long-term health and productivity of forest ecosystems while also considering social, economic, and ecological factors.
SFM has great significance in the context of environmental conservation and resource management. It denotes a holistic approach to forest management that takes into account the interconnectedness of ecological, economic, and social systems. SFM aims to balance the exploitation of forest resources with the preservation of biodiversity, carbon sequestration, and the provision of ecosystem services.
The importance of SFM lies in its ability to convey the idea of sustainable and responsible forest management. It goes beyond the simple definition of forest management and carries a broader connotation of ecological stewardship and long-term planning. SFM represents a commitment to maintaining the health and vitality of forests for future generations.
When we talk about SFM, we are not only referring to a specific set of practices and guidelines but also symbolizing the values of sustainability, conservation, and environmental protection. SFM serves to ensure that forests are managed in a way that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
In summary, SFM is an acronym that stands for Sustainable Forest Management. It serves as a representation of the concept of responsible and sustainable forest management and carries a broader connotation of environmental stewardship. SFM is of great importance in the field of forestry as it signifies the commitment to conserving forest ecosystems and ensuring their long-term health and productivity.
Subsection 2.1: Environmental Benefits of SFM
SFM, which stands for Sustainable Forest Management, is a term that carries a significant connotation in the context of environmental conservation and preservation. Its interpretation and representation go beyond a simple definition or implication. SFM denotes a set of principles and practices aimed at ensuring the responsible use of forests and their resources to meet the needs of both present and future generations.
The term SFM is an abbreviation that serves to convey the idea of managing forests sustainably. It is an acronym that symbolizes the importance of balancing environmental, social, and economic factors in forest management. By using the term SFM, it is possible to clarify the goals and objectives of sustainable forest management in a concise manner.
The significance of SFM lies in its ability to foster sustainable development while preserving the integrity and health of forests. It refers to the responsible use of forest resources, including timber, while minimizing negative impacts on the environment. The term SFM implies the need to conserve biodiversity, protect ecosystem services, and mitigate climate change through sustainable forest practices.
Understanding the environmental benefits of SFM requires a comprehensive explanation of its principles and practices. SFM aims to maintain or enhance forest ecosystem health and vitality, while also protecting and promoting the diversity of plant and animal species. It involves the prudent and efficient use of forest resources to ensure their long-term availability and to support sustainable livelihoods for local communities.
By implementing SFM, forests have the potential to contribute to the conservation of water resources, the prevention of soil erosion, and the mitigation of natural disasters. Sustainable forest management also plays a crucial role in addressing climate change, as forests can serve as carbon sinks, absorbing and storing significant amounts of CO2.
In summary, SFM represents an approach to forest management that emphasizes the importance of environmental benefits. It goes beyond a simple definition or abbreviation, as it encompasses a wide range of practices and principles. SFM signifies the responsible use of forest resources, the conservation of biodiversity, and the mitigation of climate change in the context of sustainable development.
Subsection 2.2: Economic Significance of SFM
The connotation of SFM, which stands for Sustainable Forest Management, revolves around the interpretation of its economic significance. As a term commonly used in the forestry sector, SFM holds a significant role in the sustainable use of forest resources.
When discussing the economic significance of SFM, it is important to clarify its definition and what it truly signifies. SFM is not simply an acronym or abbreviation; it is an explanation of a comprehensive approach to managing forests in a sustainable manner.
SFM denotes the representation of sustainable practices in the forestry industry, considering the social, environmental, and economic aspects. It symbolizes the responsible and long-term use of forest resources to meet both present and future needs of the society.
The significance of SFM lies in its ability to convey the importance of maintaining a balance between economic development and environmental conservation. It refers to the understanding that sustainable forest management can contribute to the growth of economies by providing a continuous supply of timber and non-timber forest products, while also preserving the biodiversity and ecosystem services that forests offer.
The economic sense of SFM is seen in its potential to create employment opportunities, generate income, and support local communities that depend on forest resources. It signifies the value of forests beyond their immediate economic benefits, including their role in carbon sequestration, water regulation, and as a habitat for various flora and fauna.
To fully understand the economic significance of SFM, it is crucial to recognize its role in promoting sustainable practices that are economically viable, socially just, and environmentally sound. By implementing SFM, forests can become a source of wealth and prosperity while preserving their ecological integrity, contributing to a more sustainable and resilient future.
Subsection 2.3: Social Impacts of SFM
SFM, which is an abbreviation for sustainable forest management, has several social impacts. These impacts can have representation and implication in various ways, depending on the context in which the term SFM is used. When people refer to SFM, they generally mean the practice of managing forests in a sustainable and responsible manner. This definition of SFM symbolizes the importance of balancing environmental, social, and economic factors in forest management.
The term SFM can denote different things to different people, depending on their interpretation. For some, SFM may convey the idea of conservation and protection of forests, ensuring that future generations can benefit from their resources. For others, SFM may mean promoting responsible logging practices, ensuring that timber is harvested sustainably without causing harm to the environment or local communities.
Social impacts of SFM have significant importance in terms of the livelihoods and well-being of local communities. Sustainable forest management can provide employment opportunities, particularly in rural areas where forests are often the primary source of income. This can contribute to poverty alleviation and improve social conditions in forest-dependent communities.
In addition, SFM can have positive impacts on indigenous peoples and local communities by recognizing and respecting their rights, traditional knowledge, and cultural values. This can help to preserve their cultural heritage and strengthen their sense of identity. SFM can also contribute to community empowerment and involvement in decision-making processes related to forest management.
However, it is important to clarify that SFM is not a one-size-fits-all concept. It can have different connotations and explanations depending on the specific context and objectives of forest management. The significance of SFM lies in its ability to balance environmental, social, and economic considerations and ensure the long-term sustainability of forests for future generations.
Section 3: Implementing SFM Practices
When discussing SFM, it is important to understand what the term actually means, as well as its significance and implication. SFM, which is an abbreviation of Sustainable Forest Management, refers to the practice of managing forests in a way that balances environmental, social, and economic factors. The term SFM is an acronym that is often used to denote this concept.
The explanation and definition of SFM can vary slightly depending on the interpretation and understanding of different individuals and organizations. However, in a general sense, SFM stands for the principles and practices that aim to ensure the long-term health and productivity of forests while also considering the needs and interests of communities and industries that rely on them.
Implementing SFM practices involves taking into account various factors, such as biodiversity, ecosystem services, and the socioeconomic well-being of local communities. It also requires considering the impacts of forest management decisions on future generations and the global environment. SFM symbolizes the commitment to sustainable practices that promote forest conservation and promote the sustainable use of forest resources.
It is important to note that SFM is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Each region and forest requires its own set of practices and strategies based on its unique ecological and social context. SFM practices can vary across different countries and regions, reflecting the specific priorities and challenges faced by each area.
In summary, implementing SFM practices requires a comprehensive approach that balances the ecological, social, and economic aspects of forest management. SFM serves as an important tool for ensuring the long-term sustainability of forests and the well-being of communities that depend on them.
Subsection 3.1: Key Principles of SFM
When discussing SFM, it is important to have a clear definition of the term. SFM, or Sustainable Forest Management, is an approach that aims to balance the environmental, social, and economic aspects of forest management. It is about making decisions and taking actions that ensure the long-term health and viability of forest ecosystems, while also providing benefits to society. SFM recognizes that forests have multiple values and functions, and seeks to manage them in a way that meets the needs of present and future generations.
Representation is another key principle of SFM. Forests are complex systems with a wide range of ecological, social, and economic dimensions. SFM requires a holistic approach to forest management that takes into account the various components and interactions within a forest ecosystem. It means considering the needs and perspectives of different stakeholders, including local communities, Indigenous peoples, industry, and government, in the decision-making process.
Symbolization is an important aspect of SFM. Symbols, such as logos or certification marks, can be used to denote that a forest or forest product has been managed in accordance with SFM principles and criteria. These symbols help consumers and other interested parties to identify and support sustainable forest practices. They provide a visual representation that communicates a commitment to responsible forest management.
SFM also requires clarification and interpretation. The term itself, as well as its abbreviation, can have different connotations and understandings in different contexts. It is important to provide clear explanations and definitions to ensure a common understanding of what SFM means and entails. This includes clarifying any misconceptions or misinterpretations that may arise, and promoting a consistent and accurate understanding of the concept.
The significance and implication of SFM are far-reaching. It is not just about managing forests sustainably, but also about contributing to broader sustainable development goals. SFM can help address issues such as climate change, biodiversity conservation, and poverty reduction. It can promote the sustainable use of forest resources, support local livelihoods, and protect and enhance ecosystem services. SFM is a powerful tool for achieving both environmental and social objectives, and it is essential for the long-term well-being of our forests and societies.
Subsection 3.2: Tools and Technologies for SFM
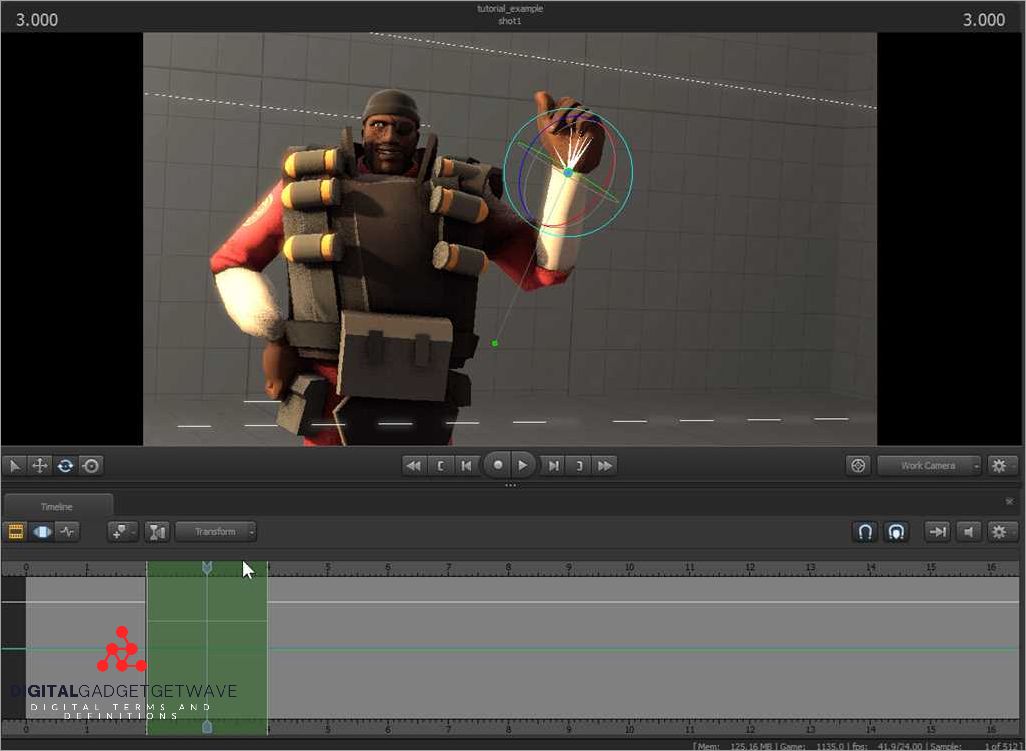
In the context of SFM, there are various tools and technologies that are utilized to aid in the process of creating and managing 3D models and animations. These tools serve to enhance the productivity and efficiency of artists and animators, allowing them to bring their ideas to life in a more streamlined and intuitive manner.
One of the key tools commonly used in SFM is Clarification. This tool allows artists to annotate and provide detailed explanations for specific elements within their creations. With Clarification, artists can denote the significance and convey the intended connotation of certain symbols or representations within their work, helping viewers better understand the underlying meaning and implication of the artwork.
Another important technology in SFM is the use of Abbreviation. Abbreviations are used to represent complex terms and concepts in a simplified manner. By using abbreviations, artists and animators can save time and effort in explaining long and intricate definitions, allowing them to focus more on the creative process.
Furthermore, SFM makes use of various acronym tools that help artists define and refer to specific elements within their work. Acronyms are essentially shortened versions of words or phrases, and they serve as a convenient way to quickly and easily identify and understand different components of a 3D model or animation.
Finally, SFM utilizes different design and rendering software to bring the created models and animations to life. These tools enable artists to manipulate and transform the objects they have created, adding movement, texture, and other visual effects to enhance the overall sense of realism and immersion.
In conclusion, the tools and technologies used in SFM play a crucial role in facilitating the creation and management of 3D models and animations. They help artists and animators clarify the meaning and implication of their work, convey complex definitions and concepts in a simplified manner, and provide a visual representation and connotation to the audience.
Subsection 3.3: Challenges and Solutions in SFM
One of the main challenges in the context of SFM is the abundance of abbreviations and acronyms used in this field. These abbreviations and acronyms can have different connotations and implications, making it difficult for individuals to understand their exact meaning. Therefore, it is crucial to provide a clear definition and clarification of these terms to ensure effective communication and understanding.
The significance of accurately conveying what these abbreviations and acronyms denote cannot be overstated. They are often used to symbolize complex concepts and refer to specific processes or procedures in SFM. Therefore, an accurate interpretation and representation of these terms is vital to avoid confusion and miscommunication within the SFM community.
Another challenge is the multiplicity of interpretations that can arise from these abbreviations and acronyms. Different individuals or organizations may have different understandings or definitions for the same term. This can lead to confusion and hinder collaboration and knowledge exchange. Therefore, it is essential to establish a common understanding and interpretation of these terms for effective communication and cooperation.
One possible solution to address these challenges is to create a comprehensive glossary that provides detailed explanations and definitions for all the relevant terms used in SFM. This glossary could serve as a reference for individuals seeking clarification or wanting to understand the meaning of specific abbreviations or acronyms. Additionally, it would help establish a common language and promote consistent communication within the SFM community.
An alternative solution could be the use of standardized terminology and nomenclature. By establishing a set of agreed-upon terms and definitions, the potential for confusion and misinterpretation is minimized. This approach would require a collaborative effort among experts and stakeholders in SFM to reach a consensus regarding the terminology and its implications. Once agreed upon, these standardized terms can be used to enhance communication and understanding across the SFM community.
In conclusion, the challenges related to abbreviations and acronyms in SFM can hinder effective communication and cause misunderstandings. To overcome these challenges, it is essential to provide clear definitions, establish common interpretations, and promote standardized terminology. By doing so, the SFM community can enhance collaboration and knowledge exchange, leading to more efficient and sustainable forest management practices.
Section 4: Examples of SFM in Action
Now that we understand what the acronym “SFM” stands for and its abbreviation for “Symbolic FM,” let’s explore some examples of SFM in action to get a better sense of its connotation and significance.
In the context of music, SFM can denote the interpretation and representation of a song or piece through symbols. For example, a musical score can use various symbols and notations to convey the desired tone, dynamics, and expression of the music.
In the field of graphic design, SFM can refer to the use of symbols and visual elements to convey a specific message or meaning. For instance, a company logo or brand identity can employ symbols and typography to represent the values, mission, and personality of the brand.
Another example of SFM is seen in the realm of mathematics and logic. Here, symbols and notations are used to clarify and understand complex equations or statements. Mathematical symbols such as “+” and “-” convey specific operations, while logical symbols like “∨” and “¬” denote logical connectives and propositions.
Furthermore, SFM can be observed in the field of linguistics and language. Symbols and signs are used to represent sounds, words, and meanings, aiding in communication and understanding. For instance, the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) uses symbols to represent the sounds of different languages, enabling accurate pronunciation and transcription.
In conclusion, SFM, or Symbolic FM, encompasses various domains where symbols and representations are used to convey meaning, clarify interpretation, and facilitate understanding. Whether in music, design, mathematics, or linguistics, SFM plays a significant role in communication and expression.
Subsection 4.1: Case Study 1: Sustainable Forest Management in Country X
In the context of sustainable forest management (SFM), the abbreviation SFM holds significant connotation and carries a specific meaning. It is important to understand what SFM means and the implications it has. SFM does not denote a single sense or interpretation, but rather, it represents a comprehensive approach to managing forests that aims to balance environmental, social, and economic factors.
SFM stands for sustainable forest management, and it refers to the responsible use and conservation of forests to ensure their long-term sustainability. The term symbolizes the need to manage forests in a way that meets the needs of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. SFM involves the integration of ecological, economic, and social considerations, and it promotes the wise use of forest resources.
The definition of SFM requires clarification and further explanation, as it encompasses various aspects and principles. These principles include maintaining forest health and biodiversity, ensuring the productive functions of forests, fostering social and economic benefits, and promoting effective governance and stakeholder involvement.
In the case study of sustainable forest management in Country X, it is crucial to analyze how SFM is implemented and what measures are taken to achieve sustainable outcomes. This case study explores the specific context and challenges faced by Country X in managing its forest resources sustainably, considering its unique ecological, economic, and social characteristics. The case study presents an opportunity to learn from Country X’s experiences and identify best practices that can be applied in other regions.
Through this case study, it becomes evident that SFM goes beyond being a mere acronym or a technical term. It represents a comprehensive approach that requires collaboration, knowledge sharing, and the integration of multiple perspectives. The case study highlights the importance of balancing environmental conservation, social well-being, and economic development in the management of forests for the benefit of present and future generations.
Subsection 4.2: Case Study 2: Successful SFM Initiatives in Company Y
In the context of SFM (Sustainable Forest Management), it is important to refer to successful case studies to understand the implications and significance of implementing SFM initiatives. In this subsection, we will discuss Case Study 2, which highlights the successful SFM initiatives undertaken by Company Y.
SFM, as we know, stands for Sustainable Forest Management. However, its connotation goes beyond just a simple definition. It denotes a set of practices and principles aimed at ensuring the long-term environmental, social, and economic sustainability of forests. In the case of Company Y, SFM represents their commitment to responsible forestry practices that prioritize environmental conservation while maintaining profitability.
Company Y’s successful SFM initiatives were driven by their interpretation of the term “sustainability.” They recognized that sustainability goes beyond managing resources efficiently and also involves incorporating social and economic aspects into forest management. Through their SFM initiatives, Company Y aimed to strike a balance between environmental conservation, community engagement, and economic growth.
The term SFM, therefore, serves as a representation of Company Y’s commitment to sustainable practices. It symbolizes their dedication to managing forests in a way that ensures a healthy ecosystem, benefits local communities, and supports their business objectives. SFM, in this context, stands for a holistic approach to forest management that considers the present as well as future generations.
This case study serves as a clarification of SFM and its implications in a real-world scenario. Company Y’s successful SFM initiatives demonstrate the positive outcomes that can be achieved when sustainable practices are implemented effectively. It highlights the importance of understanding and embracing the values that SFM symbolizes, as it is not merely an abbreviation but a comprehensive approach to responsible forest management.
Subsection 4.3: Case Study 3: Community-led SFM Projects
In this subsection, we will explore a case study that exemplifies the concept of Community-led SFM projects. But first, let’s clarify what SFM stands for and what it denotes in this context.
SFM is an acronym that stands for Sustainable Forest Management. It is a term used to convey the interpretation and understanding of practices that aim to ensure the long-term health and productivity of forests while considering social, environmental, and economic aspects.
When we refer to SFM projects, we are talking about initiatives and actions implemented by communities to achieve sustainable forest management. These projects bring together local stakeholders, such as indigenous groups, forest-dependent communities, and NGOs, to collaboratively manage and protect forest resources.
The significance of community-led SFM projects lies in their representation of a bottom-up approach. These projects empower communities and give them a sense of ownership and responsibility for the forests they depend on. They recognize and integrate traditional knowledge and practices, ensuring that sustainable management strategies are culturally appropriate and environmentally sound.
Community-led SFM projects symbolize the abbreviation SFM by putting it into action, going beyond a simple definition. They demonstrate the practical application of SFM principles, showcasing sustainable practices that promote biodiversity conservation, livelihood improvement, and the sustainable use of forest resources.
In conclusion, this case study on community-led SFM projects offers a deeper understanding of the term SFM and its connotation in the context of sustainable forest management. It highlights the importance of community engagement, collaboration, and empowerment in achieving long-term sustainability.
FAQ about topic “Understanding SFM: Decoding the Meaning behind the Acronym”
What is SFM?
SFM stands for Source Filmmaker. It is a video creation and editing software developed by Valve Corporation, the same company behind popular games like Half-Life and Team Fortress. SFM allows users to create animated movies and scenes using the assets and characters from Valve’s Source engine games.
Is SFM free to use?
Yes, SFM is available as a free download on the Steam platform. It was originally released as a tool for the community to create their own content using Valve’s games, but it has since grown in popularity and has been widely used by both amateurs and professionals in the animation industry.
Can I import my own models and assets into SFM?
Yes, SFM allows users to import their own custom models, textures, sounds, and other assets into the software. This gives users a great deal of flexibility and creativity in designing their own scenes and animations. There are also many online communities and resources where users can find and share custom assets for SFM.


