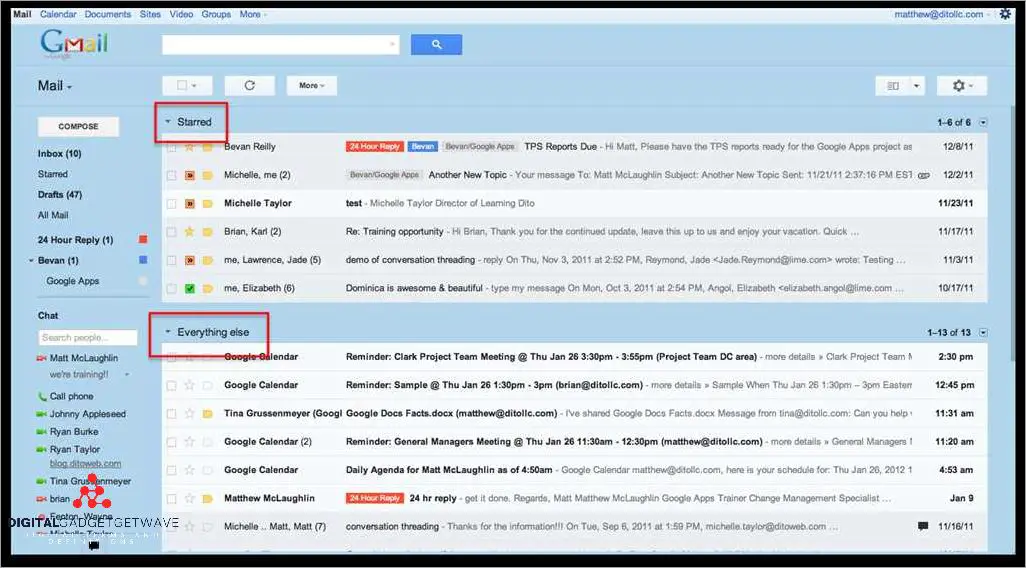
An inbox refers to the digital storage space where messages, emails, and other forms of communication are received and stored. It is a common feature in various communication platforms and email services. In an inbox, users can find their received messages, organized by date and sender, allowing for easy access and management of incoming communications.
Messages in an inbox are typically organized as individual threads, grouping conversations between the user and other parties. This thread-based organization helps users keep track of the context and history of their conversations, making it easier to follow and respond to ongoing discussions.
Within an inbox, users have several tools and functions to manage their messages effectively. They can flag important messages for quick reference or mark them as spam to filter out unwanted communications. Attachments, such as documents or images, can also be found and accessed within the inbox, allowing users to view and download files directly from their received mail.
In addition to received messages, an inbox may also contain other folders, such as the outbox, where users can find messages they have sent but not yet received a reply. There is also a drafts folder for storing unfinished or unsent messages, and an archived folder for keeping important messages for future reference.
Furthermore, an inbox can be customized with various filters and settings. Users can set up filters to automatically sort incoming emails into specific folders or to forward certain messages to other email addresses. They can also manage their subscription preferences, choosing to unsubscribe from unwanted mailing lists or subscribe to notifications for important updates.
Overall, the inbox is a central hub for managing and organizing the flow of digital communication. It is a vital tool for individuals and businesses alike, providing a convenient and efficient way to handle emails, messages, and other forms of communication.
Contents
Definition
Inbox is a folder in an email account where all the mail that a user has received is stored. The inbox displays a list of unread and read messages, allowing the user to easily manage their correspondence.
Unread messages are emails that have not been opened or viewed by the recipient. They are usually highlighted or marked differently in the inbox to indicate their status.
Attachments are files that are included with an email message. They can be documents, images, videos, or any other type of file that the sender wants to share with the recipient.
Spam refers to unsolicited, usually unwanted email messages. These messages are often sent in bulk and may contain advertisements, scams, or malicious content. Email providers usually have spam filters in place to automatically detect and block such messages.
Unsubscribe is an action that allows email recipients to opt out of receiving further emails from a specific sender or mailing list. It usually involves clicking a link included in the email or following a specific unsubscribe process.
Thread refers to a group of related email messages that are part of the same conversation. Email clients often organize threaded messages together, making it easier for users to follow the flow of the conversation.
Sent folder is a folder in an email account where all the emails that the user has sent are stored. It serves as a record of sent messages and can be used for reference or verification purposes.
Outbox is a temporary folder in an email client where outgoing messages are stored before they are sent. Once the email is successfully delivered, it is moved from the outbox to the sent folder.
Priority is a feature that allows users to assign levels of importance to their emails. It helps them differentiate and prioritize their messages based on their urgency or relevance.
Drafts folder is a storage space in an email account where users can save their unfinished or unsent email messages. It allows users to work on their emails over time and provides a convenient location to store drafts before they are ready to be sent.
Received folder is similar to the inbox, but specifically refers to a folder where all the received emails are stored. Some email clients may have separate folders for different types of received messages.
Folder is a container or directory in an email account used to organize and categorize emails. Users can create folders and move messages into them for better management and easy retrieval.
Archived messages are emails that have been intentionally removed from the inbox or other folders and are stored in an archive folder. Archiving helps users declutter their inbox while preserving important messages for future reference.
Notification is a feature that alerts the email account owner about new messages, updates, or changes within the email client. It can be in the form of a sound, pop-up message, or an email notification sent to another account.
Email is an electronic message sent and received over the internet. It allows individuals to communicate with one another through written text, attachments, and other multimedia.
Filter is a tool that allows users to automatically sort, categorize, or block certain types of emails. Filters can be applied based on various criteria like sender, subject, keywords, or other factors specified by the user.
Subscribe is an action that allows users to opt-in to receive emails or updates from a specific sender or mailing list. It usually involves providing an email address and confirming the subscription through a verification process.
Messages refer to individual emails or communications sent or received through an email account. They can contain text, attachments, multimedia, and other forms of digital content.
Understanding the concept of the inbox
The concept of the inbox is central to email communication and organization. An inbox is a digital container where received emails are stored. It serves as a central hub for managing and organizing email messages. When you subscribe to a mailing list or receive a new email, it appears in your inbox.
Filters are a crucial feature of an inbox. They allow you to automatically sort and categorize incoming emails based on specific criteria. For example, you can set up filters to send all emails from a certain sender to a designated folder or label, keeping your inbox organized.
The inbox typically displays various categories of emails, including drafts, unread messages, received emails, and priority emails. Drafts are emails that you have started composing but have not yet sent. Unread messages are emails that you have not yet opened or read. Received emails are all the emails you have received, while priority emails are those flagged as important or urgent.
In an inbox, you can also find attachments. Attachments are files that are included with an email, such as documents, images, or videos. They can be downloaded and viewed separately from the email itself.
Notifications play a vital role in keeping you informed about new emails. When a new message arrives in your inbox, you may receive a notification, either as a sound alert or a visual indicator, depending on your email settings. Notifications ensure that you don’t miss any important emails.
On the other hand, if you no longer want to receive emails from a certain sender or mailing list, you can choose to unsubscribe. Unsubscribing means opting out of further email communication from the sender or mailing list. This helps reduce unwanted emails in your inbox.
An inbox may also have other folders or labels to help you organize your emails more efficiently. For example, you can create folders for different projects, clients, or categories, and move relevant emails into those folders. Flags or markers can also be used to highlight specific emails or mark them for follow-up.
Aside from the inbox, there are other sections in an email client or service that you may come across. These include the outbox, which holds emails that you have composed but not yet sent, the sent folder, which stores copies of sent emails, and the spam folder, where suspicious or unsolicited emails are automatically diverted to.
Emails can be archived for long-term storage. Archived emails are moved out of the main inbox but can still be accessed when needed. This helps declutter the inbox while maintaining a searchable archive of past correspondence.
In conclusion, the inbox is an essential component of email communication, providing a centralized space for managing, organizing, and prioritizing incoming and outgoing messages. Understanding how to effectively use the inbox’s features, such as filters, notifications, folders, and flags, can greatly enhance productivity and efficiency in managing your email correspondences.
Usages
The inbox is where all received emails are stored. When an email is sent to you, it goes to your inbox, where you can read, reply, or delete it. The inbox also displays the priority level of each email, allowing you to quickly identify important messages.
You can flag important emails in your inbox to make them stand out. This can help you prioritize your tasks and make sure you don’t miss any important correspondence. Flagged emails are often displayed with a specific color or symbol next to them to make them more noticeable.
The unread folder in your inbox contains all the emails that you have not opened or marked as read. This folder is particularly useful for keeping track of new messages and making sure you don’t overlook any important information.
Emails that you no longer need can be moved to the archived folder in your inbox. Archiving emails helps you keep your inbox organized and clutter-free. Archived emails can be easily accessed and searched when needed.
The spam folder in your inbox is where emails that are identified as spam or junk are automatically sent. The spam filter scans incoming messages and filters out unwanted or malicious content. It helps protect your inbox from unwanted clutter and potential security threats.
You can subscribe to newsletters or mailing lists to receive regular updates and notifications. Subscription emails are often sent to your inbox, allowing you to stay informed about topics or products that interest you.
Sent messages are copies of emails that you have sent to others. These messages are stored in a separate folder in your inbox, allowing you to keep track of the emails you have sent and review the content if needed.
When you send an email and receive a reply, the conversation is displayed as a thread in your inbox. This allows you to easily follow the flow of the conversation and keep track of multiple messages related to the same topic.
Attachments, such as documents or images, can be included in emails. These attachments are stored in your inbox and can be downloaded or viewed as needed. They are often indicated by a paperclip icon or a similar symbol.
If you no longer wish to receive emails from a particular sender or mailing list, you can unsubscribe from their emails. Most unsubscribe links are included at the bottom of the email, allowing you to easily opt out and remove yourself from their mailing list.
Drafts are unfinished or unsent emails that are saved in your inbox. They can be accessed and edited at a later time before being sent. Drafts allow you to work on an email over time and make sure it is complete and error-free before sending.
How the inbox is used in email communication
In email communication, the inbox serves as the central hub where all received emails are stored. It is the first point of contact for users when they log into their email accounts. The inbox displays a list of email messages, arranged by date and time, and allows users to organize and manage their email correspondence effectively.
When a user receives a new email, it appears in their inbox as an unread message. The user can then open the email to read its content, reply to it, or take any necessary actions. Once the email has been read, it is marked as read and moved to the “read” section, making it easier for the user to identify unread messages.
Users can also organize their inbox by sorting emails into specific folders or labels. This helps in categorizing and prioritizing different types of emails, such as work-related emails, personal emails, or newsletters. Users can create custom folders or utilize pre-existing folders like drafts, sent, spam, or archived, to keep their inbox organized.
Furthermore, the inbox allows users to manage email threads or conversations. When multiple replies are exchanged in response to a single email, the inbox groups them together as a thread. This feature helps users to view the entire conversation history in a chronological order, making it easier to follow the discussion and keep track of the response chain.
The inbox also provides additional features to enhance email communication. Users can attach files or documents to their emails, making it convenient to share important information. They can also set up filtering rules to automatically sort incoming emails based on specific criteria. Additionally, users can flag important emails or set priority levels for certain messages, ensuring that they don’t get missed or overlooked.
It is worth mentioning that email communication is a two-way process. Users can both subscribe and unsubscribe from mailing lists or newsletters depending on their interests and preferences. The inbox also includes an outbox where users can view sent emails awaiting delivery. Users can receive notifications for new emails, allowing them to stay updated and promptly respond to important messages.
Other applications of the inbox in modern technology
Aside from the traditional email inbox, the concept of an inbox has found applications in various other areas of modern technology. One such application is in online messaging platforms. Similar to an email inbox, users have an inbox that displays their received messages, allowing them to manage and respond to them efficiently.
Furthermore, social media platforms also incorporate the concept of an inbox. In this context, the inbox serves as a centralized location where users can receive and send private messages to other users. Users can filter their inbox based on various criteria, such as unread messages or messages from specific contacts, to streamline their communication.
Additionally, project management tools and collaboration platforms often have an inbox feature. This inbox acts as a central hub where users can receive notifications, updates, and alerts related to their tasks and projects. It allows team members to stay informed about important discussions, upcoming deadlines, and changes made by other team members.
In the realm of file management, cloud storage services provide an inbox-like feature for handling file sharing. Users can receive notifications when others share files with them and access these files directly from their inbox. They can also sort and filter their inbox to find specific file attachments or prioritize files based on urgency.
Lastly, inbox functionality is commonly applied in email clients and applications. Users can view their received, sent, and archived emails in a unified inbox, making it easier to manage their communication. They can organize emails into folders, create filters to automatically sort incoming emails, and even thread related emails together for a more coherent view of their email conversations.
Functions

Inbox has several functions that help users manage their emails effectively:
- Priority: Users can set priority levels for their emails, indicating the importance of each message.
- Received: The inbox is the place where all incoming emails are stored and organized for easy access.
- Flag: Users can flag important emails to mark them for future reference.
- Drafts: The inbox also allows users to save draft emails that are not yet ready to be sent.
- Subscribe: Users can subscribe to receive notifications for specific topics or newsletters of interest.
- Mail: The inbox serves as the central location for all incoming and outgoing mail.
- Outbox: The outbox is where emails are temporarily stored before being sent.
- Filter: Users can create filters to automatically sort and organize incoming messages based on specific criteria.
- Messages: The inbox stores all received and sent messages in chronological order for easy reference.
- Folder: Users can create folders in their inbox to categorize and store emails more efficiently.
- Email: The inbox is primarily used for managing emails, both personal and professional.
- Archived: Users can archive old or important emails to remove them from the main inbox and keep them in a separate folder.
- Unread: Unread emails are visually highlighted in the inbox to draw attention to new messages.
- Unsubscribe: Users can easily unsubscribe from unwanted newsletters or mailing lists directly from their inbox.
- Spam: The inbox includes a spam folder where suspicious or unwanted emails are automatically filtered.
- Attachments: Users can send and receive emails with attachments, such as documents, photos, or videos.
- Sent: The inbox also keeps a record of all emails that have been sent.
Key features and functions of an inbox

An inbox is a fundamental component of an email service, providing a user with a centralized location to access and manage their messages. It offers a range of key features and functions that streamline the process of organizing and responding to emails. Here are some of the most important ones:
- Filter: The inbox allows users to set up filters to automatically sort incoming messages based on specific criteria. This helps prioritize important emails and categorize them into different folders.
- Notification: Inbox notifications alert users when new messages or replies are received, ensuring that they can stay up-to-date and respond promptly.
- Thread: Emails are often organized into threads, grouping related messages together. This makes it easier to view the entire conversation in a single thread, helping users follow the flow of communication more efficiently.
- Folder: Folders allow users to organize their emails and store them in specific categories. This helps maintain a tidy inbox and enables easy retrieval of messages in the future.
- Flag: Flagging emails allows users to mark them as important or requiring their attention. This ensures that important messages are not overlooked or forgotten.
- Archived: Archiving emails helps declutter the inbox without deleting them permanently. Archived messages can be accessed later if needed, but they are removed from the main inbox view.
- Spam: The inbox includes a spam folder to automatically filter out unwanted or unsolicited emails. This helps users avoid distractions and potential security risks.
- Attachments: Inboxes allow users to send and receive files as attachments along with their messages. This is especially useful for sharing documents, images, or other files with colleagues or friends.
- Priority: Some email services offer priority filters that automatically sort incoming messages based on their importance. This ensures that crucial emails are seen and addressed first.
- Drafts: The inbox provides a drafts folder, allowing users to save unfinished or unsent emails for later completion. This ensures that work in progress can be easily accessed and edited.
- Unread: Unread messages are visually highlighted in the inbox, making it easy for users to spot new or important emails that require attention.
- Sent: The sent folder in the inbox keeps a copy of all outgoing messages, allowing users to refer back to their sent emails if needed.
- Subscribe: Some email services provide the option to subscribe to newsletters and mailing lists directly from the inbox. This allows users to manage their subscriptions conveniently.
- Received: The inbox displays received messages in a chronological order, with the most recent emails appearing at the top. This helps users keep track of their incoming correspondence.
- Unsubscribe: Inboxes often include an unsubscribe option for newsletters and promotional emails. This allows users to easily remove themselves from mailing lists they no longer wish to be a part of.
- Messages: The main function of an inbox is to store and display email messages. It provides a user-friendly interface for reading, composing, and managing emails efficiently.
- Outbox: Outgoing messages that are in the process of being sent are stored in the outbox before they are successfully delivered. This allows users to confirm that their emails have been sent.
FAQ about topic “Understanding the Meaning, Usage, and Importance of Inbox”
What is the definition of “inbox”?
“Inbox” refers to a digital or physical container where incoming messages, emails, or other types of communication are stored until they are read or processed by the recipient.
How does an inbox work?
An inbox typically works by receiving incoming messages, organizing them chronologically or by other criteria, and allowing the recipient to view, reply, or delete them. The recipient can also use various filters or folders to manage the messages within the inbox.
What are the common features of an inbox?
Common features of an inbox include the ability to receive, categorize, sort, search, and organize incoming messages. Some advanced inboxes also offer features such as priority inbox, spam filtering, automatic message sorting, and notifications.
What is the purpose of an inbox?
The purpose of an inbox is to serve as a centralized hub for managing incoming messages or communications. It allows individuals or organizations to keep track of their correspondence, stay organized, and efficiently process the messages they receive.


